Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access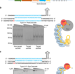 Repurposing type I–F CRISPR–Cas system as a transcriptional activation tool in human cells
Repurposing type I–F CRISPR–Cas system as a transcriptional activation tool in human cells
Class 1 type I CRISPR–Cas systems have not been as extensively developed for genome engineering as Class 2 systems. Here the authors modify the Type I–F CRISPR–Cas system for transcriptional activation of gene expression.
- Yuxi Chen
- , Jiaqi Liu
- & Zhou Songyang
-
Article
| Open Access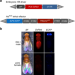 Genetic breakdown of a Tet-off conditional lethality system for insect population control
Genetic breakdown of a Tet-off conditional lethality system for insect population control
Insect population control using conditional lethal systems could break down due to spontaneous mutations that render the system ineffective. Here the authors analyse the structure and frequency of such mutations in Drosophila and suggest the use of dual lethality systems to mitigate their survival.
- Yang Zhao
- , Marc F. Schetelig
- & Alfred M. Handler
-
Article
| Open Access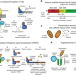 Phosphoregulated orthogonal signal transduction in mammalian cells
Phosphoregulated orthogonal signal transduction in mammalian cells
Phosphoregulation is a key mechanism of signal processing. Here the authors build a phosphoregulated relay system in mammalian cells for orthogonal signal transduction.
- Leo Scheller
- , Marc Schmollack
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of a pluripotent stem cell-derived matrix with powerful osteoregenerative capabilities
Characterization of a pluripotent stem cell-derived matrix with powerful osteoregenerative capabilities
Production of a safe and manufacturable material to mimic anabolic bone for tissue engineering has been hard to achieve to date. Here the authors use a mesenchymal stem cell line generated from induced pluripotent stem cells to produce osteogenic cell-matrix, displaying significant healing properties in mice.
- Eoin P. McNeill
- , Suzanne Zeitouni
- & Carl A. Gregory
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic and scalable DNA-based information storage
Dynamic and scalable DNA-based information storage
The physical architectures of information storage dictate how data is encoded, organised and accessed. Here the authors use DNA with a single-strand overhang as a physical address to access specific data and do in-storage file operations in a scalable and reusuable manner.
- Kevin N. Lin
- , Kevin Volkel
- & Albert J. Keung
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of ongoing APOBEC3A activity in tumor cells by monitoring RNA editing at hotspots
Quantification of ongoing APOBEC3A activity in tumor cells by monitoring RNA editing at hotspots
The DNA cytosine deaminases APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B have emerged from cancer genomics studies as drivers of mutation in cancers and tumor heterogeneity. Here the authors present a computational approach to identify the RNA mutations specifically driven by APOBEC3A, and developed an RNA mutation-based assay to quantify ongoing APOBEC3A activity in tumor cells.
- Pégah Jalili
- , Danae Bowen
- & Rémi Buisson
-
Article
| Open Access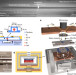 Sub-nanowatt microfluidic single-cell calorimetry
Sub-nanowatt microfluidic single-cell calorimetry
Calorimetrically measuring the heat of single cells is currently not possible due to the sensitivity of existing calorimeters. Here the authors present on-chip single cell calorimetry, with a sensitivity over ten-fold greater than the current gold-standard.
- Sahngki Hong
- , Edward Dechaumphai
- & Renkun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted inhibition of activated protein C by a non-active-site inhibitory antibody to treat hemophilia
Targeted inhibition of activated protein C by a non-active-site inhibitory antibody to treat hemophilia
Activated protein C (APC) is a plasma serine protease with antithrombotic and cytoprotective functions. Here, the authors develop a monoclonal antibody that specifically inhibits APC’s anticoagulant function without compromising its cytoprotective function, and shows efficacy in animal models.
- Xiao-Yan Zhao
- , Andreas Wilmen
- & Volker Laux
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR artificial splicing factors
CRISPR artificial splicing factors
Control over splicing could be used for both therapeutic and engineering applications. Here the authors create artificial splicing factors using RNA-targeting CRISPR systems under small molecule control.
- Menghan Du
- , Nathaniel Jillette
- & Albert Wu Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of aptamer switches with programmable pH response
Rational design of aptamer switches with programmable pH response
Previous design strategies for pH sensitive aptamers were not readily tunable across pH ranges. Here the authors present a general method to convert aptamers into pH-responsive switches using two orthogonal motifs.
- Ian A. P. Thompson
- , Liwei Zheng
- & H. Tom Soh
-
Article
| Open Access Reverse engineering synthetic antiviral amyloids
Reverse engineering synthetic antiviral amyloids
Some human amyloid proteins have been shown to interact with viral proteins, suggesting that they may have potential as therapeutic agents. Here the authors design synthetic amyloids specific for influenza A and Zika virus proteins, respectively, and show that they can inhibit viral replication.
- Emiel Michiels
- , Kenny Roose
- & Joost Schymkowitz
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of human metabolism by reducing the complexity of the genome-scale models using redHUMAN
Analysis of human metabolism by reducing the complexity of the genome-scale models using redHUMAN
The complexity of genome-scale metabolic networks (GEMs) hinders their application in specific physiological contexts. Here, the authors introduce a framework to reduce thermodynamically curated GEMs to the subnetworks of interest and demonstrate its application by deriving leukemia-specific models.
- Maria Masid
- , Meric Ataman
- & Vassily Hatzimanikatis
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed relative and absolute quantitative immunopeptidomics reveals MHC I repertoire alterations induced by CDK4/6 inhibition
Multiplexed relative and absolute quantitative immunopeptidomics reveals MHC I repertoire alterations induced by CDK4/6 inhibition
Immunopeptidomics allows identifying the cellular repertoire of MHC-bound peptides, but quantifying them remains challenging. Here, the authors present a method to efficiently generate internal peptide MHC standards and calibration curves, facilitating relative and absolute quantitative immunopeptidomics.
- Lauren E. Stopfer
- , Joshua M. Mesfin
- & Forest M. White
-
Article
| Open Access Development of an exon skipping therapy for X-linked Alport syndrome with truncating variants in COL4A5
Development of an exon skipping therapy for X-linked Alport syndrome with truncating variants in COL4A5
Alport syndrome is a progressive inherited nephritis accompanied by sensorineural loss of hearing and ocular abnormalities, for which there is currently no effective therapy. Here, the authors develop an exon-skipping therapy using an antisense-oligonucleotide and show it is effective in mouse models.
- Tomohiko Yamamura
- , Tomoko Horinouchi
- & Kandai Nozu
-
Article
| Open Access Cephalopod-inspired optical engineering of human cells
Cephalopod-inspired optical engineering of human cells
While organisms like squid can adaptively modulate the optical properties of their tissues, human cells lack analogous abilities. Here the authors engineer human cells to produce protein architectures with tunable light scattering functionalities.
- Atrouli Chatterjee
- , Juana Alejandra Cerna Sanchez
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article
| Open Access Improving the safety of human pluripotent stem cell therapies using genome-edited orthogonal safeguards
Improving the safety of human pluripotent stem cell therapies using genome-edited orthogonal safeguards
Human pluripotent stem cell derived therapies can have serious safety risks. Here the authors design two drug inducible genetic safeguards to deplete undifferentiated hPSCs and hPSC-derived cell types.
- Renata M. Martin
- , Jonas L. Fowler
- & Kyle M. Loh
-
Article
| Open Access A genome-wide gain-of-function screen identifies CDKN2C as a HBV host factor
A genome-wide gain-of-function screen identifies CDKN2C as a HBV host factor
Here the authors perform a gain-of-function screen and identify CDKN2C as a host factor for HBV replication, inducing cell cycle arrest and expression of HBV transcription enhancers. CDKN2C expression correlates with disease progression suggesting a potential role in HBV-induced liver disease.
- Carla Eller
- , Laura Heydmann
- & Thomas F. Baumert
-
Article
| Open Access Immunotherapy with engineered bacteria by targeting the STING pathway for anti-tumor immunity
Immunotherapy with engineered bacteria by targeting the STING pathway for anti-tumor immunity
Synthetic biology can be used to create rationally designed living therapeutics. Here the authors engineer E. coli Nissle to target STING activation in antigen presenting cells for the treatment of solid tumors and demonstrate preclinical activity in murine models.
- Daniel S. Leventhal
- , Anna Sokolovska
- & Jose M. Lora
-
Article
| Open Access Functional reconstruction of injured corpus cavernosa using 3D-printed hydrogel scaffolds seeded with HIF-1α-expressing stem cells
Functional reconstruction of injured corpus cavernosa using 3D-printed hydrogel scaffolds seeded with HIF-1α-expressing stem cells
Injury of corpus cavernosa results in erectile dysfunction, and repair leading to restoration of function is difficult. Here the authors construct 3D printed hydrogel constructs seeded with HIF-1α-expressing muscle derived stem cells to restore corpus function in a rabbit model.
- Geng An
- , Feixiang Guo
- & Chuanbin Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Integrative analysis of reference epigenomes in 20 rice varieties
Integrative analysis of reference epigenomes in 20 rice varieties
Comprehensive epigenomic maps of various rice varieties are still unavailable. Here, the authors report the development of eChIP as a fast and low-input upgrade of regular plant ChIP-seq protocol for epigenome analysis of 20 rice varieties and annotate over 80% of the genome with different epigenome properties for transcriptional regulation.
- Lun Zhao
- , Liang Xie
- & Xingwang Li
-
Article
| Open Access UDP-glucosyltransferase regulates grain size and abiotic stress tolerance associated with metabolic flux redirection in rice
UDP-glucosyltransferase regulates grain size and abiotic stress tolerance associated with metabolic flux redirection in rice
Increasing grain yield needs to be put in the context of environmental stress. Here, the authors reveal that a UDP-glucosyltransferase is associated with regulation of rice grain size, abiotic stress tolerance, flavonoid-mediated auxin signaling, and redirection of carbon flux to flavonoid glycosides synthesis.
- Nai-Qian Dong
- , Yuwei Sun
- & Hong-Xuan Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive digital quantification of cytokines and bacteria predicts septic shock outcomes
Ultrasensitive digital quantification of cytokines and bacteria predicts septic shock outcomes
Ultrasensitive methods for detection of biomarkers for infectious disease are needed for diagnosing, monitoring and targeting treatment. Here the authors develop a digital assay for inflammatory markers, bacterial DNA and antibotic-resistance genes and apply it to characterise asthma patients and predict mortality from septic shock.
- M. Fatih Abasıyanık
- , Krysta Wolfe
- & Savaş Tay
-
Article
| Open Access Discrete populations of isotype-switched memory B lymphocytes are maintained in murine spleen and bone marrow
Discrete populations of isotype-switched memory B lymphocytes are maintained in murine spleen and bone marrow
Memory B cells are important for protecting the host from pathogen rechallenge, but their properties and locations remain ill-defined. Here the authors show, using single-cell transcriptomics and repertoire analyses, that mouse spleen and bone marrow host distinct populations of isotype-switched memory B cells to potentially optimize for rapid recall responses.
- René Riedel
- , Richard Addo
- & Andreas Radbruch
-
Article
| Open Access Allele-aware chromosome-level genome assembly and efficient transgene-free genome editing for the autotetraploid cultivated alfalfa
Allele-aware chromosome-level genome assembly and efficient transgene-free genome editing for the autotetraploid cultivated alfalfa
Alfalfa is an important forage crop, but genetic improvement is challenging due to the lack of a reference genome and an efficient genome editing protocol. Here, the authors report the chromosome-level assembly of the autotetraploid genome and a CRISPR/Cas9-based transgene-free genome editing protocol.
- Haitao Chen
- , Yan Zeng
- & Qiang Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access The mutational impact of culturing human pluripotent and adult stem cells
The mutational impact of culturing human pluripotent and adult stem cells
Genetic changes acquired during in vitro culture pose a challenge to application of stem cells. Here the authors use whole genome sequencing to show that cultured human adult and pluripotent stem cells have a high mutational load caused by oxidative stress and reduced oxygen tension in culture lowers mutation rates.
- Ewart Kuijk
- , Myrthe Jager
- & Edwin Cuppen
-
Article
| Open Access A Cas9 with PAM recognition for adenine dinucleotides
A Cas9 with PAM recognition for adenine dinucleotides
Protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) requirements limit the target range of CRISPR endonucleases. Here, the authors graft the 5\(^{\prime}\)-NAAN-3\(^{\prime}\) PAM-interacting domain of SmacCas9 onto SpyCas9 to create adenine dinucleotide targeting chimeras.
- Pranam Chatterjee
- , Jooyoung Lee
- & Noah Jakimo
-
Article
| Open Access A redox-based electrogenetic CRISPR system to connect with and control biological information networks
A redox-based electrogenetic CRISPR system to connect with and control biological information networks
Redox-responsive transcriptional regulators can enable user-specified electronic control over biological functions. Here the authors demonstrate electronic control of CRISPRa and CRISPRi using redox signalling.
- Narendranath Bhokisham
- , Eric VanArsdale
- & William E. Bentley
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic lipid compositions for albumin receptor mediated delivery of mRNA to the liver
Synergistic lipid compositions for albumin receptor mediated delivery of mRNA to the liver
Lipid-like nanoparticles have applications as non-viral delivery systems for mRNA. Here, the authors develop biodegradable lipids with improved clearance and reduced toxicity.
- Lei Miao
- , Jiaqi Lin
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
Review Article
| Open Access Application of combinatorial optimization strategies in synthetic biology
Application of combinatorial optimization strategies in synthetic biology
Our efforts to build complex synthetic biology circuits are impeded by limited knowledge of optimal combinations. In this review, the authors consider current combinatorial methods and look to emerging technologies.
- Gita Naseri
- & Mattheos A. G. Koffas
-
Article
| Open Access Synergy between the anthocyanin and RDR6/SGS3/DCL4 siRNA pathways expose hidden features of Arabidopsis carbon metabolism
Synergy between the anthocyanin and RDR6/SGS3/DCL4 siRNA pathways expose hidden features of Arabidopsis carbon metabolism
TRANSPARENT TESTA19 (TT19) encodes a glutathione S-transferase which functions in anthocyanin stabilization and vacuolar transport. Here, by tt19 suppressor screening, the authors show that RDR6/SGS3/DCL4 siRNA pathway constituents synergistically interact with components of the flavonoid pathway to control carbon metabolism.
- Nan Jiang
- , Aimer Gutierrez-Diaz
- & Erich Grotewold
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating molecular markers into metabolic models improves genomic selection for Arabidopsis growth
Integrating molecular markers into metabolic models improves genomic selection for Arabidopsis growth
An increase in genomic selection (GS) accuracy can accelerate genetic gain by shortening the breeding cycles. Here, the authors introduce a network-based GS method that uses metabolic models and improves the prediction accuracy of Arabidopsis growth within and across environments.
- Hao Tong
- , Anika Küken
- & Zoran Nikoloski
-
Article
| Open Access Investigating the dynamics of microbial consortia in spatially structured environments
Investigating the dynamics of microbial consortia in spatially structured environments
The spatial organisation of microbial communities is caused by the interplay of biotic and abiotic factors. Here the authors design a microfluidic platform to quantify the spatiotemporal parameters influencing diffusion-mediated interactions, and use this device to investigate information transmission and metabolic cross-feeding in synthetic microbial consortia.
- Sonali Gupta
- , Tyler D. Ross
- & Ophelia S. Venturelli
-
Article
| Open Access LITESEC-T3SS - Light-controlled protein delivery into eukaryotic cells with high spatial and temporal resolution
LITESEC-T3SS - Light-controlled protein delivery into eukaryotic cells with high spatial and temporal resolution
The type III secretion system (T3SS) of bacteria can be used to inject cargo into eukaryotic cells but its lack of target specificity is a disadvantage. Here the authors place the T3SS under the regulation of light by engineering optogenetic switches into the dynamic cytosolic T3SS component SctQ.
- Florian Lindner
- , Bailey Milne-Davies
- & Andreas Diepold
-
Article
| Open Access Target-responsive vasoactive probes for ultrasensitive molecular imaging
Target-responsive vasoactive probes for ultrasensitive molecular imaging
Noninvasive detection of molecular targets in living subjects could provide valuable insights into healthy function and disease. Here, the authors develop vasoactive imaging probes which allow wide-field in vivo mapping of nanomolar-level molecular species in rat brain.
- Robert Ohlendorf
- , Agata Wiśniowska
- & Alan Jasanoff
-
Article
| Open Access ORF Capture-Seq as a versatile method for targeted identification of full-length isoforms
ORF Capture-Seq as a versatile method for targeted identification of full-length isoforms
Most human protein-coding genes are expressed as multiple isoforms. Here the authors present ORF Capture-seq that uses cloned ORFs as probes to capture and sequence full length transcript sequences. This enables highly sensitive characterization of eukaryotic transcriptomes.
- Gloria M. Sheynkman
- , Katharine S. Tuttle
- & Marc Vidal
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-omic single-cell snapshots reveal multiple independent trajectories to drug tolerance in a melanoma cell line
Multi-omic single-cell snapshots reveal multiple independent trajectories to drug tolerance in a melanoma cell line
Detailed understanding of how cancer cells transition from a drug sensitive to a tolerant state is lacking. Here, using single cell proteomic and metabolic data the authors uncover that isogenic BRAF mutant melanoma cells can take two distinct paths to become tolerant to BRAF inhibition.
- Yapeng Su
- , Melissa E. Ko
- & James R. Heath
-
Article
| Open Access Size and surface charge characterization of nanoparticles with a salt gradient
Size and surface charge characterization of nanoparticles with a salt gradient
Exosomes are used as disease biomarkers, but their characterization in biological samples is challenging. Here the authors achieve simultaneous characterization of size and zeta potential of individual nanoparticles and particle mixtures at physiological salinity conditions, exploiting a salt gradient in a capillary channel.
- Martin K. Rasmussen
- , Jonas N. Pedersen
- & Rodolphe Marie
-
Article
| Open Access Light-powered Escherichia coli cell division for chemical production
Light-powered Escherichia coli cell division for chemical production
Manipulation of genes controlling microbial shapes can affect bio-production. Here, the authors employ an optogenetic method to realize dynamic morphological engineering of E. coli replication and division and show the increased production of acetoin and poly(lactate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate).
- Qiang Ding
- , Danlei Ma
- & Xiulai Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Light-triggered release of conventional local anesthetics from a macromolecular prodrug for on-demand local anesthesia
Light-triggered release of conventional local anesthetics from a macromolecular prodrug for on-demand local anesthesia
Local anesthetic sustained release systems suffer from untriggered rapid drug release upon application. Here the authors overcome this issue by covalently linking tetracaine to a polymer gel via a photo-cleavable linkage, enabling light-triggered and repeatable drug release.
- Wei Zhang
- , Tianjiao Ji
- & Daniel S. Kohane
-
Article
| Open Access Minimal lactazole scaffold for in vitro thiopeptide bioengineering
Minimal lactazole scaffold for in vitro thiopeptide bioengineering
Lactazole A is a thiopeptide from Streptomyces lactacystinaeus, encoded by a compact 9.8 kb biosynthetic gene cluster. Here, the authors show a platform for in vitro biosynthesis of lactazole A via a combination of a flexible in vitro translation system with recombinantly produced lactazole biosynthetic enzymes.
- Alexander A. Vinogradov
- , Morito Shimomura
- & Hiroyasu Onaka
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetically driven active topography for long-term biofilm control
Magnetically driven active topography for long-term biofilm control
Biofilm formation is a major problem in indwelling medical devices. Here, the authors report on the development of a magnetically responsive micro pillar surface for the controlled prevention and removal of biofilms which also increased sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Huan Gu
- , Sang Won Lee
- & Dacheng Ren
-
Article
| Open Access A single-cell transcriptomic landscape of primate arterial aging
A single-cell transcriptomic landscape of primate arterial aging
Arterial degeneration, closely associated with cardiovascular diseases, is driven by aging-related vascular cell-specific transcriptomics changes. This study provides a single-cell transcriptomic atlas for senile aortic and coronary arteries and underscores FOXO3A-based the transcriptional network in vasoprotection during aging.
- Weiqi Zhang
- , Shu Zhang
- & Jing Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive aptamer-based screening identifies a spectrum of urinary biomarkers of lupus nephritis across ethnicities
Comprehensive aptamer-based screening identifies a spectrum of urinary biomarkers of lupus nephritis across ethnicities
Developing noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for lupus nephritis (LN) diagnosis is an important clinical goal. Here the authors identify urinary proteins correlated with active LN and disease severity, which differ across ethnicities but collectively outperform the current clinical method.
- Samantha Stanley
- , Kamala Vanarsa
- & Chandra Mohan
-
Article
| Open Access Photoactivatable Cre recombinase 3.0 for in vivo mouse applications
Photoactivatable Cre recombinase 3.0 for in vivo mouse applications
Previous versions of photoactivatable Cre recombinase (PA-Cre) suffered from unintentional recombination in dark conditions. Here, the authors develop an improved version of PA-Cre, called PA-Cre 3.0, which shows reduced leakiness and improved efficiency upon activation, and make mouse lines that express PA-Cre 3.0 conditionally.
- Kumi Morikawa
- , Kazuhiro Furuhashi
- & Masayuki Yazawa
-
Article
| Open Access Stress-induced expression is enriched for evolutionarily young genes in diverse budding yeasts
Stress-induced expression is enriched for evolutionarily young genes in diverse budding yeasts
Fermentation parameters of industrial processes are often not the ideal growth conditions for industrial microbes. Here, the authors reveal that young genes are more responsive to environmental stress than ancient genes using a new gene age assignment method and provide targeted genes for metabolic engineering.
- Tyler W. Doughty
- , Iván Domenzain
- & John P. Morrissey
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled packing and single-droplet resolution of 3D-printed functional synthetic tissues
Controlled packing and single-droplet resolution of 3D-printed functional synthetic tissues
Precise patterning of lipid-stabilised aqueous droplets is a key challenge in building synthetic tissue designs. Here, the authors show how the interactions between pairs of droplets direct the packing of droplets within 3D-printed networks, enabling the formation of synthetic tissues with high-resolution features.
- Alessandro Alcinesio
- , Oliver J. Meacock
- & Hagan Bayley
-
Article
| Open Access Model-driven generation of artificial yeast promoters
Model-driven generation of artificial yeast promoters
A small set of promoters is used for most genetic construct design in S. cerevisiae. Here, the authors develop a predictive model of promoter activity trained on a data set of over one million sequences and use it to design large sets of high-activity promoters.
- Benjamin J. Kotopka
- & Christina D. Smolke
-
Article
| Open Access Highly parallel and efficient single cell mRNA sequencing with paired picoliter chambers
Highly parallel and efficient single cell mRNA sequencing with paired picoliter chambers
Single-cell RNA-seq can reveal accurate and precise cell types and states. Here the authors present an scRNA-seq platform, Paired-seq, which uses differential flow resistance to achieve 95% cell utilisation efficiency for improved cell-free RNA removal and gene detection.
- Mingxia Zhang
- , Yuan Zou
- & Chaoyong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A drug-inducible sex-separation technique for insects
A drug-inducible sex-separation technique for insects
Sorting insects based on sex is error prone and frequently labour intensive. Here, the authors present a drug-inducible sex separation system based on sex-specific rescue from antibotic toxicity.
- Nikolay P. Kandul
- , Junru Liu
- & Omar S. Akbari
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Animal biotechnology
- Applied immunology
- Assay systems
- Biologics
- Biomaterials
- Biomimetics
- Cell delivery
- Environmental biotechnology
- Expression systems
- Functional genomics
- Gene delivery
- Gene therapy
- Genomics
- Industrial microbiology
- Metabolic engineering
- Metabolomics
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nucleic-acid therapeutics
- Oligo delivery
- Peptide delivery
- Plant biotechnology
- Protein delivery
- Proteomics
- Regenerative medicine
- Sequencing
- Stem-cell biotechnology
- Tissue engineering

 Holistic engineering of cell-free systems through proteome-reprogramming synthetic circuits
Holistic engineering of cell-free systems through proteome-reprogramming synthetic circuits