Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Hermitian control between absorption and transparency in perfect zero-reflection magnonics
Non-Hermitian control between absorption and transparency in perfect zero-reflection magnonics
Absorption, transmission and reflection are three processes characterizing optical devices. Absorption allows for signal conversion and transmission is important for signal transfer, however, reflection is frequently detrimental to device performance. Here, Qian et al demonstrate a magnonic device with controllable absorption and transmission while maintain zero reflection.
- Jie Qian
- , C. H. Meng
- & C. -M. Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Discharge domains regulation and dynamic processes of direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator
Discharge domains regulation and dynamic processes of direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator
Arising from contact electrification and electrostatic breakdown, DC triboelectric nanogenerators are a promising solution to the air breakdown bottleneck in conventional TENGs. Here, authors reveal and regulate three discharge domains enhancing the device output power by an order of magnitude.
- Jiayue Zhang
- , Yikui Gao
- & Jie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Frictional fluid instabilities shaped by viscous forces
Frictional fluid instabilities shaped by viscous forces
Fingering patterns form spontaneously when a non-wetting viscous liquid displaces a dry granular mixture in a confined flow cell. The authors show how these patterns are controlled by the balance between viscous, capillary, and frictional forces.
- Dawang Zhang
- , James M. Campbell
- & Bjørnar Sandnes
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrabroadband sound control with deep-subwavelength plasmacoustic metalayers
Ultrabroadband sound control with deep-subwavelength plasmacoustic metalayers
Controlling audible sound requires inherently broadband and subwavelength acoustic solutions. Exploiting the unique physics of plasmacoustic metalayers, we experimentally demonstrate versatile and tunable sound control over a wide frequency range.
- Stanislav Sergeev
- , Romain Fleury
- & Hervé Lissek
-
Article
| Open Access Photoacoustic 2D actuator via femtosecond pulsed laser action on van der Waals interfaces
Photoacoustic 2D actuator via femtosecond pulsed laser action on van der Waals interfaces
Optical manipulation of nanomaterials usually requires fluidic environments or microfibers. Here, the authors report a pulsed laser-induced photoacoustic driving force able to overcome the van der Waals adhesion forces between 2D semimetallic nanosheets and insulating substrates.
- Xin Chen
- , Ivan M. Kislyakov
- & Jun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical overtone frequency combs
Mechanical overtone frequency combs
The authors combined optical traps and frequency combs to create new acoustic technology – a mechanical frequency comb. The generation of this comb does not require any precision control, making it uniquely positioned for sensing, metrology, and quantum technology.
- Matthijs H. J. de Jong
- , Adarsh Ganesan
- & Richard A. Norte
-
Article
| Open Access Minimal non-abelian nodal braiding in ideal metamaterials
Minimal non-abelian nodal braiding in ideal metamaterials
The authors constructed ideal acoustic metamaterials to realize non-abelian braiding of band nodes and provided the first compelling experimental evidence, at the wavefunction level, for the creation, collision, braiding, and repulsion of band nodes.
- Huahui Qiu
- , Qicheng Zhang
- & Chunyin Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Ideal acoustic quantum spin Hall phase in a multi-topology platform
Ideal acoustic quantum spin Hall phase in a multi-topology platform
Here the authors investigate a comprehensive topological phase diagram of bilayer hexagonal acoustic lattice, including ideal quantum spin Hall phase with gapless helical edge states. They realize a broadband topological slow wave.
- Xiao-Chen Sun
- , Hao Chen
- & Yan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access General duality and magnet-free passive phononic Chern insulators
General duality and magnet-free passive phononic Chern insulators
Understanding and controlling symmetry in nature is of paramount importance. In this work, the authors reveal an unexpected effect of the general duality relation between piezoelectricity and piezomagnetism on their symmetries, enabling novel phononic Chern insulators.
- Qicheng Zhang
- , Li He
- & A. T. Charlie Johnson
-
Article
| Open Access Classification of time-reversal-invariant crystals with gauge structures
Classification of time-reversal-invariant crystals with gauge structures
Projective representations of crystal symmetries are indispensable for understanding artificial crystals. Here, authors establish a unified theory of projective crystal symmetries with time-reversal invariance, and construct models for all 458 projective symmetry algebras for the 17 two-dimensional wallpaper groups.
- Z. Y. Chen
- , Zheng Zhang
- & Y. X. Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Physical deep learning with biologically inspired training method: gradient-free approach for physical hardware
Physical deep learning with biologically inspired training method: gradient-free approach for physical hardware
Traditional learning procedures for artificial intelligence rely on digital methods not suitable for physical hardware. Here, Nakajima et al. demonstrate gradient-free physical deep learning by augmenting a biologically inspired algorithm, accelerating the computation speed on optoelectronic hardware.
- Mitsumasa Nakajima
- , Katsuma Inoue
- & Kohei Nakajima
-
Article
| Open Access Self-charging electrostatic face masks leveraging triboelectrification for prolonged air filtration
Self-charging electrostatic face masks leveraging triboelectrification for prolonged air filtration
The decay of electrostatic charges largely reduces the protective efficacy of electret masks. Here, the authors report a triboelectrification-based self-charging electrostatic face mask with high airborne particle capture efficiency and prolonged stability.
- Zehua Peng
- , Jihong Shi
- & Zhengbao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Transient non-Hermitian skin effect
Transient non-Hermitian skin effect
In this work the authors uncover a transient non-Hermitian skin effect. Using a passive system, they confirm the exact evolution of NHSE by leveraging the complex-frequency excitation. This demonstration can be extended to other non-Hermitian phenomena in various passive systems.
- Zhongming Gu
- , He Gao
- & Jie Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access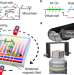 Rolling microswarms along acoustic virtual walls
Rolling microswarms along acoustic virtual walls
The application of rolling motion to microswarm navigation and cargo delivery has been constrained by the need for a physical boundary to roll along to date. Here, Zhang et al. solve this problem by introducing a reconfigurable virtual wall implemented by a combination of magnetic and acoustic fields.
- Zhiyuan Zhang
- , Alexander Sukhov
- & Daniel Ahmed
-
Article
| Open Access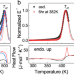 Highly tunable β-relaxation enables the tailoring of crystallization in phase-change materials
Highly tunable β-relaxation enables the tailoring of crystallization in phase-change materials
The crystallization of phase-change materials is relevant to their applications in memory and neuromorphic computing devices. Cheng et al. show that the β-relaxation in Ge15Sb85 can be controlled by thermal annealing, leading to the tunability in its crystallization kinetics by one order of magnitude.
- Yudong Cheng
- , Qun Yang
- & Shuai Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Shaping contactless radiation forces through anomalous acoustic scattering
Shaping contactless radiation forces through anomalous acoustic scattering
Here, the authors demonstrate that acoustic waves can actuate and guide large objects based on subwavelength meta-patterns on their surface.
- Matthew Stein
- , Sam Keller
- & Ognjen Ilic
-
Article
| Open Access A robot-assisted acoustofluidic end effector
A robot-assisted acoustofluidic end effector
Lab-on-a-chip systems have been widely used in microscale liquid manipulation and greatly benefit from automation. Durrer et al. show a robot-assisted acoustofluidic end effector system, comprising a robotic arm and an acoustofluidic device, that combines both robotic and microfluidic functionalities.
- Jan Durrer
- , Prajwal Agrawal
- & Daniel Ahmed
-
Article
| Open Access Common evolutionary origin of acoustic communication in choanate vertebrates
Common evolutionary origin of acoustic communication in choanate vertebrates
Here, the authors record acoustic communication in 53 species commonly considered non-vocal and reconstruct acoustic communication as originating 407 million years ago.
- Gabriel Jorgewich-Cohen
- , Simon William Townsend
- & Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra
-
Article
| Open Access Reduced rotational flows enable the translation of surface-rolling microrobots in confined spaces
Reduced rotational flows enable the translation of surface-rolling microrobots in confined spaces
The effect of geometrical confinement on the locomotion of microrobots is crucial to operating them in real-world applications. Bozuyuk et al. show that the locomotion efficiency of microrollers decreases in confined spaces at high rotation frequencies and propose a slender geometry to overcome this problem.
- Ugur Bozuyuk
- , Amirreza Aghakhani
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article
| Open Access Topological phononics arising from fluid-solid interactions
Topological phononics arising from fluid-solid interactions
Fluid-solid interaction, long investigated, is mostly neglected in topological acoustics. Here the authors find that it can give rise to intriguing topological phenomena in simple phononic crystals due to intrinsic differences between sound in fluid and solid.
- Xiaoxiao Wu
- , Haiyan Fan
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of boundary induced chiral anomaly bulk states and their transport properties
Observation of boundary induced chiral anomaly bulk states and their transport properties
Bulk and edge modes and their relation in topological materials is something researchers have been tried to harness for various applications. Here the authors provide a method to achieve chiral anomaly bulk states by applying boundary conditions to a topologically trivial crystal.
- Mudi Wang
- , Qiyun Ma
- & C. T. Chan
-
Comment
| Open AccessCritical aspects to enable viable solar-driven evaporative technologies for water treatment
While passive solar-driven evaporative systems promise higher economic and environmental sustainability in water treatment, many challenges remain for their effective adoption. Here, the author identifies three main pillars and corresponding issues which future research should focus on to bring these technologies to the next maturity level.
- Eliodoro Chiavazzo
-
Article
| Open Access Battery-free wireless imaging of underwater environments
Battery-free wireless imaging of underwater environments
The authors present an approach to underwater imaging, which does not require tethering or batteries. The low-power camera uses power from harvested acoustic energy and communicates colour images wirelessly via acoustic backscatter.
- Sayed Saad Afzal
- , Waleed Akbar
- & Fadel Adib
-
Article
| Open Access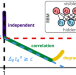 Three learning stages and accuracy–efficiency tradeoff of restricted Boltzmann machines
Three learning stages and accuracy–efficiency tradeoff of restricted Boltzmann machines
Restricted Boltzmann Machines are unsupervised machine learning model that have been applied for various tasks from image analysis to many-body physics. The authors elaborate the interplay of accuracy and efficiency of this model and define possible balance regimes for applications.
- Lennart Dabelow
- & Masahito Ueda
-
Article
| Open Access Metamaterial-based real-time communication with high information density by multipath twisting of acoustic wave
Metamaterial-based real-time communication with high information density by multipath twisting of acoustic wave
Here, the authors demonstrate multipath twisting of acoustic waves with a thin metamaterial layer enabling high-speed transfer of information with no time-consuming post-processing or sensor scanning, showing important application potential in underwater communication.
- Kai Wu
- , Jing-Jing Liu
- & Jian-Chun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Structured sonic tube with carbon nanotube-like topological edge states
Structured sonic tube with carbon nanotube-like topological edge states
Single-wall carbon nanotubes are made of carbon with diameters less than 100 nanometers. Here, the authors engineer an analogue tube with a diameter 1,000,000 times larger with the aim to explore topological properties including unusual acoustic edge states.
- Zhiwang Zhang
- , Penglin Gao
- & Johan Christensen
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven load profiles and the dynamics of residential electricity consumption
Data-driven load profiles and the dynamics of residential electricity consumption
In modern power grids, knowing the required electric power demand and its variations is necessary to balance demand and supply. The authors propose a data-driven approach to create high-resolution load profiles and characterize their fluctuations, based on recorded data of electricity consumption.
- Mehrnaz Anvari
- , Elisavet Proedrou
- & Marc Timme
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired asymmetric amphiphilic surface for triboelectric enhanced efficient water harvesting
Bioinspired asymmetric amphiphilic surface for triboelectric enhanced efficient water harvesting
The effective acquisition of clean water from atmospheric water offers a potential sustainable solution for increasing global water shortages. Here, authors developed a bioinspired asymmetric amphiphilic surface incorporating self-driven triboelectric adsorption to obtain clean water.
- Song Zhang
- , Mingchao Chi
- & Shuangxi Nie
-
Article
| Open Access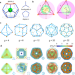 Topology mediates transport of nanoparticles in macromolecular networks
Topology mediates transport of nanoparticles in macromolecular networks
Macromolecular networks relevant for biological processes and technological applications, are often characterized by complex architectures. The authors uncover the impact of topology on the properties of nanoparticle transport in macromolecular networks.
- Xiaobin Dai
- , Xuanyu Zhang
- & Li-Tang Yan
-
Article
| Open Access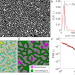 Structure induced laminar vortices control anomalous dispersion in porous media
Structure induced laminar vortices control anomalous dispersion in porous media
Most porous systems comprise structures characterized by dead-end and transmitting pores. Here, authors show that macroscopic transport through such porous medium is controlled by structure-induced laminar vortices inside each dead-end pore, and such cannot be explained by diffusion alone.
- Ankur Deep Bordoloi
- , David Scheidweiler
- & Pietro de Anna
-
Article
| Open Access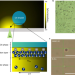 Investigating water/oil interfaces with opto-thermophoresis
Investigating water/oil interfaces with opto-thermophoresis
Charging of interfaces between water and hydrophobic media is a mysterious feature whose nature and origin remain under debate. Here, the authors use opto-thermophoretic tweezers to investigate the interfacial behavior at water/oil interfaces in terms of thermal perturbation of dipole arrangement.
- Youngsun Kim
- , Hongru Ding
- & Yuebing Zheng
-
Perspective
| Open Access A sound approach to advancing healthcare systems: the future of biomedical acoustics
A sound approach to advancing healthcare systems: the future of biomedical acoustics
Acoustic techniques are moving towards the clinic. Here the authors highlight recent developments in the areas of acoustic mechanobiology, point-of-care diagnostics, in vivo manipulation and tissues engineering, and provide their thoughts on the current challenges and directions for future work.
- Joseph Rufo
- , Peiran Zhang
- & Tony Jun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Underwater wireless communication via TENG-generated Maxwell’s displacement current
Underwater wireless communication via TENG-generated Maxwell’s displacement current
Underwater communication, despite constant development, still remains a challenging technology. Here, authors report an underwater wireless communication approach based on the triboelectric nanogenerator, which provides a self-powered communication system in complex underwater environments.
- Hongfa Zhao
- , Minyi Xu
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive detection of local acoustic vibrations at room temperature by plasmon-enhanced single-molecule fluorescence
Ultrasensitive detection of local acoustic vibrations at room temperature by plasmon-enhanced single-molecule fluorescence
.Sensitive detection of weak acoustic signals at nanometer scale is challenging. Here, the authors present an acoustic detection system based on a single molecule as a probe, where frequency and amplitude of acoustic vibrations can be extracted from its minute variations in distance to the surface of a plasmonic gold nanorod.
- Mingcai Xie
- , Hanyu Liu
- & Yuxi Tian
-
Article
| Open Access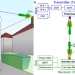 Jamming a terahertz wireless link
Jamming a terahertz wireless link
As wireless communications move towards terahertz frequencies, previously unidentified jamming vulnerabilities are revealed. Novel features not typically observed at lower frequencies are studied, including high directional attacks, beat jamming and asymmetric bit interference.
- Rabi Shrestha
- , Hichem Guerboukha
- & Daniel M. Mittleman
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile strategy for homogeneous drying patterns of dispersed particles
Versatile strategy for homogeneous drying patterns of dispersed particles
Coating technologies call for effective methods capable of suppressing the coffee-ring effect for a uniform particle deposition. Rey et al. show homogeneous drying patterns can be achieved via physically adsorbing polymers onto particle surfaces and the method is applicable to a wide range of materials regardless of the shape of the dispersed particles.
- Marcel Rey
- , Johannes Walter
- & Nicolas Vogel
-
Article
| Open Access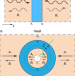 Heat transfer control using a thermal analogue of coherent perfect absorption
Heat transfer control using a thermal analogue of coherent perfect absorption
A thermal analogue of coherent perfect absorption would allow to control heat transfer using heat, but the lack of momentum propagation in a thermal field seems to prevent any role for coherence. Here, the authors allow this by introducing an imitated momentum for steady-state heat diffusion.
- Ying Li
- , Minghong Qi
- & Hongsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma-induced surface cooling
Plasma-induced surface cooling
When a plasma interacts with a surface, different thermal effects may arise. Here, the authors explore plasma interactions with a surface that produce a surface cooling effect.
- John A. Tomko
- , Michael J. Johnson
- & Patrick E. Hopkins
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinearity-mediated digitization and amplification in electromechanical phonon-cavity systems
Nonlinearity-mediated digitization and amplification in electromechanical phonon-cavity systems
Electromechanical phonon cavity systems offer advantages for solid state implementation, but thus far investigation has been limited to the linear regime. Here, Miao et al demonstrate non-linear operation of an electromechanical phonon cavity system and the drastic difference to the linear regime.
- Tongqiao Miao
- , Xin Zhou
- & Dingbang Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access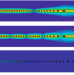 Investigating the upper bound of high-frequency electromagnetic waves on unshielded twisted copper pairs
Investigating the upper bound of high-frequency electromagnetic waves on unshielded twisted copper pairs
This paper establishes a physical limit on the ability of the ubiquitous twisted pairs to support high speed internet. This limit due to radiation from the wire is theoretically explained as well as numerically simulated and experimentally measured.
- Ergin Dinc
- , Syed Sheheryar Bukhari
- & Eloy de Lera Acedo
-
Article
| Open Access Brillouin Klein bottle from artificial gauge fields
Brillouin Klein bottle from artificial gauge fields
Topological states are exploited based on crystalline symmetry, but under artificial gauge fields, symmetries may satisfy projective algebras, which remains less studied. Here, the authors reveal that projective symmetry algebra leads to momentum-space nonsymmorphic symmetry, resulting in new topological states over a momentum-space Klein bottle.
- Z. Y. Chen
- , Shengyuan A. Yang
- & Y. X. Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Direct sound printing
Direct sound printing
Photo- and thermo-activated polymerization and melting processes are dominant in Additive Manufacturing (AM) while ultrasound activated sonochemical reactions have not been explored for AM so far. Here, the authors demonstrate 3D printing of structures using acoustic cavitation produced directly by focused ultrasound which creates sonochemical reactions in highly localized cavitation regions.
- Mohsen Habibi
- , Shervin Foroughi
- & Muthukumaran Packirisamy
-
Article
| Open Access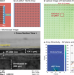 Lithium Niobate Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers for high data-rate intrabody communication
Lithium Niobate Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers for high data-rate intrabody communication
This paper demonstrates Lithium Niobate based Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers. The devices allow activation of multiple vibration modes, achieve a high communication link, and monitor an implanted medical device up to 13.5 cm inside the body.
- Flavius Pop
- , Bernard Herrera
- & Matteo Rinaldi
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-programmable analog differentiator
Meta-programmable analog differentiator
Here, the authors report purposefully perturbed wave chaos that enables analog signal processing with unprecedented fidelity and flexibility.
- Jérôme Sol
- , David R. Smith
- & Philipp del Hougne
-
Article
| Open Access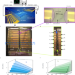 Amontons-Coulomb-like slip dynamics in acousto-microfluidics
Amontons-Coulomb-like slip dynamics in acousto-microfluidics
Acoustic waves can be used to manipulate particles and fluids in biomedical applications. The authors show that slip at the fluid-solid interface, characterized by a lower acoustic transmission into the fluid, is similar to Amontons-Coulomb friction, as found between solids.
- Aurore Quelennec
- , Jason J. Gorman
- & Darwin R. Reyes
-
Article
| Open Access Extended topological valley-locked surface acoustic waves
Extended topological valley-locked surface acoustic waves
Here the authors provide experimental evidence of extended topological valley-locked states. By splicing together Dirac semimetals and topological insulators, they demonstrate reduced backscattering and enhanced matching of SAW with interdigital transducers proposing this system for topological acoustics devices.
- Ji-Qian Wang
- , Zi-Dong Zhang
- & Yan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access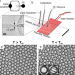 Acoustically manipulating internal structure of disk-in-sphere endoskeletal droplets
Acoustically manipulating internal structure of disk-in-sphere endoskeletal droplets
Endoskeletal droplets are a class of complex colloids containing a solid internal phase cast within a liquid emulsion droplet. Here, authors show acoustic manipulation of solid disks inside liquid droplets whose orientation can be externally controlled with the frequency.
- Gazendra Shakya
- , Tao Yang
- & Xiaoyun Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Femtometer-amplitude imaging of coherent super high frequency vibrations in micromechanical resonators
Femtometer-amplitude imaging of coherent super high frequency vibrations in micromechanical resonators
Methods for imaging vibrations in mechanical resonators have been limited to picometer amplitudes and frequencies above 2 GHz. Here, the authors use a stroboscopic optical sampling approach, with simultaneous high bandwidth and low noise-floor, and measure 70 fm displacements out to 12 GHz.
- Lei Shao
- , Vikrant J. Gokhale
- & Jason J. Gorman
-
Article
| Open Access Multiphase flow detection with photonic crystals and deep learning
Multiphase flow detection with photonic crystals and deep learning
Photonic crystal (PC)-based sensing is an attractive approach for achieving accurate environmental sensing applications due to its band structure. Here, the authors utilize microwave transmission through PCs and deep learning physics-based data analytics to characterize flowing fluid mixtures.
- Lang Feng
- , Stefan Natu
- & John J. Valenza

 Quality evaluation of ground improvement by deep cement mixing piles via ground-penetrating radar
Quality evaluation of ground improvement by deep cement mixing piles via ground-penetrating radar