Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Role of monkeys in the sylvatic cycle of chikungunya virus in Senegal
Role of monkeys in the sylvatic cycle of chikungunya virus in Senegal
The authors examine the role of monkey populations in the sylvatic cycle of chikungunya virus in the Kédougou region, Senegal. The authors show that monkeys are amplification hosts, as opposed to reservoir hosts for infection. These findings expand our knowledge of the transmission dynamics of chikungunya virus in this region of Senegal.
- Benjamin M. Althouse
- , Mathilde Guerbois
- & Kathryn A. Hanley
-
Article
| Open Access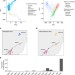 Gene-by-environment interactions in urban populations modulate risk phenotypes
Gene-by-environment interactions in urban populations modulate risk phenotypes
Individuals with different genotypes may respond differently to environmental variation. Here, Favé et al. find substantial impacts of different environment exposures on the transcriptome and clinical endophenotypes when controlling for genetic ancestry by analyzing data from ∼1000 individuals from a founder population in Quebec.
- Marie-Julie Favé
- , Fabien C. Lamaze
- & Philip Awadalla
-
Review Article
| Open Access Formalising recall by genotype as an efficient approach to detailed phenotyping and causal inference
Formalising recall by genotype as an efficient approach to detailed phenotyping and causal inference
Recall-by-Genotype (RbG) is an approach to recall participants from genetic studies based on their specific genotype for further, more extensive phenotyping. Here, the authors discuss examples of RbG as well as practical and ethical considerations and provide an online tool to aid in designing RbG studies.
- Laura J. Corbin
- , Vanessa Y. Tan
- & Nicholas J. Timpson
-
Article
| Open Access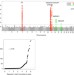 Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with multiple human pathologic conditions. In a genome-wide association study of 79,366 individuals, Jiang et al. replicate four and identify two new genetic loci for serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and find evidence for a shared genetic basis with autoimmune diseases.
- Xia Jiang
- , Paul F. O’Reilly
- & Douglas P. Kiel
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing the dynamics underlying global spread of epidemics
Characterizing the dynamics underlying global spread of epidemics
Understanding global epidemics spread is crucial for preparedness and response. Here the authors introduce an analytical framework to study epidemic spread on air transport networks, and demonstrate its power to estimate key epidemic parameters by application to the recent influenza pandemic and Ebola outbreak.
- Lin Wang
- & Joseph T. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access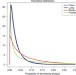 Inequality in genetic cancer risk suggests bad genes rather than bad luck
Inequality in genetic cancer risk suggests bad genes rather than bad luck
Cancer heritability estimates can be obtained via decomposing trait variance into genetic and other factors. Here, the authors obtain the distribution of absolute genetic risk for 15 common cancers, and they use a number of metrics to show that the genetic risk varies considerably across individuals.
- Mats Julius Stensrud
- & Morten Valberg
-
Article
| Open Access Counteracting structural errors in ensemble forecast of influenza outbreaks
Counteracting structural errors in ensemble forecast of influenza outbreaks
Inaccuracy of influenza forecasts based on dynamical models is partly due to nonlinear error growth. Here the authors address the error structure of a compartmental influenza model, and develop a new improved forecast approach combining dynamical error correction and statistical filtering techniques.
- Sen Pei
- & Jeffrey Shaman
-
Article
| Open Access Regional variation in health is predominantly driven by lifestyle rather than genetics
Regional variation in health is predominantly driven by lifestyle rather than genetics
Health-related traits are known to vary geographically. Here, Amador and colleagues show that regional variation of obesity-related traits in a Scottish population is influenced more by lifestyle differences than it is by genetic differences.
- Carmen Amador
- , Charley Xia
- & Chris S. Haley
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing sleep spindles in 11,630 individuals from the National Sleep Research Resource
Characterizing sleep spindles in 11,630 individuals from the National Sleep Research Resource
Sleep patterns vary and are associated with health and disease. Here Purcellet alcharacterize sleep spindle activity in 11,630 individuals and describe age-related changes, genetic influences, and possible confounding effects, serving as a resource for further understanding the physiology of sleep.
- S. M. Purcell
- , D. S. Manoach
- & R. Stickgold
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide approach identifies a novel gene-maternal pre-pregnancy BMI interaction on preterm birth
Genome-wide approach identifies a novel gene-maternal pre-pregnancy BMI interaction on preterm birth
Preterm birth (PTB) has high prevalence and PTB infants have greater risk for mortality. Here, Hong and colleagues perform a genome-wide gene × environment interaction analysis and find that maternalCOL24A1variants have a significant interaction with maternal pre-pregnancy obesity in increasing PTB risk.
- Xiumei Hong
- , Ke Hao
- & Xiaobin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide meta-analysis of 241,258 adults accounting for smoking behaviour identifies novel loci for obesity traits
Genome-wide meta-analysis of 241,258 adults accounting for smoking behaviour identifies novel loci for obesity traits
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have become a key tool to discover genetic markers for complex traits; however, environmental factors that interact with genes are rarely considered. Here, the authors conduct a GWAS of obesity traits, and find that smoking may alter genetic susceptibilities.
- Anne E. Justice
- , Thomas W. Winkler
- & L Adrienne Cupples
-
Article
| Open Access Exercise contagion in a global social network
Exercise contagion in a global social network
Some argue that health-related behaviours, such as obesity, are contagious, but empirical evidence of health contagion remains inconclusive. Here, using a large scale quasi-experiment in a global network of runners, Aral and Nicolaides show that this type of contagion exists in fitness behaviours.
- Sinan Aral
- & Christos Nicolaides
-
Article
| Open Access DNA methylation signatures in peripheral blood strongly predict all-cause mortality
DNA methylation signatures in peripheral blood strongly predict all-cause mortality
DNA methylation is modulated by environmental factors and has a role in many complex diseases. Here, the authors find that methylation at specific DNA sites is associated with all-cause mortality, and a methylation-based risk score may be informative for risk assessment and stratification.
- Yan Zhang
- , Rory Wilson
- & Hermann Brenner
-
Article
| Open Access An extended genotyping framework for Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, the cause of human typhoid
An extended genotyping framework for Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, the cause of human typhoid
Typhoid fever is caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. Typhi). This study examines ∼2,000 clinical isolates of S. Typhi to show highly structured/geographically restricted genomes except rapidly disseminating H58 subclade, and design a genotyping framework for tracking the disease.
- Vanessa K. Wong
- , Stephen Baker
- & Ben Amos
-
Article
| Open Access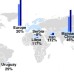 Projected increase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from 2015 to 2040
Projected increase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from 2015 to 2040
The socioeconomic burden of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is high, but the projected number of cases in the upcoming years is unclear. Here, the authors estimate the number and distribution of ALS cases to 2040, and show that cases are projected to increase, particularly in developing nations.
- Karissa C. Arthur
- , Andrea Calvo
- & Bryan J. Traynor
-
Article
| Open Access Intestinal microbiome is related to lifetime antibiotic use in Finnish pre-school children
Intestinal microbiome is related to lifetime antibiotic use in Finnish pre-school children
The impact of antibiotics on the microbiome and health of children is poorly understood. Here, Korpela et al. study the gut microbiome of 142 children and show that the use of macrolides, but not penicillins, is associated with long-lasting shifts in microbiota composition and increased risk of asthma and overweight.
- Katri Korpela
- , Anne Salonen
- & Willem M. de Vos
-
Article
| Open Access Exome-wide association analysis reveals novel coding sequence variants associated with lipid traits in Chinese
Exome-wide association analysis reveals novel coding sequence variants associated with lipid traits in Chinese
An important risk factor for coronary artery disease is the level of blood lipids. Here the authors conduct an exome-wide association study in Chinese cohorts and identify three novel loci associated with lipid levels as well as three Asian-specific variants in known loci.
- Clara S. Tang
- , He Zhang
- & Wei Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Chinese girls
Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Chinese girls
The authors perform a genome-wide association study of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients of Han Chinese descent, and identify 3 new loci for disease susceptibility.
- Zezhang Zhu
- , Nelson Leung-Sang Tang
- & Jack Chun-Yiu Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Defining the relationship between infection prevalence and clinical incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria
Defining the relationship between infection prevalence and clinical incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria
Mathematical models are used to predict malaria burden to inform disease control efforts. Here, Cameron et al. use Bayesian statistics to calibrate previous models against a data set of age-structured prevalence and incidence, generating stratified forecasts of the prevalence–incidence relationship.
- Ewan Cameron
- , Katherine E. Battle
- & Peter W. Gething
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association of polycystic ovary syndrome implicates alterations in gonadotropin secretion in European ancestry populations
Genome-wide association of polycystic ovary syndrome implicates alterations in gonadotropin secretion in European ancestry populations
Polycystic Ovary Sydrome is a highly heritable, complex reproductive disorder with unknown underlying genetic factors. Here Hayes and Urbanek et al. identify three loci in European women strongly associated with neuroendocrine changes and disease susceptibility.
- M. Geoffrey Hayes
- , Margrit Urbanek
- & Andrea Dunaif
-
Article |
 Fat, fibre and cancer risk in African Americans and rural Africans
Fat, fibre and cancer risk in African Americans and rural Africans
African Americans have much higher colon cancer rates than rural South Africans, which is associated with dietary and metabolic differences. Here, O’Keefe et al.show that switching quantities of fat and fibre leads to reciprocal changes in gut microbiota, metabolites and cancer biomarkers.
- Stephen J. D. O’Keefe
- , Jia V. Li
- & Erwin G. Zoetendal
-
Article |
 Identification of myopia-associated WNT7B polymorphisms provides insights into the mechanism underlying the development of myopia
Identification of myopia-associated WNT7B polymorphisms provides insights into the mechanism underlying the development of myopia
Myopia is a significant and increasing public health concern. Here Miyake et al. conduct a genome-wide association study and identify WNT7Bas a susceptibility gene across different ethnic groups, suggesting a possible role in the development of myopia.
- Masahiro Miyake
- , Kenji Yamashiro
- & Nagahisa Yoshimura
-
Article |
 Genome-wide association study identifies a new susceptibility locus for cleft lip with or without a cleft palate
Genome-wide association study identifies a new susceptibility locus for cleft lip with or without a cleft palate
Cleft lip is one of the most common congenital birth defects with substantial impairments to quality of life. Here, Sun et al. identify a new locus associated with cleft lip in diverse Chinese populations.
- Yimin Sun
- , Yongqing Huang
- & Yinxue Yang
-
Article |
 Evidence for zoonotic potential of ovine scrapie prions
Evidence for zoonotic potential of ovine scrapie prions
Scrapie, a form of prion disease that affects sheep and goats, is believed not to be transmissible to humans. Using transgenic mice expressing human prion protein as a model of cross-species prion transmission, the authors show that ovine scrapie may possess potential to be passed on to humans.
- Hervé Cassard
- , Juan-Maria Torres
- & Olivier Andréoletti
-
Article |
 African origin of the malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax
African origin of the malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax
Plasmodium vivax, the leading cause of human malaria in Asia and Latin America, is thought to have an Asian origin. Here, the authors show that wild chimpanzees and gorillas in Africa are infected with parasites that are closely related to P. vivax, indicating an African origin for this species.
- Weimin Liu
- , Yingying Li
- & Paul M. Sharp
-
Article
| Open Access Estimates of the changing age-burden of Plasmodium falciparum malaria disease in sub-Saharan Africa
Estimates of the changing age-burden of Plasmodium falciparum malaria disease in sub-Saharan Africa
Reduction in malaria transmission has changed the age pattern of malaria incidence. This study brings insights into the changes in age distributions of clinical malaria across Africa, with importance for improving within-population targeting of malaria control interventions.
- Jamie T. Griffin
- , Neil M. Ferguson
- & Azra C. Ghani
-
Article
| Open Access Human gut microbiota community structures in urban and rural populations in Russia
Human gut microbiota community structures in urban and rural populations in Russia
The structure of the human gut microbiota has been shown to vary between populations. Tyakht et al.analyse the gut microbiota assembly from Russian individuals living in urban and rural areas, and compare these with previously studied populations.
- Alexander V. Tyakht
- , Elena S. Kostryukova
- & Vadim M. Govorun
-
Article
| Open Access Factors determining the occurrence of submicroscopic malaria infections and their relevance for control
Factors determining the occurrence of submicroscopic malaria infections and their relevance for control
Malaria can persist at levels that escape detection by standard microscopy, but can be detected by PCR. Okell et al.now show that rates of submicroscopic infection can be predicted using more widely available microscopy data, and are most epidemiologically significant in areas with low malaria transmission.
- Lucy C. Okell
- , Teun Bousema
- & Chris J. Drakeley
-
Article
| Open Access Estimating the potential public health impact of seasonal malaria chemoprevention in African children
Estimating the potential public health impact of seasonal malaria chemoprevention in African children
Seasonal malaria chemoprevention can lower the incidence of malaria in areas where transmission is highly periodical. Combining data on rainfall, population and malaria endemicity, Cairnset al. identify geographical areas in sub-Saharan Africa where this intervention is likely to be effective and cost-effective.
- Matthew Cairns
- , Arantxa Roca-Feltrer
- & Brian M. Greenwood
-
Article |
 Isoniazid resistance without a loss of fitness in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Isoniazid resistance without a loss of fitness in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
The treatment ofMycobacterium tuberculosis with drugs such as isoniazid often results in drug resistance, but the mechanisms leading to the resistance are not fully known. In this study, an M. tuberculosisstrain lacking the sigma factor I is shown to be resistant to isoniazid.
- Jong-Hee Lee
- , Nicole C. Ammerman
- & William R. Bishai
-
Article
| Open Access Wind direction and proximity to larval sites determines malaria risk in Kilifi District in Kenya
Wind direction and proximity to larval sites determines malaria risk in Kilifi District in Kenya
Spatial epidemiology studies identify malaria hotspots, which sustain transmission and so could be targeted by control programmes. This study uses spatial data on larval sites and malaria episodes to show that transmission can be disrupted by targeting vector breeding sites close to and downwind of malaria hotspots.
- Janet T. Midega
- , Dave L. Smith
- & Philip Bejon
-
Article |
 Location-specific patterns of exposure to recent pre-pandemic strains of influenza A in southern China
Location-specific patterns of exposure to recent pre-pandemic strains of influenza A in southern China
Population demographics affect influenza transmission at large spatial scales. Here, influenza immunity is shown to vary spatially in a way unexplained by differences in demographics, suggesting that there are aspects of locations that drive influenza transmission other than individual and household risk factors.
- Justin Lessler
- , Derek A.T. Cummings
- & Steven Riley
-
Article |
 Long-term projections and acclimatization scenarios of temperature-related mortality in Europe
Long-term projections and acclimatization scenarios of temperature-related mortality in Europe
The sensitivity of human populations to rising global temperatures is not yet fully understood. The authors describe the link between temperature and daily mortality in over 200 European regions and calculate projections of mortality from climate models under greenhouse gas scenario simulations.
- Joan Ballester
- , Jean-Marie Robine
- & Xavier Rodó
-
Article
| Open Access A quantitative analysis of transmission efficiency versus intensity for malaria
A quantitative analysis of transmission efficiency versus intensity for malaria
Recent work has shown that the transmission of malaria from mosquito to human is inefficient. In this study, an analysis of published literature is used to understand this inefficiency, which is likely due to heterogeneous biting, where 20% of people receive 80% of the bites.
- David L. Smith
- , Chris J. Drakeley
- & Simon I. Hay

 Horizontal antimicrobial resistance transfer drives epidemics of multiple Shigella species
Horizontal antimicrobial resistance transfer drives epidemics of multiple Shigella species