Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of the transition frequency from 2S1/2, F = 0 to 2P1/2, F = 1 states in Muonium
Measurement of the transition frequency from 2S1/2, F = 0 to 2P1/2, F = 1 states in Muonium
Muonium is a hydrogen like bound system with a positive muon and an electron. Here the authors measure the Lamb shift and frequency of the transition from 2S1/2, F = 0 state to 2P1/2, F = 1 state in muonium atom and the hyperfine structure of the 2S level.
- Gianluca Janka
- , Ben Ohayon
- & Paolo Crivelli
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Bose-Einstein condensates of excitons in a bulk semiconductor
Observation of Bose-Einstein condensates of excitons in a bulk semiconductor
Bose-Einstein condensate of excitons is expected in photo-excited bulk semiconductors, but a direct experimental evidence has been lacking. Here the authors report the observation of a condensate of 1s paraexcitons in Cu2O using real-space mid-infrared absorption imaging realized in a dilution refrigerator.
- Yusuke Morita
- , Kosuke Yoshioka
- & Makoto Kuwata-Gonokami
-
Article
| Open Access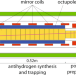 Sympathetic cooling of positrons to cryogenic temperatures for antihydrogen production
Sympathetic cooling of positrons to cryogenic temperatures for antihydrogen production
Positrons are key to the production of cold antihydrogen. Here the authors report the sympathetic cooling of positrons by interacting them with laser-cooled Be+ ions resulting in a three-fold reduction of the temperature of positrons for antihydrogen synthesis.
- C. J. Baker
- , W. Bertsche
- & J. S. Wurtele
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution and universality of two-stage Kondo effect in single manganese phthalocyanine molecule transistors
Evolution and universality of two-stage Kondo effect in single manganese phthalocyanine molecule transistors
The Kondo effect can serve as a powerful paradigm to understand strongly correlated many-body processes in physics. Here, Guo et al. utilize single molecule transistor devices as a testbed to study multi-level Kondo correlation and show electrical gate evolution and the universality of the two-stage Kondo effect.
- Xiao Guo
- , Qiuhao Zhu
- & Wenjie Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of the 5p – 4f orbital crossing and its optical clock transition in Pr9+
Detection of the 5p – 4f orbital crossing and its optical clock transition in Pr9+
Atomic clocks are based on the frequency of optical transitions and offer high precision. Here the authors demonstrate a configuration crossing in the highly charged ion praseodymium (Pr\({}^{9+}\)) and determine the frequency of a potential reference transition for a highly charged ion clock.
- H. Bekker
- , A. Borschevsky
- & J. C. Berengut
-
Article
| Open Access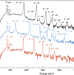 The observation of vibrating pear-shapes in radon nuclei
The observation of vibrating pear-shapes in radon nuclei
Octupole deformation in nuclei is important to understand nuclear structure and electric dipole moments of heavy atoms. Here the authors measure energies of excited quantum states in radon isotopes and find that these isotopes do not provide favourable conditions in the search for CP-violation.
- P. A. Butler
- , L. P. Gaffney
- & M. Zielinska
-
Article
| Open Access A terahertz-driven non-equilibrium phase transition in a room temperature atomic vapour
A terahertz-driven non-equilibrium phase transition in a room temperature atomic vapour
The nonlinear interaction between terahertz frequency electric fields and atoms or molecules can be used to study fundamental and technical problems. Here the authors demonstrate a THz–driven phase transition, with a potential application as a THz sensor, using Rydberg atomic states in a cesium vapor.
- C. G. Wade
- , M. Marcuzzi
- & K. J. Weatherill
-
Review Article
| Open Access Ultracold Rydberg molecules
Ultracold Rydberg molecules
Rydberg molecules have been extensively studied both theoretically and experimentally. Here the authors review the recent developments in the study of various types of Rydberg molecules and their potential for future applications in spectroscopy, sensing and quantum information.
- J. P. Shaffer
- , S. T. Rittenhouse
- & H. R. Sadeghpour
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum suppression of antihydrogen formation in positronium-antiproton scattering
Quantum suppression of antihydrogen formation in positronium-antiproton scattering
The intriguing behaviour of positronium scattering has its role in antimatter studies. Here the authors have predicted the quantum suppression of the cross-section for antihydrogen formation in positronium scattering with antiprotons, by including the excited states and using convergent close-coupling calculations.
- A. S. Kadyrov
- , I. Bray
- & I. I. Fabrikant
-
Article
| Open Access Antihydrogen accumulation for fundamental symmetry tests
Antihydrogen accumulation for fundamental symmetry tests
Antihydrogen studies are important in testing the fundamental principles of physics but producing antihydrogen in large amounts is challenging. Here the authors demonstrate an efficient and high-precision method for trapping and stacking antihydrogen by using controlled plasma.
- M. Ahmadi
- , B. X. R. Alves
- & J. S. Wurtele
-
Article
| Open Access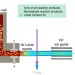 Towards high-resolution laser ionization spectroscopy of the heaviest elements in supersonic gas jet expansion
Towards high-resolution laser ionization spectroscopy of the heaviest elements in supersonic gas jet expansion
It is challenging to explore properties of heavy elements as they can only be produced artificially. Here, the authors demonstrate a high resolution spectroscopy method, studying the properties of actinium, which can be extended to the study of other elements located at the end of the periodic table.
- R. Ferrer
- , A. Barzakh
- & A. Zadvornaya
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of pendular butterfly Rydberg molecules
Observation of pendular butterfly Rydberg molecules
Rydberg molecules have potential for ultracold chemistry applications in light of their unconventional binding mechanism that provides high tunability. Here the authors observe and control butterfly Rydberg molecules, which are bound by a shape resonance in the electron-perturber scattering.
- Thomas Niederprüm
- , Oliver Thomas
- & Herwig Ott

 Exploring the vibrational series of pure trilobite Rydberg molecules
Exploring the vibrational series of pure trilobite Rydberg molecules