Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Drought triggers and sustains overnight fires in North America
Drought triggers and sustains overnight fires in North America
By examining the hourly diurnal cycle of 23,557 fires in North America during 2017–2020, 1,095 overnight burning events were identified, mostly associated with extreme fires and driven by long-term drought conditions.
- Kaiwei Luo
- , Xianli Wang
- & Mike Flannigan
-
Article |
 Fertilizer management for global ammonia emission reduction
Fertilizer management for global ammonia emission reduction
A machine learning model for generating crop-specific and spatially explicit NH3 emission factors globally shows that global NH3 emissions in 2018 were lower than previous estimates that did not fully consider fertilizer management practices.
- Peng Xu
- , Geng Li
- & Benjamin Z. Houlton
-
Article
| Open Access Global population exposure to landscape fire air pollution from 2000 to 2019
Global population exposure to landscape fire air pollution from 2000 to 2019
The global population is increasingly exposed to daily landscape fire-sourced air pollution but there are socioeconomic disparities, with this pollution four times higher in low-income countries than in high-income countries during the period 2000–2019.
- Rongbin Xu
- , Tingting Ye
- & Shanshan Li
-
Article |
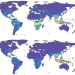 Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk
Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk
Changes in climate and land use will lead to species aggregating in new combinations at high elevations, in biodiversity hotspots and in areas of high human population density in Asia and Africa, driving the cross-species transmission of animal-associated viruses.
- Colin J. Carlson
- , Gregory F. Albery
- & Shweta Bansal
-
Article |
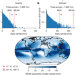 The effect of rainfall changes on economic production
The effect of rainfall changes on economic production
A global assessment shows that increases in the number of wet days and extreme daily rainfall adversely affect economic growth, particularly in high-income nations and via the services and manufacturing sectors.
- Maximilian Kotz
- , Anders Levermann
- & Leonie Wenz
-
Matters Arising |
 Concerns about reported harvests in European forests
Concerns about reported harvests in European forests
- Marc Palahí
- , Rubén Valbuena
- & Gert-Jan Nabuurs
-
Article |
 Thermal displacement by marine heatwaves
Thermal displacement by marine heatwaves
Ocean heatwaves displace surface isotherms by tens to thousands of kilometres—comparable to shifts associated with long-term warming trends—potentially driving rapid redistributions of marine species.
- Michael G. Jacox
- , Michael A. Alexander
- & James D. Scott
-
Letter |
 Future response of global coastal wetlands to sea-level rise
Future response of global coastal wetlands to sea-level rise
A global modelling approach shows that in response to rises in global sea level, gains of up to 60% in coastal wetland areas are possible, if appropriate coastal management solutions are developed to help support wetland resilience.
- Mark Schuerch
- , Tom Spencer
- & Sally Brown
-
Perspective |
 Choosing the future of Antarctica
Choosing the future of Antarctica
The future of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean by 2070 is described under two scenarios, one in which action is taken to limit greenhouse gas emissions, and one in which no action is taken.
- S. R. Rintoul
- , S. L. Chown
- & J. C. Xavier
-
Letter |
 A global slowdown of tropical-cyclone translation speed
A global slowdown of tropical-cyclone translation speed
The translation speed of tropical cyclones has decreased globally by 10% over the past 70 years, compounding the increases in cyclone-related local rainfall that have resulted from anthropogenic warming.
- James P. Kossin
-
Letter |
 Fluvial sediment supply to a mega-delta reduced by shifting tropical-cyclone activity
Fluvial sediment supply to a mega-delta reduced by shifting tropical-cyclone activity
About a third of the sediment delivery of the Mekong River is shown to be associated with rainfall generated by tropical cyclones, suggesting that future delta stability will be strongly moderated by changes to tropical cyclone intensity, frequency and track.
- Stephen E. Darby
- , Christopher R. Hackney
- & Rolf Aalto
-
Letter |
 Contribution of changes in atmospheric circulation patterns to extreme temperature trends
Contribution of changes in atmospheric circulation patterns to extreme temperature trends
This study identifies statistically significant trends in mid-atmospheric circulation patterns that partially explain observed changes in extreme temperature occurrence over Eurasia and North America; although the underlying cause of circulation pattern trends remains uncertain, most extreme temperature trends are shown to be consistent with thermodynamic warming.
- Daniel E. Horton
- , Nathaniel C. Johnson
- & Noah S. Diffenbaugh
-
Letter |
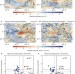 Increased frequency of extreme Indian Ocean Dipole events due to greenhouse warming
Increased frequency of extreme Indian Ocean Dipole events due to greenhouse warming
Extreme positive-Indian-Ocean-dipole events cause devastating floods in eastern tropical Africa and severe droughts in Asia; increasing greenhouse gas emissions will make these dipole events about three times more frequent in the twenty-first century.
- Wenju Cai
- , Agus Santoso
- & Toshio Yamagata
-
Letter |
 Increasing CO2 threatens human nutrition
Increasing CO2 threatens human nutrition
The largest assemblage so far of published data shows that C3 crops have decreased zinc and iron levels under CO2 conditions predicted for the middle of this century, with worldwide nutritional implications.
- Samuel S. Myers
- , Antonella Zanobetti
- & Yasuhiro Usui

 The economic commitment of climate change
The economic commitment of climate change