Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of acoustic spin transport in metasurface waveguides
Realization of acoustic spin transport in metasurface waveguides
Spin angular momenta play a crucial role in topological phases of matter, in acoustic waves they have been demonstrated recently. Here, the authors present a symmetry-breaking metasurface waveguide that assists backscattering suppression of acoustic waves, because of tight spin-momentum coupling.
- Yang Long
- , Danmei Zhang
- & Jie Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Vertical organic permeable dual-base transistors for logic circuits
Vertical organic permeable dual-base transistors for logic circuits
The development of vertical organic transistors with controllable threshold voltage is highly desirable for integrated circuit-based displays and sensors. Here, the authors report vertical organic permeable dual-based transistors with independently tunable on-currents and threshold voltages.
- Erjuan Guo
- , Zhongbin Wu
- & Hans Kleemann
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo localization of chronically implanted electrodes and optic fibers in mice
In vivo localization of chronically implanted electrodes and optic fibers in mice
Király et al. propose a method combining micro-CT and MRI imaging to precisely localize electrodes and optic fibers in the mouse brain in vivo. This allows assessing the success of targeting after surgery, depth adjustment of movable probes and identifying systematic errors in the surgical process.
- Bálint Király
- , Diána Balázsfi
- & Balázs Hangya
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial ultrasound modulation by digitally controlling microbubble arrays
Spatial ultrasound modulation by digitally controlling microbubble arrays
The authors introduce a dynamic spatial ultrasound modulator, based on digitally generated patterns of microbubbles controlled by a complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) chip. They achieve reshaping of incident plane waves into complex acoustic images and demonstrate dynamic parallel assembly of microparticles.
- Zhichao Ma
- , Kai Melde
- & Peer Fischer
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting output performance of sliding mode triboelectric nanogenerator by charge space-accumulation effect
Boosting output performance of sliding mode triboelectric nanogenerator by charge space-accumulation effect
Improving the output performance of sliding mode triboelectric nanogenerators is a great challenge. Herein, a space charge accumulation effect, based on alternating shielding and blank-tribo areas, is demonstrated and effectively promotes charge density output.
- Wencong He
- , Wenlin Liu
- & Chenguo Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially selective manipulation of cells with single-beam acoustical tweezers
Spatially selective manipulation of cells with single-beam acoustical tweezers
Acoustical tweezers can exert forces several orders of magnitude greater than optical tweezers but the absence of spatial selectivity and their limited resolution has prevented their use for many applications in microbiology. Here the authors perform spatially selective contactless manipulation and positioning of human cells.
- Michael Baudoin
- , Jean-Louis Thomas
- & Alexis Vlandas
-
Article
| Open Access Creation of acoustic vortex knots
Creation of acoustic vortex knots
Although knots in complex optical fields have been realized experimentally, the realization of acoustic vortex knots is still problematic. Here, the authors have demonstrated the creation of acoustic vortex knots by embedding the knot function into a propagating acoustic field using a metasurface hologram.
- Hongkuan Zhang
- , Weixuan Zhang
- & Xiangdong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving asymmetry and trapping in diffusion with spatiotemporal metamaterials
Achieving asymmetry and trapping in diffusion with spatiotemporal metamaterials
Being able to manipulate the temporal evolution and spatial distribution of diffusive quantities would provide exciting possibilities for applications. Here, the authors show that one can achieve large spatial asymmetric diffusion characteristics inside a metamaterial whose material parameters are space- and time-modulated.
- Miguel Camacho
- , Brian Edwards
- & Nader Engheta
-
Article
| Open Access An active mechanical Willis meta-layer with asymmetric polarizabilities
An active mechanical Willis meta-layer with asymmetric polarizabilities
Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate abilities of a mechanical Willis meta-layer, in beams and plates, for independently engineering transmission and reflection coefficients of flexural waves in both amplitude and phase and nonreciprocal wave propagation.
- Yangyang Chen
- , Xiaopeng Li
- & Guoliang Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic spin-Chern insulator induced by synthetic spin–orbit coupling with spin conservation breaking
Acoustic spin-Chern insulator induced by synthetic spin–orbit coupling with spin conservation breaking
In acoustic systems, quantum spin Hall physics is rarely observed because the crucial ingredient spin-orbit coupling is missing. Here, the authors construct an acoustic crystal with synthetic spin-orbit coupling and observe gapless helical boundary states as well as spin flipping effect.
- Weiyin Deng
- , Xueqin Huang
- & Zhengyou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Valley-locked waveguide transport in acoustic heterostructures
Valley-locked waveguide transport in acoustic heterostructures
Here, by constructing a heterostructure with sonic crystals, a topological waveguide is realized by the authors. The waveguide states feature gapless dispersion, momentum-valley locking, immunity against defects, and a high capacity for energy transport.
- Mudi Wang
- , Wenyi Zhou
- & Zhengyou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic cilia carpets with programmable metachronal waves
Magnetic cilia carpets with programmable metachronal waves
Synthetic hair-like structures (cilia) controlled by an external field have been developed, especially for microfluidic applications. Here, Gu et al. make soft artificial cilia carpets with programmable magnetization patterns and utilize them to achieve pumping and locomotion in a soft robotic model.
- Hongri Gu
- , Quentin Boehler
- & Bradley J. Nelson
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable photo-responsive elastic metamaterials
Tunable photo-responsive elastic metamaterials
Here, the authors present a light-responsive elastic metamaterial whose transmission spectrum can be tuned by light stimuli. More specifically, we demonstrate that an appropriate laser illumination is effective in reversibly widening an existing frequency band gap, doubling its initial value.
- Antonio S. Gliozzi
- , Marco Miniaci
- & Emiliano Descrovi
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of an acoustic octupole topological insulator
Observation of an acoustic octupole topological insulator
The concept of topological corner states in two dimensional topological insulators can be generalised to higher dimensions. Here, authors present a three dimensional acoustic metamaterial that exhibits the full hierarchy of topological multipole states including corner, hinge, surface and bulk states.
- Haoran Xue
- , Yong Ge
- & Baile Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrodynamic slip can align thin nanoplatelets in shear flow
Hydrodynamic slip can align thin nanoplatelets in shear flow
Current theories predict that a plate-like particle rotates continuously in a shear flow. Kamal et al. instead show that even nanometric hydrodynamic slip may induce a thin plate-like particle to adopt a stable orientation, and discuss implications of this effect for flow processing of 2D nanomaterials.
- Catherine Kamal
- , Simon Gravelle
- & Lorenzo Botto
-
Article
| Open Access Randomized resonant metamaterials for single-sensor identification of elastic vibrations
Randomized resonant metamaterials for single-sensor identification of elastic vibrations
Designing efficient and flexible metamaterial with uncorrelated transmissions for spatial vibration encoding and identification remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a randomized resonant metamaterial with randomly coupled local resonators for single-sensor identification of elastic vibrations.
- Tianxi Jiang
- , Chong Li
- & Zhi-Ke Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic analogues of three-dimensional topological insulators
Acoustic analogues of three-dimensional topological insulators
An acoustic analogue of a three-dimensional topological insulator (TI) has not been achieved, despite various realizations in other kinds of TIs. Here, the authors report a three-dimensional multi-order TI in an acoustic bilayer chiral structure, with robust surface or hinge sound transport.
- Cheng He
- , Hua-Shan Lai
- & Yan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a quantized acoustic octupole topological insulator
Demonstration of a quantized acoustic octupole topological insulator
Although multipole topological insulators have been theoretically described and experimentally observed in 2D, third-order topological insulators in 3D have not been observed yet. Here, the authors realize for the first time a quantized octupole 3D topological state in an acoustic metamaterial.
- Xiang Ni
- , Mengyao Li
- & Alexander B. Khanikaev
-
Article
| Open Access Noninvasive electromagnetic source imaging of spatiotemporally distributed epileptogenic brain sources
Noninvasive electromagnetic source imaging of spatiotemporally distributed epileptogenic brain sources
Noninvasive electromagnetic measurements are utilized effectively to estimate large scale dynamic brain networks. Sohrabpour et al. propose a novel electrophysiological source imaging approach to estimate the location and size of epileptogenic tissues in patients with epilepsy.
- Abbas Sohrabpour
- , Zhengxiang Cai
- & Bin He
-
Article
| Open Access Tactile sensory coding and learning with bio-inspired optoelectronic spiking afferent nerves
Tactile sensory coding and learning with bio-inspired optoelectronic spiking afferent nerves
Designing artificial somatosensory systems to efficiently emulate biological tactile information sensing, coding, and processing remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a tactile sensory system based on optoelectronic spiking afferent nerves with both coding and learning capabilities.
- Hongwei Tan
- , Quanzheng Tao
- & Sebastiaan van Dijken
-
Article
| Open Access Single-photon emission from single-electron transport in a SAW-driven lateral light-emitting diode
Single-photon emission from single-electron transport in a SAW-driven lateral light-emitting diode
Electron-spin to photon-polarisation conversion is a promising technology for achieving free-space or fibre coupled quantum transfer. Here, the authors demonstrate acoustically-driven single photons from single electrons, without the need for self-assembled quantum dots, using a SAW-driven lateral n-i-p junction.
- Tzu-Kan Hsiao
- , Antonio Rubino
- & Christopher J. B. Ford
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature terahertz anomalous Hall effect in Weyl antiferromagnet Mn3Sn thin films
Room-temperature terahertz anomalous Hall effect in Weyl antiferromagnet Mn3Sn thin films
Antiferromagnets promise great potential for spintronic applications due to their spin excitations at terahertz frequencies, however, read out of the spin state is hindered by the small response to external fields. Here the authors demonstrate all optical readout of the spin state of antiferromagnetic Mn3Sn at THz frequency.
- Takuya Matsuda
- , Natsuki Kanda
- & Ryusuke Matsunaga
-
Article
| Open Access Perovskite-molecule composite thin films for efficient and stable light-emitting diodes
Perovskite-molecule composite thin films for efficient and stable light-emitting diodes
The field of perovskite light-emitting diodes witnesses rapid development in both device processing strategies and performances. Here Wang et al. develop high-quality perovskite-molecule composite thin films and achieve high quantum efficiency of 17.3% and half-lifetime of 100 h.
- Heyong Wang
- , Felix Utama Kosasih
- & Feng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Supersymmetry in the time domain and its applications in optics
Supersymmetry in the time domain and its applications in optics
Supersymmetric quantum mechanics enables the description of phenomena exhibiting a supersymmetry only in the space domain. Here, the authors show an underlying time-domain supersymmetry exists in optics, acoustics, and elasticity, and study its properties and potential applicability.
- Carlos García-Meca
- , Andrés Macho Ortiz
- & Roberto Llorente Sáez
-
Article
| Open Access Dispersion tuning and route reconfiguration of acoustic waves in valley topological phononic crystals
Dispersion tuning and route reconfiguration of acoustic waves in valley topological phononic crystals
The valley degree of freedom gives additional flexibility to tunable phononic and photonic crystals. Here, the authors realise a honeycomb phononic structure where both the size of the cavities and of the air channel can be actively tuned, allowing several functionalities in a broad frequency range.
- Zhenhua Tian
- , Chen Shen
- & Tony Jun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the friction of atomically thin layered materials
Understanding the friction of atomically thin layered materials
Despite the fact that layered materials are often employed as lubricants, many of the underlying mechanisms are still controversial. Here the authors present a fundamental model for describing friction on atomically thin sheets that reveals the dynamics of strengthening and layer-number dependence of the friction.
- David Andersson
- & Astrid S. de Wijn
-
Article
| Open Access Holographic detection of nanoparticles using acoustically actuated nanolenses
Holographic detection of nanoparticles using acoustically actuated nanolenses
Detection of small, translucent particles is challenging due to their low inherent scattering. Here, the authors present an easy, high-throughput, label-free method for detecting nanoparticles in low volumes of liquids on a disposable chip, using an acoustically actuated lens-free holographic system.
- Aniruddha Ray
- , Muhammad Arslan Khalid
- & Aydogan Ozcan
-
Article
| Open Access Digitally virtualized atoms for acoustic metamaterials
Digitally virtualized atoms for acoustic metamaterials
Tuning the constitutive parameters of metamaterials in real time depends on the ability to modify the structure or external circuits attached to the metamaterials. Here, the authors propose virtualized metamaterials, allowing the tuning of acoustic parameters on-demand through software-defined frequency dispersion.
- Choonlae Cho
- , Xinhua Wen
- & Jensen Li
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetry-protected hierarchy of anomalous multipole topological band gaps in nonsymmorphic metacrystals
Symmetry-protected hierarchy of anomalous multipole topological band gaps in nonsymmorphic metacrystals
Higher-order topological phenomenologies are usually observed separately, with each system giving rise to a specific type of topological insulator. Here, the authors realise a nonsymmorphic acoustic metacrystal where the first and the second band gap host dipole and quadrupole topology respectively.
- Xiujuan Zhang
- , Zhi-Kang Lin
- & Jian-Hua Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution provided by the arbitrarily strong superlinearity of the blackbody radiation
Super-resolution provided by the arbitrarily strong superlinearity of the blackbody radiation
Here, the authors propose a new principle to achieve super-resolution for a wide class of targets. If an object is heated up by a beam, electromagnetic or acoustic, they show that the super-linearity of the induced thermal radiation leads to an arbitrarily high spatial compression factor relative to diffraction-limited beam profile.
- Guillaume Graciani
- & François Amblard
-
Article
| Open Access Taming out-of-equilibrium dynamics on interconnected networks
Taming out-of-equilibrium dynamics on interconnected networks
Network properties can be modified when they interact with other networks, yet most previous results have focused on equilibrium states exclusively. Here the authors introduce a framework to examine the out-of-equilibrium dynamics of evolutionary processes to mimic real-world interconnected networks.
- Javier M. Buldú
- , Federico Pablo-Martí
- & Jacobo Aguirre
-
Article
| Open Access Collective dynamics of strain-coupled nanomechanical pillar resonators
Collective dynamics of strain-coupled nanomechanical pillar resonators
Here, the authors demonstrate strain-induced, strong coupling between two adjacent nanomechanical pillar resonators for the investigation of collective dynamical phenomena. Both mode hybridization and the formation of an avoided level crossing in the response of the nanopillar pair are experimentally observed.
- J. Doster
- , S. Hoenl
- & E. M. Weig
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of a topological nodal surface and its surface-state arcs in an artificial acoustic crystal
Observation of a topological nodal surface and its surface-state arcs in an artificial acoustic crystal
Here, the authors report on the experimental observation of a twofold symmetry enforced topological nodal surface in a 3D chiral acoustic crystal. The demonstrated nodal surface carries a topological charge of 2, constituting the first realization of higher-dimensional topologically-charged band degeneracy.
- Yihao Yang
- , Jian-ping Xia
- & Baile Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access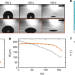 Wetting transitions in droplet drying on soft materials
Wetting transitions in droplet drying on soft materials
It has been shown previously that substrate viscoelasticity affects surface wettability. Here the authors observe a wetting transition during drying of droplets on such substrates and elucidate it with high resolution force field measurements thereby determining its dependence on substrate properties.
- Julia Gerber
- , Tobias Lendenmann
- & Dimos Poulikakos
-
Article
| Open Access Non-reciprocal robotic metamaterials
Non-reciprocal robotic metamaterials
Here, the authors demonstrate a robotic metamaterial implemented through a combination of actuators, sensors and local controllers. They show that this active metamaterial can exhibit tunable linear non-reciprocal dynamic characteristics, with a very large and broadband non-reciprocal gain.
- Martin Brandenbourger
- , Xander Locsin
- & Corentin Coulais
-
Article
| Open Access Dipole states and coherent interaction in surface-acoustic-wave coupled phononic resonators
Dipole states and coherent interaction in surface-acoustic-wave coupled phononic resonators
Here, the authors show the capability of a hybrid platform merging surface acoustic waves and coupled mechanical resonators, allowing in a reciprocal manner to coherently control the resonator motion and manipulate surface-acoustic-wave propagation at a sub-wavelength scale.
- Laetitia Raguin
- , Olivier Gaiffe
- & Sarah Benchabane
-
Article
| Open Access Sound-driven single-electron transfer in a circuit of coupled quantum rails
Sound-driven single-electron transfer in a circuit of coupled quantum rails
Surface acoustic waves are promising candidates to convey flying qubits through semiconductor circuits. The authors investigate the central building block of such a circuit in an experiment and present a route to realise quantum logic gates with flying electrons that are surfing on a sound-wave.
- Shintaro Takada
- , Hermann Edlbauer
- & Christopher Bäuerle
-
Article
| Open Access Tacticity in chiral phononic crystals
Tacticity in chiral phononic crystals
Here, the authors study the influence of tacticity on the dynamic behaviour of chiral structured periodic media comprising rotational inertia elements. This opens the way towards new mechanisms for wave control by exploiting spin-spin coupling mechanism.
- A. Bergamini
- , M. Miniaci
- & A. Zemp
-
Article
| Open Access Strong light-matter coupling for reduced photon energy losses in organic photovoltaics
Strong light-matter coupling for reduced photon energy losses in organic photovoltaics
Strong light-matter coupling can tune exciton properties but its effect in photovoltaics remains unexplored. Here Nikolis et al. show that the photon energy loss from optical gap to open-circuit voltage can be reduced to unprecedented values by embedding organic solar cells in optical microcavities.
- Vasileios C. Nikolis
- , Andreas Mischok
- & Koen Vandewal
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasonic super-oscillation wave-packets with an acoustic meta-lens
Ultrasonic super-oscillation wave-packets with an acoustic meta-lens
Here, the authors propose an ultrasonic meta-lens for generating super-oscillation wave packets with different spatial momenta and then superimposing them to a diffraction-limit-broken spot. They experimentally verify super-resolution ultrasound imaging of subwavelength objects.
- Ya-Xi Shen
- , Yu-Gui Peng
- & Xue-Feng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasound experiments on acoustical activity in chiral mechanical metamaterials
Ultrasound experiments on acoustical activity in chiral mechanical metamaterials
Here, the authors report an effect analogous to optical activity in a 3D mechanical micro-lattice composed of chiral unit cells. They spatiotemporally resolve the motion of metamaterial beams at ultrasonic frequencies with nanometric precision and show up to 22° polarization rotation per unit cell.
- Tobias Frenzel
- , Julian Köpfler
- & Martin Wegener
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic radiation pressure for nonreciprocal transmission and switch effects
Acoustic radiation pressure for nonreciprocal transmission and switch effects
Here, the authors experimentally report one-way transmission of ultrasonic waves by relying on the acoustic radiation pressure effect. This effect makes it possible to reconfigure a multilayer system by significantly deforming the water-air interface, achieving efficient nonreciprocal acoustic transmission.
- Thibaut Devaux
- , Alejandro Cebrecos
- & Vincent Tournat
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled open-cell two-dimensional liquid foam generation for micro- and nanoscale patterning of materials
Controlled open-cell two-dimensional liquid foam generation for micro- and nanoscale patterning of materials
Drying liquid foams can be used as a platform for bottom-up assembly of liquid-mediated materials, but there have been only a few utilizations to date due to the challenges in controlling fluidity. Bae et al. use a microfluidic approach to precisely control liquid foams for micro/nanoscale patterning.
- Juyeol Bae
- , Kyunghun Lee
- & Taesung Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic meta-atom with experimentally verified maximum Willis coupling
Acoustic meta-atom with experimentally verified maximum Willis coupling
Willis coupling is an additional degree of freedom, which can enhance acoustic metamaterials, by coupling monopole and dipole excitations. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate a meta-atom with Willis coupling approaching the theoretical maximum, which is robust to thermo-viscous losses.
- Anton Melnikov
- , Yan Kei Chiang
- & David Powell
-
Article
| Open Access Phononic integrated circuitry and spin–orbit interaction of phonons
Phononic integrated circuitry and spin–orbit interaction of phonons
Developing planar phononic circuits analogous to photonic circuits are of interest to provide scalable advantages and complex manipulation of phonons. Here, the authors realize a phononic integrated circuit with a Gallium Nitride-on-sapphire platform, which provides strong confinement and control of phonons.
- Wei Fu
- , Zhen Shen
- & Hong X. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access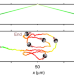 Diffusing wave paradox of phototactic particles in traveling light pulses
Diffusing wave paradox of phototactic particles in traveling light pulses
The amoebae Dictyostelium have previously been observed to migrate counter to the direction of a traveling chemical wave. Here the authors demonstrate that light-activated phototactic synthetic particles move counter to the pulse direction in a way which is reminiscent of the amoebae’s behavior.
- Celia Lozano
- & Clemens Bechinger
-
Article
| Open Access Simplicial models of social contagion
Simplicial models of social contagion
Social contagion cannot only be understood in terms of pairwise interactions among individuals. Here, the authors include higher-order social interactions, the effects of groups, in their model of social contagion, enabling insight into why critical masses are required to initiate social changes.
- Iacopo Iacopini
- , Giovanni Petri
- & Vito Latora
-
Article
| Open Access Reversal of transmission and reflection based on acoustic metagratings with integer parity design
Reversal of transmission and reflection based on acoustic metagratings with integer parity design
Phase gradient metagratings suffer from limits on conversion efficiency. Here, the authors show a refractive-type metagrating which can enable anomalous reflection and refraction with almost unity efficiency over a wide incident range and uncover how integer parity plays a role in higher order diffraction.
- Yangyang Fu
- , Chen Shen
- & Yadong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging gigahertz zero-group-velocity Lamb waves
Imaging gigahertz zero-group-velocity Lamb waves
Zero-group-velocity Lamb waves, which are surface waves with reduced losses and high Q factor, have many potential applications. The authors image such waves in 2 dimensions, and in the GHz range, with a bilayer using a time-resolved imaging technique with an ultra-short-pulse laser.
- Qingnan Xie
- , Sylvain Mezil
- & Oliver B. Wright

 Phase synchronization of fluid-fluid interfaces as hydrodynamically coupled oscillators
Phase synchronization of fluid-fluid interfaces as hydrodynamically coupled oscillators