Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The recovery of European freshwater biodiversity has come to a halt
The recovery of European freshwater biodiversity has come to a halt
Improvements in European freshwater biodiversity occurred mainly before 2010 but have since plateaued, and communities downstream of dams, urban areas and cropland were less likely to experience recovery.
- Peter Haase
- , Diana E. Bowler
- & Ellen A. R. Welti
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence for recovery of mercury-contaminated fish populations
Experimental evidence for recovery of mercury-contaminated fish populations
In a 15-year whole-ecosystem, single-factor experiment, stopping experimental mercury loading results in rapid decreases in methylmercury contamination of fish populations and almost complete recovery within the timeframe of the study.
- Paul J. Blanchfield
- , John W. M. Rudd
- & Michael T. Tate
-
Matters Arising |
 Reply to: Concerns about phytoplankton bloom trends in global lakes
Reply to: Concerns about phytoplankton bloom trends in global lakes
- Jeff C. Ho
- , Anna M. Michalak
- & Nima Pahlevan
-
Article |
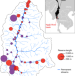 A network of grassroots reserves protects tropical river fish diversity
A network of grassroots reserves protects tropical river fish diversity
A network of small, community-run river reserves in Thailand increases local fish biomass, diversity and richness.
- Aaron A. Koning
- , K. Martin Perales
- & Peter B. McIntyre
-
Article |
 Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s
Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s
Analyses show that the peak intensity of summertime phytoplankton blooms has increased in 71 large lakes globally over the past three decades, revealing a worldwide exacerbation of bloom conditions.
- Jeff C. Ho
- , Anna M. Michalak
- & Nima Pahlevan
-
Article |
 Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers
Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers
A comprehensive assessment of the world’s rivers and their connectivity shows that only 37 per cent of rivers longer than 1,000 kilometres remain free-flowing over their entire length.
- G. Grill
- , B. Lehner
- & C. Zarfl
-
Outlook |
 Water: The flow of technology
Water: The flow of technology
Farmers must develop new approaches if they are to keep producing crops as water supplies dwindle.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
Letter |
 Biodiversity decreases disease through predictable changes in host community competence
Biodiversity decreases disease through predictable changes in host community competence
A combination of extensive field surveys and realistic experiments involving an amphibian disease system reveals that biodiversity reduces pathogen transmission due to a predictable link between species richness and the ability of communities to support infection.
- Pieter T. J. Johnson
- , Daniel L. Preston
- & Katherine L. D. Richgels
-
News |
 Yangtze finless porpoises in peril
Yangtze finless porpoises in peril
Survey finds that the freshwater mammal is in serious decline.
- Jane Qiu
-
News |
 One-fifth of invertebrate species at risk of extinction
One-fifth of invertebrate species at risk of extinction
Freshwater snails and reef-building corals among threatened groups.
- Brendan Borrell
-
News |
 Test lakes face closure
Test lakes face closure
Slashed funding threatens Canada’s unique freshwater study site.
- Hannah Hoag
-
News |
 Fish return to undammed Elwha River
Fish return to undammed Elwha River
First hope for salmon and trout restoration in biggest dam-removal project in US history.
- Wendee Holtcamp
-
Letter |
 Ecological opportunity and sexual selection together predict adaptive radiation
Ecological opportunity and sexual selection together predict adaptive radiation
Adaptive radiation of cichlid fishes in the African Great Lakes is predictable, but only when species traits and environmental factors are jointly considered.
- Catherine E. Wagner
- , Luke J. Harmon
- & Ole Seehausen
-
-
News |
 Canada's renowned freshwater research site to close
Canada's renowned freshwater research site to close
Budget fall-out hits environmental research stations.
- Hannah Hoag
-
Outlook |
 Q&A: Regime change
Q&A: Regime change
A freshwater ecologist at Queen's University in Kingston, Ontario, Canada, Smol studies lake sediments to understand climatic and environmental change. Nature Outlook asks him to share his experience.
- John P. Smol
-
News & Views |
 Species choked and blended
Species choked and blended
The appearance of new ecological niches propels the evolution of species, but the converse can also occur. A study shows that changing lake habitats have caused extinctions and reduced the genetic differences between species. See Article p.357
- Jeffrey S. McKinnon
- & Eric B. Taylor
-
News |
 Russians celebrate Vostok victory
Russians celebrate Vostok victory
Team finally drills into biggest Antarctic subglacial lake.
- Nicola Jones
-
Letter |
 Earth’s earliest non-marine eukaryotes
Earth’s earliest non-marine eukaryotes
- Paul K. Strother
- , Leila Battison
- & Charles H. Wellman
-
News & Views |
 Waltz of the weevil
Waltz of the weevil
The aquatic plant Salvinia molesta is a widespread pest of waterways in the tropics and subtropics. A study of its control by a weevil in Australian billabongs sets a new standard in ecological time-series analysis. See Letter p.86
- Lewi Stone
-
News |
 Queensland floods hit Great Barrier Reef
Queensland floods hit Great Barrier Reef
Corals threatened by huge volume of polluted fresh water pulsing into World Heritage Site.
- James Mitchell Crow
-
News & Views |
 Catfish mimics
Catfish mimics
Mutualism can be a double-edged sword if the animals concerned also compete for food. This may explain the discovery that catfish mimics in the Amazon rarely engage in mimicry with related species. See Letter p.84
- James Mallet
- & Kanchon Dasmahapatra
-
Article |
 Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity
Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity
Water security affects human wellbeing both directly and indirectly, through its effects on biodiversity. Here, a global map has been generated that shows threats to both direct and indirect water security from a full range of potential stressors. Technological investments have also been incorporated. The map shows that nearly 80% of the world's population is exposed to high levels of threat to water security. Investment enables rich nations to offset high stressor levels, but less wealthy nations remain vulnerable.
- C. J. Vörösmarty
- , P. B. McIntyre
- & P. M. Davies
-
News |
 Aquatic conservation efforts pay off
Aquatic conservation efforts pay off
Clean-up of Potomac River offers hope to environmentalists worldwide.
- Richard A. Lovett
-
News |
 Canada sees shock salmon glut
Canada sees shock salmon glut
Some 34 million of the fish are thronging British Columbia's Fraser River.
- Kate Larkin
-
News |
 Cold blamed for Bolivia's mass fish deaths
Cold blamed for Bolivia's mass fish deaths
Extreme weather wreaks havoc in the rivers.
- Anna Petherick
-
News |
 Mountain mining damages streams
Mountain mining damages streams
Study shows that stripping mountains for coal has a much greater impact than urban growth.
- Natasha Gilbert
-
News Feature |
 Evolution: Dreampond revisited
Evolution: Dreampond revisited
A once-threatened population of African fish is now providing a view of evolution in action. Laura Spinney asks what Lake Victoria cichlids have revealed about speciation.
- Laura Spinney
-
Research Highlights |
Microbiology: Hitching a ride
-
News |
 Teams set for first taste of Antarctic lakes
Teams set for first taste of Antarctic lakes
Samples could reveal unique life forms from beneath the ice.
- Quirin Schiermeier

 Predator mass mortality events restructure food webs through trophic decoupling
Predator mass mortality events restructure food webs through trophic decoupling