Featured
-
-
Article |
 Fabrication and operation of a two-dimensional ion-trap lattice on a high-voltage microchip
Fabrication and operation of a two-dimensional ion-trap lattice on a high-voltage microchip
Microfabricated ion traps offer a promising platform for scalable ion quantum computing systems. Sterling et al.realize a two-dimensional ion-trap lattice on a microchip using a new fabrication method that allows very-high voltages to be applied to the chip, enabling very deep ion traps.
- R. C. Sterling
- , H. Rattanasonti
- & W. K. Hensinger
-
Article |
 Multimodal label-free detection and discrimination for small molecules using a nanoporous resonator
Multimodal label-free detection and discrimination for small molecules using a nanoporous resonator
When molecules bind to a cantilever, their resonant frequency shifts, providing a sensitive molecular detection scheme. Park et al.coat the surfaces of such resonators with nanoporous gold, enabling them to discriminate between molecules via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
- Jinsung Park
- , Doyeon Bang
- & Sungsoo Na
-
Article |
 Visualizing the interfacial evolution from charge compensation to metallic screening across the manganite metal–insulator transition
Visualizing the interfacial evolution from charge compensation to metallic screening across the manganite metal–insulator transition
The nature of interfacial reconstructions at polar interfaces between transition metal oxides is known to be complex and difficult to characterize. Here, the authors quantify the atomic-scale charge distribution for manganite–titanate interfaces, spanning the manganite metal–insulator transition.
- Julia A. Mundy
- , Yasuyuki Hikita
- & Lena F. Kourkoutis
-
Article |
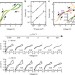 Bulk mixed ion electron conduction in amorphous gallium oxide causes memristive behaviour
Bulk mixed ion electron conduction in amorphous gallium oxide causes memristive behaviour
A memristor is the missing fourth circuit element that remembers its bias history. The storage in established devices today occurs by binary switching between ON and OFF states due to filamentary or interfacial mechanisms. Here, Aoki et al.show an analogue-type, homogeneous switching memristor system based on gallium oxide.
- Yoshitaka Aoki
- , Carsten Wiemann
- & Manfred Martin
-
Article |
 DNA origami based assembly of gold nanoparticle dimers for surface-enhanced Raman scattering
DNA origami based assembly of gold nanoparticle dimers for surface-enhanced Raman scattering
DNA origami is a versatile fabrication approach for building tailored nanostructures. Thacker et al.apply it to the assembly of gold nanoparticle dimers with sub-5 nm gaps and show how the resulting plasmonic resonances can be exploited for surface-enhanced Raman scattering.
- Vivek V. Thacker
- , Lars O. Herrmann
- & Ulrich F. Keyser
-
Article |
 Bose–Einstein condensation in an ultra-hot gas of pumped magnons
Bose–Einstein condensation in an ultra-hot gas of pumped magnons
In contrast to real atoms, Bose–Einstein condensation of quasi-particles does not require low temperature, but is obtained via external pumping. Here, the authors show an unexpected transitional dynamics of a Bose–Einstein condensate of magnons due to a nonlinear evaporative supercooling mechanism.
- Alexander A. Serga
- , Vasil S. Tiberkevich
- & Burkard Hillebrands
-
Article |
 Ultrafast angular momentum transfer in multisublattice ferrimagnets
Ultrafast angular momentum transfer in multisublattice ferrimagnets
Femtosecond laser pulses can induce ultrafast changes to the magnetization in magnetic materials. Here, the authors show that the ultrafast demagnetization in ferrimagnets is driven by the transfer of angular momenta between two coupled sublattices whilst the total angular momentum remains constant.
- N. Bergeard
- , V. López-Flores
- & C. Boeglin
-
Article |
 Scanning-aperture trapping and manipulation of single charged nanoparticles
Scanning-aperture trapping and manipulation of single charged nanoparticles
One central goal of small object manipulation is the contact-free trapping of single biomolecules or nanoparticles longer than seconds. Kim et al.develop a geometry-induced electrostatic trap using scannable nanopipettes, which is capable of manipulating nanoparticles and lipid vesicles in solutions.
- Ji Tae Kim
- , Susann Spindler
- & Vahid Sandoghdar
-
Article |
 8.4% efficient fullerene-free organic solar cells exploiting long-range exciton energy transfer
8.4% efficient fullerene-free organic solar cells exploiting long-range exciton energy transfer
Organic solar cells usually require the incorporation of costly fullerene acceptor layers. Cnops et al.report a multilayer organic solar cell that extracts photogenerated excitons by a two-step mechanism and achieves unprecedented conversion efficiencies of up to 8.4% without the use of fullerenes.
- Kjell Cnops
- , Barry P. Rand
- & Paul Heremans
-
Article |
 Large topological Hall effect in the non-collinear phase of an antiferromagnet
Large topological Hall effect in the non-collinear phase of an antiferromagnet
The topological Hall effect arises in magnetic materials with non-trivial spin arrangements and it has been suggested that they occur in non-cubic antiferromagnets. Here, the authors observe contributions to the anomalous Hall effect in the antiferromagnet Mn5Si3, which might be of topological origin.
- Christoph Sürgers
- , Gerda Fischer
- & Hilbert v. Löhneysen
-
Article |
 Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator
Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator
Efficiently harvesting energy from ambient motion is important for realising cost-effective and clean electrical energy. Here, the authors report a planar-structured rotary triboelectric generator with 24% efficiency for obtaining power from light wind, body movement and water flow.
- Guang Zhu
- , Jun Chen
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article |
 Non-reciprocal and highly nonlinear active acoustic metamaterials
Non-reciprocal and highly nonlinear active acoustic metamaterials
Unidirectional acoustic devices only permit the flow of energy one way, but most implementations are large compared to acoustic frequencies. Popa and Cummer use a metamaterial approach to build such devices that are only a tenth of a wavelength thick but retain high acoustic isolation.
- Bogdan-Ioan Popa
- & Steven A. Cummer
-
Article |
 Phase evolution for conversion reaction electrodes in lithium-ion batteries
Phase evolution for conversion reaction electrodes in lithium-ion batteries
It is a challenge to visualize phase conversion in batteries. Here Lin et al.report a grid-in-a-coin cell approach to directly probe three-dimensional morphology and charge state distribution of electrode materials, and reveal the dominance of a heterogeneous phase conversion mechanism.
- Feng Lin
- , Dennis Nordlund
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
Article |
 Pure second harmonic current-phase relation in spin-filter Josephson junctions
Pure second harmonic current-phase relation in spin-filter Josephson junctions
Conventional Josephson junctions have a dominant first harmonic in the current-phase relation. Here, the authors use a ferromagnetic insulator to create a spin-filter Josephson junction and show that the second harmonic is dominant, pointing to unconventional cooper pair transport.
- Avradeep Pal
- , Z.H. Barber
- & M.G. Blamire
-
Article |
 Photonic spin Hall effect in hyperbolic metamaterials for polarization-controlled routing of subwavelength modes
Photonic spin Hall effect in hyperbolic metamaterials for polarization-controlled routing of subwavelength modes
Metamaterials enable the control and manipulation of light on subwavelength scales, allowing numerous optical device applications. Here, the authors show the selective excitation of spatially confined modes in an anisotropic hyperbolic metamaterial, based on the photonic spin Hall effect.
- Polina V. Kapitanova
- , Pavel Ginzburg
- & Anatoly V. Zayats
-
Article |
 Silicon-based broadband antenna for high responsivity and polarization-insensitive photodetection at telecommunication wavelengths
Silicon-based broadband antenna for high responsivity and polarization-insensitive photodetection at telecommunication wavelengths
Small on-chip photodetectors are of promise for telecommunications applications. Here, Lin et al.demonstrate that metal trenches on a silicon chip enable highly sensitive photodetection at telecommunications wavelengths.
- Keng-Te Lin
- , Hsuen-Li Chen
- & Chen-Chieh Yu
-
Article |
 Solar-induced direct biomass-to-electricity hybrid fuel cell using polyoxometalates as photocatalyst and charge carrier
Solar-induced direct biomass-to-electricity hybrid fuel cell using polyoxometalates as photocatalyst and charge carrier
The direct conversion of biomass to electricity is an important process. Here, the authors use polyoxometallates as both photocatalyst and charge carrier to generate electricity in a solar-powered hybrid fuel cell that can consume natural biomass, such as cellulose or wood powders, at low temperature.
- Wei Liu
- , Wei Mu
- & Yulin Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear magnetization in gallium arsenide quantum dots at zero magnetic field
Nuclear magnetization in gallium arsenide quantum dots at zero magnetic field
Optical control of nuclear spin polarization in semiconductor quantum dots is promising for applications in NMR imaging. Sallen et al.report efficient dynamic nuclear polarization at zero magnetic field in strain-free gallium arsenide quantum dots with Knight fields dominating the nuclear quadrupole effects.
- G. Sallen
- , S. Kunz
- & B. Urbaszek
-
Article |
 Error-corrected quantum annealing with hundreds of qubits
Error-corrected quantum annealing with hundreds of qubits
Quantum annealing is a quantum computational approach exploiting ground-state dynamics of a system to find optimal solutions. Pudenz et al.present an error correction scheme for quantum annealing and show that it provides improved performance on a quantum annealer with up to 344 superconducting flux qubits.
- Kristen L. Pudenz
- , Tameem Albash
- & Daniel A. Lidar
-
Article
| Open Access Fluctuations in the electron system of a superconductor exposed to a photon flux
Fluctuations in the electron system of a superconductor exposed to a photon flux
Electromagnetic radiation detectors based on superconducting resonators have a range of potential uses from astronomy to quantum computing. De Visser et al.demonstrate a superconductor detector with unprecedented sensitivity limited only by fluctuations in the electron system of the superconductor.
- P. J. de Visser
- , J. J. A. Baselmans
- & T. M. Klapwijk
-
Article |
 A wearable and highly sensitive pressure sensor with ultrathin gold nanowires
A wearable and highly sensitive pressure sensor with ultrathin gold nanowires
Flexible electronics hold great promise for wearable biomedical sensors. Here, the authors report a pressure sensor composed of gold nanowire-impregnated tissue paper, sandwiched between polydimethylsiloxane sheets, and demonstrate that the design is appropriate for large-area flexible electronics.
- Shu Gong
- , Willem Schwalb
- & Wenlong Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Correlated spin currents generated by resonant-crossed Andreev reflections in topological superconductors
Correlated spin currents generated by resonant-crossed Andreev reflections in topological superconductors
Materials that exhibit topologically protected electronic structures are expected to enable the development of more efficient spintronic devices. He et al.suggest that combining a quantum anomalous Hall insulator with a superconductor could be used to generate correlated spin currents.
- James J. He
- , Jiansheng Wu
- & K. T. Law
-
Article |
 Graphene radio frequency receiver integrated circuit
Graphene radio frequency receiver integrated circuit
Graphene transistors are attractive for many applications but making integrated circuits without degrading their characteristics is proving challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate a radio frequency integrated receiver using a graphene-last approach compatible with conventional processing methods.
- Shu-Jen Han
- , Alberto Valdes Garcia
- & Wilfried Haensch
-
Article |
 Origami lithium-ion batteries
Origami lithium-ion batteries
Flexible batteries with good mechanical properties are highly desirable. Here Song et al.use the origami concept, an art of paper folding, to construct a lithium-ion battery, and demonstrate excellent battery stretchability as well as electrochemical performance.
- Zeming Song
- , Teng Ma
- & Hanqing Jiang
-
Article |
 Effective impedance boundary optimization and its contribution to dipole radiation and radiation pattern control
Effective impedance boundary optimization and its contribution to dipole radiation and radiation pattern control
Controlling sound waves is important to build better acoustic devices, and much can be learnt from optical approaches. To this end, Quan et al.show how periodic arrays of Helmholtz resonators on metal plates can produce dipole-like radiation patterns for sound.
- Li Quan
- , Xu Zhong
- & Paul A. Johnson
-
Article |
 Artificial synapse network on inorganic proton conductor for neuromorphic systems
Artificial synapse network on inorganic proton conductor for neuromorphic systems
Realizing artificial synapses that mirror those found in the brain is a major challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate the fabrication of a laterally coupled oxide-based artificial synapse via a self-assembling process.
- Li Qiang Zhu
- , Chang Jin Wan
- & Qing Wan
-
Article |
 Enhanced thermal transport at covalently functionalized carbon nanotube array interfaces
Enhanced thermal transport at covalently functionalized carbon nanotube array interfaces
Despite their high thermal conductivities, the large thermal interface resistance between carbon nanotubes and other components limits their practical applications. Here, the authors show that covalently bonded bridging molecules can significantly enhance the thermal transport across these interfaces.
- Sumanjeet Kaur
- , Nachiket Raravikar
- & D. Frank Ogletree
-
Article |
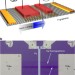 Homoepitaxial tunnel barriers with functionalized graphene-on-graphene for charge and spin transport
Homoepitaxial tunnel barriers with functionalized graphene-on-graphene for charge and spin transport
The long spin diffusion lengths in graphene make it attractive for spintronic applications but achieving efficient spin injection is proving challenging. Here, the authors show that functionalized graphene can act as a tunnel barrier, demonstrating non-local homoepitaxial spin valves.
- Adam L. Friedman
- , Olaf M. J. van ‘t Erve
- & Berend T. Jonker
-
Article |
 Direct measurement of a 27-dimensional orbital-angular-momentum state vector
Direct measurement of a 27-dimensional orbital-angular-momentum state vector
Characterizing quantum states is vital for quantum information or metrology tasks, but it remains challenging. Here, by a combination of weak and strong measurements, the authors directly measure the probability amplitudes of a pure state in the orbital angular momentum basis with dimensionality of 27.
- Mehul Malik
- , Mohammad Mirhosseini
- & Robert W. Boyd
-
Article |
 Reduced time as a unified parameter determining fixity and free recovery of shape memory polymers
Reduced time as a unified parameter determining fixity and free recovery of shape memory polymers
The performance of shape memory polymers is determined by a wide variety of factors such as programming temperature, holding times and cooling rates. Here the authors show how this dependence can be described by a unifying parameter: the reduced time.
- Kai Yu
- , Qi Ge
- & H. Jerry Qi
-
Article |
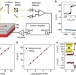 Quantifying interface and bulk contributions to spin–orbit torque in magnetic bilayers
Quantifying interface and bulk contributions to spin–orbit torque in magnetic bilayers
Spin–orbit-driven effects are of great interest for spintronic applications but the underlying mechanisms are challenging to probe. Here, the authors develop a sensitive spin–orbit torque magnetometer to quantify the interface and bulk contributions to the spin–orbit torques in magnetic bilayers.
- Xin Fan
- , Halise Celik
- & John Q. Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectric translational antiphase boundaries in nonpolar materials
Ferroelectric translational antiphase boundaries in nonpolar materials
In ferroelectrics, the domain walls can have different properties than the domains themselves. Here, Wei et al.show that certain domain walls in antiferroelectric materials are ferroelectric, which makes them interesting candidates for new non-volatile memory concepts.
- Xian-Kui Wei
- , Alexander K. Tagantsev
- & Nava Setter
-
Article |
 Photoactuators and motors based on carbon nanotubes with selective chirality distributions
Photoactuators and motors based on carbon nanotubes with selective chirality distributions
Materials that can alter their structure in response to light have potential as functional materials such as motors and actuators. Here the authors describe a low-cost system capable of rapid, reversible and wavelength-selective responses to light.
- Xiaobo Zhang
- , Zhibin Yu
- & Ali Javey
-
Article |
 Fast coherent manipulation of three-electron states in a double quantum dot
Fast coherent manipulation of three-electron states in a double quantum dot
Electron spins in quantum dots are a promising platform for quantum information technologies. Using a double quantum dot system with three electrons, Shi et al. show that certain pulse sequences allow for fast rotations to all possible states, improving the performance compared with the two electron case.
- Zhan Shi
- , C. B. Simmons
- & M. A. Eriksson
-
Article |
 Highly stable organic polymer field-effect transistor sensor for selective detection in the marine environment
Highly stable organic polymer field-effect transistor sensor for selective detection in the marine environment
Field-effect transistors are widely used for environmental sensing and monitoring applications. Here, the authors present an organic field-effect transistor with the inherent advantages of low-cost and scalable fabrication, and which is sufficiently stable to be deployed in marine environments.
- Oren Knopfmacher
- , Mallory L. Hammock
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access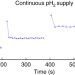 A hyperpolarized equilibrium for magnetic resonance
A hyperpolarized equilibrium for magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance is vital for analysis and diagnostics but suffers from insensitivity as only a small fraction of all NMR-active nuclei are spin-polarized and contribute to the signal. Here Hövener et al. describe an effect that replenishes nuclear spin polarization continuously for a considerably enhanced performance at low field.
- Jan-Bernd Hövener
- , Niels Schwaderlapp
- & Dominik von Elverfeldt
-
Article |
 All-back-contact ultra-thin silicon nanocone solar cells with 13.7% power conversion efficiency
All-back-contact ultra-thin silicon nanocone solar cells with 13.7% power conversion efficiency
Nanostructured solar cells should be designed to balance the photonic and electronic effects together to be highly efficient. Cui et al.demonstrate a solar cell with the all-back-contact design and nanocone structure that uses just 10-μm-thick silicon while achieving efficiencies up to 13.7%.
- Sangmoo Jeong
- , Michael D. McGehee
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated approach to realizing high-performance liquid-junction quantum dot sensitized solar cells
An integrated approach to realizing high-performance liquid-junction quantum dot sensitized solar cells
Although quantum dots are a promising alternative to dyes in sensitised solar cells, most are based on toxic heavy metals. McDaniel et al.demonstrate devices made with low-cost copper-based quantum dots that achieve certified efficiencies unprecedented for quantum dot sensitized solar cells.
- Hunter McDaniel
- , Nobuhiro Fuke
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article |
 Overcoming ultraviolet light instability of sensitized TiO2 with meso-superstructured organometal tri-halide perovskite solar cells
Overcoming ultraviolet light instability of sensitized TiO2 with meso-superstructured organometal tri-halide perovskite solar cells
Although the performance of sensitized TiO2 solar cells has increased considerably over recent years, Leijtens et al. show that they are susceptible to a light-driven instability that degrades their performance over time. They go on to show that this instability can be overcome in mesoporous TiO2-free devices.
- Tomas Leijtens
- , Giles E. Eperon
- & Henry J. Snaith
-
Article
| Open Access Long-distance distribution of genuine energy-time entanglement
Long-distance distribution of genuine energy-time entanglement
Practical implementations of quantum communication need to securely deliver information over long distances without line-of-sight. Towards this goal, Cuevas et al.use an actively stabilized interferometer to close the geometry loophole for a Bell inequality violation over 1 km of optical fibre.
- A. Cuevas
- , G. Carvacho
- & G.B. Xavier
-
Article |
 Ferroelectric polymer networks with high energy density and improved discharged efficiency for dielectric energy storage
Ferroelectric polymer networks with high energy density and improved discharged efficiency for dielectric energy storage
Ferroelectric polymers are attractive candidates as dielectric materials for electrical energy storage applications, but suffer from large dielectric loss. Here, the authors report a method for creating ferroelectric polymer networks with reduced dielectric loss and large charge–discharge efficiencies.
- Paisan Khanchaitit
- , Kuo Han
- & Qing Wang
-
Article |
 General nature of liquid–liquid transition in aqueous organic solutions
General nature of liquid–liquid transition in aqueous organic solutions
The existence of liquid–liquid transition is one hypothesis used to explain the anomalous properties of liquid water at low temperatures. Murata and Tanaka demonstrate that both this transition and the melting of ice can be controlled solely by water activity in 14 aqueous organic solutions.
- Ken-ichiro Murata
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article |
 A nanoscale shape memory oxide
A nanoscale shape memory oxide
Shape-memory materials hold great potential for actuators and aims to improve them focus on increasing the maximum strain that they exhibit in response to a stimulus. Here the authors demonstrate a large shape-memory effect in bismuth ferrite, observing a maximum strain of up to 14%.
- Jinxing Zhang
- , Xiaoxing Ke
- & Ramamoorthy Ramesh
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional optical holography using a plasmonic metasurface
Three-dimensional optical holography using a plasmonic metasurface
Holographic techniques allow for the construction of 3D images by controlling the wave front of light beams. Huang et al.develop ultrathin plasmonic metasurfaces to provide 3D optical holographic image reconstruction in the visible and near-infrared regions for circularly polarized light.
- Lingling Huang
- , Xianzhong Chen
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article |
 Metasurface holograms for visible light
Metasurface holograms for visible light
Holographic techniques provide phase and amplitude information for images of objects, but normally the hologram thickness is comparable to the light wavelength used. Ni et al.present ultra-thin plasmonic holograms that control amplitude and phase in the visible region and are just 30 nm thick.
- Xingjie Ni
- , Alexander V. Kildishev
- & Vladimir M. Shalaev
-
Article |
 Room-temperature air-stable spin transport in bathocuproine-based spin valves
Room-temperature air-stable spin transport in bathocuproine-based spin valves
Spin valves with organic semiconductors sandwiched between two ferromagnetic layers can have similar performance as their inorganic counterparts. Here, the authors fabricate bathocuproine spin valves with good air stability and show that the transport takes place through the organic layer.
- Xiangnan Sun
- , Marco Gobbi
- & Luis E Hueso
-
Article |
 Stratonovich-to-Itô transition in noisy systems with multiplicative feedback
Stratonovich-to-Itô transition in noisy systems with multiplicative feedback
The noise in a stochastic differential equation can be interpreted by Itô or by Stratonovich calculus, and which one to use has been a subject of discussion in statistical physics. Pesce et al.show that the underlying dynamics induce a shift from Stratonovic to Itô calculus in a noisy electrical circuit.
- Giuseppe Pesce
- , Austin McDaniel
- & Giovanni Volpe
-
Article |
 Mutually synchronized bottom-up multi-nanocontact spin–torque oscillators
Mutually synchronized bottom-up multi-nanocontact spin–torque oscillators
Spin–torque oscillators have potential as nanosized microwave signal generators, but presently they are limited by their small output power. Here, the authors develop a cheap lithographic method to fabricate spin–torque oscillators, which can be mutually synchronized to overcome the output-power limitation.
- S. Sani
- , J. Persson
- & J. Åkerman
-
Article |
 In situ electron holography study of charge distribution in high-κ charge-trapping memory
In situ electron holography study of charge distribution in high-κ charge-trapping memory
Charge-trapping memory offers many advantages over existing data storage media, though the spatial distribution of charge remains elusive. Here Yao et al. use electron holography to map its distribution in high-κ dielectric stacks under different applied bias.
- Y. Yao
- , C. Li
- & R. C. Yu

 High-efficiency ballistic electrostatic generator using microdroplets
High-efficiency ballistic electrostatic generator using microdroplets