Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a synthetic pathway for maleate in Escherichia coli
Engineering a synthetic pathway for maleate in Escherichia coli
Maleate is an important stock chemical for the production of polymer compounds and pharmaceuticals. Here the authors design a synthetic pathway for maleate in E. coli by combining polyketide biosynthesis and benzene ring cleavage pathways.
- Shuhei Noda
- , Tomokazu Shirai
- & Akihiko Kondo
-
Article
| Open Access Coding and noncoding landscape of extracellular RNA released by human glioma stem cells
Coding and noncoding landscape of extracellular RNA released by human glioma stem cells
While circulating DNA has been extensively explored as a potential cancer biomarker, RNA potential has been overlooked so far. Here the authors present a comprehensive analysis of extracellular RNA secreted by glioblastoma cells that could prove a valuable resource for biomarker discovery and a means of intercellular communication.
- Zhiyun Wei
- , Arsen O. Batagov
- & Anna M. Krichevsky
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient protein production by yeast requires global tuning of metabolism
Efficient protein production by yeast requires global tuning of metabolism
The contribution of metabolic pathways to protein secretion is largely unknown. Here, the authors find conserved metabolic patterns in yeast by examining genome-wide transcriptional responses in high protein secretion mutants and reveal critical factors that can be tuned for efficient protein secretion.
- Mingtao Huang
- , Jichen Bao
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical control of enzymatic actuators using DNA-based switchable memories
Hierarchical control of enzymatic actuators using DNA-based switchable memories
Naturally evolved regulatory circuits have hierarchical layers of signal generation and processing. Here, the authors emulate these networks using feedback-controlled DNA circuits that convert upstream signaling to downstream enzyme activity in a switchable memories circuit.
- Lenny H. H. Meijer
- , Alex Joesaar
- & Tom F. A. de Greef
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing a catalytic lysine residue for the one-step preparation of homogeneous antibody-drug conjugates
Harnessing a catalytic lysine residue for the one-step preparation of homogeneous antibody-drug conjugates
Current strategies for producing antibody-drug conjugates often rely on inefficient conjugation chemistry or on generating mutations in the antibody sequence. Here the authors demonstrate a mutation-free, single-step conjugation platform utilizing a buried lysine residue.
- Alex R. Nanna
- , Xiuling Li
- & Christoph Rader
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell mass cytometry and transcriptome profiling reveal the impact of graphene on human immune cells
Single-cell mass cytometry and transcriptome profiling reveal the impact of graphene on human immune cells
Understanding the interaction of nanomaterials and immune cells at the biomolecular level is of great significance in therapeutic applications. Here, the authors investigated the interaction of graphene oxide nanomaterials and several immune cell subpopulations using single-cell mass cytometry and genome-wide transcriptome analysis.
- Marco Orecchioni
- , Davide Bedognetti
- & Lucia G Delogu
-
Article
| Open Access Single nucleus sequencing reveals spermatid chromosome fragmentation as a possible cause of maize haploid induction
Single nucleus sequencing reveals spermatid chromosome fragmentation as a possible cause of maize haploid induction
Plant breeders can produce haploid maize lines using haploid inducer lines as pollen donors. Here, by sequencing the genomes of single pollen nuclei, Li et al. show that haploid inducer spermatids are frequently aneuploid and suggest chromosome fragmentation as a possible cause of haploid induction.
- Xiang Li
- , Dexuan Meng
- & Jianbing Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling Torsade de Pointes arrhythmias in vitro in 3D human iPS cell-engineered heart tissue
Modelling Torsade de Pointes arrhythmias in vitro in 3D human iPS cell-engineered heart tissue
Torsade de Pointes (TdP) is a life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia often caused by drugs. In response to an urgent need for human tissue TdP models, here the authors describe a 3D human iPS cell-engineered heart tissue that generates TdP in response to drugs, providing a suitable model for studies of TdP mechanism and drug toxicity.
- Masahide Kawatou
- , Hidetoshi Masumoto
- & Jun K. Yamashita
-
Article
| Open Access Control of enzyme reactions by a reconfigurable DNA nanovault
Control of enzyme reactions by a reconfigurable DNA nanovault
DNA nanostructures can cage enzymes but currently fall short of controlling their reactions with substrates. Here, the authors enclose an enzyme inside a dynamic DNA vault, which regulates its access to substrate molecules—and thus its enzymatic activity—through a multi-lock mechanism.
- Guido Grossi
- , Mette Dalgaard Ebbesen Jepsen
- & Ebbe Sloth Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access Computational design of small transcription activating RNAs for versatile and dynamic gene regulation
Computational design of small transcription activating RNAs for versatile and dynamic gene regulation
The structural basis of RNA-based gene control offers the possibility of de novo design. Here the authors present a computational design approach for Small Transcription Activating RNAs a bacterial RNA regulator that allows for versatile and dynamic control of genes, pathways and genetic circuits.
- James Chappell
- , Alexandra Westbrook
- & Julius B. Lucks
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the bioactivity of a peptide hormone in vivo by reversible self-assembly
Controlling the bioactivity of a peptide hormone in vivo by reversible self-assembly
The clinical potential of peptide therapeutic agents can only be fully realised once their physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties are precisely controlled. Here the authors show a reversible peptide self-assembly strategy to control and prolong the bioactivity of a native peptide hormone in vivo.
- Myriam M. Ouberai
- , Ana L. Gomes Dos Santos
- & Mark E. Welland
-
Article
| Open Access DNA-binding of the Tet-transactivator curtails antigen-induced lymphocyte activation in mice
DNA-binding of the Tet-transactivator curtails antigen-induced lymphocyte activation in mice
Tet-transactivators are used for direct regulation of gene expression, RNA interference and for CRISPR/Cas9-based systems. Here the authors show that DNA-bound Tet-transactivators can induce cell death in antigen-activated lymphocytes in vivo, putting into question the use of, and in vivo data generated with, these molecular tools.
- Eleonora Ottina
- , Victor Peperzak
- & Andreas Villunger
-
Article
| Open Access Glycaemic control boosts glucosylated nanocarrier crossing the BBB into the brain
Glycaemic control boosts glucosylated nanocarrier crossing the BBB into the brain
There are only a few examples of nanocarriers that can transport bioactive substances across the blood-brain barrier. Here the authors show that by rapid glycaemic increase the accumulation of a glucosylated nanocarrier in the brain can be controlled.
- Y. Anraku
- , H. Kuwahara
- & K. Kataoka
-
Article
| Open Access Selective binding of choline by a phosphate-coordination-based triple helicate featuring an aromatic box
Selective binding of choline by a phosphate-coordination-based triple helicate featuring an aromatic box
The choline-binding protein ChoX exhibits a synergistic dual-site binding mode that allows it to discriminate choline over structural analogues. Here, the authors design a biomimetic triple anion helicate receptor whose selectivity for choline arises from a similar binding mechanism.
- Chuandong Jia
- , Wei Zuo
- & Biao Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Electro-osmotic capture and ionic discrimination of peptide and protein biomarkers with FraC nanopores
Electro-osmotic capture and ionic discrimination of peptide and protein biomarkers with FraC nanopores
Biological nanopore–based protein sequencing and recognition is challenging due to the folded structure or non-uniform charge of peptides. Here the authors show that engineered FraC nanopores can overcome these problems and recognize biomarkers in the form of oligopeptides, polypeptides and folded proteins.
- Gang Huang
- , Kherim Willems
- & Giovanni Maglia
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule study of oxidative enzymatic deconstruction of cellulose
Single-molecule study of oxidative enzymatic deconstruction of cellulose
Understanding the role of enzymes in biomass depolymerization is essential for the development of more efficient biorefineries. Here, the authors show by atomic force microscopy the real-time mechanism of cellulose deconstruction by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases.
- Manuel Eibinger
- , Jürgen Sattelkow
- & Bernd Nidetzky
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering species-like barriers to sexual reproduction
Engineering species-like barriers to sexual reproduction
Genetic isolation of a genetically modified organism represents a useful strategy for biocontainment. Here the authors use dCas9-VP64-driven gene expression to construct a ‘species-like’ barrier to reproduction between two otherwise compatible populations.
- Maciej Maselko
- , Stephen C. Heinsch
- & Michael J. Smanski
-
Article
| Open Access Bioengineering of functional human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal grafts
Bioengineering of functional human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal grafts
There is a need for humanised grafts to treat patients with intestinal failure. Here, the authors generate intestinal grafts by recellularizing native intestinal matrix with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived epithelium and human endothelium, and show nutrient absorption after transplantation in rats.
- Kentaro Kitano
- , Dana M. Schwartz
- & Harald C. Ott
-
Article
| Open Access Alveolar macrophages are critical for broadly-reactive antibody-mediated protection against influenza A virus in mice
Alveolar macrophages are critical for broadly-reactive antibody-mediated protection against influenza A virus in mice
Broadly reactive antibodies that recognize influenza A virus HA can be protective, but the mechanism is not completely understood. Here, He et al. show that the inflammatory response and phagocytosis mediated by the interaction between protective antibodies and macrophages are essential for protection.
- Wenqian He
- , Chi-Jene Chen
- & Gene S. Tan
-
Article
| Open Access A non-classical view on calcium oxalate precipitation and the role of citrate
A non-classical view on calcium oxalate precipitation and the role of citrate
The formation mechanism of abundant calcium oxalate biomaterials is unresolved. Here the authors show the early stages of calcium oxalate formation in pure and citrate-bearing solutions by using a titration set-up in conjunction with solution quenching, transmission electron microscopy and analytical ultracentrifugation.
- Encarnación Ruiz-Agudo
- , Alejandro Burgos-Cara
- & Carlos Rodriguez-Navarro
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic microparticles conjugated with VEGF165 improve the survival of endothelial progenitor cells via microRNA-17 inhibition
Synthetic microparticles conjugated with VEGF165 improve the survival of endothelial progenitor cells via microRNA-17 inhibition
Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) enhances vascular engraftment of transplanted cells but the efficacy is low. Here, the authors show that VEGF-immobilized microparticles prolong survival of endothelial progenitors in vitro and in vivo by downregulating miR17 and upregulating CDKN1A and ZNF652.
- Sezin Aday
- , Janet Zoldan
- & Lino Ferreira
-
Article
| Open Access A DNA nanoscope via auto-cycling proximity recording
A DNA nanoscope via auto-cycling proximity recording
The spatial organisation of nanostructures is fundamental to their function. Here, the authors develop a non-destructive, proximity-based method to record extensive spatial organization information in DNA molecules for later readout.
- Thomas E. Schaus
- , Sungwook Woo
- & Peng Yin
-
Article
| Open Access In trans paired nicking triggers seamless genome editing without double-stranded DNA cutting
In trans paired nicking triggers seamless genome editing without double-stranded DNA cutting
CRISPR-Cas9-based gene editing involves double-strand breaks at target sequences, which are often repaired by mutagenic non-homologous end-joining. Here the authors use Cas9 nickases to generate coordinated single-strand breaks in donor and target DNA for precise homology-directed gene editing.
- Xiaoyu Chen
- , Josephine M. Janssen
- & Manuel A. F. V. Gonçalves
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative colloidal self-assembly of metal-protein superlattice wires
Cooperative colloidal self-assembly of metal-protein superlattice wires
Colloidal self-assembly is a unique method to produce three-dimensional materials with well-defined hierarchical structures and functionalities. Liljeström et al. show controlled preparation of macroscopic chiral wires with helical plasmonic superlattice structure composed of metal nanoparticles and viruses.
- Ville Liljeström
- , Ari Ora
- & Mauri A. Kostiainen
-
Article
| Open Access SRpHi ratiometric pH biosensors for super-resolution microscopy
SRpHi ratiometric pH biosensors for super-resolution microscopy
Ratiometric fluorescent pH probes are useful tools to monitor acidification of vesicles during endocytosis, but the size of vesicles is below the diffraction limit. Here the authors develop a family of ratiometric pH sensors for use in STED super-resolution microscopy, and optimize their delivery to endosomes.
- Douglas S. Richardson
- , Carola Gregor
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Article
| Open Access Low carbon renewable natural gas production from coalbeds and implications for carbon capture and storage
Low carbon renewable natural gas production from coalbeds and implications for carbon capture and storage
Coalbeds produce natural gas, which has been observed to be enhanced by in situ microbes. Here, the authors add plant-derived carbohydrates (monosaccharides) to coal seams to be converted by indigenous microbes into natural gas, thus demonstrating a potential low carbon renewable natural gas resource.
- Zaixing Huang
- , Christine Sednek
- & Shengpin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Checkpoint blockade immunotherapy reshapes the high-dimensional phenotypic heterogeneity of murine intratumoural neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells
Checkpoint blockade immunotherapy reshapes the high-dimensional phenotypic heterogeneity of murine intratumoural neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapies can unleash anti-tumour T-cell responses. Here the authors show, by integrating MHC tetramer multiplexing, mass cytometry and high-dimensional analyses, that neoantigen-specific, tumour-infiltrating T cells are highly heterogeneous and are subjected to ICB modulations.
- M. Fehlings
- , Y. Simoni
- & E. W. Newell
-
Article
| Open Access An injectable hydrogel enhances tissue repair after spinal cord injury by promoting extracellular matrix remodeling
An injectable hydrogel enhances tissue repair after spinal cord injury by promoting extracellular matrix remodeling
The cystic cavity that develops following injuries to brain or spinal cord is a major obstacle. Here the authors show an injection of imidazole poly(organophosphazenes), a hydrogel with thermosensitive sol–gel transition behavior, almost completely eliminates cystic cavities in a clinically relevant rat spinal cord injury model.
- Le Thi Anh Hong
- , Young-Min Kim
- & Byung Gon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Protein-driven RNA nanostructured devices that function in vitro and control mammalian cell fate
Protein-driven RNA nanostructured devices that function in vitro and control mammalian cell fate
Nucleic acid nanotechnology has great potential for future therapeutic applications. Here the authors build protein-driven RNA nanostructures that can function within mammalian cells and regulate the cell fate.
- Tomonori Shibata
- , Yoshihiko Fujita
- & Hirohide Saito
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors
Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors
A major drawback in the clinical use of the oral anticoagulants that directly inhibit factor Xa in order to prevent blood clot formation is the potential for life threatening bleeding events. Here the authors describe factor Xa variants that are refractory to inhibition by these anticoagulants and could serve as rescue agents in treated patients.
- Daniël Verhoef
- , Koen M. Visscher
- & Mettine H. A. Bos
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered proteins with sensing and activating modules for automated reprogramming of cellular functions
Engineered proteins with sensing and activating modules for automated reprogramming of cellular functions
Protein-based biosensors have been engineered to interrogate cellular signaling and manipulate function. Here the authors demonstrate iSNAP, a tool to detect tyrosine phosphorylation and activate desired protein enzymes allowing the control of phagocytosis in macrophages.
- Jie Sun
- , Lei Lei
- & Yingxiao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Multiscale cytometry and regulation of 3D cell cultures on a chip
Multiscale cytometry and regulation of 3D cell cultures on a chip
3D cell culture is more relevant than the two-dimensional format, but methods for parallel analysis and temporal regulation of the microenvironment are limited. Here the authors develop a droplet microfluidics system to perform long-term culture of 3D spheroids, enabling multiscale cytometry of individual cells within the spheroid.
- Sébastien Sart
- , Raphaël F.-X. Tomasi
- & Charles N. Baroud
-
Article
| Open Access Towards designer organelles by subverting the peroxisomal import pathway
Towards designer organelles by subverting the peroxisomal import pathway
Designer organelles could allow the isolation of synthetic biological pathways from endogenous components of the host cell. Here the authors engineer a peroxisomal protein import pathway orthogonal to the naturally occurring system.
- Laura L. Cross
- , Rupesh Paudyal
- & Stuart L. Warriner
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically engineered red cells expressing single domain camelid antibodies confer long-term protection against botulinum neurotoxin
Genetically engineered red cells expressing single domain camelid antibodies confer long-term protection against botulinum neurotoxin
The therapeutic use of single-chain antibodies (VHHs) is limited by their short half-life in the circulation. Here the authors engineer mouse and human red blood cells to express VHHs against botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A) on their surface and show that an infusion of these cells into mice confers long lasting protection against a high dose of BoNT/A.
- Nai-Jia Huang
- , Novalia Pishesha
- & Harvey F. Lodish
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a riboswitch-based genetic platform for the self-directed evolution of acid-tolerant phenotypes
Engineering a riboswitch-based genetic platform for the self-directed evolution of acid-tolerant phenotypes
Cells are exposed to shifts in environmental pH, which direct their metabolism and behavior. Here the authors design pH-sensing riboswitches to create a gene expression program, digitalize the system to respond to a narrow pH range and apply it to evolve host cells with improved tolerance to a variety of organic acids.
- Hoang Long Pham
- , Adison Wong
- & Matthew Wook Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Hit-and-run programming of therapeutic cytoreagents using mRNA nanocarriers
Hit-and-run programming of therapeutic cytoreagents using mRNA nanocarriers
Current widely used viral and electroporation methods for creating therapeutic cell-based products are complex and expensive. Here, the authors develop targeted mRNA nanocarriers that can transiently program gene expression by simply mixing them with cells, to improve their therapeutic potential.
- H. F. Moffett
- , M. E. Coon
- & M. T. Stephan
-
Article
| Open Access Matrix degradability controls multicellularity of 3D cell migration
Matrix degradability controls multicellularity of 3D cell migration
The fabrication of vascularized 3D tissues requires an understanding of how material properties govern endothelial cell invasion into the surrounding matrix. Here the authors integrate a non-swelling synthetic hydrogel with a microfluidic device to study chemokine gradient-driven angiogenic sprouting and find that matrix degradability modulates the collectivity of cell migration.
- Britta Trappmann
- , Brendon M. Baker
- & Christopher S. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo cation exchange in quantum dots for tumor-specific imaging
In vivo cation exchange in quantum dots for tumor-specific imaging
The imaging of tumors in vivo using nanoprobes has been challenging due to the lack of sufficient tumor specificity. Here, the authors develop a tumor-specific quantum dot system that permits in vivo cation exchange to achieve selective background quenching and high tumor-specific imaging.
- Xiangyou Liu
- , Gary B. Braun
- & Kazuki N. Sugahara
-
Article
| Open Access RNA-aptamers-in-droplets (RAPID) high-throughput screening for secretory phenotypes
RNA-aptamers-in-droplets (RAPID) high-throughput screening for secretory phenotypes
Screening libraries of genetically engineered microbes for secreted products is limited by the available assay throughput. Here the authors combine aptamer-based fluorescent detection with droplet microfluidics to achieve high throughput screening of yeast strains engineered for enhanced tyrosine or streptavidin production.
- Joseph Abatemarco
- , Maen F. Sarhan
- & Adam R. Abate
-
Article
| Open Access Micromotor-enabled active drug delivery for in vivo treatment of stomach infection
Micromotor-enabled active drug delivery for in vivo treatment of stomach infection
Nano- and micromotors have been demonstrated in vitro for a range of applications. Here the authors demonstrate the in-vivo therapeutic use of micromotors to treat H. pylori infection.
- Berta Esteban-Fernández de Ávila
- , Pavimol Angsantikul
- & Joseph Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Plant-made polio type 3 stabilized VLPs—a candidate synthetic polio vaccine
Plant-made polio type 3 stabilized VLPs—a candidate synthetic polio vaccine
Despite the success of current vaccination against poliomyelitis, safe, cheap and effective vaccines remain sought for continuing eradication effort. Here the authors use plants to express stabilized virus-like particles of type 3 poliovirus that can induce a protective immune response in mice transgenic for the human poliovirus receptor.
- Johanna Marsian
- , Helen Fox
- & George P. Lomonossoff
-
Article
| Open Access Living GenoChemetics by hyphenating synthetic biology and synthetic chemistry in vivo
Living GenoChemetics by hyphenating synthetic biology and synthetic chemistry in vivo
Coupling synthetic biology and chemical reactions in cells is a challenging task. The authors engineer bacteria capable of generating bromo-metabolites, develop a mild Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction compatible with cell growth and carry out the cross-coupling chemistry in live cell cultures.
- Sunil V. Sharma
- , Xiaoxue Tong
- & Rebecca J. M. Goss
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic silver nanoshells for drug and metabolite detection
Plasmonic silver nanoshells for drug and metabolite detection
Preparation of samples for diagnosis can affect the detection of biomarkers and metabolites. Here, the authors use a silver nanoparticle plasmonics approach for the detection of biomarkers in patients as well as investigate the distribution of drugs in serum and cerebral spinal fluid.
- Lin Huang
- , Jingjing Wan
- & Kun Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analyses identify bioengineered niches for enhanced maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells
Single-cell analyses identify bioengineered niches for enhanced maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells
Haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) self-renewal is not sufficiently understood to recapitulate in vitro. Here, the authors generate gene signature and cell cycle hallmarks of single murine HSCs, and use identified endothelial receptors Esam and JamC as substrates to enhance HSC growth in engineered niches.
- Aline Roch
- , Sonja Giger
- & Matthias P. Lutolf
-
Article
| Open Access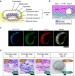 A pluripotent stem cell-based model for post-implantation human amniotic sac development
A pluripotent stem cell-based model for post-implantation human amniotic sac development
Early in human embryonic development, it is unclear how amniotic sac formation is regulated. Here, the authors use a human pluripotent stem cell-based model, termed the post-implantation amniotic sac embryoid, to recapitulate early embryogenic events of human amniotic sac development.
- Yue Shao
- , Kenichiro Taniguchi
- & Jianping Fu
-
Article
| Open Access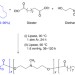 Ex vivo pretreatment of human vessels with siRNA nanoparticles provides protein silencing in endothelial cells
Ex vivo pretreatment of human vessels with siRNA nanoparticles provides protein silencing in endothelial cells
The use of gene silencing techniques in the treatment of post-transplantation host rejection is not long lasting and can have systemic effects. Here, the authors utilize a nanocarrier for siRNA for treatment of arteries ex vivo prior to implantation subsequently attenuating immune reaction in vivo.
- Jiajia Cui
- , Lingfeng Qin
- & W. Mark Saltzman
-
Article
| Open Access Two mouse models reveal an actionable PARP1 dependence in aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Two mouse models reveal an actionable PARP1 dependence in aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia
ATM and TP53 mutations are associated with poor prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). Here the authors generate mouse models of Tp53- and Atm-defective CLL mimicking the high-risk form of human disease and show that Atm-deficient CLL is sensitive to PARP1 inhibition.
- Gero Knittel
- , Tim Rehkämper
- & H. Christian Reinhardt
-
Article
| Open Access PUMA gene delivery to synoviocytes reduces inflammation and degeneration of arthritic joints
PUMA gene delivery to synoviocytes reduces inflammation and degeneration of arthritic joints
Proliferation of synoviocytes contributes to joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Here the authors show that targeting of these cells by a vector, consisting of a baculovirus conjugated to an adenovirus carrying the pro-apoptotic gene PUMA, has therapeutic efficacy in a rat arthritis model.
- Saw-See Hong
- , Hubert Marotte
- & Pierre Miossec
-
Article
| Open Access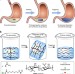 Triggerable tough hydrogels for gastric resident dosage forms
Triggerable tough hydrogels for gastric resident dosage forms
The use of drug delivery systems for the gastrointestinal tract has been faced with a number of drawbacks related to their prolonged use. Here, the authors develop a drug-loaded hydrogel with high strength to withstand long-term gastrointestinal motility and can be triggered to dissolve on demand.
- Jinyao Liu
- , Yan Pang
- & Giovanni Traverso
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Animal biotechnology
- Applied immunology
- Assay systems
- Biologics
- Biomaterials
- Biomimetics
- Cell delivery
- Environmental biotechnology
- Expression systems
- Functional genomics
- Gene delivery
- Gene therapy
- Genomics
- Industrial microbiology
- Metabolic engineering
- Metabolomics
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nucleic-acid therapeutics
- Oligo delivery
- Peptide delivery
- Plant biotechnology
- Protein delivery
- Proteomics
- Regenerative medicine
- Sequencing
- Stem-cell biotechnology
- Tissue engineering

 An automated platform for high-throughput mouse behavior and physiology with voluntary head-fixation
An automated platform for high-throughput mouse behavior and physiology with voluntary head-fixation