Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic trajectory of a dimeric nonribosomal peptide synthetase subunit with an inserted epimerase domain
Catalytic trajectory of a dimeric nonribosomal peptide synthetase subunit with an inserted epimerase domain
The catalytic domains in nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) are responsible for a choreography of events that elongates substrates into natural products. Here, the authors present cryo-EM structures of a siderophore-producing dimeric NRPS elongation module in multiple distinct conformations, which provides insight into the mechanisms of catalytic trajectory.
- Jialiang Wang
- , Dandan Li
- & Zhijun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of Vibrio collagenase VhaC provides insight into the mechanism of bacterial collagenolysis
Structure of Vibrio collagenase VhaC provides insight into the mechanism of bacterial collagenolysis
The collagenolytic mechanism of Vibrio collagenase, a virulence factor, remains unclear. Here, the authors report the structure of Vibrio collagenase VhaC and propose the mechanism for collagen recognition and degradation, providing new insight into bacterial collagenolysis.
- Yan Wang
- , Peng Wang
- & Yu-Zhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphoglycolate phosphatase homologs act as glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase to control stress and healthspan in C. elegans
Phosphoglycolate phosphatase homologs act as glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase to control stress and healthspan in C. elegans
Glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase is a recently discovered enzyme at the heart of metabolism. Here, the authors used C. elegans and showed that its activation promotes stress resistance, healthy aging and acts as a calorie restriction mimetic at normal food intake without altering fertility.
- Elite Possik
- , Clémence Schmitt
- & Marc Prentki
-
Article
| Open Access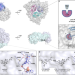 Design principles for site-selective hydroxylation by a Rieske oxygenase
Design principles for site-selective hydroxylation by a Rieske oxygenase
SxtT and GxtA are Rieske oxygenases that are involved in paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis and catalyze monohydroxylation reactions at different positions on the toxin scaffold. Here, the authors present crystal structures of SxtT and GxtA with the native substrates β-saxitoxinol and saxitoxin as well as a Xenon-pressurized structure of GxtA, which reveal a substrate access tunnel to the active site. Through structure-based mutagenesis studies the authors identify six residues in three different protein regions that determine the substrate specificity and site selectivity of SxtT and GxtA. These findings will aid the rational engineering of other Rieske oxygenases.
- Jianxin Liu
- , Jiayi Tian
- & Jennifer Bridwell-Rabb
-
Article
| Open Access Aminoacyl chain translocation catalysed by a type II thioesterase domain in an unusual non-ribosomal peptide synthetase
Aminoacyl chain translocation catalysed by a type II thioesterase domain in an unusual non-ribosomal peptide synthetase
Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthetases (NRPSs) are responsible for the construction of many types of natural products. Here the authors characterize a key type II thioesterase domain that sheds light on the chain translocation processes of legonmycin NRPSs.
- Shan Wang
- , William D. G. Brittain
- & Hai Deng
-
Article
| Open Access The catalytic activity of TCPTP is auto-regulated by its intrinsically disordered tail and activated by Integrin alpha-1
The catalytic activity of TCPTP is auto-regulated by its intrinsically disordered tail and activated by Integrin alpha-1
TCPTP is a non-receptor type protein tyrosine phosphatase involved in various signalling pathways. Here, the authors provide structural insights into TCPTP activation, showing that TCPTP is inhibited by its C-terminal tail, which can be displaced by the cytosolic tail of integrin-α1, leading to activation.
- Jai Prakash Singh
- , Yang Li
- & Tzu-Ching Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insights into the unusually promiscuous and catalytically versatile Fe(II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent oxygenase SptF
Molecular insights into the unusually promiscuous and catalytically versatile Fe(II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent oxygenase SptF
Non-heme iron and α-ketoglutarate-dependent (Fe/αKG) oxygenases have attracted attention for their application as biocatalysts due to their flexibility and high efficiency. Here, the authors show the biochemical and structural characterizations of the versatile Fe/αKG oxygenase SptF, involved in the biosynthesis of fungal meroterpenoid emervaridones.
- Hui Tao
- , Takahiro Mori
- & Ikuro Abe
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of enzymatic nitrogen-nitrogen formation by a family of zinc-binding cupin enzymes
Molecular basis of enzymatic nitrogen-nitrogen formation by a family of zinc-binding cupin enzymes
Enzymes involved in the synthesis of nitrogen-nitrogen bond containing molecules have been identified but the processes remain largely unknown. Here, the authors use biochemical characterisation and computer modelling to study the molecular basis of hydrazine bond formation by a family of di-domain enzymes.
- Guiyun Zhao
- , Wei Peng
- & Yi-Ling Du
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic flexibility of rice glycosyltransferase OsUGT91C1 for the production of palatable steviol glycosides
Catalytic flexibility of rice glycosyltransferase OsUGT91C1 for the production of palatable steviol glycosides
Steviol glycosides from the plant Stevia rebaudiana are already used as lowcalorie sweeteners, but the most abundant naturally occurring compounds have a bitter aftertaste. Here, the authors characterize and engineer rice glycosyltransferase OsUGT91C1 to facilitate the large-scale production of naturally rare but palatable glycosides Reb D and Reb M
- Jinzhu Zhang
- , Minghai Tang
- & Wei Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the E3 ligase activity enhancement of yeast Nse2 by SUMO-interacting motifs
Structural basis for the E3 ligase activity enhancement of yeast Nse2 by SUMO-interacting motifs
Nse2 is a SUMO E3 ligase component of the Smc5/6 multisubunit complex involved in the DNA repair and chromosome integrity. Here, the structure of the Nse2 in complex with an E2-SUMO thioester mimetic reveals the combined action of two SIM motifs during the E3- dependent conjugation reaction.
- Nathalia Varejão
- , Jara Lascorz
- & David Reverter
-
Article
| Open Access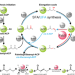 Helicobacter pylori FabX contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster essential for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis
Helicobacter pylori FabX contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster essential for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis
Helicobacter pylori FabX, a dehydrogenase/isomerase flavoprotein, is required for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis. Here, the authors characterize FabX substrate recognition and catalytic mechanism, and reveal that it contains an atypical [4Fe-4S] cluster, which is essential and participates in the catalytic cycle.
- Jiashen Zhou
- , Lin Zhang
- & Liang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access N-terminal tyrosine of ISCU2 triggers [2Fe-2S] cluster synthesis by ISCU2 dimerization
N-terminal tyrosine of ISCU2 triggers [2Fe-2S] cluster synthesis by ISCU2 dimerization
[2Fe-2S] protein cofactors are essential for life and are synthesized on ISCU2 scaffolds. Here, the authors show that hydrophobic interaction of two conserved N-terminal tyrosines induces ISCU2 dimerization and concomitant [2Fe-2S] cluster synthesis.
- Sven-A. Freibert
- , Michal T. Boniecki
- & Roland Lill
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and functional analysis of the promiscuous AcrB and AdeB efflux pumps suggests different drug binding mechanisms
Structural and functional analysis of the promiscuous AcrB and AdeB efflux pumps suggests different drug binding mechanisms
Resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND)-type tripartite efflux pumps confer multidrug resistance to Gram-negative bacteria. Here, structural and functional analyses of AdeB from Acinetobacter baumannii and AcrB from Escherichia coli provide insight into their different drug-binding and conformational drug transport states.
- Alina Ornik-Cha
- , Julia Wilhelm
- & Klaas M. Pos
-
Article
| Open Access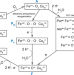 Cryo-EM structures of intermediates suggest an alternative catalytic reaction cycle for cytochrome c oxidase
Cryo-EM structures of intermediates suggest an alternative catalytic reaction cycle for cytochrome c oxidase
Cytochrome c oxidase is a fundamental enzyme of life and its mechanism is not fully understood yet. Here, the authors present four cryo-EM structures of different intermediate states, which suggest an alternative cytochrome c oxidase reaction cycle.
- F. Kolbe
- , S. Safarian
- & H. Michel
-
Article
| Open Access HPF1 dynamically controls the PARP1/2 balance between initiating and elongating ADP-ribose modifications
HPF1 dynamically controls the PARP1/2 balance between initiating and elongating ADP-ribose modifications
HPF1 controls the ADP-ribosylation activity of PARP1/2 in response to DNA breaks. Here, the authors show that HPF1 regulates the balance between ADP-ribose initiation and elongation through a dynamic interaction that accelerates the initiation rate on serine residues.
- Marie-France Langelier
- , Ramya Billur
- & John M. Pascal
-
Article
| Open Access MDA5 disease variant M854K prevents ATP-dependent structural discrimination of viral and cellular RNA
MDA5 disease variant M854K prevents ATP-dependent structural discrimination of viral and cellular RNA
MDA5 is the primary immune sensor for SARS-CoV-2 and many other viruses. Mutations in MDA5 can cause disease. Here the authors employ CryoEM and biochemical methods to show how steric constraints cause MDA5 to misrecognize endogenous RNA as viral RNA.
- Qin Yu
- , Alba Herrero del Valle
- & Yorgo Modis
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structures of the elusive Rhizobium etli l-asparaginase reveal a peculiar active site
Crystal structures of the elusive Rhizobium etli l-asparaginase reveal a peculiar active site
L-asparaginases catalyse the hydrolysis of L-asparagine to L-aspartic acid and ammonia. Here, the authors present high resolution crystal structures of Rhizobium etli L-asparaginase that contains a Zn2+ binding site without a catalytic role and discuss the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme.
- Joanna I. Loch
- , Barbara Imiolczyk
- & Mariusz Jaskolski
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein Pup in complex with depupylase Dop reveal the mechanism of catalytic phosphate formation
Structures of prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein Pup in complex with depupylase Dop reveal the mechanism of catalytic phosphate formation
Pupylation is a bacterial post-translational protein modification, where the small ubiquitin-like protein Pup is covalently attached to lysine side chains of target proteins, which is a reversible process and depupylation is catalysed by the depupylase enzyme, Dop. Here, the authors present crystal structures of Dop in different functional states, which together with biochemical experiments provide insights into the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme.
- Hengjun Cui
- , Andreas U. Müller
- & Eilika Weber-Ban
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of the regulation of the normal and oncogenic methylation of nucleosomal histone H3 Lys36 by NSD2
Structural basis of the regulation of the normal and oncogenic methylation of nucleosomal histone H3 Lys36 by NSD2
An upregulation of NSD2, a histone H3 lysine 36 (H3K36) methyltransferase is linked to multiple myeloma and other types of cancer. Here, the authors provide insights into the regulatory mechanism of NSD2 by determining the 2.8 Å cryo-EM structure of the NSD2 bound nucleosome complex, and based on MD simulations they discuss how two oncogenic mutations enhance NSD2 activity.
- Ko Sato
- , Amarjeet Kumar
- & Toru Sengoku
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of Escherichia coli cytochrome bd-II type oxidase with bound aurachin D
Structure of Escherichia coli cytochrome bd-II type oxidase with bound aurachin D
Terminal bd oxidases endow bacterial pathogens with resistance to cellular stressors. The authors report the structure of E. coli bd-II type oxidase with the bound inhibitor aurachin D, providing a structural basis for the design of specifically binding antibiotics.
- Antonia Grauel
- , Jan Kägi
- & Thorsten Friedrich
-
Article
| Open Access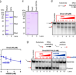 Distinct RPA domains promote recruitment and the helicase-nuclease activities of Dna2
Distinct RPA domains promote recruitment and the helicase-nuclease activities of Dna2
An enzymatic ensemble including Dna2 functions in DNA end resection; the function of the single-stranded DNA binding protein RPA in this complex has been underappreciated. Here the authors employ molecular modeling, biochemistry, and single molecule biophysics to reveal RPA directly promotes Dna2 recruitment, nuclease and helicase activities.
- Ananya Acharya
- , Kristina Kasaciunaite
- & Petr Cejka
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanisms of the CdnG-Cap5 antiphage defense system employing 3′,2′-cGAMP as the second messenger
Molecular mechanisms of the CdnG-Cap5 antiphage defense system employing 3′,2′-cGAMP as the second messenger
Many bacterial cyclic-oligonucleotide-based antiphage signaling systems (CBASS) employ effectors with SAVED domains. Here, the authors present a biochemical and structural characterization of two such CBASS, providing mechanistic insights into bacterial antiphage defense.
- Shirin Fatma
- , Arpita Chakravarti
- & Raven H. Huang
-
Article
| Open Access C-Glycoside metabolism in the gut and in nature: Identification, characterization, structural analyses and distribution of C-C bond-cleaving enzymes
C-Glycoside metabolism in the gut and in nature: Identification, characterization, structural analyses and distribution of C-C bond-cleaving enzymes
In C-glycosides the sugar moiety is linked through a carbon-carbon bond to the non-sugar moiety, which can be cleaved by intestinal microbes. Here, the authors use bioinformatics analysis to identify C-glycoside deglycosidase enzymes in intestinal and soil bacteria, biochemically characterise them and determine their structures and probe catalytic important residues in mutagenesis experiments.
- Takahiro Mori
- , Takuto Kumano
- & Michihiko Kobayashi
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for protein glutamylation by the Legionella pseudokinase SidJ
Structural basis for protein glutamylation by the Legionella pseudokinase SidJ
Legionella pneumophila (LP) employs the metaeffector SidJ to suppress the toxicity of SdeA and other LP SidE effector family members by catalysing the glutamylation of the catalytic Glu residue. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of SidJ in complex with SdeA in two different states, which together with mutagenesis analysis provide insights into the substrate recognition and the mechanism of protein glutamylation by SidJ.
- Michael Adams
- , Rahul Sharma
- & Sagar Bhogaraju
-
Article
| Open Access The RNA helicase Dbp7 promotes domain V/VI compaction and stabilization of inter-domain interactions during early 60S assembly
The RNA helicase Dbp7 promotes domain V/VI compaction and stabilization of inter-domain interactions during early 60S assembly
Early steps of large 60S ribosomal subunit biogenesis are not well understood. Here, the authors combine biochemical experiments with protein-RNA crosslinking and mass spectrometry to show that the RNA helicase Dbp7 is key player during early 60S ribosomal assembly. Dbp7 regulates a series of events driving compaction of domain V/VI in early pre60S ribosomal particles.
- Gerald Ryan R. Aquino
- , Philipp Hackert
- & Markus T. Bohnsack
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans sterylglucosidase to develop antifungal agents
Structure and inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans sterylglucosidase to develop antifungal agents
Sterylglucosidase 1 (Sgl1) is a virulence factor in Cryptococcus neoformans that modulates fungal pathogenesis and host response. Here, the authors characterize Sgl1 structurally, identify Sgl1 inhibitors, and demonstrate Sgl1 inhibition has efficacy in mouse models of infection.
- Nivea Pereira de Sa
- , Adam Taouil
- & Michael V. Airola
-
Article
| Open Access Functional basis of electron transport within photosynthetic complex I
Functional basis of electron transport within photosynthetic complex I
Photosynthetic Complex I (PS-CI) is proposed to couple ferredoxin oxidation and plastoquinone reduction to proton pumping across thylakoid membranes. Here the authors determine the reduction potentials of the iron-sulphur clusters of PS-CI and thus the bioenergetics of the electron transfer relay.
- Katherine H. Richardson
- , John J. Wright
- & Maxie M. Roessler
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational dynamics linked to domain closure and substrate binding explain the ERAP1 allosteric regulation mechanism
Conformational dynamics linked to domain closure and substrate binding explain the ERAP1 allosteric regulation mechanism
The endoplasmic-reticulum aminopeptidase ERAP1 processes peptides for antigen presentation. Here, the authors assess ERAP1 conformational states in solution, providing insight into the molecular mechanisms of ERAP1 substrate-length dependent catalytic activity and regulation, including the effects of autoimmune disease-associated polymorphism.
- Zachary Maben
- , Richa Arya
- & Lawrence J. Stern
-
Article
| Open Access UbiD domain dynamics underpins aromatic decarboxylation
UbiD domain dynamics underpins aromatic decarboxylation
Understanding the structure and dynamics of enzymes is important for a number of applications. Here, the authors report on the crystal structure of vanillic acid decarboxylase, and show how the dynamics of the UbiD superfamily enzymes relate to the covalent catalysis of aromatic (de)carboxylation.
- Stephen A. Marshall
- , Karl A. P. Payne
- & David Leys
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for proficient oxidized ribonucleotide insertion in double strand break repair
Structural basis for proficient oxidized ribonucleotide insertion in double strand break repair
The authors previously showed that pol μ lacks discrimination against oxidized dGTP (8-oxo-dGTP). Here they reveal the structural basis for proficient oxidized ribonucleotide (8-oxo-rGTP) incorporation during double strand break repair by pol μ.
- Joonas A. Jamsen
- , Akira Sassa
- & Samuel H. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Genome dependent Cas9/gRNA search time underlies sequence dependent gRNA activity
Genome dependent Cas9/gRNA search time underlies sequence dependent gRNA activity
The link between gRNA sequence and Cas9 activity is well established but the mechanism underlying this relationship is not well understood. Here the authors show that gRNA sequence primarily influences activity by dictating the time it takes for Cas9 to find the target site in a species-specific manner.
- E. A. Moreb
- & M. D. Lynch
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of a deAMPylation complex rationalise the switch between antagonistic catalytic activities of FICD
Structures of a deAMPylation complex rationalise the switch between antagonistic catalytic activities of FICD
The ER chaperone BiP is regulated by FICD-mediated AMPylation and deAMPylation. Here, the authors characterise the structure of mammalian AMPylated BiP bound to FICD, by X-ray crystallography and neutron scattering, providing insights into the mechanism of BiP AMPylation and deAMPylation.
- Luke A. Perera
- , Steffen Preissler
- & David Ron
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic insights into the three steps of poly(ADP-ribosylation) reversal
Mechanistic insights into the three steps of poly(ADP-ribosylation) reversal
PARG and ARH3 are the main hydrolases to reverse serine poly(ADP-ribosylation) yet their activities in the process differ. Here, the authors synthesise linear and branched poly(ADP-ribose) molecules, perform structure-function analysis and elucidate the mechanistic differences between PARG and ARH3.
- Johannes Gregor Matthias Rack
- , Qiang Liu
- & Ivan Ahel
-
Article
| Open Access An enzymatic activation of formaldehyde for nucleotide methylation
An enzymatic activation of formaldehyde for nucleotide methylation
The bacterial thymidylate synthase ThyX catalyzes the reductive methylation of deoxyuridylate (dUMP) into deoxythymidylate (dTMP) and requires both folate and flavin for activity. Here, the authors combine biochemical experiments, spectroscopic measurements and flavin synthesis chemistry to show that formaldehyde (CH2O) can replace the natural methylene donor of ThyX in a CH2O-shunt reaction, yielding a carbinolamine intermediate with the reduced flavin coenzyme, and they present the crystal structure of this intermediate.
- Charles Bou-Nader
- , Frederick W. Stull
- & Djemel Hamdane
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insights into the endoperoxide formation by Fe(II)/α-KG-dependent oxygenase NvfI
Molecular insights into the endoperoxide formation by Fe(II)/α-KG-dependent oxygenase NvfI
Many endoperoxide-containing natural products have been isolated, but the biosynthesis of the endoperoxides remains unclear. Here, the authors report the structural and functional analysis of the NvfI endoperoxidase that catalyzes the formation of fumigatonoid A in the biosynthesis of novofumigatonin, and show that it does not employ tyrosyl radical in the reaction.
- Takahiro Mori
- , Rui Zhai
- & Ikuro Abe
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative analysis of two paradigm bacteriophytochromes reveals opposite functionalities in two-component signaling
Comparative analysis of two paradigm bacteriophytochromes reveals opposite functionalities in two-component signaling
The bacteriophytochrome DrBphP from Deinococcus radiodurans shows high sequence homology to the histidine kinase Agp1 from Agrobacterium fabrum but lacks kinase activity. Here, the authors structurally and biochemically analyse DrBphP and Agp1, showing that DrBphP is a light-activatable phosphatase.
- Elina Multamäki
- , Rahul Nanekar
- & Heikki Takala
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of the membrane intramolecular transacylase reaction responsible for lyso-form lipoprotein synthesis
Structural basis of the membrane intramolecular transacylase reaction responsible for lyso-form lipoprotein synthesis
In Gram-positive bacteria, lipoprotein intramolecular transacylase Lit produces a lipoprotein variant with less immunogenicity. As such, Lit can be viewed as a virulence factor. Here, structural and functional characterization of the enzyme provides insight into its catalytic mechanism, setting the stage for future studies of Lit as a target for new antibiotics.
- Samir Olatunji
- , Katherine Bowen
- & Martin Caffrey
-
Article
| Open Access Exchange catalysis by tapasin exploits conserved and allele-specific features of MHC-I molecules
Exchange catalysis by tapasin exploits conserved and allele-specific features of MHC-I molecules
Tapasin is part of the peptide loading complex necessary for presenting antigenic peptides on MHC-I for the induction of adaptive immunity. Here the authors show that tapasin interacts with MHC-I in both conserved and allele-specific regions to promote antigen presentation, with tapasin L18 and K16 residues both implicated in this molecular interaction.
- Huan Lan
- , Esam T. Abualrous
- & Christian Freund
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of the stereoselective formation of the spirooxindole ring in the biosynthesis of citrinadins
Structural basis of the stereoselective formation of the spirooxindole ring in the biosynthesis of citrinadins
Prenylated indole alkaloids contain spirooxindole rings with a 3R or 3S carbon stereocenter, which determines their bioactivities, but the biocatalytic mechanism controlling the 3R- or 3S-spirooxindole formation was unclear. Here, the authors report the biochemical and structural characterization of the oxygenase/semipinacolase CtdE that catalyses the 3S-spirooxindole construction in the biosynthesis of 21R-citrinadin A.
- Zhiwen Liu
- , Fanglong Zhao
- & Xue Gao
-
Article
| Open Access DNA repair glycosylase hNEIL1 triages damaged bases via competing interaction modes
DNA repair glycosylase hNEIL1 triages damaged bases via competing interaction modes
hNEIL1 (human endonuclease VIII-like 1) is a broadly specific DNA glycosylase for base excision repair. Here, the authors show that hNEIL1 can assume activated or triage conformations: the structural basis for the mechanism that enables broad specificity and reduces futile repair of normal bases.
- Menghao Liu
- , Jun Zhang
- & Chengqi Yi
-
Article
| Open Access Allosteric drug transport mechanism of multidrug transporter AcrB
Allosteric drug transport mechanism of multidrug transporter AcrB
Gram-negative bacteria can display intrinsic antibiotic resistance due to the action of tripartite efflux pumps, which include a H+/drug antiporter component. Here, the authors present a structure-function analysis of antiporter AcrB in intermediate states of the transport cycle, showing novel drug-binding sites and transport pathways.
- Heng-Keat Tam
- , Wuen Ee Foong
- & Klaas M. Pos
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven decarboxylative deuteration enabled by a divergently engineered photodecarboxylase
Light-driven decarboxylative deuteration enabled by a divergently engineered photodecarboxylase
The chemical processes for the selective incorporation of deuterium into small molecules, of interest to organic and medicinal chemistry, are well established, while the enzymatic methods remain underdeveloped. Here, the authors use an enzymatic approach employing Chlorella variabilis NC64A photodecarboxylase that catalyses decarboxylative deuteration of various carboxylic acids with D2O, and identify enzyme variants that can employ substrates with different chain length acids.
- Jian Xu
- , Jiajie Fan
- & Qi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Physical constraints and functional plasticity of cellulases
Physical constraints and functional plasticity of cellulases
Enzyme reactions at interfaces are common in both Nature and industrial applications but no general kinetic framework exists for interfacial enzymes. Here, the authors kinetically characterize 83 cellulases and identify a scaling relationship between ligand binding strength and maximal turnover, a so-called linear free energy relationship, which may help rationalize cellulolytic mechanisms and guide the selection of technical enzymes.
- Jeppe Kari
- , Gustavo A. Molina
- & Peter Westh
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of genome instability mediated by human DNA polymerase mu misincorporation
Mechanism of genome instability mediated by human DNA polymerase mu misincorporation
Pol μ performs gap-filling repair synthesis in the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway. Here the authors provide crystal structures and kinetics of human Pol μ to reveal insights into the molecular mechanism of Pol μ during the process of dGTP misincorporation.
- Miao Guo
- , Yina Wang
- & Ye Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-Associated Primase-Polymerases are implicated in prokaryotic CRISPR-Cas adaptation
CRISPR-Associated Primase-Polymerases are implicated in prokaryotic CRISPR-Cas adaptation
CAPPs are putative Primase-Polymerases associated with CRISPR-Cas operons. Here, the authors show CAPPs genetic and physical association with Cas1 and Cas2, their capacity to function as DNA-dependent DNA primases and DNA polymerases, and that Cas1-Cas2 complex adjacent to CAPP has bona fide spacer integration activity.
- Katerina Zabrady
- , Matej Zabrady
- & Aidan J. Doherty
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of PARP2/ARTD2 by DNA damage induces conformational changes relieving enzyme autoinhibition
Activation of PARP2/ARTD2 by DNA damage induces conformational changes relieving enzyme autoinhibition
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 2 (PARP2) is activated by 5′-phosphorylated DNA breaks but the molecular mechanism is not fully understood. Here, the authors report a crystal structure of PARP2 bound to an activating DNA fragment, providing insights into the structural changes that lead to PARP2 activation.
- Ezeogo Obaji
- , Mirko M. Maksimainen
- & Lari Lehtiö
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insight on assembly-line catalysis in terpene biosynthesis
Structural insight on assembly-line catalysis in terpene biosynthesis
Substrate channeling can improve biosynthetic efficiency and has been implicated in the reactions of fusicoccadiene synthase. Here, the authors analyze this bifunctional enzyme complex by cryoEM, cross-linking MS and integrative modeling, providing structural insights into how substrate channeling is achieved.
- Jacque L. Faylo
- , Trevor van Eeuwen
- & David W. Christianson
-
Article
| Open Access Sugar phosphate activation of the stress sensor eIF2B
Sugar phosphate activation of the stress sensor eIF2B
The activity of translation initiation factor eIF2B is known to be modulated through stress-responsive phosphorylation of its substrate eIF2. Here, the authors uncover the regulation of eIF2B by the binding of sugar phosphates, suggesting a link between nutrient status and the rate of protein synthesis.
- Qi Hao
- , Jin-Mi Heo
- & Carmela Sidrauski
-
Article
| Open Access Clostridioides difficile specific DNA adenine methyltransferase CamA squeezes and flips adenine out of DNA helix
Clostridioides difficile specific DNA adenine methyltransferase CamA squeezes and flips adenine out of DNA helix
Clostridioides difficile adenine methyltransferase A (CamA) is required for the sporulation and colonization of the pathogen that causes gastrointestinal infections. Here, the authors characterise CamA kinetically and present its crystal structure bound to the DNA recognition sequence, which reveals DNA distortions including bending and the flipping of the target adenine out of the DNA helix, as well as protein conformational changes upon cofactor binding.
- Jujun Zhou
- , John R. Horton
- & Xiaodong Cheng

 The toposiomerase IIIalpha-RMI1-RMI2 complex orients human Bloom’s syndrome helicase for efficient disruption of D-loops
The toposiomerase IIIalpha-RMI1-RMI2 complex orients human Bloom’s syndrome helicase for efficient disruption of D-loops