Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic antibody-linked nanomatchmakers for therapeutic cell targeting
Magnetic antibody-linked nanomatchmakers for therapeutic cell targeting
Cell therapy requires sufficient amounts of therapeutic cells to be delivered to the injured tissue. Here the authors use magnetic iron nanoparticles conjugated with antibodies that bind therapeutic cells and cardiomyocytes to treat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats and show that targeting to the heart is enhanced upon local application of a magnetic field.
- Ke Cheng
- , Deliang Shen
- & Eduardo Marbán
-
Article
| Open Access Protein co-translocational unfolding depends on the direction of pulling
Protein co-translocational unfolding depends on the direction of pulling
Protein unfolding and translocation through membrane pores occurs in several biological processes and has implications in nanopore technologies. Here, the authors show that the kinetics of unfolding differ depending on which end of the chain enters the pore first.
- David Rodriguez-Larrea
- & Hagan Bayley
-
Article |
 Microfluidic platform for the quantitative analysis of leukocyte migration signatures
Microfluidic platform for the quantitative analysis of leukocyte migration signatures
Current leukocyte migration assays usually report bulk attractive behaviour of cells within a chemokine gradient. Here, the authors develop a microfluidic device to simultaneously measure several migration responses on exposure to commonly used leukocyte chemokines, and report previously unrecognized cell behaviour.
- Leo Boneschansker
- , Jun Yan
- & Daniel Irimia
-
Article
| Open Access An engineered pathway for the biosynthesis of renewable propane
An engineered pathway for the biosynthesis of renewable propane
Propane is the main component of liquid petroleum gas and has a wide variety of commercial applications. Here, the authors engineer a synthetic metabolic pathway in E. coli, and demonstrate for the first time the renewable production of propane.
- Pauli Kallio
- , András Pásztor
- & Patrik R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access A genome-wide map of hyper-edited RNA reveals numerous new sites
A genome-wide map of hyper-edited RNA reveals numerous new sites
Common methods to detect adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing sites rely on mapping short RNA reads to the genome while allowing only a limited number of mismatches. Here, Porath et al. present a novel RNA-seq based approach to identify hyper-edited reads that significantly expands the RNA editome.
- Hagit T. Porath
- , Shai Carmi
- & Erez Y. Levanon
-
Article |
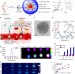 A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nanoporphyrin
A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nanoporphyrin
Nanoparticles can be used for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Here, the authors report that nanoparticles made of a single chemical building block, called nanoporphyrins, incorporate eight different functionalities, including various types of imaging, drug delivery and cancer therapy.
- Yuanpei Li
- , Tzu-yin Lin
- & Kit S. Lam
-
Article |
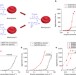 Enhancement of biological reactions on cell surfaces via macromolecular crowding
Enhancement of biological reactions on cell surfaces via macromolecular crowding
Optimizing cell-surface biological reactions is an important goal of biotechnology and industrial processes. Here the authors use macromolecular crowding to enhance the enzymatic conversion of red blood cells to the universal type O blood type, using orders of magnitude less enzyme than was previously required.
- Rafi Chapanian
- , David H. Kwan
- & Jayachandran N Kizhakkedathu
-
Article |
 Expansion of the CRISPR–Cas9 genome targeting space through the use of H1 promoter-expressed guide RNAs
Expansion of the CRISPR–Cas9 genome targeting space through the use of H1 promoter-expressed guide RNAs
Current CRISPR-mediated genome-editing methods are limited by the requirement for a specific +1 nucleotide when using the U6 promoter to drive guide RNA synthesis. Now, Ranganathan et al.report a modification of the CRISPR–Cas9 system that more than doubles the number of targetable CRISPR sites within the human genome.
- Vinod Ranganathan
- , Karl Wahlin
- & Donald J. Zack
-
Article |
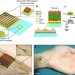 Conformable amplified lead zirconate titanate sensors with enhanced piezoelectric response for cutaneous pressure monitoring
Conformable amplified lead zirconate titanate sensors with enhanced piezoelectric response for cutaneous pressure monitoring
The development of more sensitive tools for physiological monitoring presents obvious advantages in health-care and diagnostic assessment. Here, the authors present a thin, skin-like sensor that uses enhanced responses in lead zirconate titanate for monitoring arterial pressure waves.
- Canan Dagdeviren
- , Yewang Su
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
 Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-arginine production
Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-arginine production
The amino acid, L-arginine, has important applications in the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries. Here the authors systematically engineer a Corynebacterium glutamicum strain for the production of L-arginine, and show that their metabolic engineering approach can be used for the industrial production of valuable chemicals.
- Seok Hyun Park
- , Hyun Uk Kim
- & Sang Yup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access A designer cell-based histamine-specific human allergy profiler
A designer cell-based histamine-specific human allergy profiler
The advancement of sensitive, accurate and non-invasive methods to identify the allergen that drives allergic disease in an individual remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a synthetic biology approach using human designer cells to profile allergic reactions against an array of allergens measuring histamine release from whole blood.
- David Ausländer
- , Benjamin Eggerschwiler
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article |
 Modulating the frequency and bias of stochastic switching to control phenotypic variation
Modulating the frequency and bias of stochastic switching to control phenotypic variation
Mechanisms that control gene expression variation in cells can affect factors such as population growth and adaptability. Here, the authors present a strategy that allows both the level and amount of variation in gene expression to be tuned in E. coli populations using the fimswitch.
- Michelle Hung
- , Emily Chang
- & Han N. Lim
-
Article
| Open Access Creation of a gated antibody as a conditionally functional synthetic protein
Creation of a gated antibody as a conditionally functional synthetic protein
The ability to control antibody binding could have important medical implications. Here, the authors present a method to engineer phosphatase-controllable antibodies that bind to a specific recognition site in the presence of two biomarker inputs.
- Smita B. Gunnoo
- , Helene M. Finney
- & Benjamin G. Davis
-
Article |
 Poking cells for efficient vector-free intracellular delivery
Poking cells for efficient vector-free intracellular delivery
The incorporation of foreign objects into cells can be used in various avenues of biological research, although crossing the cell membrane can be challenging. Here, the authors use a diamond nanoneedle array for enhanced delivery of various particles into cells, including neurons.
- Ying Wang
- , Yang Yang
- & Peng Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering light-inducible nuclear localization signals for precise spatiotemporal control of protein dynamics in living cells
Engineering light-inducible nuclear localization signals for precise spatiotemporal control of protein dynamics in living cells
Designing inducible and reversible nuclear localization signals would enable researchers to dissect and engineer cellular networks. Here Niopek et al.create a light-inducible nuclear localization signal to regulate gene expression and mitosis in mammalian cells, using blue light.
- Dominik Niopek
- , Dirk Benzinger
- & Barbara Di Ventura
-
Article |
 Synergistic roles for lipids and proteins in the permanent adhesive of barnacle larvae
Synergistic roles for lipids and proteins in the permanent adhesive of barnacle larvae
Using their unique bioadhesives, barnacles can adhere to a great variety of surfaces. Here, Gohad et al.show that the barnacle larval bioadhesive contains lipids and phosphoproteins that are organized in a complex structure and work together to maximize adhesion.
- Neeraj V. Gohad
- , Nick Aldred
- & Andrew S. Mount
-
Article |
 IgGs are made for walking on bacterial and viral surfaces
IgGs are made for walking on bacterial and viral surfaces
Antibody–antigen recognition is one of the important aspects of immunity, but the nanomechanical process of this recognition is not fully understood. Here, using high-speed atomic force microscopy, the authors observe that on membranes containing a high density of immobile antigens antibodies move in a ‘random walking’ motion.
- Johannes Preiner
- , Noriyuki Kodera
- & Peter Hinterdorfer
-
Article
| Open Access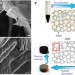 Mesoscale assembly of chemically modified graphene into complex cellular networks
Mesoscale assembly of chemically modified graphene into complex cellular networks
Graphene’s properties are well known, but turning this atomically thin material into three-dimensional devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors report an assembly process for chemically modified graphene into three-dimensional cellular networks, with control over the physical properties of the resulting materials.
- Suelen Barg
- , Felipe Macul Perez
- & Eduardo Saiz
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of free-standing RNA membranes
Self-assembly of free-standing RNA membranes
Nucleic acids possess a number of properties that can be beneficial for the fabrication of nanomaterials. Here, the authors present an enzymatically synthesised RNA membrane, and show how its physical properties can be controlled by changes to base-pairing.
- Daehoon Han
- , Yongkuk Park
- & Jong Bum Lee
-
Article |
 SNARE-fusion mediated insertion of membrane proteins into native and artificial membranes
SNARE-fusion mediated insertion of membrane proteins into native and artificial membranes
The study of cell membrane proteins can be simplified by incorporating them into lipid bilayers, but doing this for multiple proteins can be challenging. Here, the authors present a technique to achieve this, and show reconstitution of a bacterial respiratory chain from individual components.
- Gustav Nordlund
- , Peter Brzezinski
- & Christoph von Ballmoos
-
Article |
 Reconfigurable microfluidic hanging drop network for multi-tissue interaction and analysis
Reconfigurable microfluidic hanging drop network for multi-tissue interaction and analysis
Many tissues can be grown as 3D spheroid models in hanging drops of media. Here, Frey et al. develop a microfluidic, interconnected hanging drop network to facilitate inter-drop communication, and demonstrate that pro-drug conversion by liver spheroids can limit the growth of cancer spheroids in adjacent drops.
- Olivier Frey
- , Patrick M. Misun
- & Andreas Hierlemann
-
Article |
 Degradable lipid nanoparticles with predictable in vivo siRNA delivery activity
Degradable lipid nanoparticles with predictable in vivo siRNA delivery activity
Robust and reliable structure–function relationships are valuable for the development of potent drug delivery systems. Here, the authors use a library of lipid-like materials to predict in vivosiRNA delivery efficacy without any biological testing.
- Kathryn A. Whitehead
- , J. Robert Dorkin
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
Article |
 An artificial primitive mimic of the Gramicidin-A channel
An artificial primitive mimic of the Gramicidin-A channel
Gramicidin A pores are important natural structures for the transport of ions through biological membranes. Here, the authors show that this functionality can be mimicked using an artificial transmembrane channel formed of synthetic pore-forming compounds.
- Mihail Barboiu
- , Yann Le Duc
- & Thomas Fyles
-
Article |
 Glycosphingolipid-functionalized nanoparticles recapitulate CD169-dependent HIV-1 uptake and trafficking in dendritic cells
Glycosphingolipid-functionalized nanoparticles recapitulate CD169-dependent HIV-1 uptake and trafficking in dendritic cells
Ganglioside GM3, a cellular lipid included in the envelope of HIV-1 viral particles, interacts with cellular receptor CD169. Here, the authors develop artificial nanoparticles, consisting of a golden core and a GM3-containing synthetic membrane, that recapitulate the CD169-dependent uptake of viral particles.
- Xinwei Yu
- , Amin Feizpour
- & Björn M. Reinhard
-
Article
| Open Access Vanillin formation from ferulic acid in Vanilla planifolia is catalysed by a single enzyme
Vanillin formation from ferulic acid in Vanilla planifolia is catalysed by a single enzyme
Vanilla is derived from vanillin isolated from a vanillin-producing orchid, but the process is laborious, costly and results in a small yield. Here, the authors identified an enzyme from the orchid, Vanilla planifolia, that is able to catalyse the formation of vanillin and vanillin glucoside from ferulic acid and its glucoside in vitro, respectively.
- Nethaji J. Gallage
- , Esben H. Hansen
- & Birger Lindberg Møller
-
Article |
 Generation of three-dimensional retinal tissue with functional photoreceptors from human iPSCs
Generation of three-dimensional retinal tissue with functional photoreceptors from human iPSCs
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) hold great potential for modelling human developmental processes and diseases. Here the authors induce human iPSCs to spontaneously form fully laminated three-dimensional retinal tissue containing functional photoreceptor cells.
- Xiufeng Zhong
- , Christian Gutierrez
- & M. Valeria Canto-Soler
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic sex ratio distortion system for the control of the human malaria mosquito
A synthetic sex ratio distortion system for the control of the human malaria mosquito
Extreme reproductive sex ratios could result in the suppression or elimination of pest populations. Here, the authors design a synthetic sex distortion system in Anopheles gambiaethat gives rise to fertile mosquito strains that produce over 95% male offsprings and could therefore be used to suppress mosquito populations.
- Roberto Galizi
- , Lindsey A. Doyle
- & Andrea Crisanti
-
Article |
 Hypoxia-inducible hydrogels
Hypoxia-inducible hydrogels
Oxygen is vital for all multicellular organisms and oxygen deprivation, hypoxia, influences cellular functions. Here, the authors develop an oxygen-controlling hydrogel that can be used as a three-dimensional hypoxic microenvironment, and may aid the study of hypoxia-related biological conditions.
- Kyung Min Park
- & Sharon Gerecht
-
Article |
 Light-inducible receptor tyrosine kinases that regulate neurotrophin signalling
Light-inducible receptor tyrosine kinases that regulate neurotrophin signalling
Optogenetic tools allow fine spatial control of signalling pathways using light. Chang et al. present a strategy for constructing light-sensitive receptor tyrosine kinases and demonstrate that optogenetic stimulation of Trk receptors in neurons promotes neurite outgrowth.
- Ki-Young Chang
- , Doyeon Woo
- & Won Do Heo
-
Article
| Open Access Monitoring the dynamics of clonal tumour evolution in vivo using secreted luciferases
Monitoring the dynamics of clonal tumour evolution in vivo using secreted luciferases
Non-invasive monitoring of solid tumour growth in mice is difficult. In this study, the authors develop a system for monitoring the secretion of luciferase either from Gaussia princeps or Cypridina noctiluca in the blood of mice harbouring luciferase-labelled tumour cells, thus providing a system to monitor two different cell populations in vivo.
- Joël P. Charles
- , Jeannette Fuchs
- & Thorsten Stiewe
-
Article
| Open Access Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink
Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink
The application of 3D printing to biomaterials presents interesting possibilities for tissue engineering. Here, the authors show that a printing medium derived from an extracellular matrix can be applied to printing tissue analogues with enhanced cell compatibility.
- Falguni Pati
- , Jinah Jang
- & Dong-Woo Cho
-
Article |
 Genome engineering empowers the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum for biotechnology
Genome engineering empowers the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum for biotechnology
Diatoms are photosynthetic microalgae with underutilized biotechnological potential. Here, the authors carry out targeted gene modifications of lipid metabolism genes in the diatom, Phaeodactylum tricornutum, resulting in a strain that exhibits a 45-fold increase in triacylglycerol accumulation.
- Fayza Daboussi
- , Sophie Leduc
- & Philippe Duchateau
-
Article |
 A pan-cancer proteomic perspective on The Cancer Genome Atlas
A pan-cancer proteomic perspective on The Cancer Genome Atlas
Analyses of genome and transcriptome data are unable to accurately predict protein levels and function in tumour samples. Here, the authors carry out a comprehensive protein analysis in 3,467 samples from the cancer genome atlas, providing a resource to study the prognostic and therapeutic potential of tumour proteins.
- Rehan Akbani
- , Patrick Kwok Shing Ng
- & Gordon B. Mills
-
Article |
 Design of synthetic yeast promoters via tuning of nucleosome architecture
Design of synthetic yeast promoters via tuning of nucleosome architecture
Model-based part design is a key step in synthetic biology. Here, the authors report a method for tuning nucleosome architecture in order to strengthen native promoters and facilitate synthetic promoter design in yeast.
- Kathleen A. Curran
- , Nathan C. Crook
- & Hal S. Alper
-
Article |
 An improved monomeric infrared fluorescent protein for neuronal and tumour brain imaging
An improved monomeric infrared fluorescent protein for neuronal and tumour brain imaging
Infrared fluorescent proteins offer advantages for deep in vivo imaging thanks to the tissue-penetrating properties of infrared light. Here, Yu et al. design a monomeric infrared fluorescent protein that, when combined with expression of haeme oxygenase in cells, shows improved performance for in vivoimaging of neurons and brain tumours.
- Dan Yu
- , William Clay Gustafson
- & Xiaokun Shu
-
Article |
 Protein grafting of p53TAD onto a leucine zipper scaffold generates a potent HDM dual inhibitor
Protein grafting of p53TAD onto a leucine zipper scaffold generates a potent HDM dual inhibitor
The protein levels of the tumour suppressor p53 can be negatively regulated by HDM2, which is an attractive target for cancer therapy. In this study, Lee et al. graft the transactivation domain of p53 onto a scaffold protein and show that this binds to HDM2 and inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro.
- Jung-Hoon Lee
- , Eunji Kang
- & Jae Il Lee
-
Article |
 Macromolecular structures probed by combining single-shot free-electron laser diffraction with synchrotron coherent X-ray imaging
Macromolecular structures probed by combining single-shot free-electron laser diffraction with synchrotron coherent X-ray imaging
Macromolecular complexes hold promise for future generations of drug delivery carriers, but probing their structures with high resolution is challenging. Here, the authors combine X-ray free-electron laser and synchrotron approaches to reveal the core-shell structure of RNA interference microsponges.
- Marcus Gallagher-Jones
- , Yoshitaka Bessho
- & Changyong Song
-
Article
| Open Access The emerging biofuel crop Camelina sativa retains a highly undifferentiated hexaploid genome structure
The emerging biofuel crop Camelina sativa retains a highly undifferentiated hexaploid genome structure
Camelina sativa is an oilseed crop with important industrial applications. Here, the authors sequence the C. sativagenome to investigate the genome organization and evolution of this species, and to provide a valuable tool for genetic engineering and potential crop improvement.
- Sateesh Kagale
- , Chushin Koh
- & Isobel A. P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental orthotopic transplantation of a tissue-engineered oesophagus in rats
Experimental orthotopic transplantation of a tissue-engineered oesophagus in rats
Patients with oesophageal diseases may require surgical removal and replacement of the oesophagus. Here the authors seed mesenchymal stromal cells on a decellularized rat oesophagus and show that this bioengineered tissue construct restores swallowing function after transplantation into rats.
- Sebastian Sjöqvist
- , Philipp Jungebluth
- & Paolo Macchiarini
-
Article |
 Tyrosine-mediated two-dimensional peptide assembly and its role as a bio-inspired catalytic scaffold
Tyrosine-mediated two-dimensional peptide assembly and its role as a bio-inspired catalytic scaffold
It is well known that the interplay between molecular ordering and interface geometry can determine the morphology of two-dimensional systems. Here, the authors report facet formation in water droplets, driven by peptide assembly, and investigate the structural and sequence motifs that affect this behaviour.
- Hyung-Seok Jang
- , Jung-Ho Lee
- & Yoon-Sik Lee
-
Article
| Open Access The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus
The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus
The (seco)iridoids and their monoterpenoid indole alkaloid (MIA) derivatives are plant-derived compounds with pharmaceutical applications. Here, the authors identify the last four missing steps of the (seco)iridoid pathway, which they reconstitute in an alternative plant host to produce the complex MIA, strictosidine.
- Karel Miettinen
- , Lemeng Dong
- & Danièle Werck-Reichhart
-
Article |
 Three-layered polyplex micelle as a multifunctional nanocarrier platform for light-induced systemic gene transfer
Three-layered polyplex micelle as a multifunctional nanocarrier platform for light-induced systemic gene transfer
Light-controlled mechanisms for the delivery of drug molecules to cells is a promising route for non-invasive disease therapy. Here, the authors develop a photosensitive polymeric micelle for light-induced gene transfection and show its effectiveness in vivovia systemic administration.
- Takahiro Nomoto
- , Shigeto Fukushima
- & Kazunori Kataoka
-
Article
| Open Access An auto-inducible mechanism for ionic liquid resistance in microbial biofuel production
An auto-inducible mechanism for ionic liquid resistance in microbial biofuel production
Ionic liquids (ILs) are important solvents in the microbial production of biofuels, but can inhibit microbial growth. Here, the authors transfer newly discovered IL-resistance genes from rain forest soil bacteria to E. coliand report growth and biofuel production at IL levels that are otherwise toxic to native strains.
- Thomas L. Ruegg
- , Eun-Mi Kim
- & Michael P. Thelen
-
Article |
 Microfluidic probe for single-cell analysis in adherent tissue culture
Microfluidic probe for single-cell analysis in adherent tissue culture
Cellular heterogeneity is a feature of diverse disease processes, yet is masked in typical biochemical assays. Sarkar et al.develop a microfluidic device to access the contents of single cells in adherent culture, allowing biochemical measurements to be connected with phenotypic information.
- Aniruddh Sarkar
- , Sarah Kolitz
- & Jongyoon Han
-
Article |
 Bio-barcode gel assay for microRNA
Bio-barcode gel assay for microRNA
MicroRNA has been identified to play a role in cancer development, thus its detection at low concentrations would be a highly beneficial diagnostic tool. Here, the authors develop a gel-based bio-barcode assay for microRNA detection using DNA-modified gold nanoparticles, with aM limits of detection.
- Hyojin Lee
- , Jeong-Eun Park
- & Jwa-Min Nam
-
Article
| Open Access A plant factory for moth pheromone production
A plant factory for moth pheromone production
Pheromones can be used as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional pesticides. Here, the authors produce moth sex pheromones in Nicotiana benthamianaby transient expression and demonstrate that these pheromones are able to trap male moths as efficiently as their synthetic counterparts.
- Bao-Jian Ding
- , Per Hofvander
- & Christer Löfstedt
-
Article |
 Microgels on-demand
Microgels on-demand
Traditional methods for forming hydrogel particles are limited by geometry and lack of addressability after synthesis. Here the authors use digital microfluidics to form individually addressable gels with customisable shapes and compositions.
- Irwin A. Eydelnant
- , Bingyu Betty Li
- & Aaron R. Wheeler
-
Article |
 A cortical–spinal prosthesis for targeted limb movement in paralysed primate avatars
A cortical–spinal prosthesis for targeted limb movement in paralysed primate avatars
Brain–machine interfaces are being investigated for recovery of motor function after paralysis. Shanechi et al.present a neural prosthesis that decodes premotor neuronal activity in an alert monkey to activate spinal neurons and muscles that produce target-directed movements in a sedated monkey or avatar.
- Maryam M. Shanechi
- , Rollin C. Hu
- & Ziv M. Williams
-
Article |
 Lipidic cubic phase injector facilitates membrane protein serial femtosecond crystallography
Lipidic cubic phase injector facilitates membrane protein serial femtosecond crystallography
Serial femtosecond X-ray crystallography permits the use of very small protein crystals; however, a continuous flow of sample is required. Weierstall et al. design and demonstrate an injector system that can supply microcrystals in the lipidic cubic phase, dramatically reducing the quantities of protein required.
- Uwe Weierstall
- , Daniel James
- & Vadim Cherezov
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Animal biotechnology
- Applied immunology
- Assay systems
- Biologics
- Biomaterials
- Biomimetics
- Cell delivery
- Environmental biotechnology
- Expression systems
- Functional genomics
- Gene delivery
- Gene therapy
- Genomics
- Industrial microbiology
- Metabolic engineering
- Metabolomics
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nucleic-acid therapeutics
- Oligo delivery
- Peptide delivery
- Plant biotechnology
- Protein delivery
- Proteomics
- Regenerative medicine
- Sequencing
- Stem-cell biotechnology
- Tissue engineering

 Programmable biofilm-based materials from engineered curli nanofibres
Programmable biofilm-based materials from engineered curli nanofibres