Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Male fertility thermal limits predict vulnerability to climate warming
Male fertility thermal limits predict vulnerability to climate warming
Trait-based approaches assume upper critical thermal limits (CTLs) are good predictors of climate change vulnerability. Here, the authors show that male fertility thermal limits, which are lower than CTLs, are better at predicting Drosophila extinction in the lab, suggesting species may be living close to their thermal limits.
- Belinda van Heerwaarden
- & Carla M. Sgrò
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic capabilities mute positive response to direct and indirect impacts of warming throughout the soil profile
Metabolic capabilities mute positive response to direct and indirect impacts of warming throughout the soil profile
There is much uncertainty on the response of soil microbial communities to warming, particularly in the subsoil. Here, the authors investigate microbial community and metabolism response to 4.5 years of whole-profile soil warming, finding depth-dependent effects and elevated subsoil microbial respiration.
- Nicholas C. Dove
- , Margaret S. Torn
- & Neslihan Taş
-
Article
| Open Access Herbaceous perennial plants with short generation time have stronger responses to climate anomalies than those with longer generation time
Herbaceous perennial plants with short generation time have stronger responses to climate anomalies than those with longer generation time
Plant population growth rate is sensitive to annual temperature and precipitation anomalies. Here the authors analyse time series of population projection models from multiple biomes, finding a relationship between short generation times and strong demographic responses to climate—particularly precipitation—anomalies.
- Aldo Compagnoni
- , Sam Levin
- & Tiffany M. Knight
-
Article
| Open Access Diel niche variation in mammals associated with expanded trait space
Diel niche variation in mammals associated with expanded trait space
Most mammals are nocturnal, but a new analysis suggests that although most groups of species active at a particular time of day or night occupy different ecological niches, a surprisingly large proportion of species are more flexible in the timing of their activity than previously thought.
- D. T. C. Cox
- , A. S. Gardner
- & K. J. Gaston
-
Article
| Open Access Recovery of logged forest fragments in a human-modified tropical landscape during the 2015-16 El Niño
Recovery of logged forest fragments in a human-modified tropical landscape during the 2015-16 El Niño
It is unclear whether tropical forest fragments within plantation landscapes are resilient to drought. Here the authors analyse LiDAR and ground-based data from the 2015-16 El Niño event across a logging intensity gradient in Borneo. Although regenerating forests continued to grow, canopy height near oil palm plantations decreased, and a strong edge effect extended up to at least 300 m away.
- Matheus Henrique Nunes
- , Tommaso Jucker
- & David A. Coomes
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon prospecting in tropical forests for climate change mitigation
Carbon prospecting in tropical forests for climate change mitigation
Investing in forest protection is a way to generate tradable carbon credits to support biodiversity conservation and climate change mitigation. Here the authors assess and map the global supply of tropical forest carbon credits with the goal of informing climate policy and investments.
- Lian Pin Koh
- , Yiwen Zeng
- & Kelly Siman
-
Article
| Open Access Climate predicts geographic and temporal variation in mosquito-borne disease dynamics on two continents
Climate predicts geographic and temporal variation in mosquito-borne disease dynamics on two continents
The effects of climate on vector-borne disease systems are highly context-dependent. Here, the authors incorporate laboratory-measured physiological traits of the mosquito Aedes aegypti into climate-driven mechanistic models to predict number, timing, and duration of outbreaks in Ecuador and Kenya.
- Jamie M. Caldwell
- , A. Desiree LaBeaud
- & Erin A. Mordecai
-
Article
| Open Access Climate change, not human population growth, correlates with Late Quaternary megafauna declines in North America
Climate change, not human population growth, correlates with Late Quaternary megafauna declines in North America
There are a number of competing explanations for the late Pleistocene extinction of many North American megafauna species. Here, the authors apply a Bayesian regression approach that finds greater concordance between megafaunal declines and climate change than with human population growth.
- Mathew Stewart
- , W. Christopher Carleton
- & Huw S. Groucutt
-
Article
| Open Access Implications of the 2019–2020 megafires for the biogeography and conservation of Australian vegetation
Implications of the 2019–2020 megafires for the biogeography and conservation of Australian vegetation
Fires triggered by climate change threaten plant diversity in many biomes. Here the authors investigate how the catastrophic fires of 2019–2020 affected the vascular flora of SE Australia. They report that 816 species were highly impacted, including taxa of biogeographic and conservation interest.
- Robert C. Godfree
- , Nunzio Knerr
- & Linda M. Broadhurst
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonal biological carryover dominates northern vegetation growth
Seasonal biological carryover dominates northern vegetation growth
The future of terrestrial systems is influenced by their past, but this carryover effect is rarely quantified. Here, the authors provide the first quantitative evidence that a greener spring begets a greener summer and autumn, and that this carryover effect is even stronger than climate drivers.
- Xu Lian
- , Shilong Piao
- & Ranga B. Myneni
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme temperatures compromise male and female fertility in a large desert bird
Extreme temperatures compromise male and female fertility in a large desert bird
Climate change may pose a challenge not only for survival of animals but also for their reproduction. Here, Schou et al. analyse how male and female ostrich fertility relates to fluctuating temperature across 20 years, finding reduced fertility away from the thermal optimum, but also individual variation in thermal tolerance.
- Mads F. Schou
- , Maud Bonato
- & Charlie K. Cornwallis
-
Article
| Open Access Global patterns and climatic controls of forest structural complexity
Global patterns and climatic controls of forest structural complexity
Forest structure depends both on extrinsic factors such as climate and on intrinsic properties such as community composition and diversity. Here, the authors use a dataset of stand structural complexity based on LiDAR measurements to build a global map of structural complexity for primary forests, and find that precipitation variables best explain global patterns of forest structural complexity.
- Martin Ehbrecht
- , Dominik Seidel
- & Christian Ammer
-
Article
| Open Access Temporal changes in global soil respiration since 1987
Temporal changes in global soil respiration since 1987
Soils hold massive amounts of carbon that hangs in the balance of microbial respiration and climate warming. Here the authors analyze a global dataset starting in 1987 and find through modeling that though soil respiration change had flatlined, recently it has resumed increasing owing to global warming.
- Jiesi Lei
- , Xue Guo
- & Yunfeng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-scale interaction of host tree size and climatic water deficit governs bark beetle-induced tree mortality
Cross-scale interaction of host tree size and climatic water deficit governs bark beetle-induced tree mortality
The 2012–2016 drought and western pine beetle outbreaks caused unprecedented mortality of ponderosa pine in the Sierra Nevada, California. Here, the authors analyse drone-based data from almost half a million trees and find an interaction between host size and climatic water deficit, with higher mortality for large trees in dry, warm conditions but not in cooler or wetter conditions.
- Michael J. Koontz
- , Andrew M. Latimer
- & Malcolm P. North
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic symbioses reveal pathways to coral survival through prolonged heatwaves
Dynamic symbioses reveal pathways to coral survival through prolonged heatwaves
Climate change and local anthropogenic stressors threaten the persistence of coral reefs. Here the authors track coral bleaching over the course of a heatwave and find that some colonies recovered from bleaching while high temperatures persisted, but only at sites lacking in other strong anthropogenic stressors.
- Danielle C. Claar
- , Samuel Starko
- & Julia K. Baum
-
Article
| Open Access Excess forest mortality is consistently linked to drought across Europe
Excess forest mortality is consistently linked to drought across Europe
Droughts pose an increasingly important threat to forests. Here the authors analyse a high-resolution Landsat-based dataset of forest canopy mortality in Europe over 1987–2016 to show that drought is already a major driver of tree mortality.
- Cornelius Senf
- , Allan Buras
- & Rupert Seidl
-
Article
| Open Access Consistent population declines but idiosyncratic range shifts in Alpine orchids under global change
Consistent population declines but idiosyncratic range shifts in Alpine orchids under global change
Many mountain species are threatened by climate change and habitat loss. Here, the authors investigate population declines and range shifts of orchids in an alpine region in NE Italy over 28 years. For most species, population size decreased, while range shifts were idiosyncratic with over half of the species lagging behind climate change.
- Costanza Geppert
- , Giorgio Perazza
- & Lorenzo Marini
-
Article
| Open Access The thermal response of soil microbial methanogenesis decreases in magnitude with changing temperature
The thermal response of soil microbial methanogenesis decreases in magnitude with changing temperature
Soil microbes produce more methane as temperatures warm, but it is unclear if they acclimate to heat, or keep producing more of the greenhouse gas. Here the authors use artificial wetland warming experiments to show that after initial spikes in methane emissions after warming, emissions level out over time.
- Hongyang Chen
- , Ting Zhu
- & Ming Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced fish production during a period of extreme global warmth
Enhanced fish production during a period of extreme global warmth
Fish production is predicted to decrease with anthropogenic global warming. Here the authors analyse fish fossil assemblages from 62–46 My old deep-sea sediments and instead find a positive correlation between fish production and ocean temperature over geological timescales, which a data-constrained model explains in terms of trophic transfer efficiency and primary production.
- Gregory L. Britten
- & Elizabeth C. Sibert
-
Article
| Open Access Historical and projected future range sizes of the world’s mammals, birds, and amphibians
Historical and projected future range sizes of the world’s mammals, birds, and amphibians
Long-term dynamics of species’ range sizes play a crucial role in determining extinction risks. Here the authors simulate global vegetation cover and scenarios of anthropogenic land cover change to estimate habitat range sizes of thousands of mammal, bird, and amphibian species since 1700, and project trajectories up to 2100 under four emission scenarios and five socio-economic pathways.
- Robert M. Beyer
- & Andrea Manica
-
Article
| Open Access Climate reverses directionality in the richness–abundance relationship across the World’s main forest biomes
Climate reverses directionality in the richness–abundance relationship across the World’s main forest biomes
Correlations between tree species diversity and tree abundance are well established, but the direction of the relationship is unresolved. Here the authors use path models to estimate plausible causal pathways in the diversity-abundance relationship across 23 global forests regions, finding a lack of general support for a positive diversity-abundance relationship, which is prevalent in the most productive lands on Earth only
- Jaime Madrigal-González
- , Joaquín Calatayud
- & Markus Stoffel
-
Article
| Open Access Bryophytes are predicted to lag behind future climate change despite their high dispersal capacities
Bryophytes are predicted to lag behind future climate change despite their high dispersal capacities
Bryophytes tend to be sensitive to warming, but their high dispersal ability could help them track climate change. Here the authors combine correlative niche models and mechanistic dispersal models for 40 European bryophyte species under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5, finding that most of these species are unlikely to track climate change over the coming decades.
- F. Zanatta
- , R. Engler
- & A. Vanderpoorten
-
Article
| Open Access Forest production efficiency increases with growth temperature
Forest production efficiency increases with growth temperature
Many models assume a universal carbon use efficiency across forest biomes, in contrast to assumptions of other process-based models. Here the authors analyse forest production efficiency across a wide range of climates to show a positive relationship with annual temperature and precipitation, indicating that ecosystem models are overestimating forest carbon losses under warming.
- A. Collalti
- , A. Ibrom
- & I. C. Prentice
-
Article
| Open Access Plant species determine tidal wetland methane response to sea level rise
Plant species determine tidal wetland methane response to sea level rise
Coastal systems have enormous carbon-sequestering potential, but any positive climate effects can be countered by methane emissions. Here the authors use sea level rise manipulation mesocosms in tidal wetlands to show that shifts in plant community composition have the greatest effect on methane emissions.
- Peter Mueller
- , Thomas J. Mozdzer
- & J. Patrick Megonigal
-
Article
| Open Access Future climate change vulnerability of endemic island mammals
Future climate change vulnerability of endemic island mammals
Island ecosystems are notoriously vulnerable to anthropogenic species losses. Here, the authors identify insular hotspots of vulnerability to climate change (under RCPs 6.0 and 8.5) in mammals via a trait-based, quantitative vulnerability framework, finding that exposure to climate change is not a reliable proxy to assess species vulnerability, while sensitivity and adaptive capacity are crucial to understand vulnerability.
- Camille Leclerc
- , Franck Courchamp
- & Céline Bellard
-
Article
| Open Access Overestimation of the effect of climatic warming on spring phenology due to misrepresentation of chilling
Overestimation of the effect of climatic warming on spring phenology due to misrepresentation of chilling
Climate warming is advancing spring leaf unfolding, but it is also reducing the cold periods that many trees require to break winter dormancy. Here, the authors show that 7 of 12 current chilling models fail to account for the correct relationship between chilling accumulation and heat requirement, leading to substantial overestimates of the advance of spring phenology under climate change.
- Huanjiong Wang
- , Chaoyang Wu
- & Quansheng Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid climate change results in long-lasting spatial homogenization of phylogenetic diversity
Rapid climate change results in long-lasting spatial homogenization of phylogenetic diversity
How past climate change has affected biodiversity over large spatial scales remains underexplored. Here, the authors find marked homogenization in flowering plant phylogenetic diversity across Central and Northern Europe linked to rapid climate change and large distances to glacial refugia.
- Bianca Saladin
- , Loïc Pellissier
- & Niklaus E. Zimmermann
-
Article
| Open Access Ecosystem-based fisheries management forestalls climate-driven collapse
Ecosystem-based fisheries management forestalls climate-driven collapse
Ecosystem Based Management measures developed to prevent overfishing could be particularly important under climate change. Here the authors combine climate and fish stock modelling to show that EBM cap implementation reduces climate-driven fishery declines under RCP 4.5 and 8.5 before midcentury. However, there are thermal tipping points beyond which potential collapses are predicted.
- K. K. Holsman
- , A. C. Haynie
- & A. E. Punt
-
Article
| Open Access Forest carbon sink neutralized by pervasive growth-lifespan trade-offs
Forest carbon sink neutralized by pervasive growth-lifespan trade-offs
The universality of the trade-off between early growth and lifespan in trees and its implications are disputed. Analysing a global tree ring dataset and performing data-driven simulations, the authors demonstrate the pervasiveness of the trade-off and challenge current earth system models that predict a continuation of the carbon sink into mature forests under warming and increasing CO2.
- R. J. W. Brienen
- , L. Caldwell
- & E. Gloor
-
Article
| Open Access Yield reduction under climate warming varies among wheat cultivars in South Africa
Yield reduction under climate warming varies among wheat cultivars in South Africa
Wheat yield is sensitive to temperature, but there could be substantial variation in this response across cultivars. Here the authors present data on the climatic responses of wheat cultivars in South Africa, highlighting which cultivars might be better able to maintain yield under warming.
- Aaron M. Shew
- , Jesse B. Tack
- & Petronella Chaminuka
-
Article
| Open Access American mastodon mitochondrial genomes suggest multiple dispersal events in response to Pleistocene climate oscillations
American mastodon mitochondrial genomes suggest multiple dispersal events in response to Pleistocene climate oscillations
Pleistocene population dynamics can inform the consequences of current climate change. This phylogeography of 35 complete American mastodon mitochondrial genomes suggests distinct lineages in this species repeatedly expanded northwards and then went locally extinct in response to glacial cycles.
- Emil Karpinski
- , Dirk Hackenberger
- & Hendrik N. Poinar
-
Article
| Open Access Recent declines in salmon body size impact ecosystems and fisheries
Recent declines in salmon body size impact ecosystems and fisheries
The average body size of salmon has declined rapidly over recent decades. Here the authors quantify changes in body size distributions for Pacific salmon in Alaska and examine the causes and consequences of size declines for ecosystems, food security, and commercial fisheries.
- K. B. Oke
- , C. J. Cunningham
- & E. P. Palkovacs
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme environmental conditions reduce coral reef fish biodiversity and productivity
Extreme environmental conditions reduce coral reef fish biodiversity and productivity
Brandl, Johansen et al. compare organismal traits, community structure, and productivity dynamics of cryptobenthic reef fishes across two locations, the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, the former of which harbors the world’s hottest coral reefs. They show that environmental extremes in the Arabian Gulf result in dramatically less diverse, abundant, and productive cryptobenthic fish assemblages, which could foreshadow the future of coral reef biodiversity and functioning.
- Simon J. Brandl
- , Jacob L. Johansen
- & John A. Burt
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis of multidecadal biodiversity trends in Europe
Meta-analysis of multidecadal biodiversity trends in Europe
The global biodiversity decline might conceal complex local and group-specific trends. Here the authors report a quantitative synthesis of longterm biodiversity trends across Europe, showing how, despite overall increase in biodiversity metric and stability in abundance, trends differ between regions, ecosystem types, and taxa.
- Francesca Pilotto
- , Ingolf Kühn
- & Peter Haase
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Height-related changes in forest composition explain increasing tree mortality with height during an extreme drought
Height-related changes in forest composition explain increasing tree mortality with height during an extreme drought
- Nathan L. Stephenson
- & Adrian J. Das
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to “Height-related changes in forest composition explain increasing tree mortality with height during an extreme drought”
Reply to “Height-related changes in forest composition explain increasing tree mortality with height during an extreme drought”
- Atticus E. L. Stovall
- , Herman H. Shugart
- & Xi Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term droughts may drive drier tropical forests towards increased functional, taxonomic and phylogenetic homogeneity
Long-term droughts may drive drier tropical forests towards increased functional, taxonomic and phylogenetic homogeneity
Different aspects of biodiversity may not necessarily converge in their response to climate change. Here, the authors investigate 25-year shifts in taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic diversity of tropical forests along a spatial climate gradient in West Africa, showing that drier forests are less stable than wetter forests.
- Jesús Aguirre-Gutiérrez
- , Yadvinder Malhi
- & Imma Oliveras
-
Article
| Open Access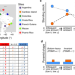 Extreme rainfall events alter the trophic structure in bromeliad tanks across the Neotropics
Extreme rainfall events alter the trophic structure in bromeliad tanks across the Neotropics
The amount and frequency of rainfall structures aquatic food webs. Here the authors show that in tropical tank bromeliads, lower trophic levels are more abundant in stable rainfall conditions, while biomass pyramids are inverted in conditions with periodic droughts.
- Gustavo Q. Romero
- , Nicholas A. C. Marino
- & Diane S. Srivastava
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality
Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality
It is often assumed that various types of anthropogenic change reduce microbial diversity and function. Here, the authors do a meta-analysis showing that global change factors affect microbial diversity inconsistently; negative effects are most likely for global change factors that affect soil pH.
- Zhenghu Zhou
- , Chuankuan Wang
- & Yiqi Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Robust leaf trait relationships across species under global environmental changes
Robust leaf trait relationships across species under global environmental changes
It is unclear whether rapid global change will lead to unexpected trait combinations. In this global meta-analysis on vascular plants, Cui et al. show that, although within-species responses do not always follow the leaf economic spectrum, the slopes of interspecific trait relationships are robust to rapid environmental change.
- Erqian Cui
- , Ensheng Weng
- & Jianyang Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Global correlates of range contractions and expansions in terrestrial mammals
Global correlates of range contractions and expansions in terrestrial mammals
Understanding why many species ranges are contracting while others are stable or expanding is important to inform conservation in an increasingly human-modified world. Here, Pacifici and colleagues investigate changes in the ranges of 204 mammals, showing that human factors mostly explain range contractions while life history explains both contraction and expansion.
- Michela Pacifici
- , Carlo Rondinini
- & Moreno Di Marco
-
Article
| Open Access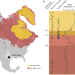 Rapid range shifts and megafaunal extinctions associated with late Pleistocene climate change
Rapid range shifts and megafaunal extinctions associated with late Pleistocene climate change
The impact of late Pleistocene climate change on ecosystems has been hard to assess. Here, the authors sequence ancient DNA from Hall’s Cave, Texas and find that both plant and vertebrate diversity decreased with cooling, and though plant diversity recovered with rewarming, megafauna went extinct.
- Frederik V. Seersholm
- , Daniel J. Werndly
- & Michael Bunce
-
Article
| Open Access Insect herbivory dampens Subarctic birch forest C sink response to warming
Insect herbivory dampens Subarctic birch forest C sink response to warming
Warming is expected to increase C sink capacity in high-latitude ecosystems, but plant-herbivore interactions could moderate or offset this effect. Here, Silfver and colleagues test individual and interactive effects of warming and insect herbivory in a field experiment in Subarctic forest, showing that even low intensity insect herbivory strongly reduces C sink potential.
- Tarja Silfver
- , Lauri Heiskanen
- & Juha Mikola
-
Article
| Open Access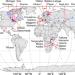 Effects of climate and land-use changes on fish catches across lakes at a global scale
Effects of climate and land-use changes on fish catches across lakes at a global scale
Lake fisheries are vulnerable to environmental changes. Here, Kao et al. develop a Bayesian networks model to analyze time-series data from 31 major fisheries lake across five continents, showing that fish catches can respond either positively or negatively to climate and land-use changes.
- Yu-Chun Kao
- , Mark W. Rogers
- & Joelle D. Young
-
Article
| Open Access Massive peatland carbon banks vulnerable to rising temperatures
Massive peatland carbon banks vulnerable to rising temperatures
One-third of Earth’s carbon is sequestered in peatlands, and its stability in the face of climate change is unknown. Here the authors show that warming leads to the release of carbon as methane, but only the most prolonged warming leads to the breakdown and release of deep, old carbon.
- A. M. Hopple
- , R. M. Wilson
- & S. D. Bridgham
-
Article
| Open Access Future ocean biomass losses may widen socioeconomic equity gaps
Future ocean biomass losses may widen socioeconomic equity gaps
Numerous marine ecosystem models are used to project animal biomass over time but integrating them can be challenging. Here the authors develop a test for statistical significance in multi-model ensemble trends, and thus relate future biomass trends to current patterns of ecological and socioeconomic status.
- Daniel G. Boyce
- , Heike K. Lotze
- & Boris Worm
-
Article
| Open Access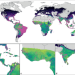 Accelerating invasion potential of disease vector Aedes aegypti under climate change
Accelerating invasion potential of disease vector Aedes aegypti under climate change
Understanding how life cycles of vectors respond to climatic factors is important to predict potential shifts in vector-borne disease risk in the coming decades. Here the authors develop a mechanistic phenological model for the invasive mosquito Aedes aegypti and apply it to project shifts under climate change scenarios.
- Takuya Iwamura
- , Adriana Guzman-Holst
- & Kris A. Murray
-
Article
| Open Access Topography and human pressure in mountain ranges alter expected species responses to climate change
Topography and human pressure in mountain ranges alter expected species responses to climate change
It is often assumed that many species will move upslope in mountainous regions as the climate warms. However, the authors show here that as many species move to higher elevations they will enter areas of lower human footprint but potentially more constraining topography.
- Paul R. Elsen
- , William B. Monahan
- & Adina M. Merenlender
-
Article
| Open Access Changing role of coral reef marine reserves in a warming climate
Changing role of coral reef marine reserves in a warming climate
It is unclear whether rapid climate change will alter the effectiveness of marine reserves. Here Graham et al. use a 20-year time-series from the Seychelles to show that marine reserves may not prevent climate-driven shifts in community composition, and that ecological responses to reserves are substantially altered.
- Nicholas A. J. Graham
- , James P. W. Robinson
- & Shaun K. Wilson

 Responses of plant diversity to precipitation change are strongest at local spatial scales and in drylands
Responses of plant diversity to precipitation change are strongest at local spatial scales and in drylands