Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access On the role of asymmetric molecular geometry in high-performance organic solar cells
On the role of asymmetric molecular geometry in high-performance organic solar cells
The correlation between asymmetric molecular geometry of non-fullerene acceptors and their optoelectronic properties was unclear. Here, the authors found asymmetric ones exhibit increased open-circuit voltage compared to their symmetric counterparts due to reduced non-radiative charge recombination.
- Jinfeng Huang
- , Tianyi Chen
- & Lijian Zuo
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum phase synchronization via exciton-vibrational energy dissipation sustains long-lived coherence in photosynthetic antennas
Quantum phase synchronization via exciton-vibrational energy dissipation sustains long-lived coherence in photosynthetic antennas
Photosynthesis in biological systems occurs in a noisy environment that reduces the lifetime of coherences in the excitation energy transfer. Here the author demonstrate that long-lasting coherences are protected by quantum phase synchronization, realized in dimers by exciton-vibrational coupling where energy dissipation occurs predominantly in resonant anti-symmetric collective modes.
- Ruidan Zhu
- , Wenjun Li
- & Yuxiang Weng
-
Article
| Open Access Spiral packing and chiral selectivity in model membranes probed by phase-resolved sum-frequency generation microscopy
Spiral packing and chiral selectivity in model membranes probed by phase-resolved sum-frequency generation microscopy
The properties of lipid membranes are intimately controlled by their complex heterogeneous structure. Here, the authors use phase-resolved sum-frequency generation microscopy to fully determine the hierarchical lipid packing from the molecular to the mesoscopic scale.
- Alexander P. Fellows
- , Ben John
- & Martin Thämer
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodiffusive desalination
Thermodiffusive desalination
Current desalination technologies are energy intensive and suffer from membrane degradation and fouling. Here, authors propose and explore the potential of thermodiffusion as a means of membrane-free, single-phase thermal desalination. A pathway towards a feasible thermodiffusive desalination is provided.
- Shuqi Xu
- , Alice J. Hutchinson
- & Juan F. Torres
-
Article
| Open Access Universal inter-molecular radical transfer reactions on metal surfaces
Universal inter-molecular radical transfer reactions on metal surfaces
Radicals are expected to be inactive on metal surfaces. Here the authors describe general intermolecular radical transfer reactions on Ag and Cu surfaces and confirm the reaction mechanism by extensive control experiments.
- Junbo Wang
- , Kaifeng Niu
- & Lifeng Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Aluminum corrosion–passivation regulation prolongs aqueous batteries life
Aluminum corrosion–passivation regulation prolongs aqueous batteries life
Aqueous batteries have a short lifespan due to Al current collector corrosion and Li loss from side reactions on the anode. Here, the authors propose a prototype of self-prolonging aqueous Li-ion batteries by introducing hydrolyzation-type anodic additives to regulate Al corrosion-passivation.
- Binghang Liu
- , Tianshi Lv
- & Liumin Suo
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast photoinduced C-H bond formation from two small inorganic molecules
Ultrafast photoinduced C-H bond formation from two small inorganic molecules
The formation of C–H bonds via reaction of small inorganic molecules is of great interest for understanding the transition from inorganic to organic matter, but the detailed mechanisms remain elusive. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time visualization and coherent control of the ultrafast C–H bond formation dynamics in a light-induced bimolecular reaction from inorganic species.
- Zhejun Jiang
- , Hao Huang
- & Jian Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of the charge transfer to solvent process in aqueous iodide
Dynamics of the charge transfer to solvent process in aqueous iodide
Solvated electrons can be formed through photo-induced charge-transfer-to-solvent electronic states of halide ions in water. Here, the authors use machine learning accelerated molecular dynamics simulations to follow the evolution of these states for aqueous iodide in detail.
- Jinggang Lan
- , Majed Chergui
- & Alfredo Pasquarello
-
Article
| Open Access Squeezing formaldehyde into C60 fullerene
Squeezing formaldehyde into C60 fullerene
The interconversion of the two spin isomers of formaldehyd has been studied in the gas phase but has never been observed experimentally in the condensed phase. Here the authors report the encapsulation of formaldehyde inside C60 cages and observe spin-isomer conversion of the formaldehyde guest molecules in the cryogenic solid state.
- Vijyesh K. Vyas
- , George R. Bacanu
- & Richard J. Whitby
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
The strong ionic bond in salt is broken by electrostatic interactions with water, but direct observation at the level of a single ion is challenging. Here, the authors have visualized the preferential dissolution of an anion by manipulating a single water molecule.
- Huijun Han
- , Yunjae Park
- & Hyung-Joon Shin
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding of complex spin up-conversion processes in charge-transfer-type organic molecules
Understanding of complex spin up-conversion processes in charge-transfer-type organic molecules
Kim et al. propose a model for the complex spin-flip process in charge-transfer-type thermally activated delayed fluorescence molecules, uncovering the origin of the high-lying triplet state, addressing a pressing issue discussed over the last decade.
- Hyung Suk Kim
- , Sang Hoon Lee
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Article
| Open Access Electrostatic potentials of atomic nanostructures at metal surfaces quantified by scanning quantum dot microscopy
Electrostatic potentials of atomic nanostructures at metal surfaces quantified by scanning quantum dot microscopy
Surface averaging techniques offer only limited access to the electrostatic potentials of nanostructures, which are determined by shape, material, and environment. Here, the authors quantify these potentials for gold and silver adatom chains, explaining the mechanisms of dipole formation.
- Rustem Bolat
- , Jose M. Guevara
- & Christian Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access A programmable hybrid digital chemical information processor based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
A programmable hybrid digital chemical information processor based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
Computing platforms based on chemical processes can be an alternative to digital computers in some scenarios but have limited programmability. Here the authors demonstrate a hybrid computing platform combining digital electronics and an oscillatory chemical reaction and demonstrate its computational capabilities.
- Abhishek Sharma
- , Marcus Tze-Kiat Ng
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Electrofreezing of liquid water at ambient conditions
Electrofreezing of liquid water at ambient conditions
By performing long ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of water under external electric fields, for up to 500 picoseconds, the authors identify a transition to a ferroelectric amorphous phase at ambient conditions.
- Giuseppe Cassone
- & Fausto Martelli
-
Article
| Open Access Unified picture of vibrational relaxation of OH stretch at the air/water interface
Unified picture of vibrational relaxation of OH stretch at the air/water interface
Using femtosecond time-resolved heterodyne-detected vibrational sum-frequency generation spectroscopy the authors determine the vibrational relaxation (T1) time of the O-H stretch at the air/water interface by observing the decay of excited-state OH signals, providing a comprehensive picture of the interfacial vibrational relaxation process of water.
- Woongmo Sung
- , Ken-ichi Inoue
- & Tahei Tahara
-
Article
| Open Access The role of interfacial donor–acceptor percolation in efficient and stable all-polymer solar cells
The role of interfacial donor–acceptor percolation in efficient and stable all-polymer solar cells
The underlying charge generation dynamics and structure-property relationships in organic solar cells are not fully understood. Here, the authors demonstrate that interfacial donor-acceptor percolation plays a key role in enabling both high charge generation efficiency and device stability.
- Zhen Wang
- , Yu Guo
- & Philip C. Y. Chow
-
Article
| Open Access Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Coacervate-based compartments are attractive as potential protocells, but formation and control of the compartments can be challenging. Here, the authors report the spontaneous formation of core-shell, cell-sized coacervate compartments driven by droplet evaporation.
- Cheng Qi
- , Xudong Ma
- & Zhou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging the state-to-state charge-transfer dynamics between the spin-orbit excited Ar+(2P1/2) ion and N2
Imaging the state-to-state charge-transfer dynamics between the spin-orbit excited Ar+(2P1/2) ion and N2
The charge-transfer reaction Ar++N2 → Ar+N2+ has been largely studied as a model gas-phase reaction but many aspects remain to be understood. Here, differential cross sections of the reaction are measured and calculated with Ar+ prepared in 2P1/2 state, showing that the charge-transfer dynamics differs significantly for Ar+(2P1/2) compared to Ar+(2P3/2) when colliding with N2.
- Guodong Zhang
- , Dandan Lu
- & Hong Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Observing growth and interfacial dynamics of nanocrystalline ice in thin amorphous ice films
Observing growth and interfacial dynamics of nanocrystalline ice in thin amorphous ice films
In-situ cryo-electron microscopy in thin amorphous ice films and ice-dynamics simulations reveal polymorph-dependent growth kinetics of nanoscale ice crystals. Hetero-crystalline ice exhibits anisotropic growth: fast-growing facets are associated with low-density interfaces, driving tetrahedral ordering of interfacial H2O molecules and accelerating ice growth.
- Minyoung Lee
- , Sang Yup Lee
- & Dong June Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Investigating the role of undercoordinated Pt sites at the surface of layered PtTe2 for methanol decomposition
Investigating the role of undercoordinated Pt sites at the surface of layered PtTe2 for methanol decomposition
Methanol on under-coordinated Pt sites at surface Te vacancies on layered PtTe2 decomposes at a probability >90 % which ultimately produces gaseous molecular hydrogen, methane, water and formaldehyde.
- Jing-Wen Hsueh
- , Lai-Hsiang Kuo
- & Meng-Fan Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Microscopic mechanisms of pressure-induced amorphous-amorphous transitions and crystallisation in silicon
Microscopic mechanisms of pressure-induced amorphous-amorphous transitions and crystallisation in silicon
The mechanism of amorphous-amorphous transitions is highly debated. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics simulations to reveal transitions via nucleation-growth or spinodal decomposition, resembling a thermodynamic phase transition but influenced by mechanics.
- Zhao Fan
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Vibronic effects on the quantum tunnelling of magnetisation in Kramers single-molecule magnets
Vibronic effects on the quantum tunnelling of magnetisation in Kramers single-molecule magnets
Quantum tunnelling of the magnetisation limits the performance of single-molecule magnets at low temperatures. Here, the authors combine ab initio and analytical methods to show that spin-phonon coupling subtly influences tunnelling via polaron formation.
- Andrea Mattioni
- , Jakob K. Staab
- & Nicholas F. Chilton
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen evolution with hot electrons on a plasmonic-molecular catalyst hybrid system
Hydrogen evolution with hot electrons on a plasmonic-molecular catalyst hybrid system
Direct participation of plasmon-induced hot electrons in the photoelectrocatalytic synthesis of hydrogen. This report solves a long-lasting contentious issue surrounding plasmonic materials on catalytic applications.
- Ananta Dey
- , Amal Mendalz
- & Jacinto Sá
-
Article
| Open Access Spin relaxation of electron and hole polarons in ambipolar conjugated polymers
Spin relaxation of electron and hole polarons in ambipolar conjugated polymers
Spin and charge dynamics are inevitably linked, the study of the one often illuminating the other. Here, the authors study spin relaxation in ambipolar polymers and, backed by simulations, show how charge dynamics and wavefunction localization together set relaxation times up to room temperature.
- Remington L. Carey
- , Samuele Giannini
- & Henning Sirringhaus
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the critical nucleus size in tetrahydrofuran clathrate hydrate formation using surface-anchored nanoparticles
Probing the critical nucleus size in tetrahydrofuran clathrate hydrate formation using surface-anchored nanoparticles
The critical nucleus, which considered a key step in the formation of clathrate hydrates, has not yet been empirically confirmed. Here, the authors probe the critical nucleus size in clathrate formation of tetrahydrofuran and thus provide mechanistic insights.
- Han Xue
- , Linhai Li
- & Jianjun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Towards a transferable fermionic neural wavefunction for molecules
Towards a transferable fermionic neural wavefunction for molecules
Neural wavefunctions have become a highly accurate approach to solve the Schrödinger equation. Here, the authors propose an approach to optimize for a generalized wavefunction across compounds, which can help developing a foundation wavefunction model.
- Michael Scherbela
- , Leon Gerard
- & Philipp Grohs
-
Article
| Open Access Colloidal pathways of amorphous calcium carbonate formation lead to distinct water environments and conductivity
Colloidal pathways of amorphous calcium carbonate formation lead to distinct water environments and conductivity
The mechanism of calcium carbonate formation has been of interest for decades, but additive-controlled systems are poorly understood. Here the authors show that polycarboxylates facilitate bicarbonate entrapment and thereby inhibit nucleation. Distinct water environments in amorphous calcium carbonate nanoparticles arise from colloidal formation pathways and lead to mineral conductivity.
- Maxim B. Gindele
- , Sanjay Vinod-Kumar
- & Guinevere Mathies
-
Article
| Open Access Initial-site characterization of hydrogen migration following strong-field double-ionization of ethanol
Initial-site characterization of hydrogen migration following strong-field double-ionization of ethanol
Excitation of hydrogen-rich molecules often causes hydrogen migration, but characterisation of the individual sites is challenging. Here, the authors show that measurements of several isotopologues of ethanol can identify each hydrogen site’s contribution to the final products.
- Travis Severt
- , Eleanor Weckwerth
- & Itzik Ben-Itzhak
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopy and dynamics of the hydrated electron at the water/air interface
Spectroscopy and dynamics of the hydrated electron at the water/air interface
Hydrated electrons at the water/air interface participate in natural and synthetic processes, but investigation of their properties remains challenging. Here the authors show that most of their electron density is solvated below the dividing surface and solvates into the bulk in around 10 picoseconds, leaving its phenoxyl radical source at the interface.
- Caleb J. C. Jordan
- , Marc P. Coons
- & Jan R. R. Verlet
-
Article
| Open Access Directing polymorph specific calcium carbonate formation with de novo protein templates
Directing polymorph specific calcium carbonate formation with de novo protein templates
Most proteins mediating biomineralization in nature are not well structured, and the structures of the relevant protein-mineral interfaces regulating mineralization are elusive. Here, the authors computationally design proteins that modulate calcium carbonate mineralization to generate hybrid materials and elucidate the roles of designed proteins in controlling mineralization.
- Fatima A. Davila-Hernandez
- , Biao Jin
- & David Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Second quantization of many-body dispersion interactions for chemical and biological systems
Second quantization of many-body dispersion interactions for chemical and biological systems
The many-body dispersion (MBD) framework models long-range electronic correlation and optical response of molecular systems. Here, the authors present a second-quantized MBD method that opens an efficient path to treating collective quantum fluctuations in molecular complexes with large number of atoms.
- Matteo Gori
- , Philip Kurian
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Nonredox trivalent nickel catalyzing nucleophilic electrooxidation of organics
Nonredox trivalent nickel catalyzing nucleophilic electrooxidation of organics
A good understanding of the mechanism behind organic electrooxidation is crucial for the development of efficient energy conversion technology. Here, the authors find that trivalent nickel is capable of oxidizing organics through a nucleophilic attack and electron transfer via a non-redox process.
- Yuandong Yan
- , Ruyi Wang
- & Zhigang Zou
-
Article
| Open Access The role of halogens in Au–S bond cleavage for energy-differentiated catalysis at the single-bond limit
The role of halogens in Au–S bond cleavage for energy-differentiated catalysis at the single-bond limit
Investigation of the reaction process at the single-bond interface is key to understanding the catalytic reaction mechanism. Here, the authors develop a STM-BJ method to monitor the catalytic process from the perspective of single-bond energy.
- Peihui Li
- , Songjun Hou
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access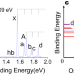 The unusual quadruple bonding of nitrogen in ThN
The unusual quadruple bonding of nitrogen in ThN
Nitrogen can form a maximum of three shared electron-pair bonds to complete its octet, suggesting the maximum bond order of nitrogen is three. Here, the authors report a joint photoelectron spectroscopy and quantum chemical study, showing a quadruple bond between nitrogen and thorium in thorium nitride.
- Zejie Fei
- , Jia-Qi Wang
- & Jun Li
-
Article
| Open Access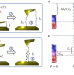 Microscopic theory, analysis, and interpretation of conductance histograms in molecular junctions
Microscopic theory, analysis, and interpretation of conductance histograms in molecular junctions
Conductance histograms are common setups to study molecular junctions, but the dispersion of the signals makes it difficult to interpret at microscopic level. Here the authors develop a physical model of molecular junctions that connects this observable with molecular properties.
- Leopoldo Mejía
- , Pilar Cossio
- & Ignacio Franco
-
Article
| Open Access Structural characterization of tin in toothpaste by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 119Sn solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Structural characterization of tin in toothpaste by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 119Sn solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Stannous fluoride (SnF2) is a common fluoride source and antimicrobial agent used in commercial toothpaste products. Here, the authors show how dynamic nuclear polarization can be used to perform 119Sn nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy experiments that probe the molecular structure of tin ions in commercial toothpastes.
- Rick W. Dorn
- , Scott L. Carnahan
- & Aaron J. Rossini
-
Article
| Open Access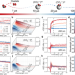 Direct time-resolved observation of surface-bound carbon dioxide radical anions on metallic nanocatalysts
Direct time-resolved observation of surface-bound carbon dioxide radical anions on metallic nanocatalysts
Understanding the activity and selectivity of metal catalysts requires elucidating the dynamics of CO2•− radicals bound to the surface. Here, the authors use pulse radiolysis to directly observe the stabilization process of CO2•− radicals at nanoscale metallic sites from nanoseconds to seconds.
- Zhiwen Jiang
- , Carine Clavaguéra
- & Mehran Mostafavi
-
Article
| Open Access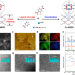 Intrinsic room-temperature ferromagnetism in a two-dimensional semiconducting metal-organic framework
Intrinsic room-temperature ferromagnetism in a two-dimensional semiconducting metal-organic framework
Two-dimensional magnetic materials present a promising platform for spintronic devices; however, these are predominantly either insulting, or metallic. Here, Feng et al demonstrate a semiconducting two-dimensional metal-organic framework with intrinsic ferromagnetism.
- Sihua Feng
- , Hengli Duan
- & Wensheng Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal dependence of the hydrated proton and optimal proton transfer in the protonated water hexamer
Thermal dependence of the hydrated proton and optimal proton transfer in the protonated water hexamer
Water’s pivotal role is tied to the quantum nature of its hydrogen bond dynamics. Here, the authors investigate the thermal behavior of the protonated water hexamer through accurate path integral molecular dynamics, revealing that near-room temperature conditions are optimal for proton transfer.
- Félix Mouhat
- , Matteo Peria
- & Michele Casula
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations of enhanced energy transfer in organic molecules under strong coupling
Multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations of enhanced energy transfer in organic molecules under strong coupling
Placing an organic material in an optical cavity can enhance exciton transport, but the mechanism is poorly understood. Here, using molecular dynamics simulations, the authors obtained atomistic insights into that mechanism.
- Ilia Sokolovskii
- , Ruth H. Tichauer
- & Gerrit Groenhof
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic high-spin cobalt(II) center for highly selective electrochemical CO reduction to CH3OH
Atomic high-spin cobalt(II) center for highly selective electrochemical CO reduction to CH3OH
Molecular catalysts provide an ideal model system to investigate the relationship between active site structure and catalytic performance. Here, the authors explore how electrochemical CO reduction to methanol can be controlled through modification of the active cobalt site in cobalt phthalocyanine.
- Jie Ding
- , Zhiming Wei
- & Bin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Universal machine learning for the response of atomistic systems to external fields
Universal machine learning for the response of atomistic systems to external fields
External fields, despite their significant influence on chemical processes, have been largely ignored in current machine learning potentials. Here, the authors introduce a field-induced model that captures system-field interactions rigorously.
- Yaolong Zhang
- & Bin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality-induced avalanche magnetization of magnetite by an RNA precursor
Chirality-induced avalanche magnetization of magnetite by an RNA precursor
Homochirality, a key feature of life, has unknown origins. Magnetic mineral surfaces can act as chiral agents, but are only weakly magnetized by nature. Here, the authors report the uniform magnetization of magnetite by an RNA precursor that spreads across the surface like an avalanche.
- S. Furkan Ozturk
- , Deb Kumar Bhowmick
- & Dimitar D. Sasselov
-
Article
| Open Access Induced photoelectron circular dichroism onto an achiral chromophore
Induced photoelectron circular dichroism onto an achiral chromophore
An achiral molecule can acquire a chiral spectroscopic signature when interacting with a chiral host. Here, the authors report the asymmetry in the electron distribution following ionisation of phenol complexed by chiral methyloxirane, which reflects an induced chirality onto the achiral phenol.
- Etienne Rouquet
- , Madhusree Roy Chowdhury
- & Anne Zehnacker
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning electronic structure methods based on the one-electron reduced density matrix
Machine learning electronic structure methods based on the one-electron reduced density matrix
Electronic structure methods are vital, yet they are often too computationally expensive. Here, the authors develop machine learned density matrices to fully represent electronic structures in a computationally cheap and accurate way.
- Xuecheng Shao
- , Lukas Paetow
- & Michele Pavanello
-
Article
| Open Access Structure determination of ζ-N2 from single-crystal X-ray diffraction and theoretical suggestion for the formation of amorphous nitrogen
Structure determination of ζ-N2 from single-crystal X-ray diffraction and theoretical suggestion for the formation of amorphous nitrogen
The ζ-N2 phase is key for comprehending the pressure-driven molecular to polymeric shift in nitrogen. Here, the authors resolved the crystal structure of ζ-N2 and identified a gradual delocalization of its electronic density under pressure, culminating in the initiation of nitrogen’s polymerization.
- Dominique Laniel
- , Florian Trybel
- & Natalia Dubrovinskaia
-
Article
| Open Access Mending cracks atom-by-atom in rutile TiO2 with electron beam radiolysis
Mending cracks atom-by-atom in rutile TiO2 with electron beam radiolysis
Radiolysis is known for damaging crystals. Here, using STEM, researchers observed radiolysis-driven bond-breakage, atomic movements, & crystal restructuring in rutile TiO2, and proposed a “2-step rolling” model of building blocks. These results open possibilities for constructive use of radiolysis.
- Silu Guo
- , Hwanhui Yun
- & K. Andre Mkhoyan
-
Article
| Open Access Strong structuring arising from weak cooperative O-H···π and C-H···O hydrogen bonding in benzene-methanol solution
Strong structuring arising from weak cooperative O-H···π and C-H···O hydrogen bonding in benzene-methanol solution
Understanding liquid behavior is a challenge due to their disorder nature and rapid molecular rearrangements. Here, the authors show how weak interactions between OH groups and aromatic rings can participate in cooperative mechanisms that give rise to highly structured molecular arrangements in the liquid state.
- Camilla Di Mino
- , Andrew G. Seel
- & Neal T. Skipper
-
Article
| Open Access Organic radical ferroelectric crystals with martensitic phase transition
Organic radical ferroelectric crystals with martensitic phase transition
Organic martensitic compounds are emerging smart materials with intriguing physical properties. Here authors show that upon H/F substitution a series of 1,4,5,8-naphthalenediimide derivatives exhibit reversible ferroelectric and martensitic transitions with a large thermal hysteresis.
- Nan Zhang
- , Wencong Sun
- & Han-Yue Zhang

 Scalable computation of anisotropic vibrations for large macromolecular assemblies
Scalable computation of anisotropic vibrations for large macromolecular assemblies