Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Protective immune trajectories in early viral containment of non-pneumonic SARS-CoV-2 infection
Protective immune trajectories in early viral containment of non-pneumonic SARS-CoV-2 infection
Infection with SARS-COV-2 can result in self-limited upper airway infection or progress to a more systemic inflammatory condition including pneumonic COVID-19. Here the authors utilise a multi-omics approach to interrogate the immune response of patients with self-limiting upper respiratory SARS-CoV-2 infection and reveal a temporal immune trajectory they associate with viral containment and restriction from pneumonic progressive disease.
- Kami Pekayvaz
- , Alexander Leunig
- & Leo Nicolai
-
Article
| Open Access Stratification of hospitalized COVID-19 patients into clinical severity progression groups by immuno-phenotyping and machine learning
Stratification of hospitalized COVID-19 patients into clinical severity progression groups by immuno-phenotyping and machine learning
Developing predictive methods to identify patients with high risk of severe COVID-19 disease is of crucial importance. Authors show here that by measuring anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody and cytokine levels at the time of hospital admission and integrating the data by unsupervised hierarchical clustering/machine learning, it is possible to predict unfavourable outcome.
- Yvonne M. Mueller
- , Thijs J. Schrama
- & Peter D. Katsikis
-
Article
| Open Access Cell specific peripheral immune responses predict survival in critical COVID-19 patients
Cell specific peripheral immune responses predict survival in critical COVID-19 patients
Infection with SARS-CoV-2 results in activation of multiple immune cell types in situ but also in the peripheral blood compartment. Here the authors apply single cell sequencing and machine learning to characterise the response and link this to confer prognostic indicators in critically ill COVID-19 patients.
- Junedh M. Amrute
- , Alexandra M. Perry
- & Ashley L. Steed
-
Article
| Open Access A pandemic-enabled comparison of discovery platforms demonstrates a naïve antibody library can match the best immune-sourced antibodies
A pandemic-enabled comparison of discovery platforms demonstrates a naïve antibody library can match the best immune-sourced antibodies
The most potent neutralizing antibodies are typically generated from convalescent patients and immunized animals. Here, the authors show it is possible to generate highly potent human neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein directly from a semisynthetic naïve antibody library.
- Fortunato Ferrara
- , M. Frank Erasmus
- & Andrew R. M. Bradbury
-
Article
| Open Access Tolerogenic nanoparticles mitigate the formation of anti-drug antibodies against pegylated uricase in patients with hyperuricemia
Tolerogenic nanoparticles mitigate the formation of anti-drug antibodies against pegylated uricase in patients with hyperuricemia
Anti-drug antibodies (ADA) induced by biologic drugs may hamper the efficacy of treatment, so inhibiting ADA induction is desirable. Here, in two clinical trials, the authors show that ImmTOR, previously reported to reduce drug immunogenicity in animal studies, helps mitigate ADA induced by pegylated uricase for treating patients with hyperuricemia.
- Earl Sands
- , Alan Kivitz
- & Takashi Kei Kishimoto
-
Article
| Open Access Oxylipin metabolism is controlled by mitochondrial β-oxidation during bacterial inflammation
Oxylipin metabolism is controlled by mitochondrial β-oxidation during bacterial inflammation
Oxylipins are lipid mediators generated during infection for regulating inflammatory responses, but how they are removed is not completely clear. Here the authors show that cellular oxylipin removal is linked to mitochondria β-oxidation by CPT1, a mitochondria lipid importer protein, to serve as a metabolic checkpoint for oxylipin homeostasis and inflammation.
- Mariya Misheva
- , Konstantinos Kotzamanis
- & Valerie B. O’Donnell
-
Article
| Open Access Investigating immune and non-immune cell interactions in head and neck tumors by single-cell RNA sequencing
Investigating immune and non-immune cell interactions in head and neck tumors by single-cell RNA sequencing
The tumor microenvironment (TME) has an important role in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) progression. Here, using single-cell RNA sequencing and multiplexed imaging, the authors report the cellular complexity of the TME in patients with HNSCC, exploring inflammatory status, stromal heterogeneity and immune checkpoint receptor-ligand interactions.
- Cornelius H. L. Kürten
- , Aditi Kulkarni
- & Robert L. Ferris
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell RNA sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from acute Kawasaki disease patients
Single-cell RNA sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from acute Kawasaki disease patients
Immune cell changes are associated with Kawasaki disease (KD) pathogenesis. Here, using single cell RNA sequencing of PBMC, the authors show monocyte inflammatory genes are over-expressed in KD and TCR and BCR clonotype sequences show oligoclonal expansions after intravenous immunoglobulin therapy.
- Zhen Wang
- , Lijian Xie
- & Min Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A modular self-adjuvanting cancer vaccine combined with an oncolytic vaccine induces potent antitumor immunity
A modular self-adjuvanting cancer vaccine combined with an oncolytic vaccine induces potent antitumor immunity
Successful cancer immune therapy correlates with a T cell-inflamed tumour microenvironment. Authors show here that co-administration of a self-adjuvanting protein vaccine and an antigen-expressing oncolytic virus in an optimised regimen strongly enhances T cell immunogenicity and may turn non-inflamed tumours proinflammatory and less resistant to checkpoint blockade therapy.
- Krishna Das
- , Elodie Belnoue
- & Guido Wollmann
-
Article
| Open Access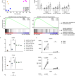 Conserved human effector Treg cell transcriptomic and epigenetic signature in arthritic joint inflammation
Conserved human effector Treg cell transcriptomic and epigenetic signature in arthritic joint inflammation
T regulatory (Treg) cells can differentiate into effector Treg (eTreg) cells that might be functional in inflammatory diseases. Using RNA sequencing and epigenetic profiling, the authors show that eTreg signatures in juvenile idiopathic arthritis joints are similar to tumour microenvironment (TME) Treg cells and are affected by tissue-specific epigenetic regulation.
- Gerdien Mijnheer
- , Lisanne Lutter
- & Femke van Wijk
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered red blood cells as an off-the-shelf allogeneic anti-tumor therapeutic
Engineered red blood cells as an off-the-shelf allogeneic anti-tumor therapeutic
Red blood cells (RBCs) have unique properties that have been exploited for therapeutic uses. Here the authors engineer RBCs to co-express tumor associated antigens on MHC I, 4-1BBL and IL-12, generating artificial antigen presenting cells that can induce antigen-specific T cell responses and antitumor immune responses in preclinical models.
- Xuqing Zhang
- , Mengyao Luo
- & Tiffany F. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Seroprevalence and correlates of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies from a population-based study in Bonn, Germany
Seroprevalence and correlates of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies from a population-based study in Bonn, Germany
Population-based studies of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence are needed to understand levels of immunity and antibody dynamics. Here, the authors show that the seroprevalence in Bonn, Germany was low (<1%) following the first epidemic wave, and that neutralising antibodies waned within a few months.
- N. Ahmad Aziz
- , Victor M. Corman
- & Monique M. B. Breteler
-
Article
| Open Access IL-22-dependent dysbiosis and mononuclear phagocyte depletion contribute to steroid-resistant gut graft-versus-host disease in mice
IL-22-dependent dysbiosis and mononuclear phagocyte depletion contribute to steroid-resistant gut graft-versus-host disease in mice
Pathogenesis of steroid-resistant gut acute graft-versus-host-disease (SR-Gut-aGVHD) remains unclear., Here the authors show in mouse models that dysbiosis caused by the expansion of Th/Tc22, as well as depletion of CX3CR1hi mononuclear phagocytes resulted from the reduction of Th/Tc1, contributes to SR-Gut-aGVHD onset.
- Qingxiao Song
- , Xiaoning Wang
- & Defu Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling the global burden of drug-resistant tuberculosis avertable by a post-exposure vaccine
Modelling the global burden of drug-resistant tuberculosis avertable by a post-exposure vaccine
Vaccines preventing tuberculosis disease progression have shown promising results in recent trials. Here, the authors use mathematical modelling to estimate that this type of vaccine could avert 10% of cases of rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis and 7% of deaths from 2020-2035.
- Han Fu
- , Joseph A. Lewnard
- & Nimalan Arinaminpathy
-
Article
| Open Access SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein vaccine candidate NVX-CoV2373 immunogenicity in baboons and protection in mice
SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein vaccine candidate NVX-CoV2373 immunogenicity in baboons and protection in mice
Here, the authors characterize a SARS-CoV-2 subunit vaccine candidate that contains full-length spike protein stabilized in its prefusion conformation, and show immunogenicity in baboons and protection in mice with Matrix-M adjuvanted vaccine.
- Jing-Hui Tian
- , Nita Patel
- & Gale Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered immunological niches to monitor disease activity and treatment efficacy in relapsing multiple sclerosis
Engineered immunological niches to monitor disease activity and treatment efficacy in relapsing multiple sclerosis
Monitoring changes in immune phenotype during the progression of multiple sclerosis can provide insight into disease progression and inform treatment. Here the authors develop engineered biomaterial-based immunological niches for easy access to innate immune cells in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.
- Aaron H. Morris
- , Kevin R. Hughes
- & Lonnie D. Shea
-
Article
| Open Access VoPo leverages cellular heterogeneity for predictive modeling of single-cell data
VoPo leverages cellular heterogeneity for predictive modeling of single-cell data
Single-cell technologies are increasingly prominent in clinical applications, but predictive modelling with such data in large cohorts has remained computationally challenging. We developed a new algorithm, ‘VoPo’, for predictive modelling and visualization of single cell data for translational applications.
- Natalie Stanley
- , Ina A. Stelzer
- & Nima Aghaeepour
-
Article
| Open Access Durable and controlled depletion of neutrophils in mice
Durable and controlled depletion of neutrophils in mice
Anti-Ly6G or ant-Gr1 antibodies are commonly used to deplete neutrophils in vivo. Here the authors provide mechanistic insight into why these approaches may not specifically or durably reduce the number of neutrophils in mice, and also present a new method that overcomes these limitations to have potentially wide applicability in experimental studies.
- Gael Boivin
- , Julien Faget
- & Etienne Meylan
-
Article
| Open Access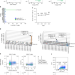 Somatic mTOR mutation in clonally expanded T lymphocytes associated with chronic graft versus host disease
Somatic mTOR mutation in clonally expanded T lymphocytes associated with chronic graft versus host disease
Chronic graft versus host disease (cGvHD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Here the authors identify a recurrent activating mTOR mutation in expanded donor T-cell clones of 3 cGvHD patients, which suggests somatic mutations may contribute to GvHD pathogenesis and opens avenues to targeted therapies.
- Daehong Kim
- , Giljun Park
- & Satu Mustjoki
-
Article
| Open Access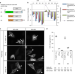 An ultra-stable cytoplasmic antibody engineered for in vivo applications
An ultra-stable cytoplasmic antibody engineered for in vivo applications
Antibodies expressed in the cytosol often form insoluble aggregates, which makes it hard to target intracellular proteins. Here the authors engineer an ultra-stable cytoplasmic antibody (STAND) with a low isoelectric point that can be used in vivo.
- Hiroyuki Kabayama
- , Makoto Takeuchi
- & Katsuhiko Mikoshiba
-
Article
| Open Access Increased yields and biological potency of knob-into-hole-based soluble MHC class II molecules
Increased yields and biological potency of knob-into-hole-based soluble MHC class II molecules
Recombinant MHC class II molecules are instrumental in antigen-specific T-cell identification assays and showed efficacy as experimental medicines. Here, the authors engineer MHC class II molecules with species-specific knob-into-hole heteromerization domains, enabling a translatable purification process with improved stability, yields, and biological potency.
- Pau Serra
- , Nahir Garabatos
- & Pere Santamaria
-
Article
| Open Access Iron-dependent histone 3 lysine 9 demethylation controls B cell proliferation and humoral immune responses
Iron-dependent histone 3 lysine 9 demethylation controls B cell proliferation and humoral immune responses
The authors show an important role for iron in B cell proliferation via histone 3 lysine 9 (H3K9) demethylation at the cyclin E1 promoter. Using a measles vaccination murine model, they show that iron-deficient individuals have a significantly reduced antibody response to the vaccine when compared to iron-normal controls.
- Yuhang Jiang
- , Cuifeng Li
- & Xiaoren Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Neutrophils promote the development of reparative macrophages mediated by ROS to orchestrate liver repair
Neutrophils promote the development of reparative macrophages mediated by ROS to orchestrate liver repair
Neutrophils and macrophages are both involved in the initiation of inflammation, but whether and how they may participate in inflammation resolution is unclear. Here the authors show that neutrophils may mediate the conversion of macrophage into a pro-resolution phenotype via reactive oxygen species production to promote liver repair.
- Wenting Yang
- , Yuandong Tao
- & Li Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Selective hematopoietic stem cell ablation using CD117-antibody-drug-conjugates enables safe and effective transplantation with immunity preservation
Selective hematopoietic stem cell ablation using CD117-antibody-drug-conjugates enables safe and effective transplantation with immunity preservation
Hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation is a desirable treatment for many non-malignant and malignant diseases, but its use requires preconditioning of recipients with irradiation or chemotherapy that often induces high toxicity. Here the authors show that antibody-drug-conjugate to CD117, a HSC marker, allows specific and efficient preconditioning for HSC therapy.
- Agnieszka Czechowicz
- , Rahul Palchaudhuri
- & Derrick J. Rossi
-
Article
| Open Access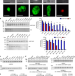 Efficient oral vaccination by bioengineering virus-like particles with protozoan surface proteins
Efficient oral vaccination by bioengineering virus-like particles with protozoan surface proteins
Giardia lamblia express a dense coat of variant-specific surface proteins (VSPs) on trophozoites that protects the parasite inside the host´s intestine. Here the authors show that stability and immunomodulatory properties of VSPs can be exploited to both protect and adjuvant vaccine antigens for oral administration.
- Marianela C. Serradell
- , Lucía L. Rupil
- & Hugo D. Luján
-
Article
| Open Access PDL2+ CD11b+ dermal dendritic cells capture topical antigen through hair follicles to prime LAP+ Tregs
PDL2+ CD11b+ dermal dendritic cells capture topical antigen through hair follicles to prime LAP+ Tregs
Antigen present and presented in the structures of the skin can result in immune responses that elicit tolerance, protective immunity or allergy, depending on the immunological context. Here the authors describe a key role for the hair follicle and CD11b+ dendritic cells in the priming of local antigenic tolerance.
- Leticia Tordesillas
- , Daniel Lozano-Ojalvo
- & M. Cecilia Berin
-
Article
| Open Access GPCR-specific autoantibody signatures are associated with physiological and pathological immune homeostasis
GPCR-specific autoantibody signatures are associated with physiological and pathological immune homeostasis
Autoantibodies are implicated in autoimmunity, but may also be present in healthy individuals. Here the authors find that the autoantibody specificity signatures against various G protein-coupled receptors are associated with multiple parameters, including disease states, to imply a physiological function in maintaining immune homeostasis.
- Otavio Cabral-Marques
- , Alexandre Marques
- & Gabriela Riemekasten
-
Article
| Open Access HLA-B57 micropolymorphism defines the sequence and conformational breadth of the immunopeptidome
HLA-B57 micropolymorphism defines the sequence and conformational breadth of the immunopeptidome
Human leukocyte antigens (HLA) are multi-allelic and polymorphic genes that present antigens to immune cells for inducing protective immunity. Here, using systems biology and structural approaches, the authors show that micropolymorphism of three HLA has effects beyond the modulation of antigen diversity.
- Patricia T. Illing
- , Phillip Pymm
- & Anthony W. Purcell
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular definition of group 1 innate lymphoid cells in the mouse uterus
Molecular definition of group 1 innate lymphoid cells in the mouse uterus
Studying the uterine lymphocyte pool is difficult due to its dynamic nature induced by various pregnancy-related factors. Here the authors provide, using transcriptome data from sorted mouse group 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC), a molecular atlas of these cells, which implicates tissue-resident natural killer cells as a hub for uterine immune crosstalk.
- Iva Filipovic
- , Laura Chiossone
- & Francesco Colucci
-
Article
| Open Access Antigen-selective modulation of AAV immunogenicity with tolerogenic rapamycin nanoparticles enables successful vector re-administration
Antigen-selective modulation of AAV immunogenicity with tolerogenic rapamycin nanoparticles enables successful vector re-administration
Immunogenicity of AAV vectors renders repeated AAV dosing ineffective. Here the authors show that coadministration of nanoparticle-encapsulated rapamycin overcomes AAV immunogenicity through Treg induction, enabling efficient AAV redosing in mice and nonhuman primates.
- Amine Meliani
- , Florence Boisgerault
- & Federico Mingozzi
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo neutralization of dendrotoxin-mediated neurotoxicity of black mamba venom by oligoclonal human IgG antibodies
In vivo neutralization of dendrotoxin-mediated neurotoxicity of black mamba venom by oligoclonal human IgG antibodies
Current anti-venoms against black mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) bites are animal-derived and associated with several limitations. Here, Laustsen and colleagues develop an experimental recombinant anti-venom based on oligoclonal human IgG antibodies and establish its potential protective value in neutralizing dendrotoxin-mediated neurotoxicity using venom challenge in vivo models.
- Andreas H. Laustsen
- , Aneesh Karatt-Vellatt
- & John McCafferty
-
Article
| Open Access Eosinophil recruitment is dynamically regulated by interplay among lung dendritic cell subsets after allergen challenge
Eosinophil recruitment is dynamically regulated by interplay among lung dendritic cell subsets after allergen challenge
Eosinophils are important mediators of allergic responses, but how they are recruited to the inflamed site is still unclear. Here the authors show that CD103+ cDC1 cells secrete CCL17 and CCL22 for eosinophil recruitment, with this process promoted by CD24−CD11b+ DC2s in the early phase but suppressed by CD24+ cDC2s in the late phase.
- Shuying Yi
- , Jing Zhai
- & Hua Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Endogenous metabolites of vitamin E limit inflammation by targeting 5-lipoxygenase
Endogenous metabolites of vitamin E limit inflammation by targeting 5-lipoxygenase
Vitamin E metabolites are proposed to have signalling capacity, but how they may regulate immune responses is still unclear. Here the authors show that a vitamin E metabolite, α-T-13′-COOH, can inhibit 5-lipoxygenase and thereby suppress the synthesis of lipid mediators of immune activation and inflammatory responses.
- Helmut Pein
- , Alexia Ville
- & Andreas Koeberle
-
Article
| Open Access γδ T cells control humoral immune response by inducing T follicular helper cell differentiation
γδ T cells control humoral immune response by inducing T follicular helper cell differentiation
Many immune functions have been reported for γδ T cells, including the regulation of antibody responses. Here the authors show that CXCR5+ γδ T cells release Wnt ligands to initiate the T follicular helper cell differentiation program and promote antibody production.
- Rafael M. Rezende
- , Amanda J. Lanser
- & Howard L. Weiner
-
Article
| Open Access Statin as a novel pharmacotherapy of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Statin as a novel pharmacotherapy of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is associated with defective macrophage clearance of surfactant. Here, the authors show that patients with PAP have altered cholesterol-to-phospholipid ratio in their surfactant, and that more importantly, statin therapy and reduction of cholesterol accumulation in macrophages can ameliorate PAP in both humans and mice.
- Cormac McCarthy
- , Elinor Lee
- & Bruce C. Trapnell
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of T cell afferent lymphatic migration by targeting LTβR-mediated non-classical NFκB signaling
Regulation of T cell afferent lymphatic migration by targeting LTβR-mediated non-classical NFκB signaling
Lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTβR) signalling regulates leukocyte migration through the lymphatic endothelial layers. Here, the authors show that treatment of an LTβR-derived decoy peptide can target the non-classical NFκB pathway to inhibit T cell and dendritic cell migration and ameliorate contact hypersensitivity in mouse models.
- Wenji Piao
- , Yanbao Xiong
- & Jonathan S. Bromberg
-
Article
| Open Access Testosterone is an endogenous regulator of BAFF and splenic B cell number
Testosterone is an endogenous regulator of BAFF and splenic B cell number
Testosterone deficiency is associated with autoimmunity and increased B cell numbers, but the underlying mechanism is unclear. Here the authors show that testosterone may modulate the production of B cell survival factor BAFF by fibroblastic reticular cells via regulation of splenic neurotransmitter levels.
- Anna S. Wilhelmson
- , Marta Lantero Rodriguez
- & Åsa Tivesten
-
Article
| Open Access The IL-33-PIN1-IRAK-M axis is critical for type 2 immunity in IL-33-induced allergic airway inflammation
The IL-33-PIN1-IRAK-M axis is critical for type 2 immunity in IL-33-induced allergic airway inflammation
IL-33 orchestrates type 2 immunity in allergic asthma. Here the authors show, using biochemical, structural and patient data, that upon IL-33 or allergic challenge, the isomerase Pin1 modifies IRAK-M to control the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the setting of airway inflammation.
- Morris Nechama
- , Jeahoo Kwon
- & Kun Ping Lu
-
Article
| Open Access A loop region of BAFF controls B cell survival and regulates recognition by different inhibitors
A loop region of BAFF controls B cell survival and regulates recognition by different inhibitors
BAFF is an important cytokine for B cell survival, and is a therapeutic target for autoimmune disorders. Here the authors show that a 'flap' region of BAFF converts BAFFR binding events into survival signals and, with structural data, that this ‘flap’ differentially modulates binding of drugs such as belimumab or atacicept.
- Michele Vigolo
- , Melissa G. Chambers
- & Pascal Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access A non-conserved amino acid variant regulates differential signalling between human and mouse CD28
A non-conserved amino acid variant regulates differential signalling between human and mouse CD28
CD28 transmits co-stimulatory signals for the activation of both mouse and human T cells, but in vivo hyperactivation of CD28 has opposite effects on system immunity. Here, the authors show that a single amino acid difference between mouse and human CD28 dictates this function distinction via differential recruitment of Nck.
- Nicla Porciello
- , Paola Grazioli
- & Loretta Tuosto
-
Article
| Open Access Bone marrow lympho-myeloid malfunction in obesity requires precursor cell-autonomous TLR4
Bone marrow lympho-myeloid malfunction in obesity requires precursor cell-autonomous TLR4
Obesity can affect bone marrow cell differentiation and the generation of myeloid and lymphoid cells. Here, the authors show that diet and obesity, as well as low-dose lipopolysaccharide, can alter Toll-like receptor 4 signaling bone marrow cells to skew the myeloid-lymphoid homeostasis in mice.
- Ailing Liu
- , Minhui Chen
- & Lisa Borghesi
-
Article
| Open Access Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a critical transcription factor for IL-10-producing B cells in autoimmune disease
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a critical transcription factor for IL-10-producing B cells in autoimmune disease
B cells are important for antigen presentation and antibody production in humoral immunity, but are also increasingly recognized for their immune regulatory functions. Here the authors show that HIF-1α, a hypoxia-induced transcription factor, is important for controlling IL-10 induction in and immune-suppressive activity of B cells.
- Xianyi Meng
- , Bettina Grötsch
- & Aline Bozec
-
Article
| Open Access Checkpoint blockade immunotherapy reshapes the high-dimensional phenotypic heterogeneity of murine intratumoural neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells
Checkpoint blockade immunotherapy reshapes the high-dimensional phenotypic heterogeneity of murine intratumoural neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapies can unleash anti-tumour T-cell responses. Here the authors show, by integrating MHC tetramer multiplexing, mass cytometry and high-dimensional analyses, that neoantigen-specific, tumour-infiltrating T cells are highly heterogeneous and are subjected to ICB modulations.
- M. Fehlings
- , Y. Simoni
- & E. W. Newell
-
Article
| Open Access Notch-mediated conversion of activated T cells into stem cell memory-like T cells for adoptive immunotherapy
Notch-mediated conversion of activated T cells into stem cell memory-like T cells for adoptive immunotherapy
Tumour-specific T cells can be expandedin vitroand adoptively transferred for therapy, but this strategy is limited by induction of short-lived T cell populations. Here the authors activate Notch signalling in cultured mouse or human T cells, resulting in the production of a long-lived stem cell memory T cell population that can fight tumours in mice.
- Taisuke Kondo
- , Rimpei Morita
- & Akihiko Yoshimura
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV spike glycoproteins reveal the dynamic receptor binding domains
Cryo-EM structures of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV spike glycoproteins reveal the dynamic receptor binding domains
Host tropism and cell entry of pathogenic coronaviruses are mediated by their envelope spike (S) proteins. Here the authors present structural analyses of trimeric MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV S proteins in pre-fusion conformation, and reveal two states of the receptor binding domain that suggest new avenues for the generation of neutralizing antibodies.
- Yuan Yuan
- , Duanfang Cao
- & George F. Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Polyglucose nanoparticles with renal elimination and macrophage avidity facilitate PET imaging in ischaemic heart disease
Polyglucose nanoparticles with renal elimination and macrophage avidity facilitate PET imaging in ischaemic heart disease
In vivo imaging of inflammation is crucial for detection and monitoring of many pathologies and noninvasive macrophage quantification has been suggested as a possible approach. Here Keliher et al. describe novel polyglucose nanoparticle tracers that are rapidly excreted by the kidney and with high affinity for macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques.
- Edmund J. Keliher
- , Yu-Xiang Ye
- & Matthias Nahrendorf
-
Article
| Open Access Immunogenomic engineering of a plug-and-(dis)play hybridoma platform
Immunogenomic engineering of a plug-and-(dis)play hybridoma platform
Hybridomas are widely used for antibody screening and production due to their genetic stability and rapid proliferation. Here the authors demonstrate the rapid reprogramming of antibody specificity in hybridomas using CRISPR-Cas9.
- Mark Pogson
- , Cristina Parola
- & Sai T. Reddy
-
Article
| Open Access Presenting native-like trimeric HIV-1 antigens with self-assembling nanoparticles
Presenting native-like trimeric HIV-1 antigens with self-assembling nanoparticles
The development of native-like envelope trimers has been a major focus in the efforts to produce HIV vaccines. Here the authors demonstrate the production and characterization of virus-like nanoparticles displaying trimeric HIV-1 antigens with the potential to elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies.
- Linling He
- , Natalia de Val
- & Jiang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Uncleaved prefusion-optimized gp140 trimers derived from analysis of HIV-1 envelope metastability
Uncleaved prefusion-optimized gp140 trimers derived from analysis of HIV-1 envelope metastability
A major goal of HIV-1 vaccine development is to produce antigens that can induce broadly neutralizing antibodies. Here the authors examine the underlying causes of HIV-1 envelope metastability and design uncleaved, prefusion-optimized gp140 trimers with potential for use as HIV-1 vaccine antigens.
- Leopold Kong
- , Linling He
- & Jiang Zhu

 Structural basis of R-loop recognition by the S9.6 monoclonal antibody
Structural basis of R-loop recognition by the S9.6 monoclonal antibody