Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access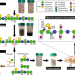 Microbiota-directed fibre activates both targeted and secondary metabolic shifts in the distal gut
Microbiota-directed fibre activates both targeted and secondary metabolic shifts in the distal gut
Here, the authors tailor an acetylated galactoglucomannan (AcGGM) fibre from spruce wood to specifically enrich Roseburia and Faecalibacterium - beneficial species which have the enzymatic machinery to breakdown the fibre and generate butyrate. They subsequently perform a piglet feeding trial, metagenomics and metaproteomics, together showing that AcGGM-fed pigs exhibit not only increased Roseburia and Faecalibacterium populations with AcGGM-specific mannan-specific esterases, but also secondary metabolic pathways.
- Leszek Michalak
- , John Christian Gaby
- & Bjørge Westereng
-
Article
| Open Access A computational method for detection of ligand-binding proteins from dose range thermal proteome profiles
A computational method for detection of ligand-binding proteins from dose range thermal proteome profiles
2D-thermal proteome profiling (2D-TPP) is a powerful assay for probing interactions of proteins with small molecules in their native context. Here the authors provide a statistical method for false discovery rate controlled analysis for 2D-TPP applications.
- Nils Kurzawa
- , Isabelle Becher
- & Mikhail M. Savitski
-
Article
| Open Access A convolutional neural network segments yeast microscopy images with high accuracy
A convolutional neural network segments yeast microscopy images with high accuracy
Current cell segmentation methods for Saccharomyces cerevisiae face challenges under a variety of standard experimental and imaging conditions. Here the authors develop a convolutional neural network for accurate, label-free cell segmentation.
- Nicola Dietler
- , Matthias Minder
- & Sahand Jamal Rahi
-
Article
| Open Access An embryonic stem cell-specific heterochromatin state promotes core histone exchange in the absence of DNA accessibility
An embryonic stem cell-specific heterochromatin state promotes core histone exchange in the absence of DNA accessibility
Nucleosome turnover concomitant with incorporation of the histone variant H3.3 is a hallmark of regulatory regions in the animal genome. Here, the authors demonstrate that fast histone turnover and H3.3 incorporation defines a dynamic heterochromatin state in pluripotent stem cells.
- Carmen Navarro
- , Jing Lyu
- & Simon J. Elsässer
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of absolute multi-omics reveals dynamic protein-to-RNA ratios and metabolic interplay within mixed-domain microbiomes
Integration of absolute multi-omics reveals dynamic protein-to-RNA ratios and metabolic interplay within mixed-domain microbiomes
Here, the authors perform a temporal multi-omic analysis of a minimalistic cellulose-degrading and methane-producing consortium at the strain level and estimate protein-to-RNA ratios and RNA-protein dynamics of the community simultaneously over time.
- F. Delogu
- , B. J. Kunath
- & P. B. Pope
-
Article
| Open Access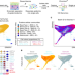 Single cell transcriptomics of human epidermis identifies basal stem cell transition states
Single cell transcriptomics of human epidermis identifies basal stem cell transition states
The mechanisms regulating stem cells to give rise to human interfollicular epidermis are unclear. Here, the authors use single cell RNA sequencing to identify heterogeneity within the human neonatal interfollicular epidermis and distinct spatial positioning of at least four basal stem cell populations.
- Shuxiong Wang
- , Michael L. Drummond
- & Scott X. Atwood
-
Article
| Open Access High throughput error corrected Nanopore single cell transcriptome sequencing
High throughput error corrected Nanopore single cell transcriptome sequencing
Droplet-based high throughput single cell sequencing techniques can often lose information on transcript splicing and heterogenity. Here the authors introduce ScNaUmi-seq, which uses Oxford Nanopore sequencing and barcoding to generate high accuracy full length sequences.
- Kevin Lebrigand
- , Virginie Magnone
- & Rainer Waldmann
-
Article
| Open Access Multiscale causal networks identify VGF as a key regulator of Alzheimer’s disease
Multiscale causal networks identify VGF as a key regulator of Alzheimer’s disease
To investigate the molecular foundation of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Beckmann et al. constructed multiscale causal networks on a large human AD multi-omics dataset, detecting AD-associated networks and their top predicted regulator, VGF, with extensive validation in the 5xFAD mouse model.
- Noam D. Beckmann
- , Wei-Jye Lin
- & Eric E. Schadt
-
Article
| Open Access Preferential inhibition of adaptive immune system dynamics by glucocorticoids in patients after acute surgical trauma
Preferential inhibition of adaptive immune system dynamics by glucocorticoids in patients after acute surgical trauma
Glucocorticoids (GC) are commonly used to suppress undesirable inflammatory responses. Here the authors show, using hi-dimensional flow cytometry data, that GC treatment following major surgeries alters adaptive immunity without significant modulation of innate immune responses or pain/functional impairment.
- Edward A. Ganio
- , Natalie Stanley
- & Brice Gaudilliere
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive characterization of claudin-low breast tumors reflects the impact of the cell-of-origin on cancer evolution
Comprehensive characterization of claudin-low breast tumors reflects the impact of the cell-of-origin on cancer evolution
Claudin-low tumors are a rare aggressive subtype of breast cancers. In this study, the authors use a multiomics approach to demonstrate that these tumors are heterogeneous and comprise three main subgroups that emerge from different evolutionary processes.
- Roxane M. Pommier
- , Amélien Sanlaville
- & Alain Puisieux
-
Article
| Open Access The mutREAD method detects mutational signatures from low quantities of cancer DNA
The mutREAD method detects mutational signatures from low quantities of cancer DNA
Sequencing tumour genomes can reveal information about the processes that drive the formation of cancer. Here, the authors describe a method that can detect these mutational signatures from small amounts of DNA and degraded samples.
- Juliane Perner
- , Sujath Abbas
- & Rebecca C. Fitzgerald
-
Article
| Open Access Substrate specificity of the TRAMP nuclear surveillance complexes
Substrate specificity of the TRAMP nuclear surveillance complexes
During nuclear surveillance in yeast and human cells, the RNA exosome functions together with the TRAMP complexes. Here, the authors defined the protein composition of the TRAMP complexes and identified specific RNA binding sites for the different TRAMP components.
- Clémentine Delan-Forino
- , Christos Spanos
- & David Tollervey
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and quality analysis of a comprehensive set of structural variants and short tandem repeats
Discovery and quality analysis of a comprehensive set of structural variants and short tandem repeats
The complexity of structural variation (SV) and short tandem repeats (STRs) makes it necessary to apply different calling and filtering strategies to sequencing datasets. Here, Jakubosky et al. report a comprehensive SV and STR callset from whole-genome sequencing of 477 individuals from iPSCORE and HipSci using five algorithms.
- David Jakubosky
- , Erin N. Smith
- & Kelly A. Frazer
-
Article
| Open Access Latent periodic process inference from single-cell RNA-seq data
Latent periodic process inference from single-cell RNA-seq data
Traditional methods for determining cell type composition lack scalability, while single-cell technologies remain costly and noisy compared to bulk RNA-seq. Here, the authors present a highly efficient tool to measure cellular heterogeneity in bulk expression through robust integration of single-cell information.
- Shaoheng Liang
- , Fang Wang
- & Ken Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Horizontal transfer and evolution of transposable elements in vertebrates
Horizontal transfer and evolution of transposable elements in vertebrates
Horizontal transfer (HT) and evolution of transposable elements (TEs) has rarely been quantified on a large scale. Here, the authors screen 307 vertebrate genomes and infer 975 HT events (93% in ray-finned fishes); all TEs involved in HT evolve within genomes under purifying selection, as do most retrotransposons.
- Hua-Hao Zhang
- , Jean Peccoud
- & Clément Gilbert
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting gene expression using morphological cell responses to nanotopography
Predicting gene expression using morphological cell responses to nanotopography
The surface nanotopography of biomaterials direct cell behavior, but screening for desired effects is inefficient. Here, the authors introduce a platform that enables prediction of nanotopography-induced gene expression changes from changes in cell morphology, including in co-culture environments.
- Marie F. A. Cutiongco
- , Bjørn Sand Jensen
- & Nikolaj Gadegaard
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive non-redundant gene catalog reveals extensive within-community intraspecies diversity in the human vagina
A comprehensive non-redundant gene catalog reveals extensive within-community intraspecies diversity in the human vagina
Reference databases are essential for studies on host-microbiota interactions. Here, the authors present the construction of VIRGO, a human vaginal non-redundant gene catalog, which represents a comprehensive resource for taxonomic and functional profiling of vaginal microbiomes from metagenomic and metatranscriptomic datasets.
- Bing Ma
- , Michael T. France
- & Jacques Ravel
-
Article
| Open Access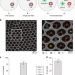 Inference and effects of barcode multiplets in droplet-based single-cell assays
Inference and effects of barcode multiplets in droplet-based single-cell assays
It is assumed that single-cell analyses capture one barcode per cell. Here, the authors show that up to 21% of cell barcodes on the 10X Chromium scATAC-seq assay may be derived from barcode multiplets.
- Caleb A. Lareau
- , Sai Ma
- & Jason D. Buenrostro
-
Article
| Open Access Single-nuclei RNA-seq on human retinal tissue provides improved transcriptome profiling
Single-nuclei RNA-seq on human retinal tissue provides improved transcriptome profiling
The retina is a heterogeneous tissue composed of multiple cell types. Via single-nuclei RNA sequencing on human neural retinal tissue, the authors characterise the transcriptome profile for individual cell types in the human retina.
- Qingnan Liang
- , Rachayata Dharmat
- & Rui Chen
-
Article
| Open Access The epigenomic landscape of transposable elements across normal human development and anatomy
The epigenomic landscape of transposable elements across normal human development and anatomy
Although most are silenced, certain transposable elements (TEs) have been co-opted by the host. Here, the authors quantify the epigenomic status of TEs using data from the Roadmap Epigenomics Project, provide a systematic profile of TE activity across normal human tissues and development, finding that TEs encompass a quarter of the human regulatory epigenome, with 47% of TEs in regulatory states.
- Erica C. Pehrsson
- , Mayank N. K. Choudhary
- & Ting Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A Bayesian mixture model for the analysis of allelic expression in single cells
A Bayesian mixture model for the analysis of allelic expression in single cells
Allele-specific expression at single-cell resolution can reveal stochastic and dynamic features of gene expression in greater detail. The authors propose scBASE, a soft zero-and-one inflated model that improves estimation of cellular allelic proportions by pooling information across cells.
- Kwangbom Choi
- , Narayanan Raghupathy
- & Gary A. Churchill
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced and unified anatomical labeling for a common mouse brain atlas
Enhanced and unified anatomical labeling for a common mouse brain atlas
Anatomical brain atlases elucidate the anatomical and functional organisation across species but different atlases have conflicting anatomical border and 3D coordinates. The authors integrated two atlases into a unified and highly segmented anatomical labelling system of the mouse brain.
- Uree Chon
- , Daniel J. Vanselow
- & Yongsoo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Microbe-host interplay in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
Microbe-host interplay in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis (PSO) are associated with dysbiosis. Here, by analyses of skin microbiome and host transcriptome of AD and PSO patients, the authors find distinct microbial and disease-related gene transcriptomic signatures that differentiate both diseases.
- Nanna Fyhrquist
- , Gareth Muirhead
- & Harri Alenius
-
Article
| Open Access Optimized CRISPR guide RNA design for two high-fidelity Cas9 variants by deep learning
Optimized CRISPR guide RNA design for two high-fidelity Cas9 variants by deep learning
Application of highly specific Cas9 variants can be restricted by the design of the guide RNA. Here the authors present DeepHF, a gRNA activity prediction tool built from genome-scale screens of 50,000 guides covering 20,000 genes.
- Daqi Wang
- , Chengdong Zhang
- & Yongming Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Proteogenomic landscape of squamous cell lung cancer
Proteogenomic landscape of squamous cell lung cancer
Squamous cell lung cancer has dismal prognosis due to the dearth of effective treatments. Here, the authors perform an integrated proteogenomic analysis of the disease, revealing three proteomics-based subtypes and suggesting potential therapeutic opportunities.
- Paul A. Stewart
- , Eric A. Welsh
- & Eric B. Haura
-
Article
| Open Access A high-speed search engine pLink 2 with systematic evaluation for proteome-scale identification of cross-linked peptides
A high-speed search engine pLink 2 with systematic evaluation for proteome-scale identification of cross-linked peptides
The identification of cross-linked peptides at a proteome scale for interactome analyses represents a complex challenge. Here the authors report an efficient and reliable search engine pLink 2 for proteome-scale cross-linking mass spectrometry analyses, and demonstrate how to systematically evaluate the credibility of search engines.
- Zhen-Lin Chen
- , Jia-Ming Meng
- & Si-Min He
-
Article
| Open Access Model-based understanding of single-cell CRISPR screening
Model-based understanding of single-cell CRISPR screening
Single-cell CRISPR screening combines pooled CRISPR screening with scRNA-seq analysis to expand the resolution power of genetic screening. Here, the authors develop MUSIC, a computational pipeline for analyzing single-cell CRISPR screening data.
- Bin Duan
- , Chi Zhou
- & Qi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Platanus-allee is a de novo haplotype assembler enabling a comprehensive access to divergent heterozygous regions
Platanus-allee is a de novo haplotype assembler enabling a comprehensive access to divergent heterozygous regions
Most phasing programmes for sequencing data work well for genomes with low heterozygosity but drop in performance in regions of high heterozygosity. Here, Kajitani et al. develop the assembler Platanus-allee and demonstrate its utility in de novo assemblies of various genomes and the human MHC region.
- Rei Kajitani
- , Dai Yoshimura
- & Takehiko Itoh
-
Article
| Open Access Global identification of functional microRNA-mRNA interactions in Drosophila
Global identification of functional microRNA-mRNA interactions in Drosophila
MicroRNAs are mediators of post-transcriptional gene expression silencing. Here authors provide a transcriptome-wide map of miRNA target sites in Drosophila.
- Hans-Hermann Wessels
- , Svetlana Lebedeva
- & Uwe Ohler
-
Article
| Open Access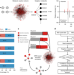 Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics
Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics
Untargeted metabolomics detects large numbers of metabolites but their annotation remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a metabolic reaction network-based recursive algorithm that expands metabolite annotation by taking advantage of the mass spectral similarity of reaction-paired neighbor metabolites.
- Xiaotao Shen
- , Ruohong Wang
- & Zheng-Jiang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Lineage tracing using a Cas9-deaminase barcoding system targeting endogenous L1 elements
Lineage tracing using a Cas9-deaminase barcoding system targeting endogenous L1 elements
Lineage tracing has provided new insights into cell fate but defining cellular diversity remains a challenge. Here the authors target endogenous repeat regions in mammalian cells with cytidine deaminase fused to nCas9 to create genetic barcodes for fine-resolution mapping.
- Byungjin Hwang
- , Wookjae Lee
- & Duhee Bang
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular interactions between Hel2 and RNA supporting ribosome-associated quality control
Molecular interactions between Hel2 and RNA supporting ribosome-associated quality control
Ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathways monitor and respond to stalling of the translating ribosome. Here the authors show that the ribosome associated RQC factor Hel2/ZNF598, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, generally interacts with mRNAs in the vicinity of stop codons.
- Marie-Luise Winz
- , Lauri Peil
- & David Tollervey
-
Article
| Open Access Pathway-based subnetworks enable cross-disease biomarker discovery
Pathway-based subnetworks enable cross-disease biomarker discovery
Accurate and actionable biomarkers that integrate diverse molecular, functional and clinical information hold great promise in precision medicine. Here, the authors develop SIMMS, a method for pathway-based cross-disease biomarker discovery.
- Syed Haider
- , Cindy Q. Yao
- & Paul C. Boutros
-
Article
| Open Access Interpretable dimensionality reduction of single cell transcriptome data with deep generative models
Interpretable dimensionality reduction of single cell transcriptome data with deep generative models
Although single-cell transcriptome data are increasingly available, their interpretation remains a challenge. Here, the authors present a dimensionality reduction approach that preserves both the local and global neighbourhood structures in the data thus enhancing its interpretability.
- Jiarui Ding
- , Anne Condon
- & Sohrab P. Shah
-
Article
| Open Access Native mass spectrometry combined with enzymatic dissection unravels glycoform heterogeneity of biopharmaceuticals
Native mass spectrometry combined with enzymatic dissection unravels glycoform heterogeneity of biopharmaceuticals
The specific glycosylation patterns of biological drugs often impact the efficacy and safety of the therapeutic product. Here the authors describe a native mass spectrometry approach that allows the resolution of highly complex glycosylation patterns on large proteins, which they apply to the therapeutic Fc-fusion protein Etanercept.
- Therese Wohlschlager
- , Kai Scheffler
- & Christian G. Huber
-
Article
| Open Access BEARscc determines robustness of single-cell clusters using simulated technical replicates
BEARscc determines robustness of single-cell clusters using simulated technical replicates
Single cell messenger RNAseq allows the study of heterogeneity in tissue samples. Here the authors present BEARscc, a tool that uses RNA spike-in controls to simulate experiment-specific technical replicates to estimate the robustness of computational predictions of subpopulations of cells.
- D. T. Severson
- , R. P. Owen
- & B. Schuster-Böckler
-
Article
| Open Access A browser-based tool for visualization and analysis of diffusion MRI data
A browser-based tool for visualization and analysis of diffusion MRI data
Data sharing is an important component of reproducible research, but meaningful data sharing can be difficult. Here authors describe a new open source tool, AFQ-Browser, that builds an interactive website allowing visualization and exploratory data analysis of published diffusion MRI data.
- Jason D. Yeatman
- , Adam Richie-Halford
- & Ariel Rokem
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying noncoding risk variants using disease-relevant gene regulatory networks
Identifying noncoding risk variants using disease-relevant gene regulatory networks
Current methods for prioritization of non-coding genetic risk variants are based on sequence and chromatin features. Here, Gao et al. develop ARVIN, which predicts causal regulatory variants using disease-relevant gene-regulatory networks, and validate this approach in reporter gene assays.
- Long Gao
- , Yasin Uzun
- & Kai Tan
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular basis of phosphite and hypophosphite recognition by ABC-transporters
The molecular basis of phosphite and hypophosphite recognition by ABC-transporters
Some bacteria can use inorganic phosphite and hypophosphite as sources of inorganic phosphorus. Here, the authors report crystal structures of the periplasmic proteins that bind these reduced phosphorus species and show that a P-H…π interaction between the ligand and binding site determines their specificity.
- Claudine Bisson
- , Nathan B. P. Adams
- & Andrew Hitchcock
-
Article
| Open Access Algorithm for post-clustering curation of DNA amplicon data yields reliable biodiversity estimates
Algorithm for post-clustering curation of DNA amplicon data yields reliable biodiversity estimates
A central problem in biodiversity estimation from genetic markers is the ability of algorithms to retain ‘true’ species while discarding artefacts. Here, the authors present a new post-clusturing curation algorithm using OTU co-occurrences to estimate plant biodiversity from soil samples.
- Tobias Guldberg Frøslev
- , Rasmus Kjøller
- & Anders Johannes Hansen
-
Article
| Open Access pGlyco 2.0 enables precision N-glycoproteomics with comprehensive quality control and one-step mass spectrometry for intact glycopeptide identification
pGlyco 2.0 enables precision N-glycoproteomics with comprehensive quality control and one-step mass spectrometry for intact glycopeptide identification
Protein glycosylation is a heterogeneous post-translational modification that generates greater proteomic diversity that is difficult to analyze. Here the authors describe pGlyco 2.0, a workflow for the precise one step identification of intact N-glycopeptides at the proteome scale.
- Ming-Qi Liu
- , Wen-Feng Zeng
- & Peng-Yuan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative 3D analysis of complex single border cell behaviors in coordinated collective cell migration
Quantitative 3D analysis of complex single border cell behaviors in coordinated collective cell migration
Quantifying cell behavioursin vivo is essential to understanding the mechanisms of collective cell migration. Here the authors present an image analysis toolkit, CCMToolKit, to describe and characterize various modes of coordinated cell movements accompanying collective cell migration in Drosophilaborder cells.
- Adam Cliffe
- , David P. Doupé
- & Weimiao Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Production of individualized V gene databases reveals high levels of immunoglobulin genetic diversity
Production of individualized V gene databases reveals high levels of immunoglobulin genetic diversity
Current databases of V genes for antibody repertoire have limitations. Here Corcoran et al. develop a computational approach named IgDiscover that can identify germline V gene sequences from expressed antibody repertoires to high specificity and completeness.
- Martin M. Corcoran
- , Ganesh E. Phad
- & Gunilla B. Karlsson Hedestam
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring time derivatives including cell growth rates using Gaussian processes
Inferring time derivatives including cell growth rates using Gaussian processes
High-throughput time-series data is increasingly available, yet estimating time-derivatives from such data can remain a challenge. Here, the authors provide a non-parametric method for inferring the first and second time-derivatives from multiple replicates of time-series data and for estimating errors in this inference and in any summary statistics.
- Peter S. Swain
- , Keiran Stevenson
- & Teuta Pilizota
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-marker association method for genome-wide association studies without the need for population structure correction
A multi-marker association method for genome-wide association studies without the need for population structure correction
Currently available methods for phenotype to genetic markers association need to account for population structure. Here, Klasen et al. devise a statistical method called Quantitative Trait Cluster Association Test (QTCAT) that overcomes the need for population structure correction.
- Jonas R. Klasen
- , Elke Barbez
- & Korbinian Schneeberger
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic identification of protein combinations mediating chromatin looping
Systematic identification of protein combinations mediating chromatin looping
The formation of chromatin loops is mainly mediated by DNA-binding proteins (DBPs) that bind to the interacting sites and form complexes in 3D space. Here, Zhang et al.present an algorithm integrating ChIP-seq and Hi-C data to systematically identify both the 1D- and 3D-cooperation between DBPs.
- Kai Zhang
- , Nan Li
- & Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate spike estimation from noisy calcium signals for ultrafast three-dimensional imaging of large neuronal populations in vivo
Accurate spike estimation from noisy calcium signals for ultrafast three-dimensional imaging of large neuronal populations in vivo
Two-photon laser scanning microscopy allows functional calcium imaging of large neuronal populations in vivo, but the recorded signals typically suffer from low signal to noise. Here the authors develop an algorithm, MLspike, which estimates action potentials from noisy calcium signals, and benchmark it against existing methods.
- Thomas Deneux
- , Attila Kaszas
- & Ivo Vanzetta
-
Article
| Open Access RNA editing generates cellular subsets with diverse sequence within populations
RNA editing generates cellular subsets with diverse sequence within populations
RNA editing rate detected from bulk RNA-seq data can vary widely. Here, by constructing a hierarchical Bayesian model, the authors report substantial variance in editing signatures detected by RNA-seq data from both single cells and a cognate bulk sample.
- Dewi Harjanto
- , Theodore Papamarkou
- & Anastasia Papavasiliou
-
Article
| Open Access RUBIC identifies driver genes by detecting recurrent DNA copy number breaks
RUBIC identifies driver genes by detecting recurrent DNA copy number breaks
Analysis of cancer genome sequencing data has been used to predict genes associated with the pathogenesis of cancer. Here, the authors propose a new algorithm entitled RUBIC that predicts breaks in DNA as opposed to previously published methods that predict amplifications and deletions of DNA.
- Ewald van Dyk
- , Marlous Hoogstraat
- & Lodewyk F. A. Wessels

 Computer vision for pattern detection in chromosome contact maps
Computer vision for pattern detection in chromosome contact maps