Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectricity by Bose–Einstein condensation in a quantum magnet
Ferroelectricity by Bose–Einstein condensation in a quantum magnet
Magnons, quantized spin excitations in magnetic materials, may undergo Bose-Einstein condensation into a macroscopic correlated quantum state at low temperature. Here, the authors demonstrate how magnon condensation in quantum magnet TlCuCl3generates an electrical polarization.
- S. Kimura
- , K. Kakihata
- & H. Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-momentum coupled Bose-Einstein condensates with lattice band pseudospins
Spin-momentum coupled Bose-Einstein condensates with lattice band pseudospins
The optical trapping of ultracold atoms allows for the simulation and controlled exploration of phenomena normally found in condensed matter systems. Here, the authors demonstrate spin–orbit coupling between lattice band pseudospins in a Bose-Einstein condensate of ultracold atoms.
- M. A. Khamehchi
- , Chunlei Qu
- & P. Engels
-
Article
| Open Access Real-space collapse of a polariton condensate
Real-space collapse of a polariton condensate
Microcavity polaritons are a fluid of coupled photonic and electronic excitations that share many of the properties of Bose–Einstein condensates. Here, the authors show that the sudden creation of these bosonic fluids at high density results in the concentration of the particles, unlike an atomic gas that would expand.
- L. Dominici
- , M. Petrov
- & D. Sanvitto
-
Article |
 Emergence of coherence via transverse condensation in a uniform quasi-two-dimensional Bose gas
Emergence of coherence via transverse condensation in a uniform quasi-two-dimensional Bose gas
Interacting quantum many-body systems in low dimensions is an active research area in ultra-cold gases. Here, Chomaz et al.study the dimensional crossover of Bose–Einstein condensation and observe the emergence of phase coherence in an ultra-cold quasi-2D Bose gas confined to a flat-bottom trapping potential.
- Lauriane Chomaz
- , Laura Corman
- & Jean Dalibard
-
Article |
 Dicke-type phase transition in a spin-orbit-coupled Bose–Einstein condensate
Dicke-type phase transition in a spin-orbit-coupled Bose–Einstein condensate
Spin-orbit coupling in a Bose–Einstein condensate provides an additional degree of freedom to explore interesting phenomena. Hamner et al.study the ground state of such a system and show that it exhibits a transition between normal and superradiant phases that can be described by the Dicke model.
- Chris Hamner
- , Chunlei Qu
- & Peter Engels
-
Article
| Open Access Interferometry with non-classical motional states of a Bose–Einstein condensate
Interferometry with non-classical motional states of a Bose–Einstein condensate
Ramsey interferometers are used to measure minute energy shifts, but they are usually only applied to simple, non-interacting ensembles. Here, the authors demonstrate a two-pulse Ramsey-type interferometer built on the motional states of an interacting Bose–Einstein condensate using optimal control.
- S. van Frank
- , A. Negretti
- & J. Schmiedmayer
-
Article |
 Efimov-driven phase transitions of the unitary Bose gas
Efimov-driven phase transitions of the unitary Bose gas
Efimov trimers are bound states of three bosons, which exist even if their attraction is too weak to form a pair state. Here, the authors explore the phase diagram of a unitary Bose gas and find a transition from a normal gas to a superfluid Efimov liquid, held together by the same effects as Efimov trimers.
- Swann Piatecki
- & Werner Krauth
-
Article |
 Bose–Einstein condensation in an ultra-hot gas of pumped magnons
Bose–Einstein condensation in an ultra-hot gas of pumped magnons
In contrast to real atoms, Bose–Einstein condensation of quasi-particles does not require low temperature, but is obtained via external pumping. Here, the authors show an unexpected transitional dynamics of a Bose–Einstein condensate of magnons due to a nonlinear evaporative supercooling mechanism.
- Alexander A. Serga
- , Vasil S. Tiberkevich
- & Burkard Hillebrands
-
Article |
 Proposed formation and dynamical signature of a chiral Bose liquid in an optical lattice
Proposed formation and dynamical signature of a chiral Bose liquid in an optical lattice
Ultracold atomic gases provide a playground for exploring exotic quantum phases, like superfluids with staggered orbital currents. Li et al.show that thermal fluctuations can destroy such a state in two stages, revealing a new intermediate chiral Bose liquid with a striking dynamical fingerprint.
- Xiaopeng Li
- , Arun Paramekanti
- & W. Vincent Liu
-
Article
| Open Access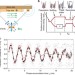 Integrated Mach–Zehnder interferometer for Bose–Einstein condensates
Integrated Mach–Zehnder interferometer for Bose–Einstein condensates
Atom interferometers exploit wave-particle duality and can be used as sensitive measurement devices. Berrada et al.present a Mach–Zehnder interferometer for Bose–Einstein condensates trapped on an atom chip and demonstrate enhanced performance using non-classical states.
- T. Berrada
- , S. van Frank
- & J Schmiedmayer

 Giant superconducting fluctuations in the compensated semimetal FeSe at the BCS–BEC crossover
Giant superconducting fluctuations in the compensated semimetal FeSe at the BCS–BEC crossover