Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access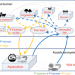 The shift of phosphorus transfers in global fisheries and aquaculture
The shift of phosphorus transfers in global fisheries and aquaculture
Despite growing aquaculture production and environmental concerns on phosphorus (P) enrichment, the P budgets of fisheries have been largely overlooked. Here, Huang et al. calculate global fishery P budgets and estimate P use efficiency for a wide range of aquaculture systems.
- Yuanyuan Huang
- , Phillipe Ciais
- & Haicheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access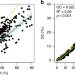 Improved estimates on global carbon stock and carbon pools in tidal wetlands
Improved estimates on global carbon stock and carbon pools in tidal wetlands
Wetlands are global hotspots of carbon storage, but errors exist with current estimates of the extent of their carbon density. Here the authors show that mangrove sediment organic carbon stock has previously been overestimated, while ecosystem carbon stock has been underestimated.
- Xiaoguang Ouyang
- & Shing Yip Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of bilaterian-type through-guts in cloudinomorphs from the terminal Ediacaran Period
Discovery of bilaterian-type through-guts in cloudinomorphs from the terminal Ediacaran Period
Cloudinomorphs were one of the few groups to survive from the Ediacaran into the Cambrian, but they are known only from their external tubes. Here, Schiffbauer et al. report soft-tissue preservation of cloudinomorphs; the internal structures are interpreted as guts characteristic of bilaterians.
- James D. Schiffbauer
- , Tara Selly
- & Emily F. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Ocean Carbon Storage across the middle Miocene: a new interpretation for the Monterey Event
Ocean Carbon Storage across the middle Miocene: a new interpretation for the Monterey Event
In this study, the authors use planktic foraminiferal data to reconstruct ocean carbonate chemistry and temperature from 16.5 to 11 Ma from a size in the tropical eastern Indian Ocean to look at the causes of the Monterey Excursion (ME). They find a positive relationship between dissolved inorganic (DIC) carbon and the ME and a negative one for DIC and the carbon maxima events.
- S. M. Sosdian
- , T. L. Babila
- & C. H. Lear
-
Article
| Open Access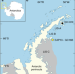 Microbial Fe(III) reduction as a potential iron source from Holocene sediments beneath Larsen Ice Shelf
Microbial Fe(III) reduction as a potential iron source from Holocene sediments beneath Larsen Ice Shelf
Recent recession of the Larsen Ice Shelf C has revealed that microbial alteration of illite can occur within marine sediments, a process previously thought to only occur abiotically during low-grade metamorphism. Here, the authors show that such microbial alteration of illite could provide a potential source of Fe release to Southern Ocean waters during Holocene glacial cycles.
- Jaewoo Jung
- , Kyu-Cheul Yoo
- & Jinwook Kim
-
Article
| Open Access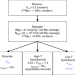 New isotope constraints on the Mg oceanic budget point to cryptic modern dolomite formation
New isotope constraints on the Mg oceanic budget point to cryptic modern dolomite formation
Earth’s carbon cycle and oceanic magnesium cycle are controlled by processes such as weathering, volcanism and precipitation of carbonates, such as dolomite. Here, the authors contradict the view that modern dolomite formation is rare and suggest instead that dolomite accounts for ~40–60% of the global oceanic Mg output in the last 20 Ma.
- Netta Shalev
- , Tomaso R. R. Bontognali
- & Derek Vance
-
Article
| Open Access Tropical carbon sink accelerated by symbiotic dinitrogen fixation
Tropical carbon sink accelerated by symbiotic dinitrogen fixation
The contribution of symbiotic dinitrogen fixation to the forest carbon sink could change throughout forest succession. Here the authors model nitrogen cycling and light competition between trees based on data from Panamanian forest plots, showing that fixation contributes substantially to the carbon sink in early successional stages.
- Jennifer H. Levy-Varon
- , Sarah A. Batterman
- & Lars O. Hedin
-
Article
| Open Access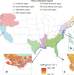 Tidal wetland resilience to sea level rise increases their carbon sequestration capacity in United States
Tidal wetland resilience to sea level rise increases their carbon sequestration capacity in United States
It remains challenging to estimate carbon accumulation rates in tidal wetlands on a scale as large as the conterminous US. Here, the authors find that mean C accumulation rates vary greatly among watershed regions but not among vegetation types, and that tidal wetlands’ C sequestration capability will remain or increase by 2100, suggesting a resilience to sea level rise.
- Faming Wang
- , Xiaoliang Lu
- & Jianwu Tang
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to ‘Pseudoreplication and greenhouse-gas emissions from rivers'
- Sophie A. Comer-Warner
- , Paul Romeijn
- & Stefan Krause
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessPseudoreplication and greenhouse-gas emissions from rivers
- Scott D. Tiegs
- & Thomas Raffel
-
Comment
| Open Access Integrating hydrology and biogeochemistry across frozen landscapes
Integrating hydrology and biogeochemistry across frozen landscapes
As climate change thaws the Arctic’s foundations, new subterranean waterways form and threaten to wash away and decompose carbon once locked in permafrost. In this Comment, Vonk and co-authors outline a cross-disciplinary strategy--with hydrology at the forefront--to better understand the fate of Arctic carbon.
- J. E. Vonk
- , S. E. Tank
- & M. A. Walvoord
-
Article
| Open Access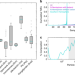 Highly variable iron content modulates iceberg-ocean fertilisation and potential carbon export
Highly variable iron content modulates iceberg-ocean fertilisation and potential carbon export
Iron is critical for fueling marine primary productivity, but its concentration is often vanishingly low in the ocean. Here, the authors show that though icebergs serve as vehicles delivering the largest supply of iron to polar oceans, the amount of iron they carry varies widely.
- Mark J. Hopwood
- , Dustin Carroll
- & Humberto E. González
-
Article
| Open Access Abiotic synthesis of graphite in hydrothermal vents
Abiotic synthesis of graphite in hydrothermal vents
Deciphering the origin, age, and composition of deep marine organic carbon remains a challenge for understanding the dynamics of the marine carbon cycle. Here, the authors identify (sub)micron-sized graphite emanating from both high and low temperature hydrothermal vents along the East Pacific Rise, and suggest graphite is a source of old carbon in the deep ocean.
- Emily R. Estes
- , Debora Berti
- & George W. Luther III
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of priming effect by soil organic matter stability over a broad geographic scale
Regulation of priming effect by soil organic matter stability over a broad geographic scale
Global soil carbon dynamics are regulated by the modification of soil organic matter (SOM) decomposition by plant carbon input (priming effect). Here, the authors collect soil data along a 2200 km grassland transect on the Tibetan Plateau and find that SOM stability is the major control on priming effect.
- Leiyi Chen
- , Li Liu
- & Yuanhe Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Global mycorrhizal plant distribution linked to terrestrial carbon stocks
Global mycorrhizal plant distribution linked to terrestrial carbon stocks
Mycorrhizas—mutualistic relationships formed between fungi and most plant species—are functionally linked to soil carbon stocks. Here the authors map the global distribution of mycorrhizal plants and quantify links between mycorrhizal vegetation patterns and terrestrial carbon stocks.
- Nadejda A. Soudzilovskaia
- , Peter M. van Bodegom
- & Leho Tedersoo
-
Article
| Open Access Isotopic composition of oceanic dissolved black carbon reveals non-riverine source
Isotopic composition of oceanic dissolved black carbon reveals non-riverine source
Rivers are thought to be the largest source of the recalcitrant and abundant black carbon in the ocean. Here, Wagner and colleagues find distinct pools of black carbon between rivers and the open ocean, challenging the long-held assumption that marine black carbon is of terrestrial origin.
- Sasha Wagner
- , Jay Brandes
- & Aron Stubbins
-
Article
| Open Access Minimal biomass deposition in banded iron formations inferred from organic matter and clay relationships
Minimal biomass deposition in banded iron formations inferred from organic matter and clay relationships
Banded iron formations could have formed in the early oceans due to microbial metabolism. Here Dodd and colleagues find little organic carbon in these formations, indicating microbial iron cycling was minimal and could have limited the recycling of important nutrients to overlying waters.
- Matthew S. Dodd
- , Dominic Papineau
- & Juha A. Karhu
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonal dynamics of stem N2O exchange follow the physiological activity of boreal trees
Seasonal dynamics of stem N2O exchange follow the physiological activity of boreal trees
Forest soil is known to be a source of the greenhouse gas N2O, but the impact of what is planted in that soil has long been overlooked. Here Machacova and colleagues quantify seasonal N2O fluxes from common boreal tree species in Finland, finding that all trees are net sources of this gas.
- Katerina Machacova
- , Elisa Vainio
- & Mari Pihlatie
-
Article
| Open Access Rice production threatened by coupled stresses of climate and soil arsenic
Rice production threatened by coupled stresses of climate and soil arsenic
Current projections on rice production do not consider the coupled stresses of impending climate change and the toxin arsenic in paddy soils. Here, the authors examined potential compounding impacts of soil arsenic and a changing climate on rice production and show that climate-induced changes in soil arsenic behaviour and plant response will lead to currently unforeseen losses in paddy rice grain productivity and quality.
- E. Marie Muehe
- , Tianmei Wang
- & Scott Fendorf
-
Article
| Open Access Soil net nitrogen mineralisation across global grasslands
Soil net nitrogen mineralisation across global grasslands
Nitrogen mineralisation (Nmin), an important index of soil fertility, is often determined in the laboratory, with an uncertain relationship to Nmin under field conditions. Here the authors show that combining laboratory measurements with environmental data greatly improves predictions of field Nmin at a global scale.
- A. C. Risch
- , S. Zimmermann
- & B. Moser
-
Article
| Open Access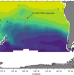 The interplay between regeneration and scavenging fluxes drives ocean iron cycling
The interplay between regeneration and scavenging fluxes drives ocean iron cycling
Iron is crucial for marine photosynthesis, but observational constraints on the magnitude of key iron cycle processes are lacking. Here the authors use a range of observational data sets to demonstrate that the balance between iron re-supply and removal in the subsurface controls upper ocean iron limitation.
- Alessandro Tagliabue
- , Andrew R. Bowie
- & Philip W. Boyd
-
Article
| Open Access Constraining the rise of oxygen with oxygen isotopes
Constraining the rise of oxygen with oxygen isotopes
The loss of anomalous sulfur isotope compositions from sedimentary rocks has been considered a symptom of permanent atmospheric oxygenation. Here the authors show sulfur and oxygen isotope evidence from < 2.31 Ga sedimentary barium sulphates (barites) from the Turee Creek Basin, W. Australia, demonstrating the influence of local non-atmospheric processes on anomalous sulfur isotope signals.
- B. A. Killingsworth
- , P. Sansjofre
- & S. V. Lalonde
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected large evasion fluxes of carbon dioxide from turbulent streams draining the world’s mountains
Unexpected large evasion fluxes of carbon dioxide from turbulent streams draining the world’s mountains
Freshwater systems are important components of the carbon cycle, but the extent of their role in CO2 fluxes is poorly understood. Here Horgby and colleagues show that mountain streams are a surprisingly large source of CO2 to the atmosphere, with annual emissions that belie their spatial extent.
- Åsa Horgby
- , Pier Luigi Segatto
- & Tom J. Battin
-
Article
| Open Access Lake sedimentary biogenic silica from diatoms constitutes a significant global sink for aluminium
Lake sedimentary biogenic silica from diatoms constitutes a significant global sink for aluminium
Diatoms drive biogeochemical cycling of aluminum by incorporating this element into their shells, but this process has not been quantified in freshwater systems. Here the authors quantify diatom-mediated aluminum fluxes in lakes and determine that they rival the aluminum sink in the global ocean.
- Dong Liu
- , Peng Yuan
- & Wenxiao Fan
-
Review Article
| Open Access The importance of Antarctic krill in biogeochemical cycles
The importance of Antarctic krill in biogeochemical cycles
Swarms of crustaceans called krill dominate Antarctic ecosystems, yet their influence on biogeochemical cycles remains a mystery. Here Cavan and colleagues review the role of krill in the Southern Ocean, and the impact of the krill fishery on ocean fertilisation and the carbon sink.
- E. L. Cavan
- , A. Belcher
- & P. W. Boyd
-
Article
| Open Access Timing and origin of natural gas accumulation in the Siljan impact structure, Sweden
Timing and origin of natural gas accumulation in the Siljan impact structure, Sweden
Fractured rocks of impact craters have been suggested to be suitable hosts for deep microbial communities on Earth, and potentially other terrestrial planets, yet direct evidence remains elusive. Here, the authors show that the Siljan impact structure is host to long-term deep methane-cycling microbial activity.
- Henrik Drake
- , Nick M. W. Roberts
- & Mats E. Åström
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to ‘Wiggle-match radiocarbon dating of the Taupo eruption’
Reply to ‘Wiggle-match radiocarbon dating of the Taupo eruption’
- Richard N. Holdaway
- , Brendan Duffy
- & Ben Kennedy
-
Article
| Open Access Marine nitrogen fixers mediate a low latitude pathway for atmospheric CO2 drawdown
Marine nitrogen fixers mediate a low latitude pathway for atmospheric CO2 drawdown
Iron fertilisation of the high latitude oceans is a well-established biological mechanism to explain the ice age drawdown of atmospheric CO2, yet modelling has so far struggled to account for a sufficient drawdown via this mechanism. Here, the authors propose that N2 fixers, which inhabit the lower latitude ocean, made a significant contribution to CO2 drawdown and so amplified the global response to iron fertilisation during ice ages.
- Pearse J. Buchanan
- , Zanna Chase
- & Nathaniel L. Bindoff
-
Article
| Open Access Global ocean methane emissions dominated by shallow coastal waters
Global ocean methane emissions dominated by shallow coastal waters
The ocean emits the greenhouse gas methane, but its vastness renders estimations challenging. Here the authors use machine learning to map global ocean methane fluxes, finding a disproportionate contribution from shallow coastal waters, and a link between primary production and methane cycling.
- Thomas Weber
- , Nicola A. Wiseman
- & Annette Kock
-
Article
| Open Access Organic sulfur was integral to the Archean sulfur cycle
Organic sulfur was integral to the Archean sulfur cycle
Marine chemistry during the Early Earth (over 2.7 billion years ago) is commonly inferred to have been inorganically sulfate-reducing. Here, the authors argue that organic sulfur cycling may have played a previously unrecognized, yet important, role in the formation of ancient Archean marine sulfides.
- Mojtaba Fakhraee
- & Sergei Katsev
-
Article
| Open Access Archaeal lipid biomarker constraints on the Paleocene-Eocene carbon isotope excursion
Archaeal lipid biomarker constraints on the Paleocene-Eocene carbon isotope excursion
The Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (c. 55 million years ago) was a period associated with massive carbon injection into the atmosphere, yet discrepancies in carbon isotope proxy records have led to substantial uncertainties in the source, scale, and timing of carbon emissions. Here, the authors propose that membrane lipids of marine planktonic archaea can reliably record the carbon isotope excursion and surface ocean warming, giving a new constraint for the source and size of the PETM carbon emissions.
- Felix J. Elling
- , Julia Gottschalk
- & Ann Pearson
-
Article
| Open Access The role of marine sediment diagenesis in the modern oceanic magnesium cycle
The role of marine sediment diagenesis in the modern oceanic magnesium cycle
The oceanic magnesium cycle is closely linked to Earth’s carbon cycle and long-term climate change, due to processes such as continental weathering and authigenic mineral formation. Here, the authors update the global oceanic magnesium budget by quantifying the flux of magnesium from oceans to marine sediments and the associated isotopic fractionation.
- Richard D. Berg
- , Evan A. Solomon
- & Fang-Zhen Teng
-
Article
| Open Access Mesophilic microorganisms build terrestrial mats analogous to Precambrian microbial jungles
Mesophilic microorganisms build terrestrial mats analogous to Precambrian microbial jungles
Microbes venturing onto land could have impacted biogeochemical cycles billions of years before terrestrial plants, but insight into this process on ancient Earth has remained elusive. With the discovery and analysis of microbial mats analogous to those of the Precambrian, Finke and colleagues infer how these microbial jungles likely shaped ecology and climate.
- N. Finke
- , R. L. Simister
- & S. A. Crowe
-
Article
| Open Access Reducing greenhouse gas emissions of Amazon hydropower with strategic dam planning
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions of Amazon hydropower with strategic dam planning
Some dams produce large amounts of GHGs and it is important to see whether future dams will satisfy sustainable energy goals. Here the authors estimate the range of GHG emission intensities expected for 351 proposed and 158 existing Amazon dams and find that existing Amazon hydropower reservoirs collectively emit 14 Tg CO2eq per year, and that if all proposed Amazon dams are built, annual emissions would increase 5-fold.
- Rafael M. Almeida
- , Qinru Shi
- & Alexander S. Flecker
-
Article
| Open Access Vegetation structural change since 1981 significantly enhanced the terrestrial carbon sink
Vegetation structural change since 1981 significantly enhanced the terrestrial carbon sink
There lacks systematic analysis on the importance of vegetation structural change in the global terrestrial carbon cycle. Here the authors conducted a multi-model comparison analysis and find that the increase in leaf area index has been responsible for 12.4% of the accumulated terrestrial carbon sink from 1981 to 2016.
- Jing M. Chen
- , Weimin Ju
- & Xuehe Lu
-
Article
| Open Access The paleoclimatic footprint in the soil carbon stock of the Tibetan permafrost region
The paleoclimatic footprint in the soil carbon stock of the Tibetan permafrost region
There was extensive degradation during the warm middle Holocene and permafrost area was reduced substantially. Here the authors synthesize data across the Tibetan permafrost region and find that paleoclimate is more important than modern climate in shaping current permafrost carbon distribution, and its importance increases with soil depth.
- Jinzhi Ding
- , Tao Wang
- & Lin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access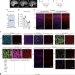 In vivo epigenetic editing of Sema6a promoter reverses transcallosal dysconnectivity caused by C11orf46/Arl14ep risk gene
In vivo epigenetic editing of Sema6a promoter reverses transcallosal dysconnectivity caused by C11orf46/Arl14ep risk gene
Although many neuropsychiatric risk genes are known to contribute to epigenetic regulation of gene expression, very little is known about specific chromatin-associated mechanisms that govern the formation and maintenance of neuronal connectivity. Here, the authors report that transcallosal connectivity is critically dependent on C11orf46/ARL14EP, a nuclear protein encoded in the chromosome 11p13 WAGR risk locus, and that RNA-guided epigenetic editing of hyperexpressed Sema6a gene promoters in C11orf46-knockdown neurons resulted in normalization of expression and rescue of transcallosal dysconnectivity via repressive chromatin remodeling.
- Cyril J. Peter
- , Atsushi Saito
- & Atsushi Kamiya
-
Article
| Open Access Marked isotopic variability within and between the Amazon River and marine dissolved black carbon pools
Marked isotopic variability within and between the Amazon River and marine dissolved black carbon pools
Black carbon produced by the burning of biomass and fuels is the most stable carbon compound in nature, yet its path from land to the deep ocean where it persists for thousands of years remains mysterious. Here Coppola and colleagues characterize the black carbon exported by the Amazon River, the largest river in the world.
- Alysha I. Coppola
- , Michael Seidel
- & Michael W. I. Schmidt
-
Perspective
| Open Access The future of Blue Carbon science
The future of Blue Carbon science
The role of Blue Carbon in climate change mitigation and adaptation has now reached international prominence. Here the authors identified the top-ten unresolved questions in the field and find that most questions relate to the precise role blue carbon can play in mitigating climate change and the most effective management actions in maximising this.
- Peter I. Macreadie
- , Andrea Anton
- & Carlos M. Duarte
-
Article
| Open Access Plant roots increase both decomposition and stable organic matter formation in boreal forest soil
Plant roots increase both decomposition and stable organic matter formation in boreal forest soil
Understanding mechanisms of soil organic matter (SOM) decomposition and stabilisation improves soil-climate feedback predictions. Here the authors show that roots in boreal forest promote organic nitrogen economy and provide a framework on how roots affect decomposition and stabilisation of SOM.
- Bartosz Adamczyk
- , Outi-Maaria Sietiö
- & Jussi Heinonsalo
-
Article
| Open Access Microscale pH variations during drying of soils and desert biocrusts affect HONO and NH3 emissions
Microscale pH variations during drying of soils and desert biocrusts affect HONO and NH3 emissions
The mechanisms that determine the composition of nitrogen gas emissions from soil remain unclear. A biocrust mechanistic model was developed to resolve puzzling dynamics of nitrous acid and ammonia emissions from drying soil pointing to previously unknown microscale pH zonation in thinning water films that affect soil biogeochemical fluxes.
- Minsu Kim
- & Dani Or
-
Article
| Open Access Significant contribution of metastable particulate organic matter to natural formation of silver nanoparticles in soils
Significant contribution of metastable particulate organic matter to natural formation of silver nanoparticles in soils
Silver nanoparticles are known environmental contaminants, however it is unclear whether they arise in soils through natural processes, anthropogenic processes, or both. Here Huang and colleagues offer fresh insight into the natural formation of these contaminants by soil particulate organic matter exposed to solar irradiation.
- Ying-Nan Huang
- , Ting-Ting Qian
- & Dong-Mei Zhou
-
Review Article
| Open Access Ice sheets matter for the global carbon cycle
Ice sheets matter for the global carbon cycle
Ice sheets have long been overlooked as regulators of the global carbon cycle. In this Review, Wadham and colleagues show how the growth and retreat of ice sheets support the productivity of the oceans and variably store or release organic carbon–in effect, these frozen landscapes must be considered in future assessments of climate impacts on biogeochemical cycling.
- J. L. Wadham
- , J. R. Hawkings
- & K. E. Kohfeld
-
Article
| Open Access Global subsoil organic carbon turnover times dominantly controlled by soil properties rather than climate
Global subsoil organic carbon turnover times dominantly controlled by soil properties rather than climate
The sensitivity of soil organic carbon (SOC) in subsoil (below 0.3 m) to climate change is poorly constrained. Here, the authors map global subsoil (0.3–1 m soil layer) SOC turnover times and find that temperature and in general climate effects are secondary to effects due to soil properties at both local and global scales—this now needs to be regarded for diagnosing subsoil SOC dynamics.
- Zhongkui Luo
- , Guocheng Wang
- & Enli Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Rainfall drives variation in rates of change in intrinsic water use efficiency of tropical forests
Rainfall drives variation in rates of change in intrinsic water use efficiency of tropical forests
How the water use efficiency of trees changes with atmospheric CO2 variations has mostly been studied on short time scales. Here, a newly compiled data set covering 1915 to 1995 shows how rates of change in water use efficiency vary with location and rainfall over the global tropics on a decadal scale.
- Mark A. Adams
- , Thomas N. Buckley
- & Tarryn L. Turnbull
-
Article
| Open Access Net carbon emissions from African biosphere dominate pan-tropical atmospheric CO2 signal
Net carbon emissions from African biosphere dominate pan-tropical atmospheric CO2 signal
Tropical land ecosystems contain vast carbon reservoirs, but their influence on atmospheric CO2 is poorly understood. Here the authors use new carbon-observing satellites to reveal a large emission source over northern tropical Africa, where there are large soil carbon stores and substantial land use changes.
- Paul I. Palmer
- , Liang Feng
- & Peter Somkuti
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial carbon use efficiency predicted from genome-scale metabolic models
Microbial carbon use efficiency predicted from genome-scale metabolic models
Microbial respiration releases carbon from the soil. Here, the authors estimate bacterial carbon use efficiency in soils for over 200 species using constraint-based modeling, incorporate the values into an ecosystem model, and find that shifts in community composition may impact carbon storage.
- Mustafa Saifuddin
- , Jennifer M. Bhatnagar
- & Adrien C. Finzi
-
Article
| Open Access Using B isotopes and B/Ca in corals from low saturation springs to constrain calcification mechanisms
Using B isotopes and B/Ca in corals from low saturation springs to constrain calcification mechanisms
Ocean acidification is expected to have a negative impact on calcifying organisms, however, our understanding of the acclimation potential of corals in their natural habit is currently limited. Here, the authors find that scleractinian corals living in high pCO2 conditions cannot fully adapt the chemistry of their internal calcifying fluid compared to corals growing in ambient conditions.
- M. Wall
- , J. Fietzke
- & A. Paytan
-
Article
| Open Access Manganese and iron deficiency in Southern Ocean Phaeocystis antarctica populations revealed through taxon-specific protein indicators
Manganese and iron deficiency in Southern Ocean Phaeocystis antarctica populations revealed through taxon-specific protein indicators
Low manganese availability could be a major control of phytoplankton growth in the Southern Ocean. Here the authors identify proteomic signatures of low manganese and iron availability in phytoplankton cultures and detect those signatures in Antarctic field samples.
- Miao Wu
- , J. Scott P. McCain
- & Erin M. Bertrand

 Earthquake slip surfaces identified by biomarker thermal maturity within the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake fault zone
Earthquake slip surfaces identified by biomarker thermal maturity within the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake fault zone