Volume 24
-
No. 12 December 2006
Polarized light micrograph (400x) of penicillin crystals, the first commercially available antibacterial, grown in an aqueous solution. To date, the penicillins, initially derived from molds, still represent the gold standard by which other antibiotics are measured. This issue reviews the current state of the science and business of antibacterials. (Jung/Photo Researchers, Inc.)
Focus
-
No. 11 November 2006
Influorescence of a tobacco plant (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Chappell and colleagues divert carbon from the plastidic and cytosolic isoprenoid bio-syntheic pathways to engineer elevated sesquiterpene and monoterpene production in tobacco (p 1441). Credit: Patrick Robert/Corbis.
-
No. 10 October 2006
Map of 15 epitopes in a primary human hepatocyte, analyzed and visualized by multi-epitope-ligand cartography (MELC). In this issue, Schubert and colleagues introduce MELC as a means of mapping large numbers of molecular components at subcellular resolution in single cells and tissue sections (p 1270). Image courtesy of Walter Schubert.
Collection
-
No. 9 September 2006
The MicroArray Quality Control Consortium, which brings together over 100 scientists from academia, industry and the government, presents the results of a detailed analysis of the performance of seven DNA microarray platforms. Cover art: Erin Boyle
-
No. 8 August 2006
In his painting Diagnostics 2, Frank Shaw presents an abstract vision of how diagnostic approaches reveal the “depth, structure and function of the elements of the body.” This issue includes a focus on recent advances in diagnostics and drug development. (http://www.frankshawart.com)
Focus
-
No. 7 July 2006
Colored scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of dividing Schizosaccharomyces pombe cells. Matsuyama et al. have cloned and partially characterized all protein-encoding open reading frames (the ORFeome) of fission yeast (p 841). Credit: Steve Gschmeissner/Science Photo Library.
-
No. 6 June 2006
Phase contrast micrograph of microwells from arrays containing monoclonal antibody-producing hybridomas. The small volumes of the microwells (~1 nL each) in the arrays described by Love et al. ensure that the antibodies produced by single cells are detectable in only 2-4 hours, compared with the 2-7 days required using current approaches, p. 703.
-
No. 5 May 2006
Vase coral (Montipora sp.). Kogure et al. have isolated a fluorescent protein, Keima, from the stony coral Montipora. A variant of Keima facilitates dual-color single-laser fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy (p 577). Credit: Jeff Rotman.
-
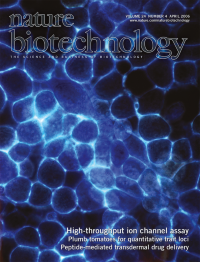
No. 4 April 2006
Fluorescence image of live human embryonic kidney cells showing voltage-gated sodium channels stained with a voltage-sensitive fluorescent dye. González and colleagues describe rapid electro-optical method for screening candidate ion-channel blockers. (p. 439)
-
No. 3 March 2006
Nature Biotechnology celebrates ten years of publishing the very best of biotech science and business. Cover art: Erin Boyle.
Focus
-
No. 2 February 2006
Colored scanning electron micrograph of Streptococcus pyogenes, a group A Streptococcus that can cause multiple infections in humans. Grandi and colleagues describe a proteomic approach to identifying novel antigens for the development of vaccines against this group of organisms, p 191. Credit: Eye of Science/Photo Researchers, Inc.
-
No. 1 January 2006
Sickle cell anemia imparts an elongated 'sickle' shape to red blood cells. Samakoglu et al. describe a therapeutic strategy that combines provision of the normal globin gene and siRNA knockdown of the mutant gene (p 89). Credit: Photo Researchers, Inc.