Abstract
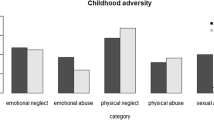
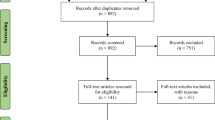
Obesity is a prevalent global-health problem associated with substantial morbidity, impairment and economic burden. Because most readily available forms of treatment are ineffective in the long term, it is essential to advance knowledge of obesity prevention by identifying potentially modifiable risk factors. Findings from experimental studies in non-human primates suggest that adverse childhood experiences may influence obesity risk. However, observations from human studies showed heterogeneous results. To address these inconsistencies, we performed Medline, PsycInfo and Embase searches till 1 August 2012 for articles examining the association between childhood maltreatment and obesity. We then conducted a meta-analysis of the identified studies and explored the effects of various possible sources of bias. A meta-analysis of 41 studies (190 285 participants) revealed that childhood maltreatment was associated with elevated risk of developing obesity over the life-course (odds ratio=1.36; 95% confidence interval=1.26–1.47). Results were not explained by publication bias or undue influence of individual studies. Overall, results were not significantly affected by the measures or definitions used for maltreatment or obesity, nor by confounding by childhood or adult socioeconomic status, current smoking, alcohol intake or physical activity. However, the association was not statistically significant in studies of children and adolescents, focusing on emotional neglect, or adjusting for current depression. Furthermore, the association was stronger in samples including more women and whites, but was not influenced by study quality. Child maltreatment is a potentially modifiable risk factor for obesity. Future research should clarify the mechanisms through which child maltreatment affects obesity risk and explore methods to remediate this effect.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM . Prevalence of obesity and trends in body mass index among US children and adolescents, 1999–2010. JAMA 2012; 307: 483–490.
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL . Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA 2012; 307: 491–497.
Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M . Obesity and diabetes in the developing world—a growing challenge. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 213–215.
Haslam DW, James WP . Obesity. Lancet 2005; 366: 1197–1209.
Van Gaal LF, Mertens IL, De Block CE . Mechanisms linking obesity with cardiovascular disease. Nature 2006; 444: 875–880.
Alley DE, Chang VW . The changing relationship of obesity and disability, 1988–2004. JAMA 2007; 298: 2020–2027.
Leblanc ES, O'Connor E, Whitlock EP, Patnode CD, Kapka T . Effectiveness of primary care-relevant treatments for obesity in adults: a systematic evidence review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med 2011; 155: 434–447.
Bouret SG, Draper SJ, Simerly RB . Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science 2004; 304: 108–110.
Mainardi M, Scabia G, Vottari T, Santini F, Pinchera A, Maffei L et al. A sensitive period for environmental regulation of eating behavior and leptin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 16673–16678.
Remmers F, Delemarre-van de Waal HA . Developmental programming of energy balance and its hypothalamic regulation. Endocr Rev 2011; 32: 272–311.
Dietz WH . Critical periods in childhood for the development of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 1994; 59: 955–959.
Gillman MW . A life course approach to overweight and obesity. In: Kuh D, Ben-Shlomo Y (eds). A Life Course Approach to Chronic Diseases Epidemiology. Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004.
McCance RA . Food, growth, and time. Lancet 1962; 2: 671–676.
Ravelli GP, Stein ZA, Susser MW . Obesity in young men after famine exposure in utero and early infancy. N Engl J Med 1976; 295: 349–353.
Kaufman D, Banerji MA, Shorman I, Smith EL, Coplan JD, Rosenblum LA et al. Early-life stress and the development of obesity and insulin resistance in juvenile bonnet macaques. Diabetes 2007; 56: 1382–1386.
Conti G, Hansman C, Heckman JJ, Novak MF, Ruggiero A, Suomi SJ . Primate evidence on the late health effects of early-life adversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 8866–8871.
Midei AJ, Matthews KA . Interpersonal violence in childhood as a risk factor for obesity: a systematic review of the literature and proposed pathways. Obes Rev 2011; 12: e159–e172.
Wardle J, Chida Y, Gibson EL, Whitaker KL, Steptoe A . Stress and adiposity: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Obesity (Silver Spring, MD) 2011; 19: 771–778.
Lipsey MW, Wilson DB . Practical Meta-Analysis. Sage Publications, 2000.
Chinn S . A simple method for converting an odds ratio to effect size for use in meta-analysis. Stat Med 2000; 19: 3127–3131.
Cochran WG . The comparison of percentages in matched samples. Biometrika 1950; 37: 256–266.
Laupacis A, Sackett DL, Roberts RS . An assessment of clinically useful measures of the consequences of treatment. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1728–1733.
Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2012; Available at: http://www.cochrane-handbook.org. (accessed on 2012).
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C . Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997; 315: 629–634.
Begg C, Mazumdar M . Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994; 50: 1088–1101.
Duval S, Tweedie R . A nonparametric ‘trim and fill’ method of accounting for publication bias in meta-analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 2000; 95: 89–98.
Fazel M, Wheeler J, Danesh J . Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7000 refugees resettled in western countries: a systematic review. Lancet 2005; 365: 1309–1314.
The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Available at: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm. (accessed on 2012).
Nanni V, Uher R, Danese A . Childhood maltreatment predicts unfavorable course of illness and treatment outcome in depression: a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 2012; 169: 141–151.
Aaron DJ, Hughes TL . Association of childhood sexual abuse with obesity in a community sample of lesbians. Obesity (Silver Spring. MD) 2007; 15: 1023–1028.
Alvarez J, Pavao J, Baumrind N, Kimerling R . The relationship between child abuse and adult obesity among california women. Am J Prev Med 2007; 33: 28–33.
Bennett DS, Wolan Sullivan M, Thompson SM, Lewis M . Early child neglect: does it predict obesity or underweight in later childhood? Child Maltreat 2010; 15: 250–254.
Bentley T, Widom CSA . 30-year follow-up of the effects of child abuse and neglect on obesity in adulthood. Obesity (Silver Spring, MD) 2009; 17: 1900–1905.
Boynton-Jarrett R, Rosenberg L, Palmer JR, Boggs DA, Wise LA . Child and adolescent abuse in relation to obesity in adulthood: The Black Women’s Health Study. Pediatrics 2012; 130: 245–253.
Brown BE, Garrison CJ . Patterns of symptomatology of adult women incest survivors. West J Nurs Res 1990; 12: 587–596, discussion 96–600.
Burke NJ, Hellman JL, Scott BG, Weems CF, Carrion VG . The impact of adverse childhood experiences on an urban pediatric population. Child Abuse Negl 2011; 35: 408–413.
Chartier MJ, Walker JR, Naimark B . Health risk behaviors and mental health problems as mediators of the relationship between childhood abuse and adult health. Am J Public Health 2009; 99: 847–854.
Clark DB, Thatcher DL, Martin CS . Child abuse and other traumatic experiences, alcohol use disorders, and health problems in adolescence and young adulthood. J Pediatr Psychol 2010; 35: 499–510.
D’Argenio A, Mazzi C, Pecchioli L, Di Lorenzo G, Siracusano A, Troisi A . Early trauma and adult obesity: is psychological dysfunction the mediating mechanism? Physiol Behav 2009; 98: 543–546.
Danese A, Caspi A, Williams B, Ambler A, Sugden K, Mika J et al. Biological embedding of stress through inflammation processes in childhood. Mol Psychiatry 2011; 16: 244–246.
Dube SR, Cook ML, Edwards VJ . Health-related outcomes of adverse childhood experiences in Texas, 2002. Prev Chronic Dis 2010; 7: A52.
Felitti VJ . Long-term medical consequences of incest, rape, and molestation. South Med J 1991; 84: 328–331.
Felitti VJ . Childhood sexual abuse, depression, and family dysfunction in adult obese patients: a case control study. South Med J 1993; 86: 732–736.
Fuemmeler BF, Dedert E, McClernon FJ, Beckham JC . Adverse childhood events are associated with obesity and disordered eating: results from a US population-based survey of young adults. J Trauma Stress 2009; 22: 329–333.
Greenfield EA, Marks NF . Violence from parents in childhood and obesity in adulthood: using food in response to stress as a mediator of risk. Soc Sci Med 2009; 68: 791–798.
Gunstad J, Paul RH, Spitznagel MB, Cohen RA, Williams LM, Kohn M et al. Exposure to early life trauma is associated with adult obesity. Psychiatry Res 2006; 142: 31–37.
Hepgul N, Pariante CM, Dipasquale S, DiForti M, Taylor H, Marques TR et al. Childhood maltreatment is associated with increased body mass index and increased C-reactive protein levels in first episode psychosis patients. Psychol Med 2012; 42: 1893–1901.
Holmberg LI, Hellberg D . Sexually abused children. Characterization of these girls when adolescents. Int J Adolesc Med Health 2010; 22: 291–300.
Jia H, Li JZ, Leserman J, Hu Y, Drossman DA . Relationship of abuse history and other risk factors with obesity among female gastrointestinal patients. Digest Dis Sci 2004; 49: 872–877.
Johnson JG, Cohen P, Kasen S, Brook JS . Childhood adversities associated with risk for eating disorders or weight problems during adolescence or early adulthood. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159: 394–400.
Knutson JF, Taber SM, Murray AJ, Valles NL, Koeppl G . The role of care neglect and supervisory neglect in childhood obesity in a disadvantaged sample. J Pediatr Psychol 2010; 35: 523–532.
Lehman BJ, Taylor SE, Kiefe CI, Seeman TE . Relation of childhood socioeconomic status and family environment to adult metabolic functioning in the CARDIA study. Psychosom Med 2005; 67: 846–854.
Lissau I, Sorensen TI . Parental neglect during childhood and increased risk of obesity in young adulthood. Lancet 1994; 343: 324–327.
Mamun AA, Lawlor DA, O'Callaghan MJ, Bor W, Williams GM, Najman JM . Does childhood sexual abuse predict young adult’s BMI? A birth cohort study. Obesity (Silver Spring, MD) 2007; 15: 2103–2110.
Midei AJ, Matthews KA, Bromberger JT . Childhood abuse is associated with adiposity in midlife women: possible pathways through trait anger and reproductive hormones. Psychosom Med 2010; 72: 215–223.
Moeller TP, Bachmann GA, Moeller JR . The combined effects of physical, sexual, and emotional abuse during childhood: long-term health consequences for women. Child Abuse Negl 1993; 17: 623–640.
Moyer DM, DiPietro L, Berkowitz RI, Stunkard AJ . Childhood sexual abuse and precursors of binge eating in an adolescent female population. Int J Eating Disord 1997; 21: 23–30.
Noll JG, Zeller MH, Trickett PK, Putnam FW . Obesity risk for female victims of childhood sexual abuse: a prospective study. Pediatrics 2007; 120: e61–e67.
Pederson CL, Wilson JF . Childhood emotional neglect related to posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms and body mass index in adult women. Psychol Rep 2009; 105: 111–126.
Rich-Edwards JW, Spiegelman D, Lividoti Hibert EN, Jun HJ, Todd TJ, Kawachi I et al. Abuse in childhood and adolescence as a predictor of type 2 diabetes in adult women. Am J Prev Med 2010; 39: 529–536.
Rodgers CS, Lang AJ, Laffaye C, Satz LE, Dresselhaus TR, Stein MB . The impact of individual forms of childhood maltreatment on health behavior. Child Abuse Negl 2004; 28: 575–586.
Rohde P, Ichikawa L, Simon GE, Ludman EJ, Linde JA, Jeffery RW et al. Associations of child sexual and physical abuse with obesity and depression in middle-aged women. Child Abuse Negl 2008; 32: 878–887.
Schneiderman JU, Mennen FE, Negriff S, Trickett PK . Overweight and obesity among maltreated young adolescents. Child Abuse Negl 2012; 36: 370–378.
Sickel AE, Noll JG, Moore PJ, Putnam FW, Trickett PK . The long-term physical health and healthcare utilization of women who were sexually abused as children. J Health Psychol 2002; 7: 583–597.
Smith HA, Markovic N, Danielson ME, Matthews A, Youk A, Talbott EO et al. Sexual abuse, sexual orientation, and obesity in women. J Women’s Health 2010; 19: 1525–1533.
Springs FE, Friedrich WN . Health risk behaviors and medical sequelae of childhood sexual abuse. Mayo Clin Proc 1992; 67: 527–532.
Thomas C, Hypponen E, Power C . Obesity and type 2 diabetes risk in midadult life: the role of childhood adversity. Pediatrics 2008; 121: e1240–e1249.
Whitaker RC, Phillips SM, Orzol SM, Burdette HL . The association between maltreatment and obesity among preschool children. Child Abuse Negl 2007; 31: 1187–1199.
Williamson DF, Thompson TJ, Anda RF, Dietz WH, Felitti V . Body weight and obesity in adults and self-reported abuse in childhood. Int J Obes 2002; 26: 1075–1082.
van Reedt Dortland AK, Giltay EJ, van Veen T, Zitman FG, Penninx BW . Personality traits and childhood trauma as correlates of metabolic risk factors: the Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety (NESDA). Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2012; 36: 85–91.
Shin SH, Miller DP . A longitudinal examination of childhood maltreatment and adolescent obesity: results from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health (AddHealth) Study. Child Abuse Negl 2012; 36: 84–94.
Luppino FS, de Wit LM, Bouvy PF, Stijnen T, Cuijpers P, Penninx BW et al. Overweight, obesity, and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010; 67: 220–229.
Deurenberg P, Yap M, van Staveren WA . Body mass index and percent body fat: a meta analysis among different ethnic groups. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998; 22: 1164–1171.
Felitti VJ, Anda RF, Nordenberg D, Williamson DF, Spitz AM, Edwards V et al. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study. Am J Prev Med 1998; 14: 245–258.
McGowan PO, Sasaki A, D'Alessio AC, Dymov S, Labonté B, Szyf M et al. Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nat Neurosci 2009; 12: 342–348.
Tyrka AR, Price LH, Marsit C, Walters OC, Carpenter LL . Childhood adversity and epigenetic modulation of the leukocyte glucocorticoid receptor: preliminary findings in healthy adults. PLoS One 2012; 7: e30148.
Danese A, McEwen BS . Adverse childhood experiences, allostasis, allostatic load, and age-related disease. Physiol Behav 2012; 106: 29–39.
Lock J, Garrett A, Beenhakker J, Reiss AL . Aberrant brain activation during a response inhibition task in adolescent eating disorder subtypes. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168: 55–64.
Welch SL, Fairburn CG . Sexual abuse and bulimia nervosa: three integrated case control comparisons. Am J Psychiatry 1994; 151: 402–407.
Dallman MF, Pecoraro N, Akana SF, La Fleur SE, Gomez F, Houshyar H et al. Chronic stress and obesity: a new view of ‘comfort food’. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 11696–11701.
Adam TC, Epel ES . Stress, eating and the reward system. Physiol Behav 2007; 91: 449–458.
Licinio J, Mantzoros C, Negrao AB, Cizza G, Wong ML, Bongiorno PB et al. Human leptin levels are pulsatile and inversely related to pituitary–adrenal function. Nat Med 1997; 3: 575–579.
Fulton S, Woodside B, Shizgal P . Modulation of brain reward circuitry by leptin. Science 2000; 287: 125–128.
Hill MN, Patel S, Campolongo P, Tasker JG, Wotjak CT, Bains JS . Functional interactions between stress and the endocannabinoid system: from synaptic signaling to behavioral output. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 14980–14986.
Pagotto U, Marsicano G, Cota D, Lutz B, Pasquali R . The emerging role of the endocannabinoid system in endocrine regulation and energy balance. Endocr Rev 2006; 27: 73–100.
Volkow ND, Wise RA . How can drug addiction help us understand obesity? Nat Neurosci 2005; 8: 555–560.
Kenny PJ . Common cellular and molecular mechanisms in obesity and drug addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011; 12: 638–651.
Dube SR, Felitti VJ, Dong M, Chapman DP, Giles WH, Anda RF . Childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction and the risk of illicit drug use: the adverse childhood experiences study. Pediatrics 2003; 111: 564–572.
Danese A, Pariante CM, Caspi A, Taylor A, Poulton R . Childhood maltreatment predicts adult inflammation in a life-course study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 1319–1324.
Miller AH, Maletic V, Raison CL . Inflammation and its discontents: the role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2009; 65: 732–741.
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW . From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2008; 9: 46–56.
Wagner IV, Sabin MA, Pfaffle RW, Hiemisch A, Sergeyev E, Körner A et al. Effects of obesity on human sexual development. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2012; 8: 246–254.
Kraemer HC, Yesavage JA, Taylor JL, Kupfer D . How can we learn about developmental processes from cross-sectional studies, or can we? Am J Psychiatry 2000; 157: 163–171.
Rose G . Incubation period of coronary heart disease. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 1982; 284: 1600–1601.
Macmillan HL, Wathen CN, Barlow J, Fergusson DM, Leventhal JM, Taussig HN . Interventions to prevent child maltreatment and associated impairment. Lancet 2009; 373: 250–266.
Chaffin M, Silovsky JF, Funderburk B, Valle LA, Brestan EV, Balachova T et al. Parent–child interaction therapy with physically abusive parents: efficacy for reducing future abuse reports. J Consult Clin Psychol 2004; 72: 500–510.
Barlow J, Johnston I, Kendrick D, Polnay L, Stewart-Brown S . Individual and group-based parenting programmes for the treatment of physical child abuse and neglect. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006; 3: CD005463.
Cohen JA, Mannarino AP, Deblinger E . Treating Trauma and Traumatic Grief in Children and Adolescents. Guilford Press, 2006.
Bisson J, Andrew M . Psychological treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007; 3: CD003388.
Radford L, Corral S, Bradley C et al Child Abuse and Neglect in UK Today. NSPCC: London, 2011.
Gilbert R, Widom CS, Browne K, Fergusson D, Webb E, Janson S . Burden and consequences of child maltreatment in high-income countries. Lancet 2009; 373: 68–81.
Shonkoff JP, Garner AS . The lifelong effects of early childhood adversity and toxic stress. Pediatrics 2012; 129: e232–e246.
Acknowledgements
Dr AD was supported by a Clinical Lectureship from the London Deanery, by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute of the US National Institutes of Health under Award Number R21HL109396, and by the UK Medical Research Council's grants G1002190 and G9806489. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the US National Institutes of Health or the UK Medical Research Council. No funding bodies had any role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript. Dr AD had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danese, A., Tan, M. Childhood maltreatment and obesity: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 19, 544–554 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.54
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.54
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multiple mediation of the association between childhood emotional abuse and adult obesity by anxiety and bulimia – a sample from bariatric surgery candidates and healthy controls
BMC Public Health (2024)
-
Weight development from childhood to motherhood—embodied experiences in women with pre-pregnancy obesity: a qualitative study
Reproductive Health (2024)
-
Alterations in adolescent brain serotonin (5HT)1A, 5HT2A, and dopamine (D)2 receptor systems in a nonhuman primate model of early life adversity
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Early life adversity and obesity risk in adolescence: a 9-year population-based prospective cohort study
Pediatric Research (2024)
-
Childhood Adversity and Adult Inflammation: Exploring the Mediating Role of Emotion Regulation in the MIDUS II Study
Journal of Child & Adolescent Trauma (2024)