Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Charting cellular differentiation trajectories with Ricci flow
Charting cellular differentiation trajectories with Ricci flow
When stem cells develop into tissues intracellular signalling is rewired, errors in this process lead to cancer. Here, authors applied tools from differential geometry made by Albert Einstein’s General Relativity to understand and predict biological network rewiring in health and disease.
- Anthony Baptista
- , Ben D. MacArthur
- & Christopher R. S. Banerji
-
Article
| Open Access Logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA for genetic tracing of cell identities and state changes
Logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA for genetic tracing of cell identities and state changes
Descriptive data in biomedical research are expanding rapidly, but functional validation methods lag behind. Here, authors present Logical Synthetic cis-regulatory DNA, a framework to design reporters that mark cellular states and pathways, showcasing its applicability to complex phenotypic states.
- Carlos Company
- , Matthias Jürgen Schmitt
- & Gaetano Gargiulo
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of aging on the human myometrium at single-cell resolution
Effect of aging on the human myometrium at single-cell resolution
Age-associated myometrial dysfunction can cause complications during pregnancy and labor. Here, the authors report that aging myometrium is characterized by diminished contractile capillary cells, altered gene expression, and disrupted cellular communication leading to impaired angiogenesis, increased fibrosis and inflammation.
- Paula Punzon-Jimenez
- , Alba Machado-Lopez
- & Aymara Mas
-
Article
| Open Access Angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing reveals spatially differential activations of autophagy along angiogenic sprouts
Angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing reveals spatially differential activations of autophagy along angiogenic sprouts
The functional heterogeneity of autophagy in endothelial cells during angiogenesis remains incompletely understood. Here, the authors apply a 3D angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing to find distinct autophagy functions in two different endothelial cell populations during angiogenic sprouting.
- Somin Lee
- , Hyunkyung Kim
- & Noo Li Jeon
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal signaling underlies progressive vascular rarefaction in myocardial infarction
Spatiotemporal signaling underlies progressive vascular rarefaction in myocardial infarction
Enhancing vascularization to improve cardiac disease outcomes is a therapeutic approach with limited success. Here, the authors show that cardiac repair is governed by spatiotemporally regulated programs and underline the signaling mechanisms driving vascular deterioration.
- Lin Wei Tung
- , Elena Groppa
- & Fabio Rossi
-
Article
| Open Access Pathway centric analysis for single-cell RNA-seq and spatial transcriptomics data with GSDensity
Pathway centric analysis for single-cell RNA-seq and spatial transcriptomics data with GSDensity
Clustering-based analysis has limited power in highly dynamic single-cell data, which is a common situation in tumour samples. Here, authors introduce GSDensity, enabling pathway-centric analysis for the direct integration of data with their domain knowledge.
- Qingnan Liang
- , Yuefan Huang
- & Ken Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Robust mapping of spatiotemporal trajectories and cell–cell interactions in healthy and diseased tissues
Robust mapping of spatiotemporal trajectories and cell–cell interactions in healthy and diseased tissues
The integration of spatial, imaging, and sequencing information enables the mapping of cellular dynamics within a tissue. Here, authors show three algorithms in stLearn software to accurately reveal spatial trajectory, detect cell-cell interactions, and impute missing data.
- Duy Pham
- , Xiao Tan
- & Quan H. Nguyen
-
Article
| Open Access Interactome profiling of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoproteins
Interactome profiling of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoproteins
Here, Ning et al report the cellular interactomes of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus glycoproteins and uncover a host restriction factor HAX1 that hijacks the viral glycoproteins to mitochondria, disabling progeny virion packaging.
- Shiyu Dai
- , Yuan-Qin Min
- & Yun-Jia Ning
-
Article
| Open Access NeST: nested hierarchical structure identification in spatial transcriptomic data
NeST: nested hierarchical structure identification in spatial transcriptomic data
A wide variety of tissues exhibit nested hierarchical organisation of cells in gene expression and activities. Here, authors present NeST, a method for spatial transcriptomics to identify such structures and uncover their functions via ligand-receptor communication, in both two and three dimensions.
- Benjamin L. Walker
- & Qing Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Coordinated single-cell tumor microenvironment dynamics reinforce pancreatic cancer subtype
Coordinated single-cell tumor microenvironment dynamics reinforce pancreatic cancer subtype
Multiple studies have characterised the tumour microenvironment (TME) of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) using single-cell RNA-seq. Here, the authors integrate the data from such single-cell studies to provide a cohesive analysis of the PDAC TME, revealing cell types and interactions that are associated with PDAC phenotypes.
- Ki Oh
- , Yun Jae Yoo
- & Richard A. Moffitt
-
Article
| Open Access GPCRome-wide analysis of G-protein-coupling diversity using a computational biology approach
GPCRome-wide analysis of G-protein-coupling diversity using a computational biology approach
Selective GPCR-G protein complexes formation is critical for signal transduction regulation. Here, the authors use a data-driven approach to show that the structures of experimental and predicted complex interfaces inform, at least partially, on G protein binding preferences.
- Marin Matic
- , Pasquale Miglionico
- & Francesco Raimondi
-
Article
| Open Access SpatialDM for rapid identification of spatially co-expressed ligand–receptor and revealing cell–cell communication patterns
SpatialDM for rapid identification of spatially co-expressed ligand–receptor and revealing cell–cell communication patterns
Spatial omics are increasingly being recognised to study cell-cell communications. Here, the authors present a bioinformatics toolbox for rapid identification of spatially co-expressed ligand-receptor and revealing cell-cell communication patterns.
- Zhuoxuan Li
- , Tianjie Wang
- & Yuanhua Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A pharmacoproteomic landscape of organotypic intervention responses in Gram-negative sepsis
A pharmacoproteomic landscape of organotypic intervention responses in Gram-negative sepsis
Sepsis can cause organ damage through disparate immunological and metabolic processes. Here the authors demonstrate a proteomics-based scoring strategy for quantifying quantitative and organotypic changes in relationship to dosing, timing, and potential synergistic intervention combinations during sepsis.
- Tirthankar Mohanty
- , Christofer A. Q. Karlsson
- & Johan Malmström
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell and spatial sequencing define processes by which keratinocytes and fibroblasts amplify inflammatory responses in psoriasis
Single cell and spatial sequencing define processes by which keratinocytes and fibroblasts amplify inflammatory responses in psoriasis
Changes in Psoriasis and other inflammatory skin diseases during severity stages can be investigated using single cell and spatial transcriptomics. Here the authors compare different inflammatory skin diseases to emphasise differences in immune cells and inflammatory markers particularly keratinocytes and fibroblasts.
- Feiyang Ma
- , Olesya Plazyo
- & Johann E. Gudjonsson
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-attribute aware community detection improves differential abundance testing from single-cell RNA-Seq data
Cell-attribute aware community detection improves differential abundance testing from single-cell RNA-Seq data
Single-cell technologies allow quantification of cell-types in human tissues, yet detecting if their abundance changes in aging or disease is challenging. By using cell-attribute aware clustering, this work presents a differential abundance testing algorithm with increased power.
- Alok K. Maity
- & Andrew E. Teschendorff
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-modal quantification of pathway activity with MAYA
Multi-modal quantification of pathway activity with MAYA
Pathways can be activated through various signaling cascades depending on cell type. Here, the authors introduce MAYA, a computational method that can detect and score multiple modes of activation for each pathway, improving the granularity of pathway analysis for single-cell datasets.
- Yuna Landais
- & Céline Vallot
-
Article
| Open Access Multiregional single-cell dissection of tumor and immune cells reveals stable lock-and-key features in liver cancer
Multiregional single-cell dissection of tumor and immune cells reveals stable lock-and-key features in liver cancer
Multiregion sequencing is needed to better capture the heterogeneity of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA). Here, the authors analyse HCC and iCCA tumours with multiregion single-cell RNA-seq, revealing cellular dynamics and communication networks with immune cells.
- Lichun Ma
- , Sophia Heinrich
- & Xin Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access SOTIP is a versatile method for microenvironment modeling with spatial omics data
SOTIP is a versatile method for microenvironment modeling with spatial omics data
Methods that analyse heterogeneity and compare tissue microenvironments using spatial omics data are challenging to develop. Here, the authors present SOTIP, a method that can perform spatial heterogeneity, spatial domain, and differential microenvironment analyses across multiple spatial omics modalities.
- Zhiyuan Yuan
- , Yisi Li
- & Michael Q. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Reversion mutations in germline BRCA1/2-mutant tumors reveal a BRCA-mediated phenotype in non-canonical histologies
Reversion mutations in germline BRCA1/2-mutant tumors reveal a BRCA-mediated phenotype in non-canonical histologies
Mutations in BRCA1/2 are associated with a homologous recombination deficiency phenotype in BRCA-associated cancers. Reversion mutations can restore BRCA1/2 function and result in treatment resistance in these cancer-types. Here, the authors show that, in select cases, reversion mutations in BRCA1/2 can indicate prior BRCA-mediated tumorigenesis in non-canonical histologies.
- Yonina R. Murciano-Goroff
- , Alison M. Schram
- & Alexander Drilon
-
Article
| Open Access Integrative analysis of KRAS wildtype metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma reveals mutation and expression-based similarities to cholangiocarcinoma
Integrative analysis of KRAS wildtype metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma reveals mutation and expression-based similarities to cholangiocarcinoma
KRAS wildtype metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (mPDAC) could represent a distinct molecular entity from other PDACs. Here, the authors analyse KRAS wildtype mPDAC tumours using genomics and transcriptomics and find molecular similarities with cholangiocarcinomas.
- James T. Topham
- , Erica S. Tsang
- & Daniel J. Renouf
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analysis highlights differences in druggable pathways underlying adaptive or fibrotic kidney regeneration
Single-cell analysis highlights differences in druggable pathways underlying adaptive or fibrotic kidney regeneration
After acute injury, kidneys either successfully repair/regenerate or become fibrotic. Here the authors use scRNA-seq to study adaptive/maladaptive kidney regeneration and identify proinflammatory/fibrotic proximal tubule cells with pharmacologically targetable pyroptosis/ferroptosis signatures.
- Michael S. Balzer
- , Tomohito Doke
- & Katalin Susztak
-
Article
| Open Access Context-aware deconvolution of cell–cell communication with Tensor-cell2cell
Context-aware deconvolution of cell–cell communication with Tensor-cell2cell
Cellular contexts such as disease state, organismal life stage and tissue microenvironment, shape intercellular communication, and ultimately affect an organism’s phenotypes. Here, the authors present Tensor-cell2cell, an unsupervised method for deciphering context-driven intercellular communication.
- Erick Armingol
- , Hratch M. Baghdassarian
- & Nathan E. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access Comparison of methods and resources for cell-cell communication inference from single-cell RNA-Seq data
Comparison of methods and resources for cell-cell communication inference from single-cell RNA-Seq data
Multiple methods to infer cell-cell communication (CCC) from single cell data are currently available. Here, the authors systematically compare 16 CCC inference resources and 7 methods, and develop the LIANA framework as an interface to use and compare all these approaches.
- Daniel Dimitrov
- , Dénes Türei
- & Julio Saez-Rodriguez
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial neural networks enable genome-scale simulations of intracellular signaling
Artificial neural networks enable genome-scale simulations of intracellular signaling
Many diseases are caused by disruptions to the network of biochemical reactions that allow cells to respond to external signals. Here Nilsson et al develop a method to simulate cellular signaling using artificial neural networks to predict cellular responses and activities of signaling molecules.
- Avlant Nilsson
- , Joshua M. Peters
- & Douglas A. Lauffenburger
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of the COPD alveolar niche using single-cell RNA sequencing
Characterization of the COPD alveolar niche using single-cell RNA sequencing
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, while our understanding of cell-specific mechanisms underlying its pathobiology remains incomplete. Here the authors perform scRNA-seq of human lung tissue to identify transcriptional changes in alveolar niche cells associated with the disease.
- Maor Sauler
- , John E. McDonough
- & Ivan O. Rosas
-
Article
| Open Access Mini-batch optimization enables training of ODE models on large-scale datasets
Mini-batch optimization enables training of ODE models on large-scale datasets
Ordinary differential equation (ODE) models are widely used to understand multiple processes. Here the authors show how the concept of mini-batch optimization can be transferred from the field of Deep Learning to ODE modelling.
- Paul Stapor
- , Leonard Schmiester
- & Jan Hasenauer
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial localisation meets biomolecular networks
Spatial localisation meets biomolecular networks
Complex biomolecular networks are fundamental to the functioning of living systems, both at the cellular level and beyond. In this paper, the authors develop a systems framework to elucidate the interplay of networks and the spatial localisation of network components.
- Govind Menon
- & J. Krishnan
-
Article
| Open Access Fractional response analysis reveals logarithmic cytokine responses in cellular populations
Fractional response analysis reveals logarithmic cytokine responses in cellular populations
Our ability to interpret single-cell multivariate signaling responses is still limited. Here the authors introduce fractional response analysis (FRA), involving fractional cell counting, capable of deconvoluting heterogeneous multivariate responses of cellular populations.
- Karol Nienałtowski
- , Rachel E. Rigby
- & Michał Komorowski
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear delay differential equations and their application to modeling biological network motifs
Nonlinear delay differential equations and their application to modeling biological network motifs
Network motif models focus on small sub-networks in biological systems to quantitatively describe overall behavior but they often overlook time delays. Here, the authors systematically examine the most common network motifs via delay differential equations (DDE), often leading to more concise descriptions.
- David S. Glass
- , Xiaofan Jin
- & Ingmar H. Riedel-Kruse
-
Article
| Open Access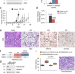 KRAS drives immune evasion in a genetic model of pancreatic cancer
KRAS drives immune evasion in a genetic model of pancreatic cancer
Oncogenic KRAS signalling is required for tumor initiation; however KRAS-dependency at advanced stages is less understood. Here, the authors show that, in established KRAS-driven pancreatic cancer, KRAS-ablation does not affect intrinsic tumorigenic capacity but elicits antitumor immune response, highlighting the importance of KRAS-driven immune suppression in tumor maintenance.
- Irene Ischenko
- , Stephen D’Amico
- & Nancy C. Reich
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying information accumulation encoded in the dynamics of biochemical signaling
Quantifying information accumulation encoded in the dynamics of biochemical signaling
Understanding how cells discriminate between stimuli is an ongoing challenge. Here, the authors propose a mathematical framework for inferring the mutual information encoded in temporal signaling dynamics and use it to study how information is transmitted over time in response to different stimuli in NFκB, MAPK and p53 signaling pathways.
- Ying Tang
- , Adewunmi Adelaja
- & Alexander Hoffmann
-
Article
| Open Access Robust inference of kinase activity using functional networks
Robust inference of kinase activity using functional networks
Kinases drive fundamental changes in cell state, but predicting kinase activity based on substrate-level changes can be challenging. Here the authors introduce a computational framework that utilizes similarities between substrates to robustly infer kinase activity.
- Serhan Yılmaz
- , Marzieh Ayati
- & Mehmet Koyutürk
-
Article
| Open Access Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat
Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat
Single-cell methods record molecule expressions of cells in a given tissue, but understanding interactions between cells remains challenging. Here the authors show by applying systems biology and machine learning approaches that they can infer and analyze cell-cell communication networks in an easily interpretable way.
- Suoqin Jin
- , Christian F. Guerrero-Juarez
- & Qing Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Dissection of intercellular communication using the transcriptome-based framework ICELLNET
Dissection of intercellular communication using the transcriptome-based framework ICELLNET
Bulk and single-cell transcriptomic data can be a source of novel insights into how cells interact with each other. Here the authors develop ICELLNET, a global, biologically validated, and easy-to-use framework to dissect cell communication from individual or multiple cell-based transcriptomic profiles.
- Floriane Noël
- , Lucile Massenet-Regad
- & Vassili Soumelis
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting cell-to-cell communication networks using NATMI
Predicting cell-to-cell communication networks using NATMI
Single cell expression data allows for inferring cell-cell communication between cells expressing ligands and those expressing their cognate receptors. Here the authors present an updated and curated database of ligand-receptor pairs and a Python-based toolkit to construct and analyse communication networks from single cell and bulk expression data.
- Rui Hou
- , Elena Denisenko
- & Alistair R. R. Forrest
-
Article
| Open Access VoPo leverages cellular heterogeneity for predictive modeling of single-cell data
VoPo leverages cellular heterogeneity for predictive modeling of single-cell data
Single-cell technologies are increasingly prominent in clinical applications, but predictive modelling with such data in large cohorts has remained computationally challenging. We developed a new algorithm, ‘VoPo’, for predictive modelling and visualization of single cell data for translational applications.
- Natalie Stanley
- , Ina A. Stelzer
- & Nima Aghaeepour
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome activity landscapes of tumor cell lines determine drug responses
Proteome activity landscapes of tumor cell lines determine drug responses
Proteome activity has a major role in cancer progression and response to drugs. Here, the authors use comprehensive proteomic and phosphoproteomic data, in conjunction with drug-sensitivity screens, to generate a community resource consisting of landscapes of pathway and kinase activity across different cell lines
- Martin Frejno
- , Chen Meng
- & Bernhard Kuster
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting and affecting response to cancer therapy based on pathway-level biomarkers
Predicting and affecting response to cancer therapy based on pathway-level biomarkers
Predicting an individual's response to therapy is an important goal for precision medicine. Here, the authors use an algorithm that takes into account the interaction type and directionality of signalling pathways in protein–protein interactions and find that their pathway analysis can predict essential genes, which may be a target for therapy.
- Rotem Ben-Hamo
- , Adi Jacob Berger
- & Ravid Straussman
-
Article
| Open Access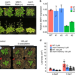 Segregation of an MSH1 RNAi transgene produces heritable non-genetic memory in association with methylome reprogramming
Segregation of an MSH1 RNAi transgene produces heritable non-genetic memory in association with methylome reprogramming
Segregation of an MSH1 RNAi transgene produces non-genetic memory that displays transgenerational inheritance in Arabidopsis. Here, the authors compare memory and non-memory full-sib progenies to show the involvement of DNA methylation reprogramming, involving the RdDM pathway, in transition to a heritable memory state.
- Xiaodong Yang
- , Robersy Sanchez
- & Sally A. Mackenzie
-
Article
| Open Access Pathway and network analysis of more than 2500 whole cancer genomes
Pathway and network analysis of more than 2500 whole cancer genomes
Understanding deregulation of biological pathways in cancer can provide insight into disease etiology and potential therapies. Here, as part of the PanCancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) consortium, the authors present pathway and network analysis of 2583 whole cancer genomes from 27 tumour types.
- Matthew A. Reyna
- , David Haan
- & Christian von Mering
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell census of human kidney organoids shows reproducibility and diminished off-target cells after transplantation
Single cell census of human kidney organoids shows reproducibility and diminished off-target cells after transplantation
How reproducible human kidney organoids derived from different iPSC lines are, and how faithful they are to human kidney tissue remain unclear. Here, the authors use four human iPSC lines to derive kidney organoids and show how organoid composition is reproducible, comparable to human tissue and of improved quality after transplantation.
- Ayshwarya Subramanian
- , Eriene-Heidi Sidhom
- & Anna Greka
-
Article
| Open Access Deep multiomics profiling of brain tumors identifies signaling networks downstream of cancer driver genes
Deep multiomics profiling of brain tumors identifies signaling networks downstream of cancer driver genes
Multi-omic profiling is a powerful approach to dissecting molecular mechanisms in disease. Here the authors generate whole proteome, phosphoproteome and transcriptome profiles from two mouse models of high-grade glioma driven by different oncogenes, and validate identified master regulators with a CRISPR screen.
- Hong Wang
- , Alexander K. Diaz
- & Junmin Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Estimating dispensable content in the human interactome
Estimating dispensable content in the human interactome
The fraction of protein-protein interactions (PPIs) that can be disrupted without fitness effect is unknown. Here, the authors model how disease-causing mutations and common mutations carried by healthy people perturb the interactome, and estimate that <20% of human PPIs are completely dispensable.
- Mohamed Ghadie
- & Yu Xia
-
Article
| Open Access A systematic approach to orient the human protein–protein interaction network
A systematic approach to orient the human protein–protein interaction network
The directions of most human protein-protein interactions (PPIs) remain unknown. Here, the authors use cancer genomic and drug response data to infer the direction of signal flow in the human PPI network and show that the directed network improves drug target and cancer driver gene prioritization.
- Dana Silverbush
- & Roded Sharan
-
Article
| Open Access Pathologic gene network rewiring implicates PPP1R3A as a central regulator in pressure overload heart failure
Pathologic gene network rewiring implicates PPP1R3A as a central regulator in pressure overload heart failure
The genetic and pathogenetic basis of heart failure is incompletely understood. Here, the authors present a high-fidelity tissue collection from rapidly preserved failing and non-failing control hearts which are used for eQTL mapping and network analysis, resulting in the prioritization of PPP1R3A as a heart failure gene.
- Pablo Cordero
- , Victoria N. Parikh
- & Euan A. Ashley
-
Article
| Open Access A systems biology approach uncovers cell-specific gene regulatory effects of genetic associations in multiple sclerosis
A systems biology approach uncovers cell-specific gene regulatory effects of genetic associations in multiple sclerosis
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have so far uncovered more than 200 loci for multiple sclerosis (MS). Here, the authors integrate data from various sources for a cell type-specific pathway analysis of MS GWAS results that specifically highlights the involvement of the immune system in disease pathogenesis.
- Lohith Madireddy
- , Nikolaos A. Patsopoulos
- & Sergio E. Baranzini
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal control nodes in disease-perturbed networks as targets for combination therapy
Optimal control nodes in disease-perturbed networks as targets for combination therapy
Synergistic interactions may arise between regulators in complex molecular networks. Here, the authors develop OptiCon, a computational method for de novo identification of synergistic key regulators and investigate their potential roles as candidate targets for combination therapy.
- Yuxuan Hu
- , Chia-hui Chen
- & Kai Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved phosphorylation hotspots in eukaryotic protein domain families
Conserved phosphorylation hotspots in eukaryotic protein domain families
Protein phosphorylation has various regulatory functions. Here, the authors map 241 phosphorylation hotspot regions across 40 eukaryotic species, showing that they are enriched at interfaces and near catalytic residues, and enable the discovery of functionally important phospho-sites.
- Marta J. Strumillo
- , Michaela Oplová
- & Pedro Beltrao
-
Article
| Open Access Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets
Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets
With the increasing obtainability of multi-OMICs data comes the need for easy to use data analysis tools. Here, the authors introduce Metascape, a biologist-oriented portal that provides a gene list annotation, enrichment and interactome resource and enables integrated analysis of multi-OMICs datasets.
- Yingyao Zhou
- , Bin Zhou
- & Sumit K. Chanda

 Network-based elucidation of colon cancer drug resistance mechanisms by phosphoproteomic time-series analysis
Network-based elucidation of colon cancer drug resistance mechanisms by phosphoproteomic time-series analysis