Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible changes in pancreatic islet structure and function produced by elevated blood glucose
Reversible changes in pancreatic islet structure and function produced by elevated blood glucose
In patients with diabetes, insulin release from pancreatic β-cells is reduced due to altered islet structure and function. Here, Brereton et al. show that elevated blood glucose underlies these changes and is sufficient to reversibly alter β-cell identity in a mouse model of β-cell dysfunction.
- Melissa F. Brereton
- , Michaela Iberl
- & Frances M. Ashcroft
-
Article
| Open Access The LKB1-salt-inducible kinase pathway functions as a key gluconeogenic suppressor in the liver
The LKB1-salt-inducible kinase pathway functions as a key gluconeogenic suppressor in the liver
The liver is an important regulator of glucose homeostasis. Here, the authors provide insight into the molecular signalling pathways controlling hepatic gluconeogenesis by showing that SIK protein kinases suppress gluconeogenesis, and that glucagon—but not insulin—regulates phosphorylation of SIK2.
- Kashyap Patel
- , Marc Foretz
- & Kei Sakamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Individual diet has sex-dependent effects on vertebrate gut microbiota
Individual diet has sex-dependent effects on vertebrate gut microbiota
Diet variations can alter gut microbial composition, but the potential influence of host genetic factors on these effects is unclear. Here, the authors show, in humans and in natural and laboratory fish populations, that such effects are dependent on the host’s sex, a genetically determined factor.
- Daniel I. Bolnick
- , Lisa K. Snowberg
- & Richard Svanbäck
-
Article |
 Modular structure facilitates mosaic evolution of the brain in chimpanzees and humans
Modular structure facilitates mosaic evolution of the brain in chimpanzees and humans
Understanding how developmental, functional and geometric factors determine brain evolution is challenging. Here, the authors show that chimpanzee and human brains have a modular structure and find that local spatial interactions pose stronger constrains to evolution than developmental and functional patterns.
- Aida Gómez-Robles
- , William D. Hopkins
- & Chet C. Sherwood
-
Article |
 An intestinal commensal symbiosis factor controls neuroinflammation via TLR2-mediated CD39 signalling
An intestinal commensal symbiosis factor controls neuroinflammation via TLR2-mediated CD39 signalling
Polysaccharide A (PSA) from the human intestinal commensal Bacteroides fragilis mediates protection against the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Here, Wang et al. show that the protective function of PSA is exerted through its action on CD39+regulatory CD4 T cells via Toll-like receptor 2 signalling.
- Yan Wang
- , Kiel M. Telesford
- & Lloyd H. Kasper
-
Article |
 WT1 controls antagonistic FGF and BMP-pSMAD pathways in early renal progenitors
WT1 controls antagonistic FGF and BMP-pSMAD pathways in early renal progenitors
The transcription factor Wilms’ tumour 1 (WT1) regulates kidney development, and Wt1 mutations are associated with renal cancer. Here the authors identify WT1 target genes in renal progenitors during early kidney development in mouse embryos and show that loss of Wt1suppresses FGF and induces BMP signalling.
- Fariba Jian Motamedi
- , Danielle A. Badro
- & Andreas Schedl
-
Article
| Open Access Tipping elements in the human intestinal ecosystem
Tipping elements in the human intestinal ecosystem
Intestinal microbes can have important effects on our health. Here, the authors analyse the gut microbiota composition in 1,000 western adults and find that certain bacteria are either abundant or nearly absent, and that these alternative states are associated with ageing and overweight.
- Leo Lahti
- , Jarkko Salojärvi
- & Willem M. de Vos
-
Article |
 Destabilization of nucleophosmin mRNA by the HuR/KSRP complex is required for muscle fibre formation
Destabilization of nucleophosmin mRNA by the HuR/KSRP complex is required for muscle fibre formation
The expression of the nucleolar protein nucleophosmin (NPM) decreases during the differentiation of various cell types. Here, the authors show that the collaboration between the RNA-binding proteins, HuR and KSRP, reduces the stability of NPM mRNA in myoblasts, thereby allowing myogenesis.
- Anne Cammas
- , Brenda Janice Sanchez
- & Imed-Eddine Gallouzi
-
Article |
 Adipocytes arise from multiple lineages that are heterogeneously and dynamically distributed
Adipocytes arise from multiple lineages that are heterogeneously and dynamically distributed
Myf5 lineage precursor cells give rise to brown adipocytes. Here, the authors show that the Myf5 lineage, as well as the Pax3 lineage, contribute to white and brite mature adipocytes and describe the effects of Myf5 lineage-specific deletion of the insulin receptor on adipose tissue formation in mice.
- Joan Sanchez-Gurmaches
- & David A. Guertin
-
Article |
 LSD1 promotes oxidative metabolism of white adipose tissue
LSD1 promotes oxidative metabolism of white adipose tissue
Brown adipocytes are rich in mitochondria and influence whole-body energy balance. Here, Duteil et al. show that the lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) controls mitochondrial biogenesis and the formation of brown-like adipocytes, and that LSD1 overexpression in white fat reduces weight gain of mice on a high-fat diet.
- Delphine Duteil
- , Eric Metzger
- & Roland Schüle
-
Article |
 Oxytocin is an age-specific circulating hormone that is necessary for muscle maintenance and regeneration
Oxytocin is an age-specific circulating hormone that is necessary for muscle maintenance and regeneration
The age-related decline in the regenerative capacity of muscle can be reversed in mice by exposure to young circulation. Elabd et al.identify the hormone, oxytocin, as a potential mediator of this effect, showing that its plasma levels decline with age and that administration of oxytocin to aged mice improves muscle regeneration.
- Christian Elabd
- , Wendy Cousin
- & Irina M. Conboy
-
Article |
 Intramuscular adipogenesis is inhibited by myo-endothelial progenitors with functioning Bmpr1a signalling
Intramuscular adipogenesis is inhibited by myo-endothelial progenitors with functioning Bmpr1a signalling
Bmp signalling is required for adult muscle maintenance and growth. Here, the authors show that ablating the expression of Bmp receptor 1a in mouse myo-endothelial cells increases intramuscular adipogenesis.
- Ping Huang
- , Tim J. Schulz
- & Emanuela Gussoni
-
Article |
 Knockdown and knockout of β1-integrin in hepatocytes impairs liver regeneration through inhibition of growth factor signalling
Knockdown and knockout of β1-integrin in hepatocytes impairs liver regeneration through inhibition of growth factor signalling
Integrin signalling has been implicated in liver regeneration but the molecular processes are not well understood. Here the authors show that β1-integrin is required for liver regeneration and that its absence impairs ligand-induced activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in mice.
- Tobias Speicher
- , Beat Siegenthaler
- & Sabine Werner
-
Article |
 High-fat maternal diet during pregnancy persistently alters the offspring microbiome in a primate model
High-fat maternal diet during pregnancy persistently alters the offspring microbiome in a primate model
The influence of diet on the establishment of gut microbiota early in life is poorly understood. Here the authors show, in a primate model, that maternal diet during pregnancy affects the offspring’s microbiome, and that dietary intervention after weaning only partially reverses this effect.
- Jun Ma
- , Amanda L. Prince
- & Kjersti M. Aagaard
-
Article |
 Ebf factors and MyoD cooperate to regulate muscle relaxation via Atp2a1
Ebf factors and MyoD cooperate to regulate muscle relaxation via Atp2a1
The specificity in myogenic transcription is poorly defined. Here, Jin et al. describe Ebf3 as a regulator of terminal muscle differentiation in the diaphragm and show that Ebf factors cooperate with the myogenic regulatory factor MyoD in the induction of muscle-specific genes.
- Saihong Jin
- , Jeehee Kim
- & Matthias Kieslinger
-
Article
| Open Access FoxO proteins restrain osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by attenuating H2O2 accumulation
FoxO proteins restrain osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by attenuating H2O2 accumulation
Osteoclasts are bone-resorbing cells responsible for the loss of bone mass in diseases such as osteoporosis. Here the authors show that osteoclast proliferation and survival is regulated by FoxO family transcription factors, which control levels of the signalling molecule hydrogen peroxide.
- Shoshana M. Bartell
- , Ha-Neui Kim
- & Maria Almeida
-
Article |
 G-protein stimulatory subunit alpha and Gq/11α G-proteins are both required to maintain quiescent stem-like chondrocytes
G-protein stimulatory subunit alpha and Gq/11α G-proteins are both required to maintain quiescent stem-like chondrocytes
The resting zone of the growth plate of mammalian long bones contains stem-like chondrocytes. Here, the authors show that G-protein stimulatory alpha subunit, Gsα, and the Gq/11α G-proteins together protect stem-like chondrocytes from apoptosis and preserve chondrocyte quiescence in mouse growth plates.
- Andrei S. Chagin
- , Karuna K. Vuppalapati
- & Henry M. Kronenberg
-
Article |
 Annexin A8 controls leukocyte recruitment to activated endothelial cells via cell surface delivery of CD63
Annexin A8 controls leukocyte recruitment to activated endothelial cells via cell surface delivery of CD63
The leukocyte receptor P-selectin translocates from Weibel-Palade bodies to the plasma membrane of activated endothelial cells, and is stabilized by CD63. Pöter et al. show that annexin A8 is required for P-selectin-mediated adhesion by regulating the supply of CD63 to the Weibel-Palade bodies.
- Michaela Poeter
- , Ines Brandherm
- & Ursula Rescher
-
Article
| Open Access Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers
Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers
Gut microbes influence our health and may contribute to human adaptation to different lifestyles. Here, the authors describe the gut microbiome of a community of hunter-gatherers and identify unique features that could be linked to a foraging lifestyle.
- Stephanie L. Schnorr
- , Marco Candela
- & Alyssa N. Crittenden
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental orthotopic transplantation of a tissue-engineered oesophagus in rats
Experimental orthotopic transplantation of a tissue-engineered oesophagus in rats
Patients with oesophageal diseases may require surgical removal and replacement of the oesophagus. Here the authors seed mesenchymal stromal cells on a decellularized rat oesophagus and show that this bioengineered tissue construct restores swallowing function after transplantation into rats.
- Sebastian Sjöqvist
- , Philipp Jungebluth
- & Paolo Macchiarini
-
Article |
 Generation of colonic IgA-secreting cells in the caecal patch
Generation of colonic IgA-secreting cells in the caecal patch
Gut-associated Peyer’s patches are lymphoid tissues that generate IgA-secreting cells, however less is known about related caecal patches. Here, Masahata et al.show that caecal patches produce IgA-positive B cells that migrate to the intestines to maintain faecal microbiota homeostasis.
- Kazunori Masahata
- , Eiji Umemoto
- & Kiyoshi Takeda
-
Article |
 Morphological and functional remodelling of the neuromuscular junction by skeletal muscle PGC-1α
Morphological and functional remodelling of the neuromuscular junction by skeletal muscle PGC-1α
The peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ co-activator 1α (PGC-1α) is implicated in regulating the morphology and function of the neuromuscular junction. Here, Arnold et al.show that PGC-1α promotes the remodeling of pre- and postsynaptic neuromuscular junction sites, even in the absence of physical activity.
- Anne-Sophie Arnold
- , Jonathan Gill
- & Christoph Handschin
-
Article |
 Hepatic IRE1α regulates fasting-induced metabolic adaptive programs through the XBP1s–PPARα axis signalling
Hepatic IRE1α regulates fasting-induced metabolic adaptive programs through the XBP1s–PPARα axis signalling
The IRE1α-XBP1 signalling pathway is part of the ER stress response but has also been linked to glucose and lipid metabolism. Here the authors show that IRE1α in the liver acts as a nutrient-sensor, regulating the metabolic adaptation to fasting and a ketogenic diet by inducing PPARα expression.
- Mengle Shao
- , Bo Shan
- & Yong Liu
-
Article |
 Lymph node-independent liver metastasis in a model of metastatic colorectal cancer
Lymph node-independent liver metastasis in a model of metastatic colorectal cancer
It remains unclear whether colorectal cancer metastases in the liver arise from intermediate metastases in the lymph nodes or directly from the primary tumour. Enquist et al.demonstrate lymph node-independent metastasis using a mouse model in which tumours are transplanted directly onto the luminal surface of the colon.
- Ida B. Enquist
- , Zinaida Good
- & Kevin G. Leong
-
Article |
 Regulation of MKL1 via actin cytoskeleton dynamics drives adipocyte differentiation
Regulation of MKL1 via actin cytoskeleton dynamics drives adipocyte differentiation
Adipocyte differentiation is accompanied by large scale changes in the actin cytoskeleton. Here, Nobusue et al.show that binding to G-actin sequesters the transcriptional coactivator MKL1 in the cytoplasm, and triggers differentiation by inducing the expression of pro-adipogenic transcription factor PPARγ.
- Hiroyuki Nobusue
- , Nobuyuki Onishi
- & Koichiro Kano
-
Article
| Open Access The origin of the bifurcated axial skeletal system in the twin-tail goldfish
The origin of the bifurcated axial skeletal system in the twin-tail goldfish
The ornamental twin-tail goldfish has a bifurcated caudal skeleton that arose during domestication, but the developmental mechanisms that generate this tail are unknown. Here, Abe et al. show that a mutation in the chordingene affects embryonic dorsal–ventral patterning causing the bifurcated tail skeleton.
- Gembu Abe
- , Shu-Hua Lee
- & Kinya G. Ota
-
Article |
 The origin of segmentation motor activity in the intestine
The origin of segmentation motor activity in the intestine
The segmentation motor activity of the small intestine is believed to be a result of alternating inhibitory and excitatory neural activity. Huizinga et al.show that the segmentation motor pattern is in fact a result of phase–amplitude interactions of slow-wave activities generated by two networks of interstitial cells of Cajal.
- Jan D. Huizinga
- , Ji-Hong Chen
- & David Chen
-
Article
| Open Access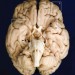 Postmortem examination of patient H.M.’s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
Postmortem examination of patient H.M.’s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
Studies on Patient H.M. showed that bilateral resection of the hippocampus results in impaired consolidation of long-term memory. Annese et al.create a digital map of Henry Molaison’s brain and find that a significant portion of the posterior hippocampus is actually histologically intact.
- Jacopo Annese
- , Natalie M. Schenker-Ahmed
- & Suzanne Corkin
-
Article |
 Antibiotic-induced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome increase susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection
Antibiotic-induced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome increase susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection
Antibiotics alter the intestinal microbiota and facilitate colonization of pathogens such as Clostridium difficile. Here, the authors show that antibiotic-induced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome are correlated with changes in levels of certain metabolites that C. difficilecan use for germination and growth.
- Casey M. Theriot
- , Mark J. Koenigsknecht
- & Vincent B. Young
-
Article |
 Gap junction signalling is a stress-regulated component of adrenal neuroendocrine stimulus-secretion coupling in vivo
Gap junction signalling is a stress-regulated component of adrenal neuroendocrine stimulus-secretion coupling in vivo
Findings from ex vivo studies suggest that gap junctional coupling contributes to hormone release in neuroendocrine/endocrine tissues. Here, the authors provide in vivo evidence that direct communication between adrenal chromaffin cells viagap junctions contributes to catecholamine secretion.
- Michel G. Desarménien
- , Carole Jourdan
- & Nathalie C. Guérineau
-
Article |
 Orai1-dependent calcium entry promotes skeletal muscle growth and limits fatigue
Orai1-dependent calcium entry promotes skeletal muscle growth and limits fatigue
The calcium-selective Orai1 channel regulates cytosolic calcium levels in a variety of cells. Here the authors use transgenic mice with muscle-specific expression of dysfunctional Orai1 to show that Orai1-mediated store-operated calcium entry promotes growth and limits fatigue of adult skeletal muscle.
- Lan Wei-LaPierre
- , Ellie M. Carrell
- & Robert T. Dirksen
-
Article |
 Polycystin-1 binds Par3/aPKC and controls convergent extension during renal tubular morphogenesis
Polycystin-1 binds Par3/aPKC and controls convergent extension during renal tubular morphogenesis
Loss-of-function mutations in PKD1, the gene encoding the plasma membrane receptor Polycystin-1, lead to renal cyst formation in polycystic kidney disease. Here, Castelli et al. show that Polycystin-1 interacts with the Par3 polarity complex and has a role in the morphogenesis of kidney tubules during mouse development.
- Maddalena Castelli
- , Manila Boca
- & Alessandra Boletta
-
Article |
 Early adipogenesis is regulated through USP7-mediated deubiquitination of the histone acetyltransferase TIP60
Early adipogenesis is regulated through USP7-mediated deubiquitination of the histone acetyltransferase TIP60
Tip60 is a transcriptional coregulator that has an important role in differentiation. Here, Gao et al. demonstrate that the deubiquitination of Tip60 by USP7, a dominant deubiquitinating enzyme, is a key mechanism in early adipogenesis regulation.
- Yuan Gao
- , Arjen Koppen
- & Eric Kalkhoven
-
Article |
 A peptide probe for targeted brown adipose tissue imaging
A peptide probe for targeted brown adipose tissue imaging
Current methods to image brown adipose tissue rely on radioactive tracers and specialized imaging equipment. Here Azhdarinia et al.report a peptide-based probe that selectively binds to the vascular endothelium of brown adipose tissue and allows the near-infrared imaging of brown fat in mice.
- Ali Azhdarinia
- , Alexes C. Daquinag
- & Mikhail G. Kolonin
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide mapping of gene–microbiota interactions in susceptibility to autoimmune skin blistering
Genome-wide mapping of gene–microbiota interactions in susceptibility to autoimmune skin blistering
The pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders afflicting the skin is multifactorial. Srinivas et al. show that diversity of the skin microbiota is a critical factor determining the susceptibility to epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, a chronic mucocutaneous autoimmune skin blistering disease.
- Girish Srinivas
- , Steffen Möller
- & Saleh M. Ibrahim
-
Article
| Open Access Genome signature-based dissection of human gut metagenomes to extract subliminal viral sequences
Genome signature-based dissection of human gut metagenomes to extract subliminal viral sequences
Bacteriophages have a significant impact on microbial ecosystems, but additional tools are needed to assess viral communities. Ogilvie et al.present a new strategy to extract viral sequences from metagenomic data sets, and present new insights on their function in the gut ecosystem.
- Lesley A. Ogilvie
- , Lucas D. Bowler
- & Brian V. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Human gut microbiota community structures in urban and rural populations in Russia
Human gut microbiota community structures in urban and rural populations in Russia
The structure of the human gut microbiota has been shown to vary between populations. Tyakht et al.analyse the gut microbiota assembly from Russian individuals living in urban and rural areas, and compare these with previously studied populations.
- Alexander V. Tyakht
- , Elena S. Kostryukova
- & Vadim M. Govorun
-
Article |
 HuR and miR-1192 regulate myogenesis by modulating the translation of HMGB1 mRNA
HuR and miR-1192 regulate myogenesis by modulating the translation of HMGB1 mRNA
The nuclear protein HMGB1 is involved in muscle fibre formation. Here, Dormoy-Raclet et al. show that during muscle cell differentiation, the RNA-binding protein HuR promotes HMGB1mRNA translation by preventing its repression by miR-1192.
- Virginie Dormoy-Raclet
- , Anne Cammas
- & Imed-Eddine Gallouzi
-
Article
| Open Access Variability in visual cortex size reflects tradeoff between local orientation sensitivity and global orientation modulation
Variability in visual cortex size reflects tradeoff between local orientation sensitivity and global orientation modulation
Surface area features of developing visual cortices are implicated in visual perception. Songet al.measure visual discrimination sensitivity in humans and find that an increase in visual cortical surface area activity is associated with improved discrimination sensitivity and degraded contextual illusions.
- Chen Song
- , Dietrich S. Schwarzkopf
- & Geraint Rees
-
Article |
 Metagenome-wide analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in a large cohort of human gut microbiota
Metagenome-wide analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in a large cohort of human gut microbiota
The appearance of antibiotic resistance has been attributed to the misuse of antibiotics. By analysing the diversity of antibiotic resistance genes present in 162 human gut microbiota samples, the authors find that Chinese individuals harbour a larger pool of resistance genes than Spanish or Danish counterparts.
- Yongfei Hu
- , Xi Yang
- & Baoli Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Structural modulation of gut microbiota in life-long calorie-restricted mice
Structural modulation of gut microbiota in life-long calorie-restricted mice
Calorie restriction has been shown to extend lifespan in diverse model systems, however, the mechanisms underlying this effect remain unclear. Zhang et al.show that calorie restriction changes the structure of the gut microbiota in mice, enriching for phylotypes positively correlated with lifespan.
- Chenhong Zhang
- , Shoufeng Li
- & Liping Zhao
-
Article |
 A stabilizing factor for mitochondrial respiratory supercomplex assembly regulates energy metabolism in muscle
A stabilizing factor for mitochondrial respiratory supercomplex assembly regulates energy metabolism in muscle
Interactions between mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes control electron transfer and oxidative phosphorylation. Here, the authors find that COX7RP regulates supercomplex assembly, and show that decreasing or increasing COX7RP expression, respectively, reduces and enhances muscular performance in mice.
- Kazuhiro Ikeda
- , Sachiko Shiba
- & Satoshi Inoue
-
Article |
 Large fibre size in skeletal muscle is metabolically advantageous
Large fibre size in skeletal muscle is metabolically advantageous
Energy demand in muscle is largely due to maintaining the membrane potential of muscle fibres. Jimenez et al.study the metabolic cost of maintaining the membrane potential of muscle fibres across different species of crustaceans and fishes, and find that larger fibres are metabolically cheaper to maintain.
- Ana Gabriela Jimenez
- , Richard M. Dillaman
- & Stephen T. Kinsey
-
Article |
 Collagen VI regulates satellite cell self-renewal and muscle regeneration
Collagen VI regulates satellite cell self-renewal and muscle regeneration
Satellite cells have important roles in homeostasis and regeneration of skeletal muscles. Urciuolo et al. show that the extracellular matrix protein collagen VI is required for preserving satellite cell self-renewal and muscle regeneration in vitro and in vivoby modulating muscle mechanical properties.
- Anna Urciuolo
- , Marco Quarta
- & Paolo Bonaldo
-
Article |
 Tribbles 3 mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle
Tribbles 3 mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is observed in diabetes and has been linked to insulin resistance in various tissues. Here, Koh and colleagues show the protein Tribbles 3, which is induced by ER stress and obesity in mice and humans, is an inhibitor of insulin signalling in skeletal muscle.
- Ho-Jin Koh
- , Taro Toyoda
- & Laurie J. Goodyear
-
Article |
 Constitutively active Foxo3 in oocytes preserves ovarian reserve in mice
Constitutively active Foxo3 in oocytes preserves ovarian reserve in mice
The number of primordial follicles, which constitute the ovarian reserve, decreases with age. By overexpressing a constitutively active version of the transcription factor FOXO3, the authors increase the ovarian reserve and fertility in aging female mice.
- Emanuele Pelosi
- , Shakib Omari
- & Chris Ottolenghi
-
Article
| Open Access The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43
The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43
The gut microbiota produces metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which can influence the development of obesity. Here Kimura et al.show that SCFAs act via the receptor GPR43, which acts as a sensor for excessive dietary energy and controls body energy utilization as well as metabolic homoeostasis.
- Ikuo Kimura
- , Kentaro Ozawa
- & Gozoh Tsujimoto
-
Article |
 Competing signals drive telencephalon diversity
Competing signals drive telencephalon diversity
The brains of rock- and sand-dwelling Lake Malawi cichlid fishes differ in telencephalon partitioning. Sylvester et al. show that these differences can be attributed to divergence in Hedgehog and Wingless signalling during development.
- J B. Sylvester
- , C A. Rich
- & J T. Streelman
-
Article |
 Normal muscle regeneration requires tight control of muscle cell fusion by tetraspanins CD9 and CD81
Normal muscle regeneration requires tight control of muscle cell fusion by tetraspanins CD9 and CD81
The skeletal muscle has a remarkable capacity to regenerate after injury. Here Charrin et al. reveal that restoration of muscle architecture after injury requires a tight control of muscle cell fusion by the tetraspanin proteins CD9 and CD81 through their interaction with the cell surface protein CD9P-1.
- Stéphanie Charrin
- , Mathilde Latil
- & Eric Rubinstein

 Cultivation-based multiplex phenotyping of human gut microbiota allows targeted recovery of previously uncultured bacteria
Cultivation-based multiplex phenotyping of human gut microbiota allows targeted recovery of previously uncultured bacteria