Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mesmerize is a dynamically adaptable user-friendly analysis platform for 2D and 3D calcium imaging data
Mesmerize is a dynamically adaptable user-friendly analysis platform for 2D and 3D calcium imaging data
Calcium imaging is valuable for understanding neuro and cell biology, but is challenging to analyze, organize, and access. Here, the authors present an efficient, expandable and user-friendly platform, which encapsulates the entire analysis process all to way to interactive visualizations.
- Kushal Kolar
- , Daniel Dondorp
- & Marios Chatzigeorgiou
-
Article
| Open Access Network analysis reveals rare disease signatures across multiple levels of biological organization
Network analysis reveals rare disease signatures across multiple levels of biological organization
Despite the clear causal relationship between genotype and phenotype in rare diseases, identifying the pathobiological mechanisms at various levels of biological organization remains a practical and conceptual challenge. Here, the authors introduce a network approach for evaluating the impact of rare gene defects across biological scales.
- Pisanu Buphamalai
- , Tomislav Kokotovic
- & Jörg Menche
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-omics analysis identifies therapeutic vulnerabilities in triple-negative breast cancer subtypes
Multi-omics analysis identifies therapeutic vulnerabilities in triple-negative breast cancer subtypes
Triple negative breast cancer can be divided into additional subtypes. Here, using omics analyses, the authors show that in the mesenchymal subtype expression of MHC-1 is repressed and that this can be restored by using drugs that target subunits of the epigenetic modifier PRC2.
- Brian D. Lehmann
- , Antonio Colaprico
- & X. Steven Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial deconvolution of HER2-positive breast cancer delineates tumor-associated cell type interactions
Spatial deconvolution of HER2-positive breast cancer delineates tumor-associated cell type interactions
While transcriptomics have enhanced our understanding for cancer, spatial transcriptomics enable the characterisation of cellular interactions. Here, the authors integrate single cell data with spatial information for HER2 + tumours and develop tools for the prediction of interactions between tumour-infiltrating cells.
- Alma Andersson
- , Ludvig Larsson
- & Joakim Lundeberg
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient and precise single-cell reference atlas mapping with Symphony
Efficient and precise single-cell reference atlas mapping with Symphony
The number of single-cell RNA-seq datasets generated is increasing rapidly, making methods that map cell types to well-curated references increasingly important. Here, the authors propose an accurate method for mapping single cells onto a reference atlas in seconds.
- Joyce B. Kang
- , Aparna Nathan
- & Soumya Raychaudhuri
-
Article
| Open Access A scalable, secure, and interoperable platform for deep data-driven health management
A scalable, secure, and interoperable platform for deep data-driven health management
The increasing scale and scope of biomedical data is generating tremendous opportunities for improving health outcomes, but also raises new challenges ranging from data acquisition and storage to data analysis and utilization. To meet these challenges, the authors develop the Personal Health Dashboard, which provides an end-to-end solution for deep biomedical data analytics.
- Amir Bahmani
- , Arash Alavi
- & Michael P. Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved and species-specific chromatin remodeling and regulatory dynamics during mouse and chicken limb bud development
Conserved and species-specific chromatin remodeling and regulatory dynamics during mouse and chicken limb bud development
The vertebrate limb bud is a paradigm to uncover the fundamental mechanisms that govern embryogenesis and evolutionary diversification. Here the authors compare mouse and chicken limb bud development to study the impact of genome evolution on conserved and divergent gene regulatory interactions.
- Shalu Jhanwar
- , Jonas Malkmus
- & Rolf Zeller
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell ATAC and RNA sequencing reveal pre-existing and persistent cells associated with prostate cancer relapse
Single-cell ATAC and RNA sequencing reveal pre-existing and persistent cells associated with prostate cancer relapse
Identifying the molecular mechanisms of response to systemic therapy in prostate cancer remains crucial. Here, the authors apply single cell-ATAC and RNAseq to models of early treatment response and resistance to enzalutamide and identify chromatin and gene expression patterns that can predict treatment response.
- S. Taavitsainen
- , N. Engedal
- & A. Urbanucci
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive characterization of 536 patient-derived xenograft models prioritizes candidates for targeted treatment
Comprehensive characterization of 536 patient-derived xenograft models prioritizes candidates for targeted treatment
Patient-derived xenograft models (PDX) have been extensively used to study the molecular and clinical features of cancers. Here the authors present a cohort of 536 PDX models from 25 cancers, as well as their genomic and evolutionary profiles and their suitability for clinical trials.
- Hua Sun
- , Song Cao
- & Li Ding
-
Article
| Open Access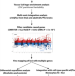 Multi-omics integration analysis identifies novel genes for alcoholism with potential overlap with neurodegenerative diseases
Multi-omics integration analysis identifies novel genes for alcoholism with potential overlap with neurodegenerative diseases
Alcohol use disorder and drinks per week both have been studied genetically and have different correlations with psychiatric diseases. Here the authors integrate multi-omics data to identify unique and shared variants, genes and pathways for alcohol use disorder and drinks per week.
- Manav Kapoor
- , Michael J. Chao
- & Alison Goate
-
Article
| Open Access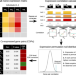 The molecular basis, genetic control and pleiotropic effects of local gene co-expression
The molecular basis, genetic control and pleiotropic effects of local gene co-expression
Local gene co-expression is found throughout the genome, but systematic analysis of these co-expressed genes is needed. Here, the authors identify local co-expressed genes in 49 tissues and characterize the genetic variants which may affect their expression and contribute to disease.
- Diogo M. Ribeiro
- , Simone Rubinacci
- & Olivier Delaneau
-
Article
| Open Access Fractional response analysis reveals logarithmic cytokine responses in cellular populations
Fractional response analysis reveals logarithmic cytokine responses in cellular populations
Our ability to interpret single-cell multivariate signaling responses is still limited. Here the authors introduce fractional response analysis (FRA), involving fractional cell counting, capable of deconvoluting heterogeneous multivariate responses of cellular populations.
- Karol Nienałtowski
- , Rachel E. Rigby
- & Michał Komorowski
-
Article
| Open Access Landscape of allele-specific transcription factor binding in the human genome
Landscape of allele-specific transcription factor binding in the human genome
Single-nucleotide variants in enhancers or promoters may affect gene transcription by altering transcription factor binding sites. Here the authors present a meta-analysis empowered by a new statistical method covering thousands of ChIP-Seq experiments resulting in the identification of more than 500 thousand allele-specific binding (ASB) events in the human genome.
- Sergey Abramov
- , Alexandr Boytsov
- & Ivan V. Kulakovskiy
-
Article
| Open Access multiSLIDE is a web server for exploring connected elements of biological pathways in multi-omics data
multiSLIDE is a web server for exploring connected elements of biological pathways in multi-omics data
The integration and interpretation of different omics data types is an ongoing challenge for biologists. Here, the authors present a web-based, interactive tool called multiSLIDE for the visualization of protein, phosphoprotein, and RNA data presented as interlinked heatmaps.
- Soumita Ghosh
- , Abhik Datta
- & Hyungwon Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell regulatory landscape of the mouse kidney highlights cellular differentiation programs and disease targets
Single cell regulatory landscape of the mouse kidney highlights cellular differentiation programs and disease targets
Epigenetic and transcriptional dynamics are critical for both tissue homeostasis and injury response in the kidney. Leveraging a single cell multiomics atlas of the developing mouse kidney, the authors reveal key events in chromatin regulation and gene expression dynamics during postnatal development.
- Zhen Miao
- , Michael S. Balzer
- & Katalin Susztak
-
Article
| Open Access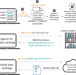 Go Get Data (GGD) is a framework that facilitates reproducible access to genomic data
Go Get Data (GGD) is a framework that facilitates reproducible access to genomic data
Modern biological research is complicated by the difficulty of collecting, transforming, annotating, and integrating datasets. Here, the authors present Go Get Data, a fast, reproducible approach to installing standardized data recipes, with an application to genomics data.
- Michael J. Cormier
- , Jonathan R. Belyeu
- & Aaron R. Quinlan
-
Article
| Open Access RA3 is a reference-guided approach for epigenetic characterization of single cells
RA3 is a reference-guided approach for epigenetic characterization of single cells
Methods for profiling differences between individual cells are constantly expanding. Here, the authors present a computational framework for the analysis of chromatin accessibility data at the single-cell level that takes into account previous knowledge and data-specific characteristics.
- Shengquan Chen
- , Guanao Yan
- & Zhixiang Lin
-
Article
| Open Access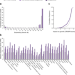 The landscape of molecular chaperones across human tissues reveals a layered architecture of core and variable chaperones
The landscape of molecular chaperones across human tissues reveals a layered architecture of core and variable chaperones
Tissue-specific differences in protein folding capacities are poorly understood. Here, the authors show that the human chaperone system consists of ubiquitous core chaperones and tissue-specific variable chaperones, perturbation of which leads to tissue-specific phenotypes.
- Netta Shemesh
- , Juman Jubran
- & Esti Yeger-Lotem
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of disease treatment mechanisms through the multiscale interactome
Identification of disease treatment mechanisms through the multiscale interactome
Most diseases disrupt multiple proteins, and drugs treat such diseases by restoring the functions of the disrupted proteins; how drugs restore these functions, however, is often unknown. Here, the authors develop the multiscale interactome, a powerful approach to explain disease treatment.
- Camilo Ruiz
- , Marinka Zitnik
- & Jure Leskovec
-
Article
| Open Access A computer-guided design tool to increase the efficiency of cellular conversions
A computer-guided design tool to increase the efficiency of cellular conversions
Transcription factor over-expression-based cellular conversion methods often endure low conversion efficiency. Here the authors show how to increase conversion efficiency by combining a computational method for prioritizing more efficient TF combinations with a transposon-based genomic integration system for delivery.
- Sascha Jung
- , Evan Appleton
- & Antonio del Sol
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated cross-study datasets of genetic dependencies in cancer
Integrated cross-study datasets of genetic dependencies in cancer
The integration of independent pan-cancer CRISPR-Cas9 datasets allows better representation of genomic heterogeneity across different cancer types. Here, the authors propose a strategy for the integration of two large CRISPR-Cas9 screens and report increased coverage of molecular diversity and genetic dependencies.
- Clare Pacini
- , Joshua M. Dempster
- & Francesco Iorio
-
Article
| Open Access Inflammation status modulates the effect of host genetic variation on intestinal gene expression in inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammation status modulates the effect of host genetic variation on intestinal gene expression in inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel diseases are heterogeneous, and little is known about how underlying genetic variation can affect their development. Here, the authors report that intestinal inflammation modulates the effect of host genetics on the gut mucosal expression of 190 genes in the context of inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Shixian Hu
- , Werna T. Uniken Venema
- & Rinse K. Weersma
-
Article
| Open Access Causal network models of SARS-CoV-2 expression and aging to identify candidates for drug repurposing
Causal network models of SARS-CoV-2 expression and aging to identify candidates for drug repurposing
Given the severity of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, a major challenge is to rapidly repurpose existing approved drugs for clinical interventions. Here, the authors identify robust druggable protein targets within a principled causal framework that makes use of multiple data modalities and integrates aging signatures.
- Anastasiya Belyaeva
- , Louis Cammarata
- & Caroline Uhler
-
Article
| Open Access Forecasting influenza activity using machine-learned mobility map
Forecasting influenza activity using machine-learned mobility map
Human mobility plays a central role in the spread of infectious diseases and can help in forecasting incidence. Here the authors show a comparison of multiple mobility benchmarks in forecasting influenza, and demonstrate the value of a machine-learned mobility map with global coverage at multiple spatial scales.
- Srinivasan Venkatramanan
- , Adam Sadilek
- & Madhav Marathe
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide fine-mapping identifies pleiotropic and functional variants that predict many traits across global cattle populations
Genome-wide fine-mapping identifies pleiotropic and functional variants that predict many traits across global cattle populations
Genomic prediction of phenotype may be improved by using DNA mutations with functional, evolutionary, and pleiotropic consequences. Here the authors describe a method for genome-wide fine-mapping of QTLs and develop a genotyping array for improved prediction of genetic values for cattle traits.
- Ruidong Xiang
- , Iona M. MacLeod
- & Michael E. Goddard
-
Article
| Open Access The natural history of symptomatic COVID-19 during the first wave in Catalonia
The natural history of symptomatic COVID-19 during the first wave in Catalonia
Establishing the natural history of COVID-19 requires longitudinal data from population-based cohorts. Here, the authors use linked primary care, testing, and hospital data to describe the disease in ~100,000 individuals with a COVID-19 diagnosis among a population of ~5.5 million in Catalonia, Spain.
- Edward Burn
- , Cristian Tebé
- & Talita Duarte-Salles
-
Article
| Open Access Lossless integration of multiple electronic health records for identifying pleiotropy using summary statistics
Lossless integration of multiple electronic health records for identifying pleiotropy using summary statistics
Thus far, pleiotropy analysis using individual-level Electronic Health Records data has been limited to data from one site. Here, the authors introduce Sum-Share, a method designed to efficiently and losslessly integrate EHR and genetic data from multiple sites to perform pleiotropy analysis.
- Ruowang Li
- , Rui Duan
- & Jason H. Moore
-
Article
| Open Access Benchmarking joint multi-omics dimensionality reduction approaches for the study of cancer
Benchmarking joint multi-omics dimensionality reduction approaches for the study of cancer
Advances in omics technology have resulted in the generation of multi-view data for cancer samples. Here, the authors compare dimensionality reduction techniques using simulated and TCGA data and identify the features of the methods with superior performance.
- Laura Cantini
- , Pooya Zakeri
- & Anaïs Baudot
-
Article
| Open Access Global computational alignment of tumor and cell line transcriptional profiles
Global computational alignment of tumor and cell line transcriptional profiles
The determination of whether cancer cell lines recapitulate the molecular features of corresponding patient tumours remains essential for the selection of appropriate cell line models for preclinical studies. The method developed here, Celligner, integrates cancer cell line and tumour RNA-seq datasets and reveals large differences in their concordance across cell lines and cancer types.
- Allison Warren
- , Yejia Chen
- & James M. McFarland
-
Article
| Open Access The aging transcriptome and cellular landscape of the human lung in relation to SARS-CoV-2
The aging transcriptome and cellular landscape of the human lung in relation to SARS-CoV-2
Age is one of the strongest risk factors for severe illness from COVID-19. By integrating human lung transcriptomes with experimental data on SARS-CoV-2, the authors pinpoint specific age-associated factors that could contribute to the heightened severity of COVID-19 in older populations.
- Ryan D. Chow
- , Medha Majety
- & Sidi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Long first exons and epigenetic marks distinguish conserved pachytene piRNA clusters from other mammalian genes
Long first exons and epigenetic marks distinguish conserved pachytene piRNA clusters from other mammalian genes
The pachytene piRNA loci are transcribed by RNA polymerase II in the male germline of placental mammals. Here the authors show that a long first exon or a long unspliced transcript correlates with germline-specific production of piRNA precursor transcripts and mature piRNAs.
- Tianxiong Yu
- , Kaili Fan
- & Zhiping Weng
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-domain translation between single-cell imaging and sequencing data using autoencoders
Multi-domain translation between single-cell imaging and sequencing data using autoencoders
Integration of single cell data modalities increases the richness of information about the heterogeneity of cell states, but integration of imaging and transcriptomics is an open challenge. Here the authors use autoencoders to learn a probabilistic coupling and map these modalities to a shared latent space.
- Karren Dai Yang
- , Anastasiya Belyaeva
- & Caroline Uhler
-
Article
| Open Access Structural modularity of the XIST ribonucleoprotein complex
Structural modularity of the XIST ribonucleoprotein complex
The long noncoding RNA XIST plays a central role in sex-specific gene expression in humans by silencing one of two X chromosomes in female cells. Here the authors show that higher order secondary structure creates the modular domain structure of XIST ribonucleoprotein complex and spatial separation of functions.
- Zhipeng Lu
- , Jimmy K. Guo
- & Howard Y. Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Chromatin accessibility landscape and regulatory network of high-altitude hypoxia adaptation
Chromatin accessibility landscape and regulatory network of high-altitude hypoxia adaptation
Tibetan adaptation to the high-altitude environment represents a case of natural selection during recent human evolution. Here the authors investigated the chromatin and transcriptional landscape of umbilical endothelial cells from Tibetan and Han Chinese donors and provide genome-wide characterization of the hypoxia regulatory network associated high-altitude adaptation.
- Jingxue Xin
- , Hui Zhang
- & Bing Su
-
Article
| Open Access A data-driven simulation platform to predict cultivars’ performances under uncertain weather conditions
A data-driven simulation platform to predict cultivars’ performances under uncertain weather conditions
Predicting crop performance in environments with limited field testing is challenging. Here the authors combine field experimental, DNA sequence, and weather data to predict genotypes’ future performance. They demonstrate the potential of this approach on a large dataset of wheat grain yield.
- Gustavo de los Campos
- , Paulino Pérez-Rodríguez
- & José Crossa
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of molecular profiles in a longitudinal wellness profiling cohort
Integration of molecular profiles in a longitudinal wellness profiling cohort
An important aspect of precision medicine is to probe the stability in molecular profiles among healthy individuals over time. Here, the authors sample a longitudinal wellness cohort and analyse blood molecular profiles as well as gut microbiota composition.
- Abdellah Tebani
- , Anders Gummesson
- & Linn Fagerberg
-
Article
| Open Access CORE GREML for estimating covariance between random effects in linear mixed models for complex trait analyses
CORE GREML for estimating covariance between random effects in linear mixed models for complex trait analyses
Linear mixed models have bias due to the assumed independence between random effects. Here, the authors describe a genome-based restricted maximum likelihood, CORE GREML, which estimates covariance between random effects. Application to UK Biobank data highlights this as an important parameter for multi-omics analyses of phenotypic variance.
- Xuan Zhou
- , Hae Kyung Im
- & S. Hong Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Testing and controlling for horizontal pleiotropy with probabilistic Mendelian randomization in transcriptome-wide association studies
Testing and controlling for horizontal pleiotropy with probabilistic Mendelian randomization in transcriptome-wide association studies
Transcriptome-wide association studies integrate GWAS and transcriptome data to examine the molecular mechanisms underlying disease etiology. Here the authors present PMR-Egger, a powerful TWAS method based on probabilistic Mendelian Randomization.
- Zhongshang Yuan
- , Huanhuan Zhu
- & Xiang Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptional activity and strain-specific history of mouse pseudogenes
Transcriptional activity and strain-specific history of mouse pseudogenes
Pseudogenes are key markers of genome remodelling processes. Here the authors present genome-wide annotation of the pseudogenes in the mouse reference genome and 18 inbred mouse strains, update human pseudogene annotations, and characterise the transcription and evolution of mouse pseudogenes.
- Cristina Sisu
- , Paul Muir
- & Mark Gerstein
-
Article
| Open Access An integrative ENCODE resource for cancer genomics
An integrative ENCODE resource for cancer genomics
ENCODE is a resource comprising thousands of functional genomic datasets. Here, the authors present custom annotation within ENCODE for cancer, highlighting a workflow that can help prioritise key elements in oncogenesis.
- Jing Zhang
- , Donghoon Lee
- & Mark Gerstein
-
Article
| Open Access Accounting for diverse evolutionary forces reveals mosaic patterns of selection on human preterm birth loci
Accounting for diverse evolutionary forces reveals mosaic patterns of selection on human preterm birth loci
There is a need for analytical frameworks to investigate the evolution of complex genetic traits. Here, the authors develop an approach to simultaneously evaluate different evolutionary signatures on trait-associated genetic variants for complex traits and apply it to study spontaneous preterm birth.
- Abigail L. LaBella
- , Abin Abraham
- & John A. Capra
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-faceted epigenetic dysregulation of gene expression promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Multi-faceted epigenetic dysregulation of gene expression promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
The epigenetic landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) at genome-wide high resolution is incompletely studied. Here, the authors performed an integrated multi-omics analysis of ESCC and non-tumor tissues to define the genome-wide methylome landscape and epigenetic alterations to uncover oncogenic drivers of ESCC.
- Wei Cao
- , Hayan Lee
- & Trever G. Bivona
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning for genomics using Janggu
Deep learning for genomics using Janggu
Deep learning is becoming a popular approach for understanding biological processes but can be hard to adapt to new questions. Here, the authors develop Janggu, a python library that aims to ease data acquisition and model evaluation and facilitate deep learning applications in genomics.
- Wolfgang Kopp
- , Remo Monti
- & Altuna Akalin
-
Article
| Open Access Searching large-scale scRNA-seq databases via unbiased cell embedding with Cell BLAST
Searching large-scale scRNA-seq databases via unbiased cell embedding with Cell BLAST
Single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) is being widely used to resolve cellular heterogeneity. Here, the authors present a cell-querying method built on a neural network-based generative model and a customized cell-to-cell similarity metric.
- Zhi-Jie Cao
- , Lin Wei
- & Ge Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible experimental designs for valid single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments allowing batch effects correction
Flexible experimental designs for valid single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments allowing batch effects correction
It is not clear which designs, other than completely randomized ones, are valid for scRNA-seq experiments so that batch effects can be adjusted. Here the authors show that under flexible reference panel and chain-type designs, biological variability can also be separated from batch effects, at least by BUSseq.
- Fangda Song
- , Ga Ming Angus Chan
- & Yingying Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonization of quality metrics and power calculation in multi-omic studies
Harmonization of quality metrics and power calculation in multi-omic studies
Multi-omics studies are popular but lack rigorous criteria for experimental design. We define Figures of Merit across omics to comparatively describe their performance, and present new algorithms for sample size calculation in multi-omics experiments aiming either at feature selection or sample classification.
- Sonia Tarazona
- , Leandro Balzano-Nogueira
- & Ana Conesa
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-trait analysis of rare-variant association summary statistics using MTAR
Multi-trait analysis of rare-variant association summary statistics using MTAR
Methods to integrate association evidence across multiple traits often focus on individual common variants GWAS. Here the authors present multi-trait analysis of rare-variant associations (MTAR), a framework for joint analysis of association summary statistics between multiple rare variants and different traits.
- Lan Luo
- , Judong Shen
- & Zheng-Zheng Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of human metabolism by reducing the complexity of the genome-scale models using redHUMAN
Analysis of human metabolism by reducing the complexity of the genome-scale models using redHUMAN
The complexity of genome-scale metabolic networks (GEMs) hinders their application in specific physiological contexts. Here, the authors introduce a framework to reduce thermodynamically curated GEMs to the subnetworks of interest and demonstrate its application by deriving leukemia-specific models.
- Maria Masid
- , Meric Ataman
- & Vassily Hatzimanikatis
-
Article
| Open Access The RNA fold interactome of evolutionary conserved RNA structures in S. cerevisiae
The RNA fold interactome of evolutionary conserved RNA structures in S. cerevisiae
Previous study identified in vivo structured mRNA regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by dimethyl sulfate-sequencing. Here the authors use quantitative proteomics to identify protein interactors of 186 RNA folds in S. cerevisiae, providing functional links between RNA binding proteins and distinct mRNA fold.
- Nuria Casas-Vila
- , Sergi Sayols
- & Falk Butter

 Machine learning of genomic features in organotropic metastases stratifies progression risk of primary tumors
Machine learning of genomic features in organotropic metastases stratifies progression risk of primary tumors