Featured
-
-
Article |
 Control of osteoblast regeneration by a train of Erk activity waves
Control of osteoblast regeneration by a train of Erk activity waves
The rate of scale regeneration in zebrafish is controlled by the frequency of rhythmic travelling waves of Erk activity, which are broadcast from a central source to induce ring-like patterns of osteoblast tissue growth.
- Alessandro De Simone
- , Maya N. Evanitsky
- & Stefano Di Talia
-
Letter |
 HIF-1α metabolically controls collagen synthesis and modification in chondrocytes
HIF-1α metabolically controls collagen synthesis and modification in chondrocytes
Increased glutamine metabolism caused by unregulated HIF-1α signalling in mouse chondrocytes results in increased post-translational modification of collagen and skeletal dysplasia, demonstrating that strict regulation of HIF-1α signalling in chondrocytes is essential for normal bone growth.
- Steve Stegen
- , Kjell Laperre
- & Geert Carmeliet
-
Letter |
 Resting zone of the growth plate houses a unique class of skeletal stem cells
Resting zone of the growth plate houses a unique class of skeletal stem cells
In a mouse model, PTHrP-positive chondrocytes in the resting zone of the growth plate constitute a unique stem-cell population, which is initially unipotent and makes columnar chondrocytes that later exhibit multipotency.
- Koji Mizuhashi
- , Wanida Ono
- & Noriaki Ono
-
Letter |
 Discovery of a periosteal stem cell mediating intramembranous bone formation
Discovery of a periosteal stem cell mediating intramembranous bone formation
A periosteal stem cell specialized in intramembranous bone formation has been identified and was found to be essential for normal bone development and fracture healing.
- Shawon Debnath
- , Alisha R. Yallowitz
- & Matthew B. Greenblatt
-
Letter |
 FGF signalling regulates bone growth through autophagy
FGF signalling regulates bone growth through autophagy
During postnatal development in mice, the growth factor FGF18 induces autophagy in the chondrocyte cells of the growth plate to regulate the secretion of type II collagen, a process required for bone growth.
- Laura Cinque
- , Alison Forrester
- & Carmine Settembre
-
Letter |
 Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone
Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone
Blood vessel growth in bone is revealed to require Notch signalling and involve a specialized form of angiogenesis that does not involve endothelial sprouts.
- Saravana K. Ramasamy
- , Anjali P. Kusumbe
- & Ralf H. Adams
-
Article |
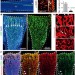 Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone
Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone
Bone homeostasis and repair declines with ageing and the mechanisms regulating the relationship between bone growth and blood vessel formation have remained unknown; this mouse study identifies the endothelial cells that promote the formation of new bone, a small microvessel subtype that can be identified by high CD31 and high Emcn expression.
- Anjali P. Kusumbe
- , Saravana K. Ramasamy
- & Ralf H. Adams
-
Letter |
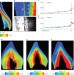 Barium distributions in teeth reveal early-life dietary transitions in primates
Barium distributions in teeth reveal early-life dietary transitions in primates
The patterning of barium in tooth enamel is shown to be a reliable marker of lactation in humans and macaques; furthermore, the study of a tooth from a Neanderthal child reveals the weaning process in this extinct species.
- Christine Austin
- , Tanya M. Smith
- & Manish Arora
-
News & Views |
 A bone for all seasons
A bone for all seasons
Because mammals have such high metabolic rates, it has long been thought that their growth is invulnerable to seasonal variation. But their bones turn out to contain annual lines, just as those of cold-blooded animals do. See Letter p.358
- Kevin Padian
-
Article |
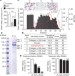 Osteoprotection by semaphorin 3A
Osteoprotection by semaphorin 3A
Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A) is shown to function as a protector of bone, by synchronously inhibiting osteoclastic bone resorption and promoting osteoblastic bone formation.
- Mikihito Hayashi
- , Tomoki Nakashima
- & Hiroshi Takayanagi
-
Research Highlights |
Developmental biology: Blood-vessel cells turn to bone

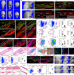 A multi-stem cell basis for craniosynostosis and calvarial mineralization
A multi-stem cell basis for craniosynostosis and calvarial mineralization