Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cultured meat with enriched organoleptic properties by regulating cell differentiation
Cultured meat with enriched organoleptic properties by regulating cell differentiation
Achieving organoleptic properties of conventional meat is important for cultured meat production. Here, the authors demonstrate that the texture, flavor, and nutritional content of cultured meat can be significantly enhanced by regulating cell differentiation inside hydrogel scaffolds.
- Milae Lee
- , Sohyeon Park
- & Jinkee Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering sulfonate group donor regeneration systems to boost biosynthesis of sulfated compounds
Engineering sulfonate group donor regeneration systems to boost biosynthesis of sulfated compounds
Sufficient supply of sulfonate group donor is critical to biomanufacturing of the sulfate containing compounds. Here, the authors engineer two sulfonate group donor regeneration systems, including 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate and the newly discovered 5'-phosphosulfate, to boost biosynthesis of sulfated compounds.
- Ruirui Xu
- , Weijao Zhang
- & Zhen Kang
-
Article
| Open Access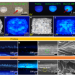 Upcycling fish scales through heating for steganography and Rhodamine B adsorption application
Upcycling fish scales through heating for steganography and Rhodamine B adsorption application
Waste materials including fish scales are increasingly being developed for alternative applications, but simple processing is required. Here, the authors report the treatment of fish scales to give fluorescent materials suitable for dye absorption.
- Malcolm Miao Geng Sow
- , Zheng Zhang
- & Sharon Xiaodai Lim
-
Article
| Open Access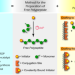 A nanoscale MOF-based heterogeneous catalytic system for the polymerization of N-carboxyanhydrides enables direct routes toward both polypeptides and related hybrid materials
A nanoscale MOF-based heterogeneous catalytic system for the polymerization of N-carboxyanhydrides enables direct routes toward both polypeptides and related hybrid materials
Metal-based heterogeneous catalysts are widely employed in ring-opening polymerization (ROP) but up to now the exploration of metal-organic frameworks (MOF) as catalysts in ROP remains underdeveloped. Here, the authors report a MOF heterogeneous catalytic system for fast, controllable, air- and moisture-insensitive ring-opening polymerization of α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides, and its seamless integration with hybrid material preparation.
- Ying Liu
- , Zhongwu Ren
- & Yugang Bai
-
Article
| Open Access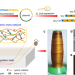 Protein fibers with self-recoverable mechanical properties via dynamic imine chemistry
Protein fibers with self-recoverable mechanical properties via dynamic imine chemistry
Manipulating the internal interactions within biological fibers to tune macroscopic properties is important but challenging, and can limit applications. Here, the authors report the use of dynamic imine chemistry for engineering molecular interactions and forming strong and tough protein fibers.
- Jing Sun
- , Haonan He
- & Kai Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A single-domain green fluorescent protein catenane
A single-domain green fluorescent protein catenane
Natural proteins exhibit rich structural diversity based on the folds of an invariably linear chain. Here the authors design a single-domain GFP catenane as the counterpart of conventional linear GFP with enhanced thermal resilience and to provide a robust scaffold for making fusion protein catenanes.
- Zhiyu Qu
- , Jing Fang
- & Wen-Bin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially non-uniform condensates emerge from dynamically arrested phase separation
Spatially non-uniform condensates emerge from dynamically arrested phase separation
Biomolecular condensates with internal structure allow cells to further organise their processes. In this work the authors investigate how condensates can obtain an internal structure with droplets of dilute phase inside via kinetic, rather than purely thermodynamic driving forces.
- Nadia A. Erkamp
- , Tomas Sneideris
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access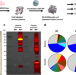 Endosomal sorting results in a selective separation of the protein corona from nanoparticles
Endosomal sorting results in a selective separation of the protein corona from nanoparticles
Protein corona formation on nanoparticles and the resultant effects on cellular interactions is well documented, where less is known about the fate of the corona in the cell. Here, the authors track the protein corona and nanoparticles in cells and describe the separation and different processing within different cellular compartments.
- Shen Han
- , Richard da Costa Marques
- & Ingo Lieberwirth
-
Article
| Open Access Aqueous synthesis of highly functional, hydrophobic, and chemically recyclable cellulose nanomaterials through oxime ligation
Aqueous synthesis of highly functional, hydrophobic, and chemically recyclable cellulose nanomaterials through oxime ligation
Water is a standing challenge in the chemical modification of cellulose nanofibrils. Here, authors employ oxime-ligation to solve this by direct covalent chemistry on dialdehyde-CNF in water and assess the material for potential applications in green electronics and triboelectric nanogenerators.
- Elena Subbotina
- , Farsa Ram
- & Peter Olsén
-
Article
| Open Access Untangling the threads of cellulose mercerization
Untangling the threads of cellulose mercerization
During mercerization, cellulose undergoes a conversion from form I to form II which involves change of the direction of every other cellulose chain but a clear understanding of how this change happens is lacking. Here, the authors use neutron diffraction on deuterium labelled cellulose to demonstrate that chains fold back on themselves in a zigzag pattern to form crystalline anti-parallel domains.
- Daisuke Sawada
- , Yoshiharu Nishiyama
- & Paul Langan
-
Article
| Open Access Multivalent interactions between molecular components involved in fast endophilin mediated endocytosis drive protein phase separation
Multivalent interactions between molecular components involved in fast endophilin mediated endocytosis drive protein phase separation
Here the authors show that protein phase separation is a key mechanism in cellular receptor internalization via fast endophilin mediated endocytosis (FEME). Phase separation facilitates multivalent FEME-protein assembly in this clathrin-independent pathway.
- Samsuzzoha Mondal
- , Karthik Narayan
- & Tobias Baumgart
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of bioactive (1→6)-β-glucose branched poly-amido-saccharides that stimulate and induce M1 polarization in macrophages
Synthesis of bioactive (1→6)-β-glucose branched poly-amido-saccharides that stimulate and induce M1 polarization in macrophages
Difficulty with purification, structural heterogenicity, and limited water solubility of β-glucans has significantly limited their therapeutic applications. Here, the authors report the synthesis of (1→6)-β-glucose-branched poly-amido-saccharides as glycan-mimetics and demonstrate macrophage stimulation and polarization.
- Ruiqing Xiao
- , Jialiu Zeng
- & Mark W. Grinstaff
-
Article
| Open Access Signal-processing and adaptive prototissue formation in metabolic DNA protocells
Signal-processing and adaptive prototissue formation in metabolic DNA protocells
Signal processing for downstream functional and morphological adaptations is crucial for understanding and re-enacting features of living systems. Here, the authors show DNAzyme-containing, metabolic protocells that induce prototissue formation via chemical messenger communication due to in situ cleavage of upstream DNA signals.
- Avik Samanta
- , Maximilian Hörner
- & Andreas Walther
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient aqueous remote loading of peptides in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
Efficient aqueous remote loading of peptides in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
Encapsulation of bioactive peptides in slow-release particles is complex and relies on organic solvents. Here, the authors absorb peptides in a polymer phase from water, creating a simple low-cost encapsulation process in a class of polymer depot.
- Morgan B. Giles
- , Justin K. Y. Hong
- & Steven P. Schwendeman
-
Article
| Open Access Vinyl copolymers with faster hydrolytic degradation than aliphatic polyesters and tunable upper critical solution temperatures
Vinyl copolymers with faster hydrolytic degradation than aliphatic polyesters and tunable upper critical solution temperatures
The non-degradability of vinyl polymers has long limited their use in biomedical applications. In this article, the authors demonstrate a system based on acrylamide and cyclic ketene acetals to obtain copolymers with faster degradation rates for potential drug release and environmental applications.
- Amaury Bossion
- , Chen Zhu
- & Julien Nicolas
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic glycans control gut microbiome structure and mitigate colitis in mice
Synthetic glycans control gut microbiome structure and mitigate colitis in mice
Here, the authors characterize the gut microbiome fermentation properties and therapeutic potential of chemically diverse synthetic glycans (SGs), showing they promote specific shifts in taxonomic and metabolite profiles, and exhibit therapeutic benefits in mouse models of colonic inflammation, together implying SGs as a potential avenue to treat disease by modulating the composition and metabolites produced by the gut microbiome.
- Andrew C. Tolonen
- , Nicholas Beauchemin
- & Johan E. T. van Hylckama Vlieg
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralong phosphorescence cellulose with excellent anti-bacterial, water-resistant and ease-to-process performance
Ultralong phosphorescence cellulose with excellent anti-bacterial, water-resistant and ease-to-process performance
Organic room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) materials often suffer from poor processability because of their crystalline or cross-linked nature. Here, the authors demonstrate phosphorescence in a processable cellulose derivative by introducing cationic groups such as imidazolium cations which are able to promote intersystem crossing and to form hydrogen bonds, inhibiting non-radiative transitions.
- Xin Zhang
- , Yaohui Cheng
- & Jun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Carbohydrate-aromatic interface and molecular architecture of lignocellulose
Carbohydrate-aromatic interface and molecular architecture of lignocellulose
The plant biomass is a composite formed by a variety of polysaccharides and an aromatic polymer named lignin. Here, the authors use solid-state NMR spectroscopy to unveil the carbohydrate-aromatic interface that leads to the variable architecture of lignocellulose biomaterials.
- Alex Kirui
- , Wancheng Zhao
- & Tuo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering shape memory and morphing protein hydrogels based on protein unfolding and folding
Engineering shape memory and morphing protein hydrogels based on protein unfolding and folding
Engineering shape memory and morphing materials achieved considerable progress in polymer-based systems, but protein-based shape memory and morphing materials remain less investigated. Here, the authors report the engineering of protein-based shape memory and morphing hydrogels using protein folding-unfolding as a general mechanism to trigger shape morphing in protein-bilayer structures.
- Qingyuan Bian
- , Linglan Fu
- & Hongbin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable, biodegradable grafting-from glycopolypeptide bottlebrush polymers
Tunable, biodegradable grafting-from glycopolypeptide bottlebrush polymers
Synthetic mimics of glycoproteins and proteoglycans have wide applications in biomedicine, yet preparation has been challenged by their high grafting and glycosylation densities. Here the authors show one-pot dual-catalysis polymerization of glycan-bearing α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides to form glycopolypeptide brushes.
- Zachary S. Clauss
- , Casia L. Wardzala
- & Jessica R. Kramer
-
Article
| Open Access Addressing MRSA infection and antibacterial resistance with peptoid polymers
Addressing MRSA infection and antibacterial resistance with peptoid polymers
Antibiotic resistance is a major issue in medicine and new antimicrobials for treating resistant infection are needed. Here, the authors report on antibacterial peptoid polymers, prepared via NNCA ring-opening polymerization, demonstrating antibacterial function against MRSA in vitro and in in vivo infection models.
- Jiayang Xie
- , Min Zhou
- & Runhui Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A moisture-tolerant route to unprotected α/β-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides and facile synthesis of hyperbranched polypeptides
A moisture-tolerant route to unprotected α/β-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides and facile synthesis of hyperbranched polypeptides
Synthetic polypeptides are biomimetic materials that are commonly prepared by ring-opening polymerization of amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides (NCAs), but the methods for NCA synthesis usually require anhydrous and air-free conditions. Here, the authors report a method for the synthesis of NCAs under atmospheric conditions and room temperature, based on the use of epoxides as acid scavengers.
- Zi-You Tian
- , Zhengchu Zhang
- & Hua Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial production of megadalton titin yields fibers with advantageous mechanical properties
Microbial production of megadalton titin yields fibers with advantageous mechanical properties
Here, the authors engineer microbial production of muscle titin fibers with highly desirable mechanical properties and provide structural analyses that explain the molecular mechanisms underlying high performance of this polymer with potential uses in biomedicine and textile industries, among others.
- Christopher H. Bowen
- , Cameron J. Sargent
- & Fuzhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A minimalistic cyclic ice-binding peptide from phage display
A minimalistic cyclic ice-binding peptide from phage display
Developing molecules that emulate the properties of naturally occurring ice-binding proteins (IBPs) is a daunting challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of phage display for the identification of short peptide mimics of IBPs, which resulted in the identification of a cyclic ice-binding peptide containing just 14 amino acids.
- Corey A. Stevens
- , Fabienne Bachtiger
- & Harm-Anton Klok
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperproduction of 3-hydroxypropionate by Halomonas bluephagenesis
Hyperproduction of 3-hydroxypropionate by Halomonas bluephagenesis
3-Hydroxypropionic acid (3HP) is an important platform chemical. Here, the authors engineer Halomonas bluephagenesis by deleting newly identified degradation pathway and balancing redox state to achieve high level production of 3HP and its copolymer under open and unsterile conditions.
- Xiao-Ran Jiang
- , Xu Yan
- & Guo-Qiang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Selective hydrogenolysis of catechyl lignin into propenylcatechol over an atomically dispersed ruthenium catalyst
Selective hydrogenolysis of catechyl lignin into propenylcatechol over an atomically dispersed ruthenium catalyst
C-lignin represents an ideal feedstock for producing catechol derivatives. Here, the authors engineered an atomically dispersed Ru catalyst, which can cleave C−O bonds efficiently and circumvent C=C bonds hydrogenation selectively, thus leading to propenylcatechol in high yields with high TONs.
- Shuizhong Wang
- , Kaili Zhang
- & Guoyong Song
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced dispersion stability of gold nanoparticles by the physisorption of cyclic poly(ethylene glycol)
Enhanced dispersion stability of gold nanoparticles by the physisorption of cyclic poly(ethylene glycol)
Many nanoparticles are stabilised by chemical functionalisation with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). Here, the authors report on the functionalisation of gold nanoparticles by the physical absorption of cyclic PEG and demonstrate superior stabilisation against heating, freezing and lyophilisation.
- Yubo Wang
- , Jose Enrico Q. Quinsaat
- & Takuya Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Proton-enabled activation of peptide materials for biological bimodal memory
Proton-enabled activation of peptide materials for biological bimodal memory
The structural programmability and functionality of peptide materials can be leverage for various next-generation devices such as non-volatile memories. The authors report a proton-coupled mechanism in tyrosine-rich peptides for realizing multimodal memory devices.
- Min-Kyu Song
- , Seok Daniel Namgung
- & Jang-Yeon Kwon
-
Article
| Open Access Rational flux-tuning of Halomonas bluephagenesis for co-production of bioplastic PHB and ectoine
Rational flux-tuning of Halomonas bluephagenesis for co-production of bioplastic PHB and ectoine
Halomonas bluephagenesis is a halophilic platform bacterium for next generation industrial biotechnology. Here, the authors employ a stimulus response-based flux-tuning method for coproduction of bioplastic PHB and ectoine under open unsterile and continuous growth conditions.
- Hong Ma
- , Yiqing Zhao
- & Guo-Qiang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Spider-silk inspired polymeric networks by harnessing the mechanical potential of β-sheets through network guided assembly
Spider-silk inspired polymeric networks by harnessing the mechanical potential of β-sheets through network guided assembly
It is known the β-sheet structures in silk-inspired materials generate increased mechanical properties. Here, the authors report on a method of creating silk-inspired materials using in situ formation of β-sheets in an amorphous polymer to replicate the structure of silk and increase the mechanical properties.
- Nicholas Jun-An Chan
- , Dunyin Gu
- & Greg G. Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Biobased chiral semi-crystalline or amorphous high-performance polyamides and their scalable stereoselective synthesis
Biobased chiral semi-crystalline or amorphous high-performance polyamides and their scalable stereoselective synthesis
Bio‐based compounds often suffer from high production cost and low performance when used to synthesise macromolecules. Here the authors show the conversion of (+)‐3‐ carene, a by‐product of the cellulose industry, into its ε‐lactams and then to polyamides with high‐performance thermal properties.
- Paul N. Stockmann
- , Daniel Van Opdenbosch
- & Volker Sieber
-
Article
| Open Access Enzyme-mimetic self-catalyzed polymerization of polypeptide helices
Enzyme-mimetic self-catalyzed polymerization of polypeptide helices
The folding-dependent catalytic behavior of enzymes is of fundamental biological importance, yet mechanistically underexplored. Here, the authors show that an α-helix, commonly found in proteins, can facilitate its own growth through the self-catalyzed polymerization of N-carboxyanhydride in solvents with low polarity.
- Ziyuan Song
- , Hailin Fu
- & Jianjun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Single-crosslink microscopy in a biopolymer network dissects local elasticity from molecular fluctuations
Single-crosslink microscopy in a biopolymer network dissects local elasticity from molecular fluctuations
The intrinsic inhomogeneity of polymer networks is masked by the usual ensemble-averaged measurements. Here the authors construct direct maps of crosslinks in an actin network by selective labeling the crosslinks with fluorescent markers and characterize the local elasticity and cross-correlation between crosslinks.
- Lingxiang Jiang
- , Qingqiao Xie
- & Steve Granick
-
Article
| Open Access Amine-responsive cellulose-based ratiometric fluorescent materials for real-time and visual detection of shrimp and crab freshness
Amine-responsive cellulose-based ratiometric fluorescent materials for real-time and visual detection of shrimp and crab freshness
Simple, fast, and accurate detection of food freshness has great significance to food safety and business. Here, the authors develop cellulose-based ratiometric fluorescent materials with superior amine-response, which can be used for visual monitoring the freshness of shrimp and crab.
- Ruonan Jia
- , Weiguo Tian
- & Jun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Lithium hexamethyldisilazide initiated superfast ring opening polymerization of alpha-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides
Lithium hexamethyldisilazide initiated superfast ring opening polymerization of alpha-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides
Ring-opening polymerizations of α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides to form polypeptides are usually sensitive to moisture, slow and can undergo side reactions. Here the authors use lithium hexamethyldisilazide to initiate α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydride polymerizations that is very fast and can be conducted in an open vessel.
- Yueming Wu
- , Danfeng Zhang
- & Runhui Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A macromolecular approach to eradicate multidrug resistant bacterial infections while mitigating drug resistance onset
A macromolecular approach to eradicate multidrug resistant bacterial infections while mitigating drug resistance onset
Antibiotic resistance is a major threat across the whole healthcare spectrum. Here, the authors report on the development of biodegradable guanidinium functionalized polycarbonates and demonstrate antimicrobial activity against drug resistant infections.
- Willy Chin
- , Guansheng Zhong
- & Yi Yan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access One-step fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains
One-step fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains
Fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose has been unsuccessful. Here, the authors achieve the objective by one-step fermentation of metabolically engineered E. coli expressing a isocaprenoyl-CoA:2-hydroxyisocaproate CoA-transferase and an evolved polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase.
- Jung Eun Yang
- , Si Jae Park
- & Sang Yup Lee
-
Review Article
| Open Access Polymer mimics of biomacromolecular antifreezes
Polymer mimics of biomacromolecular antifreezes
Ice crystal growth is a major problem in cell and tissue cryopreservation for transplantation, transfusion, icing of aircraft wings and many other applications. Here the authors review the emerging field of synthetic macromolecular mimics of antifreeze proteins that can be used overcome such problems.
- Caroline I. Biggs
- , Trisha L. Bailey
- & Matthew I. Gibson
-
Article
| Open Access Intracellular construction of topology-controlled polypeptide nanostructures with diverse biological functions
Intracellular construction of topology-controlled polypeptide nanostructures with diverse biological functions
The intracellular topology of a nanostructure plays a major role in its interactions with the cell and accordingly, its biological applications. Here, the authors design peptides that intracellularly polymerize into elastin-like polypeptides and assemble into various topologies, each of which exhibits a distinct set of biological functions.
- Li-Li Li
- , Sheng-Lin Qiao
- & Hao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanoresponsive lipid-protein nanoglobules facilitate reversible fibre formation in velvet worm slime
Mechanoresponsive lipid-protein nanoglobules facilitate reversible fibre formation in velvet worm slime
Velvet worms expel a fluid slime that, under shear force, forms stiff fibres that can be dissolved and then regenerated. Here, the authors reveal that the recyclability of these biopolymers relies on mechanoresponsive lipid-protein nanoglobules in the slime that reversibly self-assemble into fibrils.
- Alexander Baer
- , Stephan Schmidt
- & Matthew J. Harrington
-
Article
| Open Access Modulation of polypeptide conformation through donor–acceptor transformation of side-chain hydrogen bonding ligands
Modulation of polypeptide conformation through donor–acceptor transformation of side-chain hydrogen bonding ligands
Hydrogen bonding plays a major role in determining the tridimensional structure of biopolymers. Here, the authors show that control over a polypeptide conformation can be achieved by altering the donor-acceptor properties of side-chain triazole units via protonation-deprotonation.
- Ziyuan Song
- , Rachael A. Mansbach
- & Jianjun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid self-assembly of complex biomolecular architectures during mussel byssus biofabrication
Rapid self-assembly of complex biomolecular architectures during mussel byssus biofabrication
Mussels attach to rocks using a byssus, which possesses unique properties of adhesion, toughness and self-healing. Here, the authors explore the fabrication process of mussel byssus demonstrating the self-assembly of specific proteins into multi-scale organized structures using artificially induced byssus threads.
- Tobias Priemel
- , Elena Degtyar
- & Matthew J. Harrington
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-based polycarbonate as synthetic toolbox
Bio-based polycarbonate as synthetic toolbox
With growing concerns over the sustainability of petroleum-based polymers, poly(limonene carbonate) is offered as a renewable alternative. Here, Greiner and co-workers have managed to tune the properties of poly(limonene carbonate) by carrying out several different chemical modifications.
- O. Hauenstein
- , S. Agarwal
- & A. Greiner
-
Article
| Open Access Printable enzyme-embedded materials for methane to methanol conversion
Printable enzyme-embedded materials for methane to methanol conversion
There is a need for small-scale reactors that convert methane emissions to more valuable products to reduce climate impacts. Here, the authors show that printing 3D structures of the pMMO enzyme enables continuous methane conversion under ambient conditions and reduces mass transfer limitations.
- Craig D. Blanchette
- , Jennifer M. Knipe
- & Sarah E. Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-scale thermal stability of a hard thermoplastic protein-based material
Multi-scale thermal stability of a hard thermoplastic protein-based material
Sucker ring teeth from squid and cuttlefish represent rare examples of thermoplastic biopolymers. Here, the authors demonstrate how these materials may be processed for implementation in biomedical and 3D printing applications.
- Victoria Latza
- , Paul A. Guerette
- & Admir Masic
-
Review Article |
 Electrochemical tunnelling sensors and their potential applications
Electrochemical tunnelling sensors and their potential applications
Quantum-mechanical tunnelling currents across nanometre-scale gaps between electrodes are sensitive to the medium in the gap. Albrecht reviews progress towards using tunnelling currents to probe single-molecule processes, and in biosensor and sequencing applications.
- T. Albrecht

 Endogenous stimuli-responsive separating microneedles to inhibit hypertrophic scar through remodeling the pathological microenvironment
Endogenous stimuli-responsive separating microneedles to inhibit hypertrophic scar through remodeling the pathological microenvironment