Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access γ-secretase directly sheds the survival receptor BCMA from plasma cells
γ-secretase directly sheds the survival receptor BCMA from plasma cells
B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) regulates the survival of B cells and is essential for the maintenance of long-lived plasma cells. Here, the authors show that γ-secretase directly sheds BCMA from the cell surface and therefore regulates the number of plasma cells.
- Sarah A. Laurent
- , Franziska S. Hoffmann
- & Edgar Meinl
-
Article |
 The CREB/CRTC2 pathway modulates autoimmune disease by promoting Th17 differentiation
The CREB/CRTC2 pathway modulates autoimmune disease by promoting Th17 differentiation
Multiple sclerosis is caused by autoreactive Th17 lymphocytes. Here the authors show that prostaglandin E2 promotes Th17 differentiation by activating transcription of IL-17 by CREB/CRTC2 complex, and that ablation of CRTC2 prevents Th17 differentiation and multiple sclerosis in a mouse model.
- Jeniffer B. Hernandez
- , Christina Chang
- & Marc Montminy
-
Article
| Open Access CD11c-mediated deletion of Flip promotes autoreactivity and inflammatory arthritis
CD11c-mediated deletion of Flip promotes autoreactivity and inflammatory arthritis
Dendritic cells are critical for initiation of immune responses and for induction of tolerance. Here the authors show that deletion of survival factor c-flip in CD11c-expressing cells subset perturbs CD8a+dendritic cell, NK and macrophage pools, and leads to development of autoimmune arthritis.
- Qi-Quan Huang
- , Harris Perlman
- & Richard M. Pope
-
Article |
 MiR-125a targets effector programs to stabilize Treg-mediated immune homeostasis
MiR-125a targets effector programs to stabilize Treg-mediated immune homeostasis
Compromised function of regulatory T cells can lead to autoimmunity. Here the authors show that miR-125a stabilizes regulatory T-cell function and is downregulated in lupus and Crohn’s disease, as well as autoimmune mouse models, and that a chemical miR-125a analogue reverts established disease in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.
- Wen Pan
- , Shu Zhu
- & Nan Shen
-
Article |
 Absence of surrogate light chain results in spontaneous autoreactive germinal centres expanding VH81X-expressing B cells
Absence of surrogate light chain results in spontaneous autoreactive germinal centres expanding VH81X-expressing B cells
Self-reactive B cells producing autoantibodies are associated with autoimmune conditions. Here, the authors show that in mice lacking the surrogate light chain, which normally assembles with antibody heavy chain to form a pre-B-cell receptor, the autoantibody-producing cells derive from germinal centres.
- Ola Grimsholm
- , Weicheng Ren
- & Inga-Lill Mårtensson
-
Article |
 Enhanced meta-analysis and replication studies identify five new psoriasis susceptibility loci
Enhanced meta-analysis and replication studies identify five new psoriasis susceptibility loci
About 2% of the population are affected by psoriasis, a chronic skin disease with complex genetics. Here Tsoi et al.conduct a meta-analysis of several genome-wide association studies and identify five novel loci, helping to further our understanding of the biology behind this condition.
- Lam C. Tsoi
- , Sarah L. Spain
- & James T. Elder
-
Article |
 Crossreactivity to vinculin and microbes provides a molecular basis for HLA-based protection against rheumatoid arthritis
Crossreactivity to vinculin and microbes provides a molecular basis for HLA-based protection against rheumatoid arthritis
Autoantibodies targeting citrunillated proteins are common in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Here the authors show that vinculin (a human protein) and some microbial proteins are recognized by these antibodies and by CD4+T cells, and this response is absent in patients carrying a protective HLA allele.
- Jurgen van Heemst
- , Diahann T. S. L. Jansen
- & René E. Toes
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for binding of human IgG1 to its high-affinity human receptor FcγRI
Structural basis for binding of human IgG1 to its high-affinity human receptor FcγRI
FcγRs are cell-surface receptors for IgGs that play key roles in the humoral and cellular immune response to infection. Here, the authors present a high-resolution crystal structure of the hFcγRI-Fc complex to reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying the high specificity of this important immunological interaction.
- Masato Kiyoshi
- , Jose M.M. Caaveiro
- & Kouhei Tsumoto
-
Article |
 Manipulation of B-cell responses with histone deacetylase inhibitors
Manipulation of B-cell responses with histone deacetylase inhibitors
Histone deaceytelase inhibitors are used in the treatment of haematological malignancies but can also act as modulators of the immune system. Here, the authors show that histone deaceytelase inhibitors are capable of modulating B-cell functions leading to improved outcome in autoimmune conditions.
- Michaela Waibel
- , Ailsa J. Christiansen
- & Edwin D. Hawkins
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies multiple novel associations and ethnic heterogeneity of psoriasis susceptibility
Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies multiple novel associations and ethnic heterogeneity of psoriasis susceptibility
Psoriasis is a common inflammatory skin disease with complex genetics and different degrees of prevalence across ethnic populations. Here Yin et al. conduct a large trans-ethnic genome-wide meta-analysis and identify novel loci that contribute to population-specific susceptibility.
- Xianyong Yin
- , Hui Qi Low
- & Jianjun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access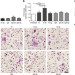 Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss
Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss
The IgG sugar moiety modulates the binding of immune complexes to their Fcγ receptors resulting in pro- or anti-inflammatory response. This study shows that IgG sialylation also affects osteoclastogenesis and bone mass in mice and humans, identifying a new link between bone and the immune system.
- Ulrike Harre
- , Stefanie C. Lang
- & Georg Schett
-
Article
| Open Access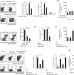 TGF-β3-expressing CD4+CD25−LAG3+ regulatory T cells control humoral immune responses
TGF-β3-expressing CD4+CD25−LAG3+ regulatory T cells control humoral immune responses
B cells reactive against self antigens can cause autoimmune disease, but are normally suppressed by regulatory T cells (Tregs). Here the authors show that a subset of Tregs can suppress lupus in a mouse model by making TGF-β3 cytokine and by engaging an inhibitory PD-1 receptor on B cells.
- Tomohisa Okamura
- , Shuji Sumitomo
- & Kazuhiko Yamamoto
-
Article |
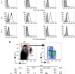 Targeting cell surface TLR7 for therapeutic intervention in autoimmune diseases
Targeting cell surface TLR7 for therapeutic intervention in autoimmune diseases
TLR7 triggers immune responses upon sensing microbial RNA, and its endosomal localization is thought to prevent TLR7 activation by host RNA. Here, Kanno et al. show that TLR7 is also present on the surface of immune cells, and that anti-TLR7 antibody can prevent TLR7-mediated autoimmunity.
- Atsuo Kanno
- , Natsuko Tanimura
- & Kensuke Miyake
-
Article |
 PD-L1hi B cells are critical regulators of humoral immunity
PD-L1hi B cells are critical regulators of humoral immunity
Follicular helper T cells promote antibody production by B cells, and regulatory B cells, in turn, can restrain T cell activation. Here, Khan et al. show that PD-L1 plays a critical role in regulatory B cell function, curbing excessive immune responses by engaging the PD-1 receptor on follicular helper T cells.
- Adnan R. Khan
- , Emily Hams
- & Padraic G. Fallon
-
Article |
 Genome-wide meta-analysis in alopecia areata resolves HLA associations and reveals two new susceptibility loci
Genome-wide meta-analysis in alopecia areata resolves HLA associations and reveals two new susceptibility loci
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune disease with a known genetic component. Here, the authors analyse 3,253 AA patients and 7,543 healthy controls, and identify two new risk loci and disrupted immune response pathways associated with the disease.
- Regina C. Betz
- , Lynn Petukhova
- & Angela M. Christiano
-
Article |
 The HLA-DRβ1 amino acid positions 11–13–26 explain the majority of SLE–MHC associations
The HLA-DRβ1 amino acid positions 11–13–26 explain the majority of SLE–MHC associations
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease with a complex genetic basis. Here the authors carry out a fine-mapping analysis of the major histocompatibility complex region and identify amino acids that have a causal role in SLE aetiology.
- Kwangwoo Kim
- , So-Young Bang
- & Sang-Cheol Bae
-
Article |
 The antimicrobial peptide LL37 is a T-cell autoantigen in psoriasis
The antimicrobial peptide LL37 is a T-cell autoantigen in psoriasis
LL37 is an antimicrobial peptide that is overexpressed in skin lesions from psoriasis patients and activates innate immunity. Here the authors show that CD4 and CD8 T cells specific for LL37 are present in the circulation of patients with psoriasis, produce inflammatory cytokines and correlate with disease activity.
- Roberto Lande
- , Elisabetta Botti
- & Loredana Frasca
-
Article
| Open Access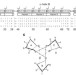 Structural basis of IL-23 antagonism by an Alphabody protein scaffold
Structural basis of IL-23 antagonism by an Alphabody protein scaffold
Protein scaffolds can serve as alternatives to antibodies in a range of applications. Here, the authors report the design and development of Alphabody™, a protein scaffold featuring a single-chain antiparallel triple-helix coiled-coil fold that the authors use to develop Alphabodies that can neutralize human IL-23 with high specificity and affinity.
- Johan Desmet
- , Kenneth Verstraete
- & Savvas N. Savvides
-
Article
| Open Access NAD+ protects against EAE by regulating CD4+ T-cell differentiation
NAD+ protects against EAE by regulating CD4+ T-cell differentiation
The mechanism by which NAD+ alters the systemic immune response is unclear. Here the authors show that NAD+ induces systemic homeostasis and protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a mouse model of multiple sclerosis, by regulating CD4+T cell differentiation and promoting myelin and axonal regeneration.
- Stefan G. Tullius
- , Hector Rodriguez Cetina Biefer
- & Abdallah ElKhal
-
Article |
 Multiple sclerosis-associated IL2RA polymorphism controls GM-CSF production in human TH cells
Multiple sclerosis-associated IL2RA polymorphism controls GM-CSF production in human TH cells
Genetic studies have connected polymorphisms in the IL-2 receptor alpha (IL2RA) gene with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis, but the mechanisms underlying this association are not clear. Here, the authors show that a polymorphism in IL2RA increases responsiveness to IL-2 and GM-CSF production in human THcells.
- Felix J. Hartmann
- , Mohsen Khademi
- & Burkhard Becher
-
Article |
 Shared VH1-46 gene usage by pemphigus vulgaris autoantibodies indicates common humoral immune responses among patients
Shared VH1-46 gene usage by pemphigus vulgaris autoantibodies indicates common humoral immune responses among patients
Pemphingus vulgaris is known to be caused by anti-desmoglein 3 autoantibodies, but how these antibodies arise is not clear. Here, the authors show that VH gene usage is shared among patients and that few or no somatic mutations are required for these autoantibodies to acquire autoreactivity.
- Michael Jeffrey Cho
- , Agnes S.Y. Lo
- & Aimee S. Payne
-
Article
| Open Access Restricted VH/VL usage and limited mutations in gluten-specific IgA of coeliac disease lesion plasma cells
Restricted VH/VL usage and limited mutations in gluten-specific IgA of coeliac disease lesion plasma cells
Coeliac disease is characterized by an inappropriate immune response to dietary gluten proteins, involving the production of antibodies reactive to gluten. Here, the authors study the intestinal antibody response against gluten and show that gluten-specific antibodies have a low degree of somatic hypermutations.
- Øyvind Steinsbø
- , Carole J. Henry Dunand
- & Ludvig M. Sollid
-
Article |
 The phosphatase JKAP/DUSP22 inhibits T-cell receptor signalling and autoimmunity by inactivating Lck
The phosphatase JKAP/DUSP22 inhibits T-cell receptor signalling and autoimmunity by inactivating Lck
JNK pathway-associated phosphatase (JKAP) is a dual-specificity phosphatase known to regulate substrates in several signalling cascades. Here, Li et al. demonstrate that JKAP has a key role in negative regulation of proximal T-cell receptor signalling and suppression of T-cell-mediated autoimmunity.
- Ju-Pi Li
- , Chia-Yu Yang
- & Tse-Hua Tan
-
Article |
 Bhlhe40 controls cytokine production by T cells and is essential for pathogenicity in autoimmune neuroinflammation
Bhlhe40 controls cytokine production by T cells and is essential for pathogenicity in autoimmune neuroinflammation
T cells that mediate neuroinflammation in EAE, a mouse model of multiple sclerosis, act through their production of cytokines. Here, the authors show that the transcription factor Bhlhe40 regulates the expression of GM-CSF and IL-10 by autoreactive T cells and is crucial for EAE induction.
- Chih-Chung Lin
- , Tara R. Bradstreet
- & Brian T. Edelson
-
Article |
 p85α recruitment by the CD300f phosphatidylserine receptor mediates apoptotic cell clearance required for autoimmunity suppression
p85α recruitment by the CD300f phosphatidylserine receptor mediates apoptotic cell clearance required for autoimmunity suppression
Apoptotic cell clearance is important for the maintenance of immune homeostasis. Here, Tian et al. reveal how a phosphatidylserine (PS) receptor participates in the clearance of apoptotic cells, and show that loss of the receptor can lead to autoimmunity.
- Linjie Tian
- , Seung-Chul Choi
- & John E. Coligan
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide mapping of gene–microbiota interactions in susceptibility to autoimmune skin blistering
Genome-wide mapping of gene–microbiota interactions in susceptibility to autoimmune skin blistering
The pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders afflicting the skin is multifactorial. Srinivas et al. show that diversity of the skin microbiota is a critical factor determining the susceptibility to epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, a chronic mucocutaneous autoimmune skin blistering disease.
- Girish Srinivas
- , Steffen Möller
- & Saleh M. Ibrahim
-
Article
| Open Access A chronic model of arthritis supported by a strain-specific periarticular lymph node in BALB/c mice
A chronic model of arthritis supported by a strain-specific periarticular lymph node in BALB/c mice
Mouse models of arthritis generally do not result in both chronic disease and autoantibody production—two key features of the human disease. Here the authors obtain both features by combining two common protocols, and find that disease severity is associated with the presence of a previously unidentified lymph node.
- Uta Baddack
- , Sven Hartmann
- & Gerd Müller
-
Article
| Open Access GRK6 deficiency in mice causes autoimmune disease due to impaired apoptotic cell clearance
GRK6 deficiency in mice causes autoimmune disease due to impaired apoptotic cell clearance
The clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages is important for tissue homoeostasis. Here Nakaya et al. reveal a role for GRK6 in the regulation of apoptotic engulfment and show that GRK6 deficiency in mice leads to autoimmune disease and iron accumulation in the spleen.
- Michio Nakaya
- , Mitsuru Tajima
- & Hitoshi Kurose
-
Article
| Open Access Genetics and the environment converge to dysregulate N-glycosylation in multiple sclerosis
Genetics and the environment converge to dysregulate N-glycosylation in multiple sclerosis
Complex diseases such as multiple sclerosis have both genetic and environmental components. This study demonstrates that variants of genes implicated in multiple sclerosis, and alterations in cellular metabolism and vitamin D3 levels, alterN-glycosylation, a post-translational modification causal of the disease in mice.
- Haik Mkhikian
- , Ani Grigorian
- & Michael Demetriou

 Neutralization and clearance of GM-CSF by autoantibodies in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Neutralization and clearance of GM-CSF by autoantibodies in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis