Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and mechanism of the K+/H+ exchanger KefC
Structure and mechanism of the K+/H+ exchanger KefC
Intracellular potassium (K+) homeostasis is achieved by activity of both ion channels and transporters. Here, the authors report structures of E. coli glutathione (GSH)-gated K+ efflux transporter KefC with bound K+ and conclude that the ion-binding site is adapted for binding a dehydrated ion.
- Ashutosh Gulati
- , Surabhi Kokane
- & David Drew
-
Article
| Open Access Potent activity of polymyxin B is associated with long-lived super-stoichiometric accumulation mediated by weak-affinity binding to lipid A
Potent activity of polymyxin B is associated with long-lived super-stoichiometric accumulation mediated by weak-affinity binding to lipid A
Polymyxins are last-resort antibiotics targeting lipid A in the gram-negative outer membrane. Here, the authors use surface plasmon resonance-based kinetics to reveal a three-state mechanism governing superstoichiometric accumulation of polymyxins.
- Kerry R. Buchholz
- , Mike Reichelt
- & John G. Quinn
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative growth in microbial communities is a driver of multistability
Cooperative growth in microbial communities is a driver of multistability
This study explores alternative stable states in microbial communities. Focusing on a respiratory tract community of 6 species, the authors identified four distinct stable states that are predicted to be driven by cooperative growth. The findings contrast with the common association between competitive interactions and multistability in microbial communities.
- William Lopes
- , Daniel R. Amor
- & Jeff Gore
-
Article
| Open Access Lipid unsaturation promotes BAX and BAK pore activity during apoptosis
Lipid unsaturation promotes BAX and BAK pore activity during apoptosis
BAX and BAK are proapoptotic proteins that directly mediate mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Here, lipidomics and other data provide insight on how local lipid environment affects BAX and BAK function during apoptosis, suggesting that unsaturated lipids promote BAX pore activity.
- Shashank Dadsena
- , Rodrigo Cuevas Arenas
- & Ana J. García-Sáez
-
Article
| Open Access Co-aggregation with Apolipoprotein E modulates the function of Amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s disease
Co-aggregation with Apolipoprotein E modulates the function of Amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s disease
Here the authors connect inherited Apolipoprotein E genotype with the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease by demonstrating how, in an isoform- and lipidation-specific way, apoE modulates the aggregation, clearance and toxicity of Amyloid-beta.
- Zengjie Xia
- , Emily E. Prescott
- & Suman De
-
Article
| Open Access Atomistic mechanism of coupling between cytosolic sensor domain and selectivity filter in TREK K2P channels
Atomistic mechanism of coupling between cytosolic sensor domain and selectivity filter in TREK K2P channels
The TREK K2P channel activity is dynamically regulated by protein kinase-dependent signaling pathways involved in the development of various human diseases. Here, the authors report how phosphorylation at the proximal C-terminus induces allosteric deactivation of the selectivity filter gate.
- Berke Türkaydin
- , Marcus Schewe
- & Han Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Structural conversion of the spidroin C-terminal domain during assembly of spider silk fibers
Structural conversion of the spidroin C-terminal domain during assembly of spider silk fibers
The mechanical properties of spider silk are a consequence of the structural organisation of proteins known as spidroins. Here the authors investigate the structure of the fibers formed by a C-terminal domain of a major spidroin: the study elucidates the mechanisms by which spidroins are transformed from soluble form into a fiber.
- Danilo Hirabae De Oliveira
- , Vasantha Gowda
- & My Hedhammar
-
Article
| Open Access Loop-extruders alter bacterial chromosome topology to direct entropic forces for segregation
Loop-extruders alter bacterial chromosome topology to direct entropic forces for segregation
Bacterial chromosomes segregate while undergoing replication. Here the authors show that such concurrent replication and segregation cannot be achieved by passive entropic forces alone, and that loop-extruders could be sufficient to explain segregation.
- Janni Harju
- , Muriel C. F. van Teeseling
- & Chase P. Broedersz
-
Article
| Open Access G protein-specific mechanisms in the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor regulate psychosis-related effects and memory deficits
G protein-specific mechanisms in the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor regulate psychosis-related effects and memory deficits
Here authors aim to understand the 5-HT2AR coupling signature in response to different signaling probes and their physiological impacts using computational modeling, in vitro and in vivo experiments, and analysis of human brain tissue.
- Elk Kossatz
- , Rebeca Diez-Alarcia
- & Jana Selent
-
Article
| Open Access Control of artificial membrane fusion in physiological ionic solutions beyond the limits of electroformation
Control of artificial membrane fusion in physiological ionic solutions beyond the limits of electroformation
Membrane fusion is crucial for fabricating artificial membranes. Here, the authors present an approach combining electric field with hydraulic pressure to physically control the fusion, enabling tuning of the shape and size of the 3D freestanding lipid bilayers in physiological solutions.
- Bong Kyu Kim
- , Dong-Hyun Kang
- & Tae Song Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Proton-coupled transport mechanism of the efflux pump NorA
Proton-coupled transport mechanism of the efflux pump NorA
Efflux pumps confer antibiotic resistance by coupling proton import with drug export. In this work, the authors uncover the proton-coupled transport mechanism for the clinically relevant efflux pump NorA from the pathogenic bacterium S. aureus.
- Jianping Li
- , Yan Li
- & Nathaniel J. Traaseth
-
Article
| Open Access Structural domain in the Titin N2B-us region binds to FHL2 in a force-activation dependent manner
Structural domain in the Titin N2B-us region binds to FHL2 in a force-activation dependent manner
Titin N2B unique sequence (N2B-us) is a 572 amino acid sequence that acts as an elastic spring to regulate muscle passive elasticity. Here the authors identify a mechanosensitive structural domain within the titin (N2B-us), and a force-dependent interaction between (N2B-us) and the protein FHL2.
- Yuze Sun
- , Xuyao Liu
- & Jie Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Hairpin protein partitioning from the ER to lipid droplets involves major structural rearrangements
Hairpin protein partitioning from the ER to lipid droplets involves major structural rearrangements
Lipid droplet (LD) function relies on protein partitioning between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and LD. The authors show that UBXD8 adopts distinct conformations in both membranes and undergoes structural rearrangements during ER-to-LD partitioning.
- Ravi Dhiman
- , Rehani S. Perera
- & Bianca Schrul
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast energy quenching mechanism of LHCSR3-dependent photoprotection in Chlamydomonas
Ultrafast energy quenching mechanism of LHCSR3-dependent photoprotection in Chlamydomonas
The Light Harvesting Complex Stress-Related Protein (LHCSR) can protect algae from severe photodamage via energy-dependent quenching (qE). Here, the authors find that a photoproduct of carotenoid S1 state is populated in qE and depopulated in 7.5 ps.
- Mengyuan Zheng
- , Xiaojie Pang
- & Lijin Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and inhibition of the human lysosomal transporter Sialin
Structure and inhibition of the human lysosomal transporter Sialin
Sialin transports multiple substrates including sialic acid out of lysosomes, and neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles. This study reports the cryo-EM structures of Sialin in multiple states revealing its transport and pH-sensing mechanisms.
- Philip Schmiege
- , Linda Donnelly
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Angle between DNA linker and nucleosome core particle regulates array compaction revealed by individual-particle cryo-electron tomography
Angle between DNA linker and nucleosome core particle regulates array compaction revealed by individual-particle cryo-electron tomography
Here, using cryo-ET, the 3D structures of individual nucleosome particles were characterized to observe changes under varying ionic strengths and in the presence of protein H1, revealing key regulatory roles in chromatin organization dynamics.
- Meng Zhang
- , César Díaz-Celis
- & Gang Ren
-
Article
| Open Access The patatin-like protein PlpD forms structurally dynamic homodimers in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane
The patatin-like protein PlpD forms structurally dynamic homodimers in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane
The Omp85 superfamily is a widely distributed class of outer membrane proteins found in Gram-negative bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts. Here the authors show that PlpD has a different structure and topology than other Omp85 proteins that have been studied.
- Sarah E. Hanson
- , Tyrone Dowdy
- & Harris D. Bernstein
-
Article
| Open Access Solutes unmask differences in clustering versus phase separation of FET proteins
Solutes unmask differences in clustering versus phase separation of FET proteins
Biomolecular condensates form via phase separation of multivalent macromolecules. Phase separation is governed by solubility whereas multivalence drives percolation, also known as gelation. The authors in this work identify the distinct energy and length scales that influence phase separation versus percolation.
- Mrityunjoy Kar
- , Laura T. Vogel
- & Rohit V. Pappu
-
Perspective
| Open Access Rediscovery of mononuclear phagocyte system blockade for nanoparticle drug delivery
Rediscovery of mononuclear phagocyte system blockade for nanoparticle drug delivery
Temporal blockade of the mononuclear phagocyte system is an approach to enhance the therapeutic efficiency of nanocarrier drug-delivery systems but the broad applicability is hindered by the complexity of optimisation and management of potential side effects. Here, the authors review the development of this technique and show its efficiency using meta-analysis of the published data and discuss essential features for its successful translation to clinic.
- Ivan V. Zelepukin
- , Konstantin G. Shevchenko
- & Sergey M. Deyev
-
Article
| Open Access Active transcription and epigenetic reactions synergistically regulate meso-scale genomic organization
Active transcription and epigenetic reactions synergistically regulate meso-scale genomic organization
Chromatin within interphase nuclei forms compacted nanoscale DNA domains of uniform size. By integrating theory and imaging, here the authors show how the interplay between transcription and epigenetic mechanisms determine this size, independent of cell type.
- Aayush Kant
- , Zixian Guo
- & Vivek B. Shenoy
-
Article
| Open Access Heliorhodopsin-mediated light-modulation of ABC transporter
Heliorhodopsin-mediated light-modulation of ABC transporter
Here, authors classify genes flanking the Heliorhodopsin (HeR)-encoding genes and identify highly conserved residues for protein–protein interactions, revealing a function of HeR as regulatory rhodopsin for multidrug resistance.
- Shin-Gyu Cho
- , Ji-Hyun Kim
- & Kwang-Hwan Jung
-
Article
| Open Access The actin cytoskeleton plays multiple roles in structural colour formation in butterfly wing scales
The actin cytoskeleton plays multiple roles in structural colour formation in butterfly wing scales
NCOMMS-23-44446C Vivid structural colours in butterflies are caused by photonic nanostructures scattering light, however insight into the development of such structures in vivo remains scarce. Here the authors show that actin plays a vital and direct templating role during structural colour formation in butterfly scales, providing ridge patterning mechanisms that are likely universal across lepidoptera.
- Victoria J. Lloyd
- , Stephanie L. Burg
- & Andrew J. Parnell
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput mechanical phenotyping and transcriptomics of single cells
High-throughput mechanical phenotyping and transcriptomics of single cells
The molecular system regulating cell surface mechanics remains largely unexplored at single-cell resolution. Here, the authors report a high-throughput single-cell assay, ELASTomics, which integrates mechanical phenotyping with unbiased transcriptomics.
- Akifumi Shiomi
- , Taikopaul Kaneko
- & Hirofumi Shintaku
-
Article
| Open Access Differential SNARE chaperoning by Munc13-1 and Munc18-1 dictates fusion pore fate at the release site
Differential SNARE chaperoning by Munc13-1 and Munc18-1 dictates fusion pore fate at the release site
How heterogeneously distributed SNARE complexes synchronize fusion pore assemblies during vesicular secretion is unknown. Here, the authors demonstrate a role for SNARE chaperones in coordinating differential release of chemical messengers.
- Bhavya R. Bhaskar
- , Laxmi Yadav
- & Debasis Das
-
Article
| Open Access Correlative single molecule lattice light sheet imaging reveals the dynamic relationship between nucleosomes and the local chromatin environment
Correlative single molecule lattice light sheet imaging reveals the dynamic relationship between nucleosomes and the local chromatin environment
This study combines lattice light sheet microscopy and single molecule imaging to study protein dynamics and chromatin structure in live cells. The authors describe how nucleosomes and proteins move and are organised in relation to chromatin density.
- Timothy A. Daugird
- , Yu Shi
- & Wesley R. Legant
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay between Mg2+ and Ca2+ at multiple sites of the ryanodine receptor
Interplay between Mg2+ and Ca2+ at multiple sites of the ryanodine receptor
Skeletal ryanodine receptor controls calcium mobilization indispensable for muscle contraction. Here, authors combine cryo-EM and molecular dynamics to uncover the structural basis of the intricate regulation of this channel by calcium and magnesium.
- Ashok R. Nayak
- , Warin Rangubpit
- & Montserrat Samsó
-
Article
| Open Access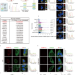 TRIM25 predominately associates with anti-viral stress granules
TRIM25 predominately associates with anti-viral stress granules
Different environmental stressors induce different subtypes of stress granules (SGs), and each of them presumably have distinct functions. Here the authors provide a framework for understanding the compositional and functional heterogeneity of SGs, and see that TRIM25 mainly associates with anti-viral SGs.
- Zehua Shang
- , Sitao Zhang
- & Da Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamin1 long- and short-tail isoforms exploit distinct recruitment and spatial patterns to form endocytic nanoclusters
Dynamin1 long- and short-tail isoforms exploit distinct recruitment and spatial patterns to form endocytic nanoclusters
Dynamins are required at nascent endosomes to promote membrane fission. Here, the authors use super-resolution microscopy to show that dynamin-1 recruitment relies on pre-existing nanoclusters and trapping of molecules laterally diffusing on the plasma membrane.
- Anmin Jiang
- , Kye Kudo
- & Frédéric A. Meunier
-
Article
| Open Access Multiscale modelling of chromatin 4D organization in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells
Multiscale modelling of chromatin 4D organization in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells
In this work, the authors apply polymer models to reconstruct the 3D structure of the genome during SARS-CoV-2 infection and examine how the virus impacts key mechanisms of chromatin organization.
- Andrea M. Chiariello
- , Alex Abraham
- & Mario Nicodemi
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of human NOX5 activation
Structural basis of human NOX5 activation
NADPH oxidase 5 (NOX5) is activated by Ca2+ signaling, catalyzing superoxide production by transferring electrons from intracellular NADPH to extracellular oxygen. Here the authors uncover the molecular basis of NOX5 activation and electron transfer.
- Chenxi Cui
- , Meiqin Jiang
- & Ji Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into drug transport by an aquaglyceroporin
Structural insights into drug transport by an aquaglyceroporin
Pentamidine and melarsoprol are drugs used to treat sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma brucei. Here, authors present cryo-EM structures of TbAQP2 with molecular dynamic simulations, revealing mechanisms shaping substrate specificity and drug permeation.
- Wanbiao Chen
- , Rongfeng Zou
- & Chongyuan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access High-confidence 3D template matching for cryo-electron tomography
High-confidence 3D template matching for cryo-electron tomography
Enabling visual proteomics with high-confidence 3D template matching (TM) in CryoET. 3D TM precisely localizes macromolecular complexes, individual subunits, and different functional states in situ, revealing molecular interactions within cells.
- Sergio Cruz-León
- , Tomáš Majtner
- & Gerhard Hummer
-
Article
| Open Access A nascent riboswitch helix orchestrates robust transcriptional regulation through signal integration
A nascent riboswitch helix orchestrates robust transcriptional regulation through signal integration
Here the authors unveil an intermediate state during the folding of the manganese riboswitch from L. lactis. This transient state allows the integration of multiple cellular signals including RNA polymerase pausing and transcription factor NusA.
- Adrien Chauvier
- , Shiba S. Dandpat
- & Nils G. Walter
-
Article
| Open Access 5′UTR G-quadruplex structure enhances translation in size dependent manner
5′UTR G-quadruplex structure enhances translation in size dependent manner
In eukaryotes, G-quadruplex in mRNA (RG4) 5′ UTR inhibit translation initiation. Here the authors employ single molecule assay to show that RG4 in E. coli reporter increases translation efficiency by preventing ribosome dislodging.
- Chun-Ying Lee
- , Meera Joshi
- & Sua Myong
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-separated droplets swim to their dissolution
Phase-separated droplets swim to their dissolution
Here the authors identify a generic coupling in phase-separated liquids between motility and phase equilibria perturbations: phase-separated droplets swim to their dissolution. This suggests alternative transport mechanism for biomolecular condensates.
- Etienne Jambon-Puillet
- , Andrea Testa
- & Eric R. Dufresne
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis and synergism of ATP and Na+ activation in bacterial K+ uptake system KtrAB
Structural basis and synergism of ATP and Na+ activation in bacterial K+ uptake system KtrAB
KtrAB complex is essential in K+ uptake for bacteria. Here authors illustrate the synergism of ATP and Na+ in activating K+ uptake of KtrAB from Bacillus subtilis and its gating mechanism, which may also shed light on other Na+-activated K+ channels.
- Wesley Tien Chiang
- , Yao-Kai Chang
- & Nien-Jen Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic basis of the dynamic response of TWIK1 ionic selectivity to pH
Mechanistic basis of the dynamic response of TWIK1 ionic selectivity to pH
Using computer simulations authors identify the dynamic molecular motions controlling the structural conformation of the TWIK1 ion channel, showing that its ability to transport sodium upon acidification result from the evolution of the classical potassium-selective pore.
- Franck C. Chatelain
- , Nicolas Gilbert
- & Olivier Bignucolo
-
Article
| Open Access Pharmacological inhibition of α-synuclein aggregation within liquid condensates
Pharmacological inhibition of α-synuclein aggregation within liquid condensates
Aggregated forms of α-synuclein are characteristic of Parkinson’s disease. Here the authors show that the condensation-driven aggregation pathway of α-synuclein can be inhibited using small molecules: the aminosterol claramine stabilizes α-synuclein condensates and inhibits α-synuclein primary nucleation in the aggregation process.
- Samuel T. Dada
- , Zenon Toprakcioglu
- & Michele Vendruscolo
-
Article
| Open Access SARS-CoV-2 Mpro responds to oxidation by forming disulfide and NOS/SONOS bonds
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro responds to oxidation by forming disulfide and NOS/SONOS bonds
The main protease, a key enzyme of SARS-CoV-2, can protect itself from oxidative damage. Here, Reinke, Schubert, and colleagues used XFEL radiation to image the enzyme, revealing the disulfide and NOS/SONOS bonds that form in response to oxygen.
- Patrick Y. A. Reinke
- , Robin Schubert
- & Thomas J. Lane
-
Article
| Open Access Cardiac function is regulated by the sodium-dependent inhibition of the sodium-calcium exchanger NCX1
Cardiac function is regulated by the sodium-dependent inhibition of the sodium-calcium exchanger NCX1
The sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX1) is the primary calcium extrusion mechanism of cardiac myocytes. Here, the authors show that removal of a long questioned allosteric regulation of NCX1 by intracellular sodium alters cardiac excitation-contraction coupling.
- Kyle Scranton
- , Scott John
- & Michela Ottolia
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering DED assembly mechanisms in FADD-procaspase-8-cFLIP complexes regulating apoptosis
Deciphering DED assembly mechanisms in FADD-procaspase-8-cFLIP complexes regulating apoptosis
Here the authors structurally and mechanistically characterize the assembly of FADD, procaspase-8, and cFLIP through their death-effector domains (DEDs), providing insights into the regulation of apoptotic and necroptotic signalling.
- Chao-Yu Yang
- , Chia-I Lien
- & Su-Chang Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Giant organelle vesicles to uncover intracellular membrane mechanics and plasticity
Giant organelle vesicles to uncover intracellular membrane mechanics and plasticity
The biophysical properties of cellular organelles are difficult to study directly. Here, the authors generate and characterize osmotically-expanded giant vesicles of several organelles, which maintain some of their functional properties.
- Alexandre Santinho
- , Maxime Carpentier
- & Abdou Rachid Thiam
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous dynamics of a passive droplet in active turbulence
Anomalous dynamics of a passive droplet in active turbulence
The fluctuating dynamics of a passive object suspended in an active fluid can provide fundamental insight into the fundamental non-equilibrium behavior of the fluid. Singh and Chaudhuri theoretically investigate the dynamics of a passive deformable droplet in active nematic turbulence and show how the motion of the droplet is influenced by the interplay of spatial correlations of the flow and the size of the droplet.
- Chamkor Singh
- & Abhishek Chaudhuri
-
Article
| Open Access Structural mechanism of voltage-gated sodium channel slow inactivation
Structural mechanism of voltage-gated sodium channel slow inactivation
Inactivation is an intrinsic property of NaV channel, but the mechanism for slow inactivation is not fully understood. Here, authors show a NaVEh structure in a potential slow-inactivated state, elucidating structural basis for slow inactivation.
- Huiwen Chen
- , Zhanyi Xia
- & Daohua Jiang
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access On the statistical foundation of a recent single molecule FRET benchmark
On the statistical foundation of a recent single molecule FRET benchmark
- Ayush Saurabh
- , Lance W. Q. Xu
- & Steve Pressé
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to: On the statistical foundation of a recent single molecule FRET benchmark
Reply to: On the statistical foundation of a recent single molecule FRET benchmark
- Markus Götz
- , Anders Barth
- & Sonja Schmid
-
Article
| Open Access Stress-shape misalignment in confluent cell layers
Stress-shape misalignment in confluent cell layers
When studying nematic ordering of cells in a monolayer, it is commonly assumed that the principal stress and cell shape axes are tightly coupled. Here, the authors measure cell shape and cell-generated contractile stresses and show that cells in monolayers form correlated, dynamic domains in which the stresses are systematically misaligned with the cell bodies.
- Mehrana R. Nejad
- , Liam J. Ruske
- & Julia M. Yeomans
-
Article
| Open Access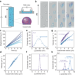 Probing the surface charge of condensates using microelectrophoresis
Probing the surface charge of condensates using microelectrophoresis
The surface charge and ζ-potential of biomolecular condensates is key to their interactions with membranes and proteins. Here, the authors developed a method to determine the ζ-potential of condensates using microelectrophoresis and single-droplet tracking.
- Merlijn H. I. van Haren
- , Brent S. Visser
- & Evan Spruijt
-
Article
| Open Access Disordered clock protein interactions and charge blocks turn an hourglass into a persistent circadian oscillator
Disordered clock protein interactions and charge blocks turn an hourglass into a persistent circadian oscillator
Many clock proteins contain intrinsically disordered regions, but how these regions mediate protein interactions is poorly understood. Here, the authors identify charge blocks within a disordered clock protein that regulate circadian timing.
- Meaghan S. Jankowski
- , Daniel Griffith
- & Jennifer M. Hurley

 Inhibition and transport mechanisms of the ABC transporter hMRP5
Inhibition and transport mechanisms of the ABC transporter hMRP5