Abstract
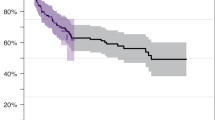
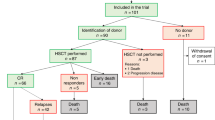
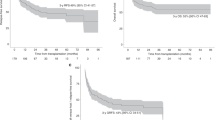
Administration of alkylating agents (Alk), topoisomerase II inhibitors (Topo II) and radiotherapy (RT) can result in therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myelogenous leukaemia (t-MDS/t-AML), the optimal treatment for which is allo-SCT. A retrospective review was performed of 24 patients who underwent related- or unrelated-donor SCT for t-MDS/t-AML at our institution. Eight patients remain alive and in continuous remission (median follow-up 54 months (range, 12–161)) with estimated 5-year EFS being 30% (95% confidence intervals 16–58%). Corresponding actuarial risks of relapse and non-relapse mortality (NRM) are 39% (19–60%) and 30% (13–50%), respectively. EFS was 40% in Alk/RT-related t-MDS/t-AML and 11% in Topo II-related t-MDS/t-AML (P=0.05), with an increased risk of relapse in the latter (56 vs 29%, respectively (P=0.05)). In multivariate analysis, development of acute GVHD (P=0.009) and Topo II-related t-MDS/t-AML (P=0.018) were associated with inferior EFS. Patients with acute GVHD had an increased risk of NRM (P=0.03) whereas risk of relapse was higher for patients of advanced age (P=0.046) and for patients who underwent bone marrow (vs blood) SCT (P=0.032). Allo-SCT can result in long-term survival for individuals with t-MDS/t-AML although outcome in Topo II-related t-MDS/t-AML patients remains suboptimal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michels SD, McKenna RW, Arthur DC, Brunning RD . Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: a clinical and morphologic study of 65 cases. Blood 1985; 65: 1364–1372.
Smith SM, Le Beau MM, Huo D, Karrison T, Sobecks RM, Anastasi J et al. Clinical-cytogenetic associations in 306 patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia: the University of Chicago experience. Blood 2003; 102: 43–52.
Singh ZN, Huo D, Anastasi J, Smith SM, Karrison T, Le Beau MM et al. Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome: morphologic subclassification may not be clinically relevant. Am J Clin Pathol 2007; 127: 197–205.
Pui CH, Relling MV, Rivera GK, Hancock ML, Raimondi SC, Heslop HE et al. Epipodophyllotoxin-related acute myeloid leukemia: a study of 35 cases. Leukemia 1995; 9: 1990–1996.
Pui CH, Relling MV . Topoisomerase II inhibitor-related acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2000; 109: 13–23.
Vardiman JW, Harris NL, Brunning RD . The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood 2002; 100: 2292–2302.
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley K, Harrison C, Harrison G et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. Blood 1998; 92: 2322–2333.
Kantarjian HM, Estey EH, Keating MJ . Treatment of therapy-related leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Hematol/Oncol Clin N Am 1993; 7: 81–106.
Kröger N, Brand R, van Biezen A, Cahn J-Y, Slavin S, Blaise D et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 183–189.
Forrest DL, Nevill TJ, Horsman DE, Brockington DA, Fung HC, Toze CL et al. Bone marrow transplantation for adults with acute leukaemia and 11q23 chromosomal abnormalities. Br J Haematol 1998; 103: 630–638.
Fung HC, Nantel SH, Phillips GL, Shepherd JD, Sutherland HJ, Klingemann H-G et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) for adults with secondary myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or secondary acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Blood 1995; 86 (suppl 1): 96a.
Anderson JE, Gooley TA, Schoch G, Anasetti C, Bensinger WI, Clift RA et al. Stem cell transplantation for secondary acute myeloid leukemia: evaluation of transplantation as initial therapy or following induction chemotherapy. Blood 1997; 89: 2578–2585.
Ballen KK, Gilliland DG, Guinan EC, Hsieh C-C, Parsons SK, Rimm IJ et al. Bone marrow transplantation for therapy-related myelodysplasia: comparison with primary myelodysplasia. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 737–743.
Nevill TJ, Shepherd JD, Brockington DA, Le A, Sutherland HJ, Toze CL et al. High-dose chemo/radiotherapy and stem cell transplantation for therapy-induced myelodysplasia or acute myelogenous leukemia: outcome analysis and significance of marrow karyotype. Leuk Res 2001; 25 (suppl 1): S35–S36.
Barnard DR, Lange B, Alonzo TA, Buckley J, Kobrinsky JN, Gold S et al. Acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome in children treated for cancer: comparison with primary presentation. Blood 2002; 100: 427–434.
Nevill TJ, Fung HC, Shepherd JD, Horsman DE, Nantel SH, Klingemann HG et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities in primary myelodysplastic syndrome are highly predictive of outcome after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1998; 92: 1910–1917.
Greenberg P, Cox C, Le Beau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Grigg A, Shepherd JD, Phillips GL . Busulphan and phenytoin. Ann Intern Med 1989; 111: 1049–1050 (letter) (correction 112:313,1990).
Storb R, Deeg HJ, Whitehead J, Appelbaum F, Beatty P, Bensinger W et al. Methotrexate and cyclosporine compared with cyclosporine alone for prophylaxis of acute graft versus host disease after marrow transplantation for leukemia. N Engl J Med 1986; 314: 729–735.
Thomas TE, Abraham SJR, Phillips GL, Lansdorp PE . Depletion of CD3+ cells from allogeneic bone marrow grafts using high gradient magnetic separation. Clin Invest Med 1994; 17 (suppl B): B58.
Attal M, Huguet F, Rubie H, Huynh A, Charet JP, Payen JL et al. Prevention of hepatic veno-occlusive disease after bone marrow transplantation by continuous infusion low-dose heparin: a prospective, randomized trial. Blood 1992; 79: 2834–2840.
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Gray JR . A class of K-sample tests for comparing the cumulative incidence of a competing risk. Ann Stat 1988; 16: 1141–1154.
Cox DR . Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc B 1972; 34: 187–220.
Longmore G, Guinan EC, Weinstein HJ, Gelber RD, Rappeport JM, Antin JH . Bone marrow transplantation for myelodysplasia and secondary acute non-lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 1990; 8: 1707–1714.
Sargur M, Buckner CD, Appelbaum FR, Stewart P, Deeg HJ, Weiden PL et al. Marrow transplantation for acute nonlymphocytic leukemia following therapy for Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Oncol 1987; 5: 731–734.
Yakoub-Agha I, de La Salmoniére P, Ribaud P, Sutton L, Wattel E, Kuentz M et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia: a long-term study of 70 patients—report of the French Society of Bone Marrow Transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 963–971.
Chang C, Storer BE, Scott BL, Bryant EM, Shulman HM, Flowers ME et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia arising from myelodysplastic syndrome: similar outcomes in patients with de novo disease and disease following prior therapy or antecedent hematologic disorders. Blood 2007; 110: 1379–1387.
Kroeger N, Brand R, van Biezen A, Niederwieser D, de Witte T . Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome (t-MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia. A report from the MDS subcommittee of the chronic leukemia working party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Blood 2007; 110: 81a.
Witherspoon RP, Deeg HJ, Storer B, Anasetti C, Storb R, Appelbaum FR . Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for treatment-related leukemia or myelodysplasia. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 2134–2141.
Pui CH, Ribeiro RC, Hancock ML, Rivera GK, Evans WE, Raimondi SC et al. Acute myeloid leukemia in children treated with epipodophyllotoxins for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 1682–1687.
Sandler ES, Friedman DJ, Mustafa MM, Winick NJ, Bowman WP, Buchanan GR . Treatment of children with epipodophyllotoxin-induced secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 1997; 79: 1049–1054.
Leahey AM, Friedman DL, Bunin NJ . Bone marrow transplantation in pediatric patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia and leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 23: 21–25.
Hale GA, Heslop HE, Bowman LC, Rochester RA, Pui C-H, Brenner MK et al. Bone marrow transplantation for therapy-induced acute myeloid leukemia in children with previous lymphoid malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 735–739.
Andersen MK, Larson RA, Mauritzon N, Schnittger S, Jhanwar SC, Pedersen-Bjergaard J . Balanced chromosome abnormalities inv(16) and t(15;17) in therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes and acute leukemia: report from an international workshop. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002; 33: 395–400.
Ho A, Pagliuca A, Kenyon M, Parker JE, Mijovic A, Devereux S et al. Reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia with multilineage dysplasia using fludarabine, busulphan, and alemtuzumab (FBC) conditioning. Blood 2004; 104: 1616–1623.
Nakamura R, Rodriguez R, Palmer J, Stein A, Naing A, Tsai N et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with fludarabine and mephalan is associated with durable disease control in myelodysplastic syndrome. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 843–850.
Scott BL, Storer B, Loken MR, Storb R, Appelbaum FR, Deeg HJ . Pretransplantation induction chemotherapy and post-transplantation relapse in patients with advanced myelodysplastic syndrome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 65–73.
Bensinger WI, Martin RJ, Storer B, Clift R, Forman SJ, Negrin R et al. Transplantation of bone marrow as compared with peripheral-blood cells from HLA-identical relatives in patients with hematologic cancers. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 175–181.
Couban S, Simpson DR, Barnett MJ, Bredeson C, Huebsch L, Howsan-Jan K et al. A randomized multicenter comparison of bone marrow and peripheral blood in recipients of matched sibling allogeneic transplants for myeloid malignancies. Blood 2002; 100: 1525–1531.
Acknowledgements
We thank the nursing and support staff of Wards T15 and CP6 of the Vancouver General Hospital for the superb care given to the patients of the Leukaemia/BMT Program of British Columbia and Alan Le and Yung-Feng Dai for their assistance with the graphics in the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nevill, T., Hogge, D., Toze, C. et al. Predictors of outcome following myeloablative allo-SCT for therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome and AML. Bone Marrow Transplant 42, 659–666 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.226
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.226
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome and acute leukemia: a single-center analysis of 47 patients
International Journal of Hematology (2010)
-
The evolution of hematopoietic SCT in myelodysplastic syndrome
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2009)