Abstract
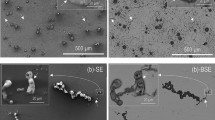
The development of porous anodic films on aluminium in the major forming acids has been established1–5. However, little information has been provided to explain the markedly different rates of steady-state film growth for anodizing in constant voltage conditions in these acids, with the anodic film cell parameters dependent on the cell voltage1. The regular cellular morphology of the steady-state films and the substructure developed in the forming acids are revealed in Fig. 1. The characteristic parallel-sided pores, at the centres of approximately hexagonal cells, pass normal to the macroscopic metal surface but are separated from it by the barrier layer. Here, from considerations of the film material substructure and the distribution of species within the film derived from the forming acid, it is postulated that the likely variations in the local field strengths across the barrier layers can explain the steady-state anodizing behaviour observed in the different acids in constant voltage conditions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Sullivan, J. P. & Wood, G. C. Proc. R. Soc. A317, 511–543 (1979).
Thompson, G. E., Furneaux, R. C., Goode, J. S. & Wood, G. C. Trans. Inst. Metal Finishing 56, 159–167 (1978).
Thompson, G. E., Furneaux, R. C. & Wood, G. C. Trans. Inst. Metal Finishing 55, 117–128 (1977).
Bailey, G. & Wood, G. C. Trans. Inst. Metal Finishing 52, 187–199 (1975).
Thompson, G. E., Wood, G. C. & Hutchings, R. Trans. Inst. Metal Finishing 58, 21–25 (1980).
Thompson, G. E., Furneaux, R. C. & Wood, G. C. Corros. Sci. 18, 481–498 (1978).
Thompson, G. E., Furneaux, R. C., Wood, G. C. & Hutchings, R. J. electrochem. Soc. 125, 1480–1482 (1978).
Thompson, G. E., Furneaux, R. C., Wood, G. C., Richardson, J. A. & Goode, J. S. Nature 272, 433–435 (1978).
Dell'Oca, C. J. & Young, L. J. electrochem. Soc. 117, 1548–1551 (1970).
Dignam, M. J. J. electrochem. Soc. 126, 2188–2195 (1979).
Furneaux, R. C., Thompson, G. E. & Wood, G. C. Corros. Sci. 18, 853–881 (1978).
Matyevic, E., Bell, A., Brace, R. & McFadyen, P. J. electrochem. Soc. 120, 893–899 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, G., Wood, G. Porous anodic film formation on aluminium. Nature 290, 230–232 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/290230a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/290230a0
This article is cited by
-
Porous alumina–lithium composites for novel lithium-ion batteries
Journal of Applied Electrochemistry (2024)
-
Self-ordered nanospike porous alumina fabricated under a new regime by an anodizing process in alkaline media
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Preparation and mechanism of honeycomb-like nanoporous SnO2 by anodization
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2021)
-
Nanoelectrode design from microminiaturized honeycomb monolith with ultrathin and stiff nanoscaffold for high-energy micro-supercapacitors
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Synthesis of single-phase Au nanorods in an anodic aluminum oxide template with an optimized process for a highly sensitive and non-enzyme methyl mercaptan gas detector
Microsystem Technologies (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.