Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Labeled oxytocin administered via the intranasal route reaches the brain in rhesus macaques
Labeled oxytocin administered via the intranasal route reaches the brain in rhesus macaques
The location and extent of intranasal oxytocin brain penetrance has not been shown. Here the authors show that oxytocin, administered intranasally, enters brain regions along the trajectories of the olfactory and trigeminal nerves and there, reaches biologically relevant concentrations.
- M. R. Lee
- , T. A. Shnitko
- & L. Leggio
-
Article
| Open Access Skeletal muscle enhancer interactions identify genes controlling whole-body metabolism
Skeletal muscle enhancer interactions identify genes controlling whole-body metabolism
Obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D) are metabolic disorders characterized by insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Here, the authors map skeletal muscle enhancer elements dynamically regulated after exposure to free fatty acid palmitate or inflammatory cytokine TNFα and identify target genes involved in metabolic dysfunction in skeletal muscle.
- Kristine Williams
- , Lars R. Ingerslev
- & Romain Barrès
-
Article
| Open Access The neuropeptide substance P regulates aldosterone secretion in human adrenals
The neuropeptide substance P regulates aldosterone secretion in human adrenals
Adrenal aldosterone production is regulated by plasma angiotensin and potassium levels. Here the authors report that the neuropeptide substance P stimulates aldosterone production via neurokinin type 1 receptors (NK1R), and report a proof-of-concept placebo controlled clinical trial showing that a NK1R antagonist decreases aldosterone levels.
- Julien Wils
- , Céline Duparc
- & Hervé Lefebvre
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated multi-omics approach identifies the landscape of interferon-α-mediated responses of human pancreatic beta cells
An integrated multi-omics approach identifies the landscape of interferon-α-mediated responses of human pancreatic beta cells
The cytokine IFNα is expressed in the islets of individuals with type 1 diabetes and contributes to local inflammation and destruction of beta cells. Here, the authors provide a global multiomics view of IFNα-induced changes in human beta cells at the level of chromatin, mRNA and protein expression.
- Maikel L. Colli
- , Mireia Ramos-Rodríguez
- & Décio L. Eizirik
-
Article
| Open Access FoxO1–Dio2 signaling axis governs cardiomyocyte thyroid hormone metabolism and hypertrophic growth
FoxO1–Dio2 signaling axis governs cardiomyocyte thyroid hormone metabolism and hypertrophic growth
Disease stress-induced cardiac hypertrophy is a major mechanism of pathological cardiac remodeling. Here, the authors unveil a previously unrecognized role of a FoxO1–Dio2 signaling axis in maladaptive, afterload-induced cardiac hypertrophy and intracellular thyroid hormone homeostasis.
- Anwarul Ferdous
- , Zhao V. Wang
- & Joseph A. Hill
-
Article
| Open Access Raptor determines β-cell identity and plasticity independent of hyperglycemia in mice
Raptor determines β-cell identity and plasticity independent of hyperglycemia in mice
During the progression of type 2 diabetes, insulin-producing β-cells can lose their identity and become reprogrammed into other cell types. Here the authors show that murine diabetic β-cells require the protein Raptor for maintaining β-cell health and preventing them from turning into α-cells, independent of Raptor’s involvement in regulating blood sugar levels.
- Qinglei Yin
- , Qicheng Ni
- & Guang Ning
-
Article
| Open Access Somatic SF3B1 hotspot mutation in prolactinomas
Somatic SF3B1 hotspot mutation in prolactinomas
The genetic basis of prolactinomas remains poorly understood. Here, the authors find a recurrent hotspot somatic mutation in the splicing factor 3 subunit B1 (SF3B1R625H) in prolactinomas, and show that this mutation causes aberrant splicing of ESRRG mRNA leading to up-regulation of prolactin.
- Chuzhong Li
- , Weiyan Xie
- & Yazhuo Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial uncoupler BAM15 reverses diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice
Mitochondrial uncoupler BAM15 reverses diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice
Obesity is a global pandemic with limited treatment options. Here, the authors show evidence in mice that the mitochondrial uncoupler BAM15 effectively induces fat loss without affecting food intake or compromising lean body mass.
- Stephanie J. Alexopoulos
- , Sing-Young Chen
- & Kyle L. Hoehn
-
Article
| Open Access The scaffold protein p62 regulates adaptive thermogenesis through ATF2 nuclear target activation
The scaffold protein p62 regulates adaptive thermogenesis through ATF2 nuclear target activation
Beta-adrenergic stimulation of brown adipose tissue leads to thermogenesis via the activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2) mediated expression of the thermogenic genes Ucp1 and Pgc-1α. Here, the authors show that the scaffold protein p62 regulates brown adipose tissue function through modifying ATF2 genomic binding and subsequent Ucp1 and Pgc-1α induction.
- Katrin Fischer
- , Anna Fenzl
- & Timo D. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Estrogen receptor-α expressing neurons in the ventrolateral VMH regulate glucose balance
Estrogen receptor-α expressing neurons in the ventrolateral VMH regulate glucose balance
Glucose-sensing neurons are found in the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus (VMH). Here the authors identify the role of estrogen receptor-α expressing neurons in the ventrolateral subdivision of the VMH in sensing hypoglycemia.
- Yanlin He
- , Pingwen Xu
- & Yong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access The kallikrein–kinin pathway as a mechanism for auto-control of brown adipose tissue activity
The kallikrein–kinin pathway as a mechanism for auto-control of brown adipose tissue activity
Brown adipose tissue, known produce heat by metabolizing fat, is also secretes molecules capable of communicating with other organs. Here the authors show that brown adipose tissue secretes kininogen, a component of heat system regulation, that provides auto-regulatory inhibitory signaling in brown adipose tissue.
- Marion Peyrou
- , Rubén Cereijo
- & Francesc Villarroya
-
Article
| Open Access MD2 activation by direct AGE interaction drives inflammatory diabetic cardiomyopathy
MD2 activation by direct AGE interaction drives inflammatory diabetic cardiomyopathy
The mechanisms underlying cardiac inflammation in diabetic cardiomyopathy are incompletely understood. Here the authors show that advanced glycation end products bind to the TLR4 co-receptor MD2 initiating pro-inflammatory pathways.
- Yi Wang
- , Wu Luo
- & Guang Liang
-
Article
| Open Access SGLT2 inhibition modulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity via ketones and insulin in diabetes with cardiovascular disease
SGLT2 inhibition modulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity via ketones and insulin in diabetes with cardiovascular disease
SGLT2 inhibitors, a class of type 2 diabetes medication, reduce cardiovascular events in patients beyond expectation from blood sugar control. Here the authors report a randomized controlled trial showing that SGLT2 inhibitors reduce inflammasome activation in peripheral macrophages, which may contribute to the cardiovascular protection.
- So Ra Kim
- , Sang-Guk Lee
- & Yong-ho Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Partial impairment of insulin receptor expression mimics fasting to prevent diet-induced fatty liver disease
Partial impairment of insulin receptor expression mimics fasting to prevent diet-induced fatty liver disease
Hyper-insulinemia associated with excess calorie intake may cause metabolic dysfunction. Here the authors report that mice with partially reduced insulin receptor expression in peripheral tissues are protected from and experience reversal of fatty liver disease.
- Troy L. Merry
- , Chris P. Hedges
- & Michael Ristow
-
Article
| Open Access Apolipoprotein J is a hepatokine regulating muscle glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity
Apolipoprotein J is a hepatokine regulating muscle glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity
Hepatokines are proteins secreted by the liver that can regulate whole body metabolism. Here the authors identify apolipoprotein J as a hepatokine that regulates muscle glucose metabolism and insulin resistance through a low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein−2 mediated mechanism in mice.
- Ji A Seo
- , Min-Cheol Kang
- & Young-Bum Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Hepatic saturated fatty acid fraction is associated with de novo lipogenesis and hepatic insulin resistance
Hepatic saturated fatty acid fraction is associated with de novo lipogenesis and hepatic insulin resistance
Hepatic steatosis is associated with poor cardiometabolic health, with de novo lipogenesis (DNL) contributing to hepatic steatosis and subsequent insulin resistance. Here, the authors use 1H-MRS methodology to show hepatic SFA fraction is a measure of DNL and specifically may hamper hepatic insulin sensitivity.
- Kay H. M. Roumans
- , Lucas Lindeboom
- & Vera B. Schrauwen-Hinderling
-
Article
| Open Access Brain insulin sensitivity is linked to adiposity and body fat distribution
Brain insulin sensitivity is linked to adiposity and body fat distribution
Brain insulin action regulates eating behavior and whole-body energy fluxes, however the impact of brain insulin resistance on long-term weight and body fat composition is unknown. Here, the authors show that high brain insulin sensitivity is linked to weight loss during lifestyle intervention and associates with a favorable body fat distribution.
- Stephanie Kullmann
- , Vera Valenta
- & Martin Heni
-
Article
| Open Access METTL3 is essential for postnatal development of brown adipose tissue and energy expenditure in mice
METTL3 is essential for postnatal development of brown adipose tissue and energy expenditure in mice
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most prevalent mRNA modifications in eukaryotes. Here the authors show that the m6A writer protein methyltransferase-like (METTL) 3 plays an important role for the development of brown adipose tissue.
- Yuqin Wang
- , Ming Gao
- & Zheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access ASK1 inhibits browning of white adipose tissue in obesity
ASK1 inhibits browning of white adipose tissue in obesity
Understanding the regulatory mechanisms governing brown and beige adipose mediated thermogenesis is of interest in order to develop therapeutic strategies to treat obesity. Here, the authors show that adipocyte-expressed apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) inhibits browning in response to cold, β3 receptor activation, and LPS.
- Fabrizio C. Lucchini
- , Stephan Wueest
- & Daniel Konrad
-
Article
| Open Access The secreted protease Adamts18 links hormone action to activation of the mammary stem cell niche
The secreted protease Adamts18 links hormone action to activation of the mammary stem cell niche
How hormonal signaling in the mammary epithelium controls the surrounding extracellular matrix is unclear. Here, the authors show that a secreted protease, Adamts18, induced by upstream estrogen-progesterone activated Wnt4 in myoepithelial cells, remodels the basement membrane and contributes to mammary epithelial stemness.
- Dalya Ataca
- , Patrick Aouad
- & Cathrin Brisken
-
Article
| Open Access Housing temperature influences exercise training adaptations in mice
Housing temperature influences exercise training adaptations in mice
Exercise has been shown to be an effective approach to ameliorate metabolic disease in mice housed at ambient temperatures, a condition of mild cold stress to mice. Here the authors show that molecular and metabolic adaptations to exercise are blunted when mice are housed in thermoneutral conditions.
- Steffen H. Raun
- , Carlos Henriquez-Olguín
- & Lykke Sylow
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic analysis of male puberty timing highlights shared genetic basis with hair colour and lifespan
Genomic analysis of male puberty timing highlights shared genetic basis with hair colour and lifespan
Age at voice-breaking is used to determine puberty timing in men, recall of which is considered less accurate than age at first menarche in women. Here, the authors perform multi-trait GWAS for male puberty timing by including both age at voice breaking and age of first facial hair for improved phenotype definition and power.
- Ben Hollis
- , Felix R. Day
- & John R. B. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access FAM13A affects body fat distribution and adipocyte function
FAM13A affects body fat distribution and adipocyte function
Genetic variants in the FAM13A locus have been associated with anthropometric and glycemic traits. Here, using fine-mapping, in vitro knockdown studies in pre-adipocytes and in vivo knockout in mice, the authors show that FAM13A is involved in regulating fat distribution and metabolic traits.
- Mohsen Fathzadeh
- , Jiehan Li
- & Joshua W. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular progenitors generated from tankyrase inhibitor-regulated naïve diabetic human iPSC potentiate efficient revascularization of ischemic retina
Vascular progenitors generated from tankyrase inhibitor-regulated naïve diabetic human iPSC potentiate efficient revascularization of ischemic retina
hPSCs in culture acquire a more naïve pluripotent state upon tankyrase inhibition. Here, the authors show that tankyrase inhibitor-regulated naïve hiPSCs from diabetic donors generate more vascular progenitors and more efficient engraftment into mouse retina than conventional PSCs.
- Tea Soon Park
- , Ludovic Zimmerlin
- & Elias T. Zambidis
-
Article
| Open Access Collaborative interactions of heterogenous ribonucleoproteins contribute to transcriptional regulation of sterol metabolism in mice
Collaborative interactions of heterogenous ribonucleoproteins contribute to transcriptional regulation of sterol metabolism in mice
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) play critical roles in the biogenesis, localization and transport of RNA. Here authors investigate a role for hnRNPs in sterol metabolism in mice and provide insights into their role in selective promoter activation.
- Zhengyi Zhang
- , An-Chieh Feng
- & Tamer Sallam
-
Article
| Open Access Maternal paraben exposure triggers childhood overweight development
Maternal paraben exposure triggers childhood overweight development
Parabens are preservatives widely used in consumer products including cosmetics and food. Here the authors demonstrate that maternal paraben exposure may contribute to childhood overweight development by an altered neuronal appetite regulation.
- Beate Leppert
- , Sandra Strunz
- & Tobias Polte
-
Article
| Open Access A MAFG-lncRNA axis links systemic nutrient abundance to hepatic glucose metabolism
A MAFG-lncRNA axis links systemic nutrient abundance to hepatic glucose metabolism
Despite widespread transcription of LncRNA in mammalian systems, their contribution to metabolic homeostasis at the cellular and tissue level remains elusive. Here Pradas-Juni et al. describe a transcription factor–LncRNA pathway that couples hepatocyte nutrient sensing to regulation of glucose metabolism in mice.
- Marta Pradas-Juni
- , Nils R. Hansmeier
- & Jan-Wilhelm Kornfeld
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution microscopy compatible fluorescent probes reveal endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor distribution and dynamics
Super-resolution microscopy compatible fluorescent probes reveal endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor distribution and dynamics
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is an important regulator of appetite and glucose homeostasis. Here the authors describe super-resolution microscopy and in vivo imaging compatible fluorescent probes, which reveal endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor distribution and dynamics in islets and brain.
- Julia Ast
- , Anastasia Arvaniti
- & David J. Hodson
-
Article
| Open Access PTH induces bone loss via microbial-dependent expansion of intestinal TNF+ T cells and Th17 cells
PTH induces bone loss via microbial-dependent expansion of intestinal TNF+ T cells and Th17 cells
T cells are involved in the bone loss induced by parathyroid hormone (PTH), but their origin is unknown. Here, the authors show that the intestinal microbiota is required for PTH to induce bone loss and describes mechanisms for microbiota-mediated gut–bone crosstalk in mouse models of hyperparathyroidism.
- Mingcan Yu
- , Abdul Malik Tyagi
- & Roberto Pacifici
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelial ZEB1 promotes angiogenesis-dependent bone formation and reverses osteoporosis
Endothelial ZEB1 promotes angiogenesis-dependent bone formation and reverses osteoporosis
An endothelial cell subtype, expressing endomucin and CD31, has been reported to couple angiogenesis with osteogenesis. Here, the authors show that loss of ZEB1 in these cells epigenetically suppresses Notch signaling, leading to impaired angiogenesis and osteogenesis, and that Zeb1 delivery via liposomes ameliorates bone loss in osteoporotic mice
- Rong Fu
- , Wen-Cong Lv
- & Zhao-Qiu Wu
-
Article
| Open Access The RNA-binding protein HuR is a negative regulator in adipogenesis
The RNA-binding protein HuR is a negative regulator in adipogenesis
Human antigen R (HuR) is an RNA binding protein that promotes mRNA stability. Here the authors show that HuR represses adipogenesis in white and brown adipose tissue by stabilizing Insig1 and other targets.
- Diana Teh Chee Siang
- , Yen Ching Lim
- & Dan Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting optical coherence tomography-derived diabetic macular edema grades from fundus photographs using deep learning
Predicting optical coherence tomography-derived diabetic macular edema grades from fundus photographs using deep learning
Diabetic eye disease is a cause of preventable blindness and accurate and timely referral of patients with diabetic macular edema is important to start treatment. Here the authors present a deep learning model that can predict the presence of diabetic macular edema from color fundus photographs with superior specificity and positive predictive value compared to retinal specialists.
- Avinash V. Varadarajan
- , Pinal Bavishi
- & Dale R. Webster
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of osteoclast-osteoblast coupling factors in humans reveals links between bone and energy metabolism
Identification of osteoclast-osteoblast coupling factors in humans reveals links between bone and energy metabolism
Anti-resorptive bone therapies also inhibit bone formation, as osteoclasts secrete factors that stimulate bone formation by osteoblasts. Here, the authors identify osteoclast-secreted factors that couple bone resorption to bone formation in healthy subjects, and show that osteoclast-derived DPP4 may be a factor coupling bone resorption to energy metabolism.
- Megan M. Weivoda
- , Chee Kian Chew
- & Sundeep Khosla
-
Article
| Open Access Glucose homeostasis is regulated by pancreatic β-cell cilia via endosomal EphA-processing
Glucose homeostasis is regulated by pancreatic β-cell cilia via endosomal EphA-processing
Primary cilia have been proposed to regulate glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in beta cells, but it is not known how. Here the authors show that primary cilia play a role in adult β-cell function via a mechanism involving endosomal EphA-processing.
- Francesco Volta
- , M. Julia Scerbo
- & Jantje M. Gerdes
-
Article
| Open Access Flagellin-elicited adaptive immunity suppresses flagellated microbiota and vaccinates against chronic inflammatory diseases
Flagellin-elicited adaptive immunity suppresses flagellated microbiota and vaccinates against chronic inflammatory diseases
Gut microbiota alterations, including enrichment of flagellated bacteria, are associated with metabolic syndrome and chronic inflammatory diseases. Here, Tran et al. show, in mice, that elicitation of mucosal anti-flagellin antibodies protects against experimental colitis and ameliorates diet-induced obesity.
- Hao Q. Tran
- , Ruth E. Ley
- & Benoit Chassaing
-
Article
| Open Access Leptin induces TNFα-dependent inflammation in acquired generalized lipodystrophy and combined Crohn’s disease
Leptin induces TNFα-dependent inflammation in acquired generalized lipodystrophy and combined Crohn’s disease
The adipokine leptin modulates intestinal inflammation in mice. Here the authors describe a patient with inflammatory bowel disease and lipodystrophy, providing evidence that leptin aggravates intestinal inflammation with proinflammatory effects on leukocytes that are reversible by TNFα blockade.
- Jörn F. Ziegler
- , Chotima Böttcher
- & Carl Weidinger
-
Article
| Open Access Thyroid hormone induces progression and invasiveness of squamous cell carcinomas by promoting a ZEB-1/E-cadherin switch
Thyroid hormone induces progression and invasiveness of squamous cell carcinomas by promoting a ZEB-1/E-cadherin switch
The invasion of epithelial tumours often depends on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Here, the authors report that intracellular activation of thyroid hormone by the D2 deiodinase enzyme promotes invasion and progression of squamous cell carcinoma by transcriptionally up-regulating ZEB-1.
- Caterina Miro
- , Emery Di Cicco
- & Monica Dentice
-
Article
| Open Access Elevated aldosterone and blood pressure in a mouse model of familial hyperaldosteronism with ClC-2 mutation
Elevated aldosterone and blood pressure in a mouse model of familial hyperaldosteronism with ClC-2 mutation
Mutations in the chloride channel ClC-2 have been associated with familial forms of hyperaldosteronism. Here, Schewe et al. generated a mouse model carrying the most common mutation found in patients and find it recapitulates key features of the disease, providing a unique tool for future studies on its pathogenesis.
- Julia Schewe
- , Eric Seidel
- & Ute Scholl
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-ancestry sleep-by-SNP interaction analysis in 126,926 individuals reveals lipid loci stratified by sleep duration
Multi-ancestry sleep-by-SNP interaction analysis in 126,926 individuals reveals lipid loci stratified by sleep duration
Sleep duration is associated with an adverse lipid profile. Here, the authors perform genome-wide gene-by-sleep interaction analysis and find 49 previously unreported lipid loci when considering short or long total sleep time.
- Raymond Noordam
- , Maxime M. Bos
- & Susan Redline
-
Article
| Open Access Neratinib protects pancreatic beta cells in diabetes
Neratinib protects pancreatic beta cells in diabetes
Type 1 as well as type 2 diabetes are characterized by a loss of insulin-producing β-cells. Here the authors show that the FDA-approved drug neratinib has beneficial effects on β-cell survival, insulin secretion, and glycemic control in mouse models of diabetes.
- Amin Ardestani
- , Sijia Li
- & Kathrin Maedler
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphate acts directly on the calcium-sensing receptor to stimulate parathyroid hormone secretion
Phosphate acts directly on the calcium-sensing receptor to stimulate parathyroid hormone secretion
Elevated inorganic phosphate levels promote excessive parathyroid hormone secretion, which contributes to the aetiology of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Here, the authors show that phosphate directly inhibits the calcium-sensing receptor, the main regulator of parathyroid hormone secretion.
- Patricia P. Centeno
- , Amanda Herberger
- & Donald T. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Pathogenesis of hypertension in a mouse model for human CLCN2 related hyperaldosteronism
Pathogenesis of hypertension in a mouse model for human CLCN2 related hyperaldosteronism
Mutations in the chloride channel ClC-2 have been found in primary aldosteronism (PA). Here, Göppner et al. generate transgenic mice expressing a mutant form of ClC-2 that displays increased chloride currents like patient mutations, and find it recapitulates the key pathological features of PA.
- Corinna Göppner
- , Ian J. Orozco
- & Thomas J. Jentsch
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic changes of muscle insulin sensitivity after metabolic surgery
Dynamic changes of muscle insulin sensitivity after metabolic surgery
Surgical weight-loss interventions improve insulin sensitivity via incompletely understood mechanisms. Here the authors assess skeletal muscle epigenetic changes in individuals with obesity following metabolic surgery and compare them with data from individuals without obesity.
- Sofiya Gancheva
- , Meriem Ouni
- & Michael Roden
-
Article
| Open Access Gut-associated IgA+ immune cells regulate obesity-related insulin resistance
Gut-associated IgA+ immune cells regulate obesity-related insulin resistance
The effect of diet-induced obesity on intestinal B cell populations is not well understood despite emerging evidence of a critical role for the intestinal immune system in contributing to insulin resistance. Here, the authors show important functions of IgA in regulating metabolic disease and for intestinal immunity in modulating systemic glucose metabolism.
- Helen Luck
- , Saad Khan
- & Daniel A. Winer
-
Article
| Open Access S100A9 extends lifespan in insulin deficiency
S100A9 extends lifespan in insulin deficiency
Insulin replacement is a valuable therapy for insulin deficiency, however, other therapies are being investigated to restore metabolic homeostasis. Here, the authors identify S100A9 as a leptin induced circulating cue that improves glucose and lipid homeostasis and extends survival in insulin deficient mice.
- Giorgio Ramadori
- , Sanda Ljubicic
- & Roberto Coppari
-
Article
| Open Access Angptl8 mediates food-driven resetting of hepatic circadian clock in mice
Angptl8 mediates food-driven resetting of hepatic circadian clock in mice
The circadian clock regulates rhythms of behavior and physiology and the timing of circadian rhythms in liver is influenced by food intake. Here, the authors identify the hepatokine Angptl8 as a mediator of liver clock food entrainment.
- Siyu Chen
- , Mengyang Feng
- & Chang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Lysosomal degradation of newly formed insulin granules contributes to β cell failure in diabetes
Lysosomal degradation of newly formed insulin granules contributes to β cell failure in diabetes
Impaired beta-cell insulin secretion is a key pathological feature of type 2 diabetes. Here, the authors describe metabolic stress induced lysosomal degradation of newly formed insulin granules, independent of macroautophagy, as a potential mechanism for beta-cell dysfunction.
- Adrien Pasquier
- , Kevin Vivot
- & Romeo Ricci
-
Article
| Open Access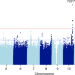 ZRANB3 is an African-specific type 2 diabetes locus associated with beta-cell mass and insulin response
ZRANB3 is an African-specific type 2 diabetes locus associated with beta-cell mass and insulin response
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is prevalent in populations worldwide, however, mostly studied in European and mixed-ancestry populations. Here, the authors perform a genome-wide association study for T2D in over 5,000 sub-Saharan Africans and identify a locus, ZRANB3, that is specific for this population.
- Adebowale A. Adeyemo
- , Norann A. Zaghloul
- & Charles N. Rotimi
-
Article
| Open Access IAPP toxicity activates HIF1α/PFKFB3 signaling delaying β-cell loss at the expense of β-cell function
IAPP toxicity activates HIF1α/PFKFB3 signaling delaying β-cell loss at the expense of β-cell function
Type 2 diabetes is associated with islet amyloid deposits derived from islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) expressed by β-cells. Here the authors show that IAPP misfolded protein stress induces the hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha injury repair pathway and activates survival metabolic changes mediated by PFKFB3.
- Chiara Montemurro
- , Hiroshi Nomoto
- & Slavica Tudzarova

 The circadian phase of antenatal glucocorticoid treatment affects the risk of behavioral disorders
The circadian phase of antenatal glucocorticoid treatment affects the risk of behavioral disorders