Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Environmental-social-economic footprints of consumption and trade in the Asia-Pacific region
Environmental-social-economic footprints of consumption and trade in the Asia-Pacific region
The environmental and socio-economic implications of the growth in welfare and trade in Asia-Pacific (APAC) remain unclear. Here the authors show that over the past two decades (1995–2015), owing to intraregional trade, the APAC economies have grown increasingly interdependent in natural resource use, air emissions, and labor and economic productivity.
- Lan Yang
- , Yutao Wang
- & Yuanbo Qiao
-
Comment
| Open AccessNew priorities for climate science and climate economics in the 2020s
Climate science and climate economics are critical sources of expertise in our pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals. Effective use of this expertise requires a strengthening of its epistemic foundations and a renewed focus on more practical policy problems.
- David A. Stainforth
- & Raphael Calel
-
Article
| Open Access Global consumption and international trade in deforestation-associated commodities could influence malaria risk
Global consumption and international trade in deforestation-associated commodities could influence malaria risk
Because many primary commodities cause deforestation and deforestation can increase malaria transmission, international trade can thus indirectly influence malaria risk. Here the authors use trade databases for commodites associated with deforestation to demonstrate that consumption of such commodities in developed nations could increase malaria risk in developing nations.
- Leonardo Suveges Moreira Chaves
- , Jacob Fry
- & Manfred Lenzen
-
Article
| Open Access Towards a more effective climate policy on international trade
Towards a more effective climate policy on international trade
Partners who actually reduce global emissions can be penalized under carbon accounting methods based on production or consumption give an idea of responsibility. Here the authors propose a new framework, emission responsibility allotment that penalizes/credits those that increase/decrease global emissions.
- Erik Dietzenbacher
- , Ignacio Cazcarro
- & Iñaki Arto
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of two of the world's largest protected areas on longline fishery catch rates
Impact of two of the world's largest protected areas on longline fishery catch rates
There are concerns that expansion of marine protected areas could have negative effects on the fishing industry. Here Lynham et al. demonstrate that the expansion of two of the world’s largest protected areas did not have a negative impact on catch rates in the Hawaii longline fishery.
- John Lynham
- , Anton Nikolaev
- & Juan Carlos Villaseñor-Derbez
-
Article
| Open Access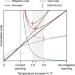 Paris Climate Agreement passes the cost-benefit test
Paris Climate Agreement passes the cost-benefit test
Relative economic benefits of achieving temperature targets have not properly accounted for damages at higher temperatures. Here the authors integrate dynamic cost-benefit analysis with a damage-cost curve and show that the Paris Climate Agreement constitutes the economically optimal policy pathway for the future.
- Nicole Glanemann
- , Sven N. Willner
- & Anders Levermann
-
Perspective
| Open Access Economic value of protected areas via visitor mental health
Economic value of protected areas via visitor mental health
Parks have a previously unquantified economic value attributable to mental health, a health services value. Here, the authors proposed three methods to estimate this, and applied one of these methods to show that this value is at least US$6 trillion per annum worldwide.
- Ralf Buckley
- , Paula Brough
- & Neil Harris
-
Article
| Open Access The role of irrigation in changing wheat yields and heat sensitivity in India
The role of irrigation in changing wheat yields and heat sensitivity in India
Irrigation buffers crop yields from extreme weather, but comes at environmental costs. Here the authors show that in India irrigation has improved wheat yield and reduced its sensitivity to heat, yet further increases are unlikely to offset the impact of warming.
- Esha Zaveri
- & David B. Lobell
-
Article
| Open Access Low-carbon innovation induced by emissions trading in China
Low-carbon innovation induced by emissions trading in China
It is unclear what opportunities for policy evaluation can be created by various independent Emission Trading Scheme (ETS). Here the authors presented the firm-level evidence of policy effects directly from emissions trading and differential program designs in China and find that China’s pilots largely induced low-carbon innovation of ETS firms without crowding out other technology innovation.
- Junming Zhu
- , Yichun Fan
- & Lan Xue
-
Comment
| Open Access On the financial viability of negative emissions
On the financial viability of negative emissions
Recent publications have raised concerns regarding the actual feasibility Negative Emission Technologies (NETs). Here the authors commented on the financial viability of large-scale late century NETs and suggested that expenditure peak will occur in the end of the century, which would require massive global subsidy program.
- Johannes Bednar
- , Michael Obersteiner
- & Fabian Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access The carbon footprint of the U.S. multinationals’ foreign affiliates
The carbon footprint of the U.S. multinationals’ foreign affiliates
Multinational enterprises (MNE) play a key role in climate mitigation as the significance of the environmental impacts of MNE. Here the authors measured the carbon footprint of U.S. MNE affiliates throughout their global value chains and show their carbon footprint beyond borders at 0.5082 GtCO2 in 2009.
- Luis-Antonio López
- , María-Ángeles Cadarso
- & Guadalupe Arce
-
Article
| Open Access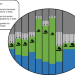 Over-exploitation of natural resources is followed by inevitable declines in economic growth and discount rate
Over-exploitation of natural resources is followed by inevitable declines in economic growth and discount rate
The exploitation of ecosystems has long-lasting consequences for the future provision of natural resources and ecosystem services. Here the author showed that the transition to sustainable harvest after a period of over-harvesting leads to a decline in welfare, economic growth, and in the discount rate.
- Adam Lampert
-
Article
| Open Access Global state and potential scope of investments in watershed services for large cities
Global state and potential scope of investments in watershed services for large cities
Investment in watershed services programs is growing, however the factors that contribute to sustainability of such programs are unclear. Here the authors use a large database of cities around the world to show that payment schemes are more likely to be present in watersheds with more agricultural land and less protected areas.
- Chelsie L. Romulo
- , Stephen Posner
- & Robert I. McDonald
-
Article
| Open Access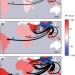 The rise of South–South trade and its effect on global CO2 emissions
The rise of South–South trade and its effect on global CO2 emissions
The rapid growth of South–South trade reflects a new phase of globalization. Here the authors show that some energy-intensive production activities, particularly raw materials and intermediate goods, and related CO2 emissions are relocating from China and India to other developing countries.
- Jing Meng
- , Zhifu Mi
- & Steven J. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Factoring economic costs into conservation planning may not improve agreement over priorities for protection
Factoring economic costs into conservation planning may not improve agreement over priorities for protection
Prioritising areas for conservation is hindered by disagreements over ecological targets. Here, Armsworth et al. combine a simulation approach and case study to test if considering economic return on investment aids in prioritisation, and find that its impact on reaching agreements varies greatly.
- Paul R. Armsworth
- , Heather B. Jackson
- & Nathan A. Sutton
-
Article
| Open Access New science of climate change impacts on agriculture implies higher social cost of carbon
New science of climate change impacts on agriculture implies higher social cost of carbon
Climate change impacts in models used to calculate the social cost of carbon (SCC) are either poorly documented or based on a small number of dated studies. Here, the authors estimate new damages for the agricultural sector and find that updating this sector alone causes the SCC to increase substantially.
- Frances C. Moore
- , Uris Baldos
- & Delavane Diaz
-
Article
| Open Access Reduced ultrafine particle levels in São Paulo’s atmosphere during shifts from gasoline to ethanol use
Reduced ultrafine particle levels in São Paulo’s atmosphere during shifts from gasoline to ethanol use
The biofuel ethanol has been introduced into urban transportation in many countries. Here, by measuring aerosols in São Paulo, the authors find that high ethanol prices coincided with an increase in harmful nanoparticles by a third, as drivers switched from ethanol to cheaper gasoline, showing a benefit of ethanol.
- Alberto Salvo
- , Joel Brito
- & Franz M. Geiger
-
Article
| Open Access The social inefficiency of regulating indirect land use change due to biofuels
The social inefficiency of regulating indirect land use change due to biofuels
A Low Carbon Fuel Standard seeks to regulate indirect land use change by including its related carbon emissions in the carbon intensity of biofuels. Khannaet al. show the economic cost of abatement achieved by including this factor is much larger than the social cost of carbon.
- Madhu Khanna
- , Weiwei Wang
- & Evan H. DeLucia
-
Article
| Open Access A coupled human-Earth model perspective on long-term trends in the global marine fishery
A coupled human-Earth model perspective on long-term trends in the global marine fishery
Global marine fish harvest increased over the 20th century, reaching a peak in the 1990s. Here, Galbraith and colleagues analyse a model combining both ecological and economic drivers to weigh the factors most likely to contribute to long-term changes in fish harvests.
- E. D. Galbraith
- , D. A. Carozza
- & D. Bianchi
-
Article
| Open Access Fisheries portfolio diversification and turnover buffer Alaskan fishing communities from abrupt resource and market changes
Fisheries portfolio diversification and turnover buffer Alaskan fishing communities from abrupt resource and market changes
Economies dependent on natural resources could gain resilience to abrupt ecosystem and market shifts through proactive risk-buffering approaches. Using data from Alaskan fisheries, Clineet al. show that communities relying on diverse fisheries were more resilient to major ocean and market regime shifts in 1989.
- Timothy J. Cline
- , Daniel E. Schindler
- & Ray Hilborn
-
Article
| Open Access Estimating economic losses to tourism in Africa from the illegal killing of elephants
Estimating economic losses to tourism in Africa from the illegal killing of elephants
An ongoing elephant poaching crisis is threatening not only elephant populations but also the local economies that rely on nature-based tourism. Here, Naidoo and colleagues use an economic model to estimate the financial contribution of elephants to tourism and the possible consequences of their loss.
- Robin Naidoo
- , Brendan Fisher
- & Andrew Balmford
-
Article
| Open Access Land-use choices follow profitability at the expense of ecological functions in Indonesian smallholder landscapes
Land-use choices follow profitability at the expense of ecological functions in Indonesian smallholder landscapes
Small-scale farmers in Southeast Asia are increasingly turning to monocultures of oil palm and rubber to maximize income. Clough and colleagues demonstrate that this land-use change in Indonesia comes at a cost to a wide array of ecosystem functions and biodiversity.
- Yann Clough
- , Vijesh V. Krishna
- & Stefan Scheu
-
Article
| Open Access Opportunities for biodiversity gains under the world’s largest reforestation programme
Opportunities for biodiversity gains under the world’s largest reforestation programme
China’s Grain for Green Program is the world’s largest reforestation program, encompassing tens of millions of hectares since 1999. Here, Hua et al. show that the majority of areas have been reforested with tree monocultures, but that planting mixed forests could increase animal biodiversity without imposing additional economic costs.
- Fangyuan Hua
- , Xiaoyang Wang
- & David S. Wilcove
-
Article
| Open Access Factoring attitudes towards armed conflict risk into selection of protected areas for conservation
Factoring attitudes towards armed conflict risk into selection of protected areas for conservation
Armed conflicts pose significant problems for ensuring that regional conservation plans are implemented. Here, Hammill et al. show that offsetting the impacts of protected area loss through protection of additional areas during conflicts provides the greatest return on investment for conservation programs.
- E. Hammill
- , A. I. T. Tulloch
- & K. A. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Alternative futures for Borneo show the value of integrating economic and conservation targets across borders
Alternative futures for Borneo show the value of integrating economic and conservation targets across borders
Balancing biological conservation with economic development is a challenge for policymakers. Analysing a range of possible future scenarios, Runting et al, show that coordinated planning would allow the island of Borneo to simultaneously retain forested land, protect species and meet economic goals.
- Rebecca K. Runting
- , Erik Meijaard
- & Kerrie A. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access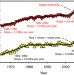 Distinguishing between yield advances and yield plateaus in historical crop production trends
Distinguishing between yield advances and yield plateaus in historical crop production trends
Food security and the conservation of natural ecosystems largely rely on the increase in crop yields. Here, the authors examine global crop yield trends since 1960, and establish a robust statistical framework for estimating historical trajectories and identifying yield plateaus.
- Patricio Grassini
- , Kent M. Eskridge
- & Kenneth G. Cassman

 Carbon pricing and planetary boundaries
Carbon pricing and planetary boundaries