Abstract
Rh is one of the most important noble metals for industrial applications. A major fraction of Rh is used as a catalyst for emission control in automotive catalytic converters because of its unparalleled activity toward NOx reduction. However, Rh is a rare and extremely expensive element; thus, the development of Rh alternative composed of abundant elements is desirable. Pd and Ru are located at the right and left of Rh in the periodic table, respectively, nevertheless this combination of elements is immiscible in the bulk state. Here, we report a Pd–Ru solid-solution-alloy nanoparticle (PdxRu1-x NP) catalyst exhibiting better NOx reduction activity than Rh. Theoretical calculations show that the electronic structure of Pd0.5Ru0.5 is similar to that of Rh, indicating that Pd0.5Ru0.5 can be regarded as a pseudo-Rh. Pd0.5Ru0.5 exhibits better activity than natural Rh, which implies promising applications not only for exhaust-gas cleaning but also for various chemical reactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Rh is an important element that exhibits excellent activity in numerous catalytic reactions1,2,3,4,5,6,7. However, the abundance of Rh is only one-fifth of Pt and it is one of the least abundant elements in the Earth’s crust8,9. Such rarity makes the price of Rh very volatile and high; for example, Rh reached a record price of $210,000 per kilogram in 200810. The high cost of Rh limits its applicability. The vast majority of Rh (more than 80% of the Rh production in the world9) is used for emission-control catalysts in vehicles with modern internal combustion engines; these catalysts have contributed to reducing smog and acid rain in developed countries. Such catalysts, referred to as three-way catalysts, simultaneously eliminate NOx, CO and residual hydrocarbons, which are the major pollutants in exhaust emissions. Rh plays an important role in NOx reduction as a component of the catalytic converter1,2,11,12. Because of the drastic growth in automobile demand in developing countries and increasingly stringent regulations of exhaust emissions from vehicles, the development of an inexpensive and highly active NOx reduction catalyst has become increasingly important. Thus far, extensive effort has been devoted to decreasing the Rh content in NOx reduction catalysts11,12,13,14,15,16,17; however, to the best of our knowledge, no research on the development of alternative Rh-free catalysts has been reported in the literature.
Pd and Ru are the immediate right and left neighbour of Rh in the periodic table, respectively and are much less expensive than Rh. On the basis of our concept “interelement fusion”18 where solid-solution alloying offers new properties by changing the compositions and/or combinations of alloys’ constituent elements, we expect that a homogeneous mixture of Pd and Ru, i.e. Pd–Ru solid-solution alloy nanoparticles (NPs), will result in a less expensive alternative with characteristics similar to those of Rh. However, this approach faces a challenge, because binary combinations of Pd-Ru are well known to be immiscible at the atomic level and form segregated domain structures in the bulk at all temperatures up to their melting points19,20,21. Recently, Kusada et al. have successfully synthesized Pd-Ru NPs over the entire compositional range via a chemical reduction method based on “non-equilibrium synthesis” and “nano-size effect”22. In the work, solid solution alloying of Pd and Ru enhanced several properties of NPs. However, it is not uncovered whether Pd-Ru NPs show comparable catalytic performance to that of Rh in the reaction which is invaluably catalysed by Rh. Therefore, the application of the Pd-Ru NPs for NOx reduction is interesting. Here, we report the Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs catalyst exhibiting excellent NOx reduction activity, which is a most crucial properties of three-way catalysts1,2,11,12, with its electronic structure similar to that of Rh. In other words, Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs behave like synthetic pseudo-Rh. This strategy is in line with direction of “elements strategy” driven in the world23.
Results
Preparation of PdxRu1-x NPs and supported catalysts
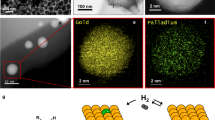
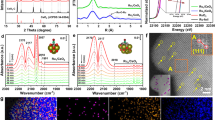
PdxRu1-x NPs were synthesized via a previously reported chemical reduction method using Pd and Ru precursors. Monometallic Pd, Ru and Rh NPs were also prepared using the same procedure. The PdxRu1-x, as well as NPs of Pd, Ru and Rh (equivalent to 1 wt% of the catalyst), were deposited onto γ-Al2O3 supports (Fig. 1a) via a standard impregnation method22. High-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF–STEM) image and elemental maps using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) of the γ-Al2O3-supported Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs are shown in Fig. 1. As shown in Fig. 1a, a few primary NPs are forming small secondary particles and those secondary NPs were well dispersed over γ-Al2O3 support. Figure 1b shows a magnified view of loaded NPs. One can find the overlap of NPs that appear as brighter region in the figure. In addition, the EDX maps of Pd, Ru and their superpositions (Fig. 1c–e) reveal that Pd and Ru atoms were homogeneously dispersed throughout the NPs. Crystalline structure of Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs are confirmed to be fcc-rich, but contains hcp phase also. As the Pd ratio in PdxRu1-x increases, fcc phase becomes more dominant. Charge transfer from Pd to Ru at the surface of PdxRu1-x alloy was also demonstrated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic measurement. Further details are reported elsewhere22.
Catalytic performance for NOx reduction
To investigate the catalytic activity of the Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs for NOx reduction, we carried out activity tests using a fixed-bed flow reactor. Pelletized γ-Al2O3-supported Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs were packed into a tubular reactor and we supplied a reaction mixture simulating automotive exhaust with a theoretical air-to-fuel ratio such that the CO and the C3H6 in the fuel were stoichiometrically combusted by NO and O2. The catalyst bed was heated from ambient temperature to 600 °C at a constant rate of 10 °C min−1 and the effluent gas was analysed during the heating. For comparison, γ-Al2O3-supported Pd, Ru and Rh NPs were also tested under the same conditions (Fig. 2). The NOx conversion rate for Pd0.5Ru0.5, Ru and Rh NPs increased smoothly with increasing temperature. By contrast, the Pd NPs exhibited a small peak in their conversion rate at 250 °C, followed by an increase in activity starting from approximately 300 °C, as has been frequently reported in previous studies24,25. An inspection of Fig. 2 reveals that the Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs exhibited equal or greater NOx reduction activity when compared with Rh NPs, which have been considered the most active NOx reduction catalyst. At low temperatures, in particular, the Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs exhibited excellent NOx reduction activity that exceeded that of the Rh NPs. The temperatures corresponding to 50% NOx conversion (T50) for the Pd0.5Ru0.5, Rh, Ru and Pd NPs were 180, 193, 282 and 344 °C, respectively, demonstrating that the Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs exhibited the highest NOx reduction activity among the investigated catalysts. Influence of reaction temperature on concentrations of gasses containing nitrogen atom is displayed in Supplementary Fig. S1. N2 was major product and NOx was almost completely converted to N2 above 350 °C. In addition, N2O was also produced from 200 °C. Selectivity of N2O increased with increase in the temperature by 250 °C but decreased gradually above the temperature. The catalytic activity of the physical mixture of Pd and Ru (0.5 wt% of Ru NPs and 0.5 wt% of Pd NPs) was also measured for comparison (Supplementary Fig. S2); these mixed NPs exhibited slightly better NOx reduction activity than the unmixed, single-component Pd and Ru NPs. However, the temperature dependence of the catalytic activity for the physical mixture of NPs differed from that of the Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs and the activity of the mixture was substantially lower than that of the Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs. These results demonstrate that the atomic-level alloying of Pd and Ru in the NPs plays a key role in the emergence of their excellent NOx reduction activity.
Electronic structure of Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs
The dissociative chemisorption of NO is well known to be the first step in NO reduction and is also known to be favoured on the Rh surface2,11. Both the electron donation from the NO 5σ orbital to the Rh 4d orbital and the electron back-donation from the Rh 4d orbital to the anti-bonding NO 2π orbital, which lead to weakening of the NO bond, have been reported to be important for the activation of the NO molecule for dissociation26,27,28. Therefore, we used first-principles methods to investigate the electronic structure, i.e., the density of states (DOS), of the Pd0.5Ru0.5 alloy system and the Rh, Pd and Ru NP systems (Fig. 3). The Rh energy band ranges from approximately +1 eV to −6 eV, with a maximum peak intensity of approximately 3 electrons/eV and three characteristic peaks at +0.39, −2.58 and −5.07 eV. These features are clearly observed in the Pd0.5Ru0.5 band structure, which differs substantially from those of the Pd and Ru systems. Estimation of d-band center in relative to Fermi energy was −2.866 and −2.821 eV for Pd0.5Ru0.5 and Rh, respectively, while those for Pd and Ru are estimated as −2.306 and −3.075 eV, respectively. Inspection of the partial DOS of Pd and Ru in the Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs readily shows that the alloying does not result in a simple linear combination of the electronic structures of Pd and Ru but rather gives rise to an Rh-like electronic structure (Supplementary Fig. S3). This result indicates that the Pd0.5Ru0.5 alloy can be regarded as a pseudo-Rh in terms of its bulk electronic structure, which should lead to a high catalytic activity similar to that of Rh. Furthermore, the similarity between the Rh and Pd0.5Ru0.5 DOS observed here suggests that the DOS of a target monometal can be reproduced via the alloying of other elements. To see the correlation between Rh-like electronic structure and the NOx reduction activity, NO adsorption properties onto fcc Pd0.5Ru0.5(111) as well as Rh(111) are investigated as a first step to screen the activity toward NO molecule. Supplementary Fig. S4 shows the relation between the NO adsorption energy and the N-O bond distance. Compared to the N-O distance of gas phase NO molecule, i.e. 1.172 Å, elongations of N-O distance is observed for all the cases investigated, indicating the activation of NO molecule for the decomposition. Four points for NO adsorption on Rh(111) surface correspond to ontop, bridge, fcc-3-fold and hcp-3-fold sites, respectively. One can see a general tendency that activation is more evident for bridge than ontop, 3-fold than bridge site adsorption, corresponding to the stronger backdonation in such order. NO adsorption properties on Pd0.5Ru0.5 shows a complex feature. NO adsorption on Pd ontop site is weaker in adsorption energy and Ru ontop is stronger, while the adsorption on both ontop sites are associated with only a slight activation of NO molecule in terms of N-O distance. For other cases of bridge and hollow-site adsorption, we can see a general trend like Rh, i.e. stronger adsorption energy is associated with the higher activation of NO molecule. Further, it is noted that we can find greater activations of NO molecule on Pd0.5Ru0.5 at a certain configuration investigated.
Influence of Pd–Ru composition on catalyst performance
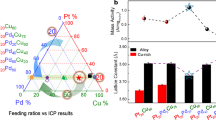
To investigate the influence of the PdxRu1-x composition on the NPs’ activity towards NOx reduction, we carried out activity tests using γ-Al2O3-supported PdxRu1-x NPs with various Pd–Ru compositions (x = 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9, 1) (Fig. 4a). Note that mean diameters of the alloy NPs investigated are in the similar range, i.e. ca. 10 nm, except for the Ru as shown in Supplementary Table S1. The T50 for NOx conversion observed for all of the PdxRu1-x NPs was lower than those of the monometallic Pd and Ru NPs (Fig. 4b). Thus, these results reveal a positive alloying effect over the whole solid-solution composition range. Furthermore, the NOx reduction activity of the PdxRu1-x NPs changes continuously with the atomic ratio of Pd and Ru, showing an inverse volcano-type behaviour. In particular, PdxRu1-x with x = 0.5 and 0.7 exhibited excellent NOx reduction activities that exceeded that of Rh. DOS of PdxRu1-x in Supplementary Fig. S5 shows that features of DOS of Rh, i.e. band width, positions and intensities of three characteristic peaks, are retained in the composition calculated. As reported in the preceding work22, the fcc phase becomes richer as the Pd composition in PdxRu1-x increases. In addition, the DOS of hcp phase of Pd0.5Ru0.5 is different from that of Rh as shown in Supplementary Fig. S3. Thus, the high activity of PdxRu1-x with x = 0.5 and 0.7 can be interpreted to originate from the similarity of DOS of PdxRu1-x in fcc phase, while we admit the potential complex factors behind the observed activity. It is well known that the commodity prices of Pd and Ru are substantially lower than that of Rh9, thus PdxRu1-x can contribute to the cost reduction of NOx reduction catalyst system. Considering that the price of Ru is lower than Pd, Pd0.5Ru0.5 NPs represent a promising new NOx reduction catalyst that costs one-third as much as Rh. A drastic activity enhancement in the case of the PdxRu1-x NPs was also observed for the elimination of CO and hydrocarbon (C3H6), which are other major pollutants in exhaust emissions (Supplementary Figs S6,S7).
Conclusion
In summary, we developed PdxRu1-x NPs with excellent NOx reduction activity compared to that of Rh, which is currently the most active and widely used NOx reduction catalyst. DOS features similar to those of the Rh DOS were observed for bulk Pd0.5Ru0.5, indicating that the catalytic activity of Pd0.5Ru0.5 towards NOx reduction is a consequence of its Rh-like electronic structure. These findings predict that PdxRu1-x NPs have potential applications as catalysts for various reactions currently catalysed by Rh. The alloying of immiscible elements provides a new direction for the design of novel materials for simultaneous enhancement of catalytic activity and reduction of the materials costs. Our concept of designing materials with desirable and suitable properties via the atomic-level mixing of elements was demonstrated for PdxRu1-x NPs and this approach should be applicable to numerous other combinations of elements and various classes of catalytic reactions, thereby initiating a new scientific field of study.
Methods
Synthesis of NPs and supported catalysts
For a typical synthesis of PdxRu1-x NPs (x = 0.5), poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) (PVP, 444 mg, MW ≈ 40 000, Wako) was dissolved in triethylene glycol (TEG, 100 mL, Wako) and the resulting solution was heated to 200 °C under magnetic stirring. Meanwhile, K2[PdCl4] (163.4 mg, Aldrich) and RuCl3·nH2O (131.1 mg, Wako) were dissolved in deionized water (40 mL). The resulting aqueous solution was then slowly added to the TEG solution, which was maintained at 200 °C during the addition for 20 to 40 min. After cooling to room temperature, the prepared NPs were separated by centrifugation. Other PdxRu1-x (x = 0.1, 0.3, 0.7, 0.9) NPs were prepared by controlling the molar ratio between Pd2+ and Ru3+ions.
Ru, Rh, Pd and PdxRu1-x alloy NPs and a physical mixture (Ru and Pd NPs) supported on γ-Al2O3 catalysts were prepared by wet impregnation. Each NP sample (equivalent to 1 wt% of γ-Al2O3) was ultrasonically dispersed in purified water. A high-purity γ-Al2O3 support (AKP-GO15, Sumitomo Chemical) that had been precalcined at 800 °C for 5 h was placed into each aqueous NP solution and the suspended solutions were stirred for 12 h. After being stirred, the suspended solutions were heated to 60 °C and then dried under vacuum. The resulting powders were maintained at 120 °C for 8 h to completely remove water.
High-resolution TEM (HRTEM), HAADF–STEM and EDX analyses
Samples were dispersed in ethanol, dropped onto a carbon-coated copper grid and dried by exposure to ambient conditions for 24 h. HRTEM, HAADF–STEM and EDX mapping images were collected using a JEM-ARM200F (JEOL) transmission electron microscope operated at 200 kV.
Theoretical calculations
All calculations were performed using the VASP29,30,31,32. The crystal structures of bulk Rh (fcc), Pd (fcc), Ru (hcp) and Pd0.5Ru0.5 (fcc/hcp) were reproduced using four-atom unit cells with periodic boundary conditions for both fcc and hcp lattices. We prepared three-layers 2 × 2 supercell slab models to study the surface properties. 20 different configurations are prepared for Pd0.5Ru0.5 surface model to see the influence of configurations of Pd and Ru on the adsorption properties. For each configuration, all possible adsorption sites are tested as the initial structure. The geometries for bulk Rh, Pd, Ru and the PdxRu1-x alloys were optimized under the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) with the Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) exchange-correlation functional33. Cut off energy is set to be 400 eV and the projector-augmented wave method34,35 is adopted. Monkhorst–Pack k-point grid sampling36 was used with the k-points of 14 × 14 × 14 and 7 × 7 × 1 for optimization of bulk and surface models, respectively. The DOS were analysed with further refined condition with the cut off of 700 eV and k-points of 23 × 23 × 23.
Catalytic activity tests
Powders of the γ-Al2O3-supported catalysts were pressed into pellets at 52 MPa for 5 min. They were then crushed and sieved to obtain grains with diameters of 250–500 μm. For each test, 200 mg of catalyst grains was loaded into a tubular quartz reactor (internal diameter = 7 mm) and quartz wool was then packed around the catalyst. In addition, a k-type thermocouple was inserted into the catalyst bed to measure the temperature for feedback control of the system. A feed-gas mixture containing NO (1161 ppm), CO (5750 ppm), C3H6, (467 ppm), O2 (5050 ppm), H2 (1760 ppm), CO2 (12.5%) and He (balance) was passed over each catalyst (total flow rate = 200 mL min−1; space velocity = 60 000 h−1). The gas mixture was designed to mimic the air-to-fuel ratio of automotive emissions. The catalyst bed was heated from ambient temperature to 600 °C at 10 °C min−1 under the flowing reaction mixture. The outlet gas composition was continuously monitored with a chemiluminescence NOx analyser (VA3000, HORIBA and Model 42i-HL, Thermo Fisher Scientific), a non-dispersive infrared gas analyser (VA3000, HORIBA) and gas chromatograph (490 Micro GC, Agilent Technologies).
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Sato, K. et al. A Synthetic Pseudo-Rh: NOx Reduction Activity and Electronic Structure of Pd–Ru Solid-solution Alloy Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 6, 28265; doi: 10.1038/srep28265 (2016).
References
Gandhi, H. Automotive exhaust catalysis. J. Catal. 216, 433–442 (2003).
Shelef, M. & Graham, G. W. Why rhodium in automotive three-way catalysts? Catal. Rev.: Sci. Eng. 36, 433–457 (1994).
Colby, D. A., Bergman, R. G. & Ellman, J. A. Rhodium-catalyzed C-C bond formation via heteroatom-directed C-H bond activation. Chem. Rev. 110, 624–655 (2010).
Blaser, H.-U. et al. Selective Hydrogenation for Fine Chemicals: Recent Trends and New Developments. Adv. Synth. Catal. 345, 103–151 (2003).
Lin, M. & Sen, A. Direct catalytic conversion of methane to acetic acid in an aqueous medium. Nature 368, 613–615 (1994).
Hickman, D. A. & Schmidt, L. D. Production of syngas by direct catalytic oxidation of methane. Science 259, 343–346 (1993).
Maeda, K. et al. Photocatalyst releasing hydrogen from water. Nature 440, 295 (2006).
Hans Wedepohl, K. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 1217–1232 (1995).
Loferski, P. J. PLATINUM-GROUP METALS. In MINERAL COMMODITY SUMMARIES 2015 (U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey) http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/mcs/2015/mcs2015.pdf. (Accessed: 22nd February 2016).
Loferski, P. J. 2012 MINERALS YEARBOOK PLATINUM-GROUP METALS [ADVANCE RELEASE] (U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey) http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/platinum/myb1-2012-plati.pdf. (Accessed: 22nd February 2016).
Bowker, M. Automotive catalysis studied by surface science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 37, 2204–2211 (2008).
Twigg, M. V. Progress and future challenges in controlling automotive exhaust gas emissions. Appl. Catal. B 70, 2–15 (2007).
Arnold, L. et al. Development and Application of New Low Rhodium Three-Way Catalyst Technology. SAE Tech. Pap. Ser. 2007-01-0046 (doi: 10.4271/2007-01-0046) (2007).
Lafyatis, D. S. et al. Comparison of Pd-only vs. Pd-Rh Catalysts: Effects of Sulfur, Temperature and Space Velocity. SAE Tech. Pap. Ser. 199-01-0309 (doi: 10.4271/1999-01-0309) (1999).
Inderwildi, O. R., Jenkins, S. J. & King, D. A. When adding an unreactive metal enhances catalytic activity: NOx decomposition over silver–rhodium bimetallic surfaces. Surf. Sci. 601, L103–L108 (2007).
Li, M. et al. NO reduction by CO over Rh/Al2O3 and Rh/AlPO4 catalysts: Metal-support interaction and thermal aging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 408, 157–163 (2013).
Nagao, Y. et al. Rh/ZrP2O7 as an Efficient Automotive Catalyst for NOx Reduction under Slightly Lean Conditions. ACS Catal. 5, 1986–1994 (2015).
Kobayashi, H., Kusada, K. & Kitagawa, H. Creation of Novel Solid-Solution Alloy Nanoparticles on the Basis of Density-of-States Engineering by Interelement Fusion. Acc. Chem. Res. 48, 1551–1559 (2015).
Zarkevich, N., Tan, T. & Johnson, D. First-principles prediction of phase-segregating alloy phase diagrams and a rapid design estimate of their transition temperatures. Phys. Rev. B 75, Article number 104203 (2007).
Massalski, T. B., Okamoto, H., Subramanian, P. R. & Kacprzak, L. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams. (ASM International, 1996).
Tripathi, S. N., Bharadwaj, S. R. & Dharwadkar, S. R. The Pd-Ru system (palladium-ruthenium). J. Phase Equilib. 14, 638–642 (1993).
Kusada, K. et al. Solid solution alloy nanoparticles of immiscible Pd and Ru elements neighboring on Rh: changeover of the thermodynamic behavior for hydrogen storage and enhanced CO-oxidizing ability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 1864–1871 (2014).
Nakamura, E. & Sato, K. Managing the scarcity of chemical elements. Nat. Mater. 10, 158–161 (2011).
Matam, S. K. et al. Thermal and chemical aging of model three-way catalyst Pd/Al2O3 and its impact on the conversion of CNG vehicle exhaust. Catal. Today 184, 237–244 (2012).
Birgersson, H. et al. An investigation of a new regeneration method of commercial aged three-way catalysts. Appl. Catal., B 65, 93–100 (2006).
Ward, T. R., Hoffmann, R. & Shelef, M. Coupling nitrosyls as the first step in the reduction of NO on metal surfaces: the special role of rhodium. Surf. Sci. 289, 85–99 (1993).
Loffreda, D., Simon, D. & Sautet, P. Molecular and dissociative chemisorption of NO on palladium and rhodium (100) and (111) surfaces: A density-functional periodic study. J. Chem. Phys. 108, 6447 (1998).
Hammer, B. & Nørskov, J. K. Theoretical surface science and catalysis—calculations and concepts. Adv. Catal. 45, 71–129 (2000).
Kresse, G. & Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B, 47, 558–561 (1993).
Kresse, G. & Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular-dynamics simulation of the liquids-metal-amorphous-semiconductor transition in germanium. Phys. Rev. B 49, 14251–14271 (1994).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 6, 15–50 (1996).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169–11186 (1996).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Blöchl, P. E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 50, 17953–17979 (1994).
Kresse, G. & Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758–1775 (1999).
Monkhorst, H. J. & Pack, J. D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 13, 5188–5192 (1976).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the JST-CREST program. STEM/TEM observations were performed as part of a program conducted by the Advanced Characterization Nanotechnology Platform sponsored by the MEXT of the Japanese Government. The activities of the INAMORI Frontier Research Center, Kyushu University are supported by KYOCERA Corporation. The authors thank Dr. J. Taylor (Kyoto University) for comments on the manuscript and Mr. Y. Wada, Ms. A. Miyazawa and Mr. Y. Nishida (Oita University) for assistance with the catalytic activity tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.N. and H. Kitagawa designed this study. K.S., H.T. and K.K. prepared samples. K.S. and H.T. carried out catalytic activity tests. T.Y. and S.M. conducted HAADF-STEM and EDX mapping. N.D.B.Z., T.I. and M.K. performed theoretical calculations. All authors discussed the results and commented on the study. K.S., K.K., H. Kobayashi, M.K., K.N. and H. Kitagawa co-wrote the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, K., Tomonaga, H., Yamamoto, T. et al. A Synthetic Pseudo-Rh: NOx Reduction Activity and Electronic Structure of Pd–Ru Solid-solution Alloy Nanoparticles. Sci Rep 6, 28265 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28265
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28265
This article is cited by
-
Technological solutions for NOx, SOx, and VOC abatement: recent breakthroughs and future directions
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
Atom-hybridization for synthesis of polymetallic clusters
Nature Communications (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.