Abstract
IL-27 could inhibit the development of Th17 cells, and the Th17/regulatory T-cell imbalance may reverse maternal tolerance in pre-eclampsia (PE). The aim of this study was to investigate the association between genetic polymorphisms in IL27 with PE. Three SNPs in IL27 (rs153109, rs17855750, and rs181206) were genotyped in a Chinese Han cohort of 1040 PE patients and 1247 normal pregnant women using the TaqMan allelic discrimination real-time PCR method. The CC genotypic distribution of rs153109 was significantly higher among cases than controls (19.1% versus 13.3%, odds ratio [OR]: 1.54, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.23–1.93, p < 0.001), and the CT genotype was found to be significantly lower in cases than controls (41.7% versus 49.0%, OR: 0.74, 95% CI: 0.63–0.88, p < 0.001), disputing existing reports indicating the allele frequency of rs153109 is not significantly different between PE patients and controls. Additionally, the CC genotype of rs153109 was significantly more prevalent in PE cases than controls using a recessive model (p < 0.001). The allelic and genotypic frequencies of rs17855750 and rs181206 were not significantly different between two groups. Our results reveal that IL27 polymorphisms may be involved in the development of PE in Chinese Han population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is a relatively common, systemic pregnancy disorder characterized by the development of concurrent hypertension (>140/90 mmHg) and proteinuria (>300 mg/24 h) at ≥20 weeks of gestation, that may also be associated with a myriad of other symptoms such as edema, headache, blurred vision, irritability, abdominal pain, and thrombocytopenia1,2. This gestation-specific syndrome affects about 2–8% of all pregnancies, and is a major cause of maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality worldwide3. Although the etiology and pathogenesis of PE have not been clearly identified, key pathogenic factors may include immunologic factors, shallow extravillous trophoblast invasion into the uterine spiral arteries, genetic and environmental factors, and chronic inflammation. Many parts of the inflammatory network are involved, yielding minor systemic changes that have been considered to be part of the physiology of normal pregnancy; however, the systemic inflammatory response in PE is more severe than in normal pregnancy4. This excessive systemic inflammatory response of PE results in endothelial dysfunction and associates increased vascular reactivity preceding the onset of symptomatic clinical disease5,6. Th17 cells, characterized by the production of IL-17, participate in successful pregnancy as well as in the pathogenesis of diseases of pregnancy, such as recurrent spontaneous abortion and PE. Excessive Th17 cell numbers and high levels of IL-17, IL-6, and IL-1β have been identified in PE, and uncontrolled Th17 cells may emerge as important mediators of inflammation and tissue damage7.
Interleukin-27 (IL-27) belongs to the IL-12 family of heterodimeric cytokines including IL-12, IL-23, and IL-35, which help the differentiation and maintenance of Th1 subset cells8. IL-27 is a key cytokine that plays a unique role in regulating the initial step of Th cell differentiation8. Th17 cells and IL-17 cytokines are regulated by a complex immune network. IL-27 suppresses Th17 differentiation and IL-17 production. Yin et al. observed that the expression levels of IL-27 and IL-27 receptor α were significantly elevated in trophoblastic cells from the placenta of patients with PE compared with control specimens9. Furthermore, the evidence from family-based studies suggests that PE has a heritable component, and genetic involvement plays an important role in its development10. Several studies have indicated that many candidate cytokine genes, such as IL10, IL6, TNF-α, and TGF-β1, are thought to be associated with the susceptibility of PE11,12,13,14. Considering that IL27 polymorphisms might influence the susceptibility, severity, and outcome of PE15, the purpose of study here was to investigate the correlation between IL27 polymorphisms (rs153109, rs17855750, and rs181206) and the clinical implication of PE in a Chinese Han population, to illustrate whether these SNPs were involved in the development of PE.
Results
Clinical characteristics of PE and control groups
The case-control study included 1040 PE patients (30.06 ± 5.69 years old) and 1247 controls (30.32 ± 4.10 years old). The distribution of selected epidemiologic and clinical factors in cases and controls were shown in Table 1. The demographics such as age, age of menarche, and triglyceride levels were similar between the cases and controls (all, p > 0.05). The PE group had earlier neonatal gestational age, lower birth weight, higher blood pressure, and higher levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), urea nitrogen, and creatinine (all, p < 0.001).
Genetic analysis
Allelic and genotypic frequencies of the three polymorphisms in IL27 (rs153109, rs17855750, and rs181206) among cases and controls were depicted in Table 2. The genotypic distributions of these SNPs were within Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium in the control group (for rs153109, p = 0.147; rs17855750, p = 0.11; and rs181206, p = 0.07).
No significant differences were observed among case and control groups in relation to allelic frequency for rs153109 (40.0% vs. 37.8%, p > 0.05). Contrary to this, the CC genotype of rs153109 was associated with a higher risk of presenting PE (OR: 1.54, 95% CI: 1.23–1.93, p < 0.001), as the prevalence of this genotype was found to be significantly higher among PE cases as compared with controls (19.1% vs. 13.3%, p < 0.001). The CT genotype might be a factor protecting from PE (OR: 0.74, 95% CI: 0.63–0.88, p < 0.001), as the prevalence of this genotype was detected to be significantly lower in PE cases than controls (41.7% vs. 49.0%, p < 0.001). The proportions of the minor allele for rs17855750 and rs181206 were 0.14 and 0.15, respectively, in cases, and 0.15 and 0.14, respectively, in controls. We did not observe significant differences between individual allelic or genotypic frequencies of the studied IL27 SNPs in these two groups (p > 0.05).
In genetic association studies, statistical power to detect disease susceptibility loci depended on the genetic models tested. Therefore, the genotype frequencies were further analyzed by three genetic models: additive, dominant, and recessive. For rs153109, weak association was also found under the recessive model (CC/CT + TT) (OR: 1.54, 95% CI: 1.23–1.93, p = 1.63 × 10−4), while rs17855750 and rs181206 were not risk factors for PE based on the three genetic models (all, p > 0.05) (Table 3).
Analysis of Genotype-Phenotype Relationship
Analysis of the rs153109 genotypes and phenotypic characteristics among PE patients were depicted in Table 4. Gestational age at diagnosis, neonatal gestational age, and birth weight of offspring showed statistically significant differences among the three genotypes (all, p < 0.05). Patients carrying the CT genotype had lower gestational age at diagnosis (35.04 ± 3.66 vs. 35.81 ± 3.48 weeks, PC = 0.006), neonatal gestational age (35.91 ± 3.19 vs. 36.61 ± 2.93 weeks, PC = 0.006), and birth weight of offspring (2507 ± 915 vs. 2686 ± 906 g, PC = 0.024) than ones with the TT genotype. Additionally, the level of serum TC was higher in patients with the CT genotype than ones carrying the TT genotype.
Linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis of the SNPs
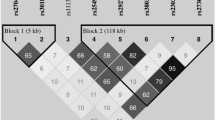
Haploview software was used to further analyze the LD analysis in the IL27 SNPs. The results from the LD analysis of the SNPs (rs153109, rs17855750, and rs181206) in our study and the data from the HapMap CHB population were shown in Fig. 1. Data from HapMap CHB and the present study illustrated a litter differences.
The LD plots were generated by Haploview software v4.2. The number (divided by 100) in the small square represents r2 value and ranges from 0 to 1 (the numbers in the figure just shown two digits behind the decimal point). (a) The data from HapMap CHB. (b) The data analysis between PE patients and healthy controls from our study.
Discussion
PE is a common systemic obstetric disorder characterized by the state of excessive inflammatory response. The balance of immunoregulation plays a critical role in the development of PE, which strong activation of the innate immune and a shift towards an inflammatory cytokine profile have been found16. Production of Th1 and Th2 cytokines is elevated in PE patients, therefore these cytokines are of interest as possible markers for the development of this disorder17,18. Significantly higher levels of cytokines such as IL-2, TNF-α, and IFN-γ, but significantly lower levels of IL-4 and IL-10, have been identified in PE patients19. Regulatory T (Treg) cells play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of tolerance in peripheral tissues and the induction of transplantation tolerance, as well as in the maintenance of maternal-fetal tolerance16,20. It has been reported that the decreased number and function of Treg cells may be contributed to induce activate of the inflammatory response characteristic of PE, and increase of Th17 immunity is related to the activation of a Th1 response through modulation of the Th1/Th2 immune balance in PE19. Th17/Treg imbalance may reverse maternal tolerance in PE.
IL-27, a complex cytokine with multiple functions, is produced by antigen-presenting cells when they are activated through Toll-like receptor signaling21,22. IL-27 is a key cytokine that plays a unique role in the regulation of Th differentiation at the initial step, promoting Th1 differentiation and enhancing the activities of Th1 cells8. Additionally, IL-27 is also known to act by inhibiting the differentiation of Th2 and Th17 cells23,24. Th17 cells, characterized by the production of IL-17, have also been shown to participate in the pathogenesis of PE. A predominantly Th17- and Th1-type response and decreased Treg immunity have been found in PE25. Excessive Th17 cell numbers and high levels of IL-17, IL-6, and IL-1β have been identified in PE7, indicating that uncontrolled Th17 cells may emerge as important mediators of inflammation and tissue damage in diseases of pregnancy. IL-27 counters the polarization of naive CD4+ T cells, resulting in the inhibition of Th17 cell development. IL-27 creates a high variety of biological activities that initiate and perpetuate an inflammatory response. Yin et al. observed that the expression of IL-27 and IL-27 receptor α were observely upregulation in trophoblastic cells from the placenta of PE compared with control subjects9.
The functional polymorphisms of cytokine genes was considered important for susceptibility, severity, and outcome of PE, therefore great attention has been focused on the role that these polymorphisms may play in the development of the diseases11,26,27. The production of cytokines is regulated by homologous genes, then these SNPs may play a important roles in the development of PE. Genetics and epigenetic may be involved in determining the phenotypes of diseases, and further study is needed to better understand the effect of genes with allelic or genetic heterogeneity on disease risk. Different polymorphisms in IL27 have been found in association with a number of disorders, such as SLE28 and RA29. Among the IL27 polymorphisms identified, rs153109 has been reported to be associated with the risk of asthma30, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease31, and inflammatory bowel diseases32, although it has no association with immune thrombocytopenia33.
In this study, we examined the genetic contribution of three polymorphisms in IL27, including rs153109 (5′ UTR region), rs17855750 (Exon 2/missense), and rs181206 (Exon 4/missense). To our knowledge, this is the first report investigation of the relationship between IL27 polymorphisms and susceptibility to PE. Our results indicate that the frequency of the CC genotype of rs153109 is associated with a higher risk of presenting PE. The pregnant women bearing the CC genotype showed a 1.54-fold risk of developing PE, while the CT genotype was found to have a protective effect on PE. The distributions of genotypes and alleles of rs17855750 and rs181206 showed no difference in cases and controls. In conclusion, our study indicates that polymorphisms IL-27 may be involved in the development of PE in a Chinese Han population. Additionally, several studies have indicated that many candidate cytokine genes are thought to be associated with susceptibility to PE. Zubor et al. reported that the TNF-α G308A polymorphism was significantly associated with PE34, and IFN-γ (+874A) and IL-1β (-31C/T and -511T/C) are also associated with the risk of PE11,14. Besides, the little different between our data and data from HapMap may because that our current cases come from central China, while the populations examined by HapMap were from nouthern China. It is well known that various ethnic and environmental factors influence the analysis of LD plots and PE susceptibility. Therefore, we are unable to make comparisons between cohorts.
During the development and disease progression of PE, the basic pathological changes of systemic small vessel spasm often induce multi-organ disturbances, such as activation of the clotting system and impaired liver and renal function35. Our study showed that the serum levels of ALT, AST, urea nitrogen, and creatinine were higher in the PE patients compared with the controls, one reason may be that impaired liver and renal functions are common in PE patients. In our study, PE patients usually had an earlier gestational age at delivery and lower birth weight of offspring, leading to premature delivery.
This study has some inherent limitations that should be considered when interpreting our findings. First, there were a small number of patients diagnosed with partial or full HELLP syndrome or other severity of PE in this study. We didn’t distinct them due to severity of PE in small size, but this could add to the possible contribution of the SNP studied to the severity of the disease. Second, we only assessed three SNPs of IL27. The results obtained by this study may not completely represent the association between these SNPs and PE risk, and therefore the examination of more loci is needed to verify the association between IL27 and PE. Third, because of the significant ethnic differences and population heterogeneity of PE patients worldwide, our study may not represent other ethnic groups. It remains important to determine whether IL27 SNPs are associated with PE in multiple populations. Further functional analyses also need to be performed to clarify the potential mechanisms underlying the linkage between the rs153109 SNP and susceptibility to PE.
Methods
Study population
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University. Additionally, informed consent was obtained from all individuals after a thorough explanation of the procedure and its risk in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. PE patients and normal pregnant women (controls) were enrolled from the same geographic location, which included 1040 PE patients and 1247 controls from the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Linyi People’s Hospital and Heze Municipal Hospital, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantaishan Hospital, Liaocheng People’s Hospital, and the Maternal and Child Health Care of Zaozhuang. The PE diagnosis was based on the criteria from the Report of the ‘National High Blood Pressure Education Program’36. Exclusion criteria included multiple pregnancies, fetal death, chronic hypertension and renal disease, uterine malformation, in vitro fertilization treatment, placental abruption, infection, cancer, gestational diabetes mellitus, or any other systemic disease, including pre-existing hypertension, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The controls were in the third trimester of normal pregnancy and had to be normotensive in the index pregnancy, without any fetal disorder, multiple pregnancy, or pathological states. Moreover, the controls were followed up and none of them developed PE after birth.
The research staffs filled out the questionnaire to all study objects, that contained maternal and gestational age, gravidity, the number of abortions, detailed medical, pregnancy and family history, systemic physical (including blood pressure) and pelvic examinations, complete blood counts, urinary analysis, blood clotting state, and routine biochemical.
Genotyping
Genomic DNA was extracted from 2 mL ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid anti-coagulated peripheral blood samples using Qiagen DNA extraction kits (Qiagen, Shanghai, China). A spectrophotometer was used to test the concentration and quality of DNA. The purified DNA was stored at −80 °C until use. SNP genotyping was conducted using the TaqMan allelic discrimination real-time PCR method. The amplification primers used were as follows: rs153109 locus: forward 5′-TCGGGGCTCAGCCTGTGGCCAGGCT-3′, reverse 5′-GAGTTGAGTGAGGTCAGGATCAGGG-3′, rs17855750 locus: forward 5′-CCTGCATCTCGCCAGGAAGCTGCTC-3′, reverse 5′-CCGAGGTTCGGGGCCAGGCCCACCG-3′, rs181206 locus: forward 5′-ACCACGCTTCAGCCCTTCCATGCCC-3′, reverse 5′-GCTGGGAGGGCTGGGGACCCAGGGC-3′, which were designed and synthesized by Applied Biosystems by Life Technologies. Real-time PCR was performed on a LightCycler® 96 System (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Germany), and the amplifications were carried out with the following protocol: 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 45 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min. For each cycle, the fluorescent signal from the VIC- or FAM-labeled probe was determined.
Statistical analysis
Each SNP was assessed in the control group for departures from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium using the Chi-squared (χ2) test. The χ2 test was used to compare the allelic and genotypic frequencies between the case and control groups using PLINK v1.07 (http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/Bpurcell/plink/). The analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to analyze the laboratory examination of PE among different genotypes. The Pearson’s χ2 or Student’s t-test was used to test the comparisons of clinical data between groups. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant, and OR were calculated with exact CI of 95%. Three logistic regression models (additive, dominant, and recessive) were used to analyze the SNPs.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Liu, B. et al. Polymorphisms of the IL27 gene in a Chinese Han population complicated with pre-eclampsia. Sci. Rep. 6, 23029; doi: 10.1038/srep23029 (2016).
References
Redman, C. W. & Sargent, I. L. Latest advances in understanding preeclampsia. Science 308, 1592–4 (2005).
ACOG Committee on Practice Bulletins–Obstetrics. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Number 33, January 2002. Obstet Gynecol 99, 159–67 (2002).
Steegers, E. A., von Dadelszen, P., Duvekot, J. J. & Pijnenborg, R. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 376, 631–44 (2010).
Redman, C. W. & Sargent, I. L. Pre-eclampsia, the placenta and the maternal systemic inflammatory response–a review. Placenta 24 Suppl A, S21–7 (2003).
Redman, C. W. & Sargent, I. L. Placental stress and pre-eclampsia: a revised view. Placenta 30 Suppl A, S38–42 (2009).
Myers, J., Mires, G., Macleod, M. & Baker, P. In preeclampsia, the circulating factors capable of altering in vitro endothelial function precede clinical disease. Hypertension 45, 258–63 (2005).
Fu, B., Tian, Z. & Wei, H. TH17 cells in human recurrent pregnancy loss and pre-eclampsia. Cell Mol Immunol 11, 564–70 (2014).
Yoshida, H., Nakaya, M. & Miyazaki, Y. Interleukin 27: a double-edged sword for offense and defense. J Leukoc Biol 86, 1295–303 (2009).
Yin, N. et al. IL-27 activates human trophoblasts to express IP-10 and IL-6: implications in the immunopathophysiology of preeclampsia. Mediators Inflamm 2014, 926875 (2014).
Sutherland, A., Cooper, D. W., Howie, P. W., Liston, W. A. & MacGillivray, I. The indicence of severe pre-eclampsia amongst mothers and mothers-in-law of pre-eclamptics and controls. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 88, 785–91 (1981).
de Lima, T. H. et al. Cytokine gene polymorphisms in preeclampsia and eclampsia. Hypertens Res 32, 565–9 (2009).
Daher, S., Sass, N., Oliveira, L. G. & Mattar, R. Cytokine genotyping in preeclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol 55, 130–5 (2006).
Stonek, F. et al. Absence of an association of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha G308A, interleukin-6 (IL-6) G174C and interleukin-10 (IL-10) G1082A polymorphism in women with preeclampsia. J Reprod Immunol 77, 85–90 (2008).
Wang, X. et al. Interleukin-1beta-31C/T and -511T/C polymorphisms were associated with preeclampsia in Chinese Han population. Plos One 9, e106919 (2014).
Molvarec, A. et al. Association between estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) gene polymorphisms and severe preeclampsia. Hypertens Res 30, 205–11 (2007).
Perez-Sepulveda, A., Torres, M. J., Khoury, M. & Illanes, S. E. Innate immune system and preeclampsia. Front Immunol 5, 244 (2014).
Saito, S., Shiozaki, A., Nakashima, A., Sakai, M. & Sasaki, Y. The role of the immune system in preeclampsia. Mol Aspects Med 28, 192–209 (2007).
Saito, S. & Sakai, M. Th1/Th2 balance in preeclampsia. J Reprod Immunol 59, 161–73 (2003).
Darmochwal-Kolarz, D. & Oleszczuk, J. The critical role of Th17 cells, Treg cells and co-stimulatory molecules in the development of pre-eclampsia. Dev Period Med 18, 141–7 (2014).
Ohkura, N. & Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells: roles of T cell receptor for their development and function. Semin Immunopathol 32, 95–106 (2010).
Molle, C. et al. IL-27 synthesis induced by TLR ligation critically depends on IFN regulatory factor 3. J Immunol 178, 7607–15 (2007).
Schuetze, N. et al. IL-12 family members: differential kinetics of their TLR4-mediated induction by Salmonella enteritidis and the impact of IL-10 in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Int Immunol 17, 649–59 (2005).
Yoshimoto, T., Yoshimoto, T., Yasuda, K., Mizuguchi, J. & Nakanishi, K. IL-27 suppresses Th2 cell development and Th2 cytokines production from polarized Th2 cells: a novel therapeutic way for Th2-mediated allergic inflammation. J Immunol 179, 4415–23 (2007).
Diveu, C. et al. IL-27 blocks RORc expression to inhibit lineage commitment of Th17 cells. J Immunol 182, 5748–56 (2009).
Jianjun, Z., Yali, H., Zhiqun, W., Mingming, Z. & Xia, Z. Imbalance of T-cell transcription factors contributes to the Th1 type immunity predominant in pre-eclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol 63, 38–45 (2010).
Mohajertehran, F., Tavakkol, A. J., Rezaieyazdi, Z. & Ghomian, N. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1-beta genes in patients with pre-eclampsia. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 11, 224–9 (2012).
Li, J. et al. Genetic variations in IL1A and IL1RN are associated with the risk of preeclampsia in Chinese Han population. Sci Rep 4, 5250 (2014).
Li, T. T. et al. Low level of serum interleukin 27 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Investig Med 58, 737–9 (2010).
Wong, C. K. et al. Effects of inflammatory cytokine IL-27 on the activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 12, R129 (2010).
Chae, S. C. et al. Identification of polymorphisms in human interleukin-27 and their association with asthma in a Korean population. J Hum Genet 52, 355–61 (2007).
Huang, N. et al. Association of interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-27 gene polymorphisms with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a Chinese population. DNA Cell Biol 27, 527–31 (2008).
Li, C. S. et al. Interleukin-27 polymorphisms are associated with inflammatory bowel diseases in a Korean population. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24, 1692–6 (2009).
Zhao, H., Zhang, Y., Xue, F., Xu, J. & Fang, Z. Interleukin-27 rs153109 polymorphism and the risk for immune thrombocytopenia. Autoimmunity 46, 509–12 (2013).
Zubor, P. et al. TNF alpha G308A gene polymorphism has an impact on renal function, microvascular permeability, organ involvement and severity of preeclampsia. Gynecol Obstet Invest 78, 150–61 (2014).
Kobayashi, T., Tokunaga, N., Isoda, H., Kanayama, N. & Terao, T. Vasospasms are characteristic in cases with eclampsia/preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome: proposal of an angiospastic syndrome of pregnancy. Semin Thromb Hemost 27, 131–5 (2001).
Report of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 183, S1–S22 (2000).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences Foundation of China (81241094, 81371499 and 30971586) and Science and Technology program of basic research projects of Qingdao City (no. 13-1-4-138-jch).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.L., J.L. and S.L. conceived the experiment, Y.L., Y.Y., H. Li and H. Liang conducted the experiment, Y.L., M.X., L.W. and L.Z. analysed the results. B.L., S.L. and Y.L. wrote this article. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Li, Y., Yao, Y. et al. Polymorphisms of the IL27 gene in a Chinese Han population complicated with pre-eclampsia. Sci Rep 6, 23029 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23029
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23029
This article is cited by
-
Genetic polymorphisms of IL-27 and risk of systemic lupus erythematosus disease in the Egyptian population
Clinical Rheumatology (2021)
-
IL-27 variants might be genetic risk factors for preeclampsia: based on genetic polymorphisms, haplotypes and in silico approach
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.