Abstract
Functional glass surfaces with the properties of superhydrophobicity/or superhydrohydrophilicity, anti-condensation or low reflectance require nano- or micro-scale roughness, which is difficult to fabricate directly on glass surfaces. Here, we report a novel non-lithographic method for the fabrication of nanostructures on glass; this method introduces a sacrificial SiO2 layer for anisotropic plasma etching. The first step was to form nanopillars on SiO2 layer-coated glass by using preferential CF4 plasma etching. With continuous plasma etching, the SiO2 pillars become etch-resistant masks on the glass; thus, the glass regions covered by the SiO2 pillars are etched slowly and the regions with no SiO2 pillars are etched rapidly, resulting in nanopatterned glass. The glass surface that is etched with CF4 plasma becomes superhydrophilic because of its high surface energy, as well as its nano-scale roughness and high aspect ratio. Upon applying a subsequent hydrophobic coating to the nanostructured glass, a superhydrophobic surface was achieved. The light transmission of the glass was relatively unaffected by the nanostructures, whereas the reflectance was significantly reduced by the increase in nanopattern roughness on the glass.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Functional glass with superhydrophobicity/hydrophilicity, anti-condensation or low-reflectance has been developed for various applications, including windows for automobiles, vehicles or ships; inner or outer buildings windows; and display panels for electronic and medical devices and other optical equipment1,2,3. Functional glass surfaces require nano- or micro-scale roughness, which is difficult to fabricate directly on glass surfaces4,5. Hydrophobic and superhydrophobic surfaces are obtained by applying coatings of a low-surface-energy material to nanostructured surfaces; these coated surfaces can mimic micro-, nano- or hybrid structures, such as that of the lotus leaf, which has a high water contact angle (CA) and low contact angle hysteresis (CAH)3. Conversely, superhydrophilic glass with extreme wettability has been developed for anti-fogging, self-cleaning and water collecting surfaces6,7. Superhydrophilicity is improved by the presence of surface nanostructures coated with high-surface-energy materials8. Therefore, surface coatings on glass surfaces are required to both control the surface energy and introduce extreme wettability.
Recently, several studies have focused on the fabrication of regular nano- or microscale patterns on glass to improve its wettability or anti-reflectance. Some researchers have reported a fabrication method for introducing surface roughness onto glass by using a self-mask pattern and a thin metal layer such as used in the Ni dewetting method. Using the inductively coupled plasma etching method, nanostructured glass with a high aspect ratio has been fabricated for use on solar panels. However, this method requires an additional step for removing the metallic mask with acidic chemicals9,10. Zeze et al. reported a lithography-free method for the fabrication of high aspect ratio quartz columns, by using reactive ion etching or chemical etching with a CF4 and Ar gas mixture11. They suggested that the preferential etching to form columnar structures is due to the presence of localized metallic impurities in the quartz matrix and to the non-uniform distribution of the electrostatic fields at the rounded edges of the contact mask. However, the suggested methods are limited by the low density of the columnar structures on the SiO2-based quartz-type glass. It has been reported that in contrast to quartz or Si formation using volatile compounds such as SiFx, the surface roughness of soda-lime glass would not be affected by reactive ion etching with CF4 or SF6 plasma treatment because of the presence of nonvolatile oxide components such as CaO and Na2O12. It has also been suggested that because of the production of nonvolatile products (such as NaF or AlF3) during etching with halogen gases (such as CF4 or SF6), glass surfaces containing Na or Al would be protected from etching4. The etch rate of soda-lime glass by CF4/CHF3 plasma, 4 nm/min, is much lower than that of glass that does not contain Ca or Na, 45 nm/min, under the same processing conditions12. It is a challenge that glasses containing nonvolatile elements form surface nanostructures under a plasma-based anisotropic etching method. Owing to the difficulty of directly forming nanostructures on general glass, researchers have suggested the introduction of an additional layer on the glass via spraying nano- or microscale particles13 or via sol-gel coating with a porous thin film. However, the low interfacial adhesion strength between the glass and the additional layer presents a limitation to the widespread application of this technique14.
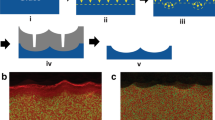
In this work, we provide a novel non-lithographic method for fabricating nanostructures directly on glass via the introduction of a sacrificial SiO2 layer and subsequent anisotropic plasma etching with reactive plasma. The SiO2 layer was deposited onto glass as a sacrificial layer that was subsequently CF4 plasma-treated to form a nanostructure by using a well-known anisotropic plasma etching technique (Figure 1a)15. In turn, SiO2 nanoscale pillars acted as surfaces that resisted the continuous plasma etching (Figure 1b), resulting in nanostructure formation on the glass surfaces. The glass regions covered with SiO2 pillars are etched slowly, whereas the regions with no SiO2 pillars are etched rapidly, resulting in the formation of nanopatterns on the glass. Our process requires post-processing via water hydrolysis to remove residual metal fluoride and to enhance the nanopattern roughness. With CF4 plasma treatment alone, the roughness caused the nanostructured glass to become superhydrophilic16. Subsequently, a low-surface-energy material was coated on the nanostructured surfaces to render them superhydrophobic (Figure 1c)17.
Schematic representation of the fabrication process of nanostructured glass.
(a) Application of a sacrificial layer of SiO2 and reactive ion etching by CF4 plasma treatment. (b) Cross-sectional SEM images of SiO2-coated glass before nanostructuring (left) and CF4 plasma-etched glass with a SiO2 coating before (middle) and after (right) pp-HDMSO coating. Scale bar is 500 nm. (c) Optical images of pristine (left), superhydrophilic (middle) and superhydrophobic (right) glasses. Water was dyed red.
A surface analysis of the plasma-treated surfaces was conducted. Water CA and CAH measurements were taken and water condensation experiments were performed to characterize the effects of the surface treatments on the wettability and nucleation/growth of water droplets, respectively. Changes in optical transmittance were also investigated by using UV-vis spectroscopy to estimate the effects of nanostructure formation, under various plasma durations, on the anti-reflectance of the glass substrates.
Results
Morphology and microstructure
Soda-lime glass surfaces were etched with CF4 plasma for varied durations, as shown in Figure 2a–c. No noticeable surface roughness was observed on the bare glass after up to 60 min of plasma etching. Using AFM, it was found that the roughness was slightly increased, from 0.095 nm for pristine glass to 1.849 nm after 60 min of CF4 plasma etching. Glass surfaces can be uniformly etched with reactive plasma ions because they contain Ca and Na, which protects them from being etched by the plasma-based anisotropic etching mechanism4,12. For glass coated with a 1-μm-thick sacrificial layer of SiO2, the nanostructures on the sacrificial layer evolved into pillar shapes with a high aspect-ratio, 6.6:1. A side view of these pillars can be observed in Figure 2d–e, where the SiO2 layer is brighter than that of the glass substrate in the SEM image. With continuous CF4 plasma etching, the SiO2 nanopillars can serve as etching masks for the selective etching of the glass substrates, resulting in the formation of nanostructures on the glass, as shown in Figure 2f. Here, the SiO2 pillars were etched away, providing a glass surface with hierarchical nanostructures featuring 500-nm-wide bumps decorated with 15- to 30-nm-wide pillars. The surface roughness was measured on the glass with and without the SiO2 sacrificial layer following varied CF4 plasma etching durations, as shown in Figure 2g. By estimating the width, d and the height, h, of a nanostructure, as well as the distance between nearest nanostructures, s, an equation for the dimensionless parameter of roughness, r, was adopted from Ref. 18: r = 1 + πdh/(d + s)2, where the minimum roughness of a flat surface is 1. Based on the measured geometries shown in Figure S1, the roughness of the pristine glass was measured as 1.001 and that of the plasma treated glass without nanopillars was below 1.01. In the case of the nanostructured glass, the roughness was measured to be greater than 3, which is significantly greater than that of the glass without the SiO2 layer.
SEM images of CF4 plasma-etched glass surfaces and soda-lime glass cross-sections with varied CF4 plasma etching duration: (a) 15, (b) 30 and (c) 60 min. Schematic representation and SEM cross-sectional images of SiO2-coated glasses with varied CF4 plasma duration: (d) 15, (e) 30 and (f) 60 min. Scale bar is 500 nm. (g) Roughness measured on glasses with (blue) and without (black) SiO2 layer.
Wetting properties
With increased plasma treatment duration, the surface morphologies changed, which affected the wetting behavior, as shown in Figure 3. The water CA and CAH were measured on nanostructured glass before and after the application of a hydrophobic coating. The glass without the SiO2 layer has no significant surface features; therefore, the CA before and after CF4 plasma etching was almost unchanged, at approximately 30°. The CA of glass without the SiO2 layer increased to 90° with the hydrophobic coating, which is similar to the value for the flat surfaces coated with plasma-polymerized hexamethyldisiloxane (pp-HMDSO), as shown in Figure 3a and b. In the case of the nanostructured glass, the surface wettability was significantly improved by a combination of the high surface energy of the plasma treated glass or SiO2 surface and its nanoscale roughness, resulting in a large reduction of the CA to less than 5° after 5 min of plasma treatment. With the hydrophobic coating, superhydrophobic surfaces were achieved after 15 min of CF4 plasma treatment and the CAH was measured to be as low as 3°. As shown in Figure 3c, the long-term durability of the superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic properties was assessed over 50 days and was found to be almost unchanged for both properties because of the nanostructure effect10,19.
The superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic nanostructured glasses were tested for anti-condensation with a simple water spraying test under ambient air conditions and with a temperature change from −17 to 25°C under supersaturation conditions, as shown in Figure 4. As the micro-scale water droplets were sprayed onto the superhydrophobic lens of the eye glass, the water droplets showed high mobility with a very low CAH, resulting in dropwise condensation. Similar to the well-known lotus effect, the droplets all rolled off the superhydrophobic glass surface, as shown on the left side of the glasses in Figure 4a and Figures S2 and S3 in supplementary information. Conversely, liquid film formation was observed on the superhydrophilic surfaces, as shown on the right side of the glasses in Figure 4a and Figures S4 and S5. With the continued addition of water vapor, no water droplets were observed and the transparency of the superhydrophilic surface was unaffected. This result was expected because it is known that superhydrophilic glass surfaces can be used for anti-fogging or anti-condensation applications under supersaturation conditions20,21.
Discussion
EPMA analysis was performed to investigate the surface chemical compositions of bare and nanostructured soda-lime glasses after CF4 plasma etching, as shown in Figure 5a and b, respectively. In the case of bare glass, Fe and F were weakly detected (Figure 5a). Randomly oriented nanopatterns on the nanostructured glass were analyzed by using SEM in backscattered electron (BSE) mode and the corresponding EPMA intensities for Fe and F components were measured, as shown in Figure 5c. The large increases in these two components on the nanostructured glass indicate the formation of metal fluoride, as shown in Figure 5b and c. The regions covered with metal fluoride are not easily etched, whereas the regions without metal fluoride can be rapidly etched through mechanical or chemical reaction etching. It should be noted that the unetchable metal fluoride on the nanostructures can be removed via a hydrolysis reaction in water22,23. Note that the conventional self-masking method by metal film dewetting requires post-processing with toxic acids to remove the metallic masks on top of the glass nanostructures9,10. Additional TEM observation on a 500 nm high/300 nm wide nanopillar (Figure 5d and e) revealed that Fe and F surrounded the nanopillar, whereas Ca and Si were in the body of the pillar, as shown in Figure 5f. From this result, it can be hypothesized that Fe, which originated from the chamber cathode upon the irradiation of F ions, would form the metal fluoride FeFx. Upon the formation of metal fluoride clusters on the SiO2-coated glass surfaces, the F ions may be etched by physical sputtering, whereas the surfaces that do not contain metal fluoride may be etched by both physical sputtering and chemical reaction mechanisms by forming SiFx-like volatile species24.
SEM image (left) and EPMA mapping (middle and right) analysis of glass surfaces for (a) SiO2-coated glass and (b) bare glass with F and Fe as the selected surface atoms. Scale bars are 1 μm. (c) EPMA intensity for Fe and F components on the samples in (a) and (b). (d) SEM image of nanostructured glass at an 80° tilt. Scale bar is 500 nm (e) TEM image of a single glass nanopillar and (f) its EELS area mapping of four components (Si, Ca, Fe and F) where all components are false colored. (e) and (f) image scale bars are 300 nm
Water condensation (or anti-fogging) tests on glasses with different wettabilities were performed by increasing the air temperature from −17 (inside a freezer) to 25°C (in ambient air), as shown in Figure 4b. It was observed that the superhydrophobic surface was easily fogged with water vapor condensation as the temperature increased, whereas the superhydrophilic surfaces maintained their transparency, indicating that no water condensation occurred. It has been reported that the condensation behavior of superhydrophobic surfaces is related to the aspect ratio of the surface nanostructures. In the structures formed on the glasses in this study, the pillar height was not sufficient to resist dew formation; thus, water droplets of a few micrometers in size from a sprayed vapor may adhere to, rather than roll off, the glass surface at low temperatures, causing the glass surface to be blurred. Conversely, the superhydrophilic surface has sufficiently high surface energy to quickly form a thin water film, maintaining the glass surface transparency25.
Functional glass used in applications such as solar cell panels, automobile side mirrors or optical glasses for medical devices or surgery require anti-reflection properties as well as self-cleaning and anti-fogging properties. The optical anti-reflectance is related to the surface roughness and is an essential requirement for improving the optical efficiency of glass. In addition to increasing the hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity, controlled roughness plays a crucial role in reducing light reflectance by enhancing light scattering, which is similar to the moth-eye effect. Soda-lime glass without any plasma etching exhibits some incident light reflection and has a water CA of 30°, whereas the nanostructured glass surfaces show very low water wetting angles in the non-coated condition but a high wetting angle following pp-HMDSO coating, as shown in Figure 6a. Note that the nanostructured glass surfaces with or without hydrophobic pp-HMDSO coatings have very low light reflection and that a comparison of the transmittance spectra of the pristine glass before and after the hydrophobic coating process indicates that no significant decrease in transparency occurred as a result of the very thin layer (20 nm) of pp-HMDSO coating. Transmittance on the glasses without the SiO2 coating was slightly altered as the CF4 plasma etching duration was increased, as shown in Figure 6b. In the case of the nanostructured superhydrophobic glasses with etch durations of less than 30 min shown in Figure 6c, the surfaces remained transparent, whereas those with longer etch durations of 60 min had drastically decreased transmittance in the near-violet region due to the larger pillar size, as shown in Figure 2f. Compared with the pristine glass, the reflectance was not changed on the glasses without SiO2 coating, regardless of the plasma etching duration, as shown in Figure 6d, whereas a large reduction in the reflectance from 9 to 3 at the wavelength of 600 nm was observed on the superhydrophobic glasses shown in Figure 6e. Overall, the light transmission on the nanostructured glass surfaces was relatively unaffected by the nanostructures, whereas the reflectance was considerably reduced by longer CF4 plasma etching durations.
(a) Optical microscopic images of water droplets on three glass surfaces: pristine (left), superhydrophilic (middle) and superhydrophobic (right). Optical transmittance of the CF4 treated glass surfaces (b) without and (c) with the SiO2 coating. Optical reflectance (d) without and (e) with the SiO2 coating.
This simple and novel method to fabricate nanostructures for functional glass with superhydrophobicity/hydrophilicity, anti-condensation properties and low reflectance can be applied in various fields, such as for self-cleaning mirrors or windows in automobiles, vehicles and ships; windows inside and outside buildings; display panels for electronics; and other optical equipment for biomedical applications.
Methods
Soda–lime glass (Marienfeld, 1000412) with a thickness of 1 mm was utilized in the experiments. The glass surfaces were cleaned with acetone, methanol and 2-propanol. Then, a 1-μm-thick SiO2 overlayer was deposited onto the glass using plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) with a mixture of N2O gas and SiH4 gas26. After coating, the samples were etched using a glow discharge of CF4 gas with a treatment duration from 5 to 60 min by PECVD, as shown in Figure 1. The gas pressure and bias voltage were maintained at 30 mTorr and −600 Vb, respectively.
After CF4 plasma etching, nanostructures were developed on the SiO2 layer-coated glass via the well-known method of preferential etching with a reactive ion. With continuous CF4 plasma etching, the SiO2 pillars became etching masks for the glass, resulting in nanopillars on the glass surfaces. The nanostructured glass was subjected to a hydrolysis process to remove metal fluorides from the surface, by using the water treatment method27. The glass surfaces were found to be superhydrophilic after nanostructuring. To reduce the surface energy of the nanostructured glass surfaces, a hydrophobic material was deposited onto the surface by the plasma polymerization of HMDSO (C:H:Si:O) using PECVD. The gas pressure was fixed at 10 mTorr, the bias voltage was −400 Vb and the deposition time was 15 sec28.
The wettability of the nanostructured glass surface was characterized by deionized (DI) water droplet CA and CAH measurements. For these measurements, water droplets of approximately 5 μL with radii of approximately 1 mm were gently deposited onto the surfaces using a micro-syringe. The advancing CA was measured by adding a sessile drop of DI water (~5 μL) and the receding CA was measured by removal of a sessile drop of DI water. The CAH was calculated as the difference between the advancing and receding CAs. All measurements were taken using a CA goniometer (Rame-Hart) in ambient air at 25°C with a relative humidity of 20–35%. The reported CAs were determined by averaging the measurements from five different locations on each sample. Glass with the two extreme wetting conditions, superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity, on each side was tested for water repellence and anti-fogging properties. Glass samples were stored in a freezer at −17°C for 60 min for the anti-condensation and anti-fogging tests and then the condensation experiments were performed under ambient conditions.
The surface nanostructures were observed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM, NovaSEM, FEI) and their geometries were measured with an atomic force microscope (AFM, XE70, Park Systems). The surface atomic dispersion was measured with a field emission electron probe micro-analyzer (FE-EPMA, JXA-8500F, JEOL) and a transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEM-3000F, JEOL). UV-vis measurements were performed in the wavelength range of 250 to 900 nm using a spectrophotometer (Perkin-Elmer, Lambda 20) at room temperature. The spectra were recorded with air as the reference.
References
Raut, H. K., Ganesh, V. A., Nair, A. S. & Ramakrishna, S. Anti-reflective coatings: A critical, in-depth review. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 3779–3804 (2011).
Chattopadhyay, S. et al. Anti-reflecting and photonic nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. R-Rep. 69, 1–35 (2010)
Zhang, X. et al. Superhydrophobic surfaces: from structural control to functional application. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 621–633 (2008)
Li, X., Abe, T. & Esashi, M. Deep reactive ion etching of Pyrex glass using SF6 plasma. Sens. Actuators A 87, 139–145 (2001)
Hein, E., Fox, D. & Fouckhardt, H. Self-masking controlled by metallic seed layer during glass dry-etching for optically scattering surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 033301 (2010)
Howarter, J. A. & Youngbloodm, J. P. Self-cleaning and next generation anti-fog surfaces and coatings. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 29, 455–466 (2008)
Lee, A. et al. Water harvest via dewing. Langmuir 28, 10183–10191 (2012)
Drelich, J., Chibowski, E., Meng, D. D. & Terpilowski, K. Hydrophilic and superhydrophilic surfaces and materials. Soft Matter 7, 9804–9828 (2011)
Verma, L. K. et al. Self-cleaning and antireflective packaging glass for solar modules. Renew. Energy 36, 2489–2493 (2011)
Son, J. et al. Practical superhydrophilic self cleaning and antireflective surface for outdoor photovoltaic applications. Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. 98, 46–51 (2012)
Zeze, D. A., Cox, D. C., Weiss, B. L. & Silva, S. R. P. Lithography-free high aspect ratio submicron quartz columns by reactive ion etching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1362–1364 (2004)
Leech, P. W. Reactive ion etching of quartz and silica-based glasses in CF4/CHF3 plasmas. Vacuum 55, 191–196 (1999)
Ebert, D. & Bhushan, B. Transparent, superhydrophobic and wear-resistant coatings on glass and polymer substrates using SiO2, ZnO and ITO nanoparticles. Langmuir 28, 11391–11399 (2012)
Ling, X. Y. et al. Stable and transparent superhydrophobic nanoparticle films. Langmuir 25, 3260–3263 (2009)
d'Agostino, R. & Flamm, D. L. Plasma etching of Si and SiO2 in SF6–O2 mixtures. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 162–167 (1981)
Zhang, L., Zhao, N. & Xu, J. Fabrication and application of superhydrophilic surfaces: a review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 28, 769–790 (2014)
Nwankire, C. E., Favaro, G., Duong, Q.-H. & Dowling, D. P. Enhancing the mechanical properties of superhydrophobic atmospheric pressure plasma deposited siloxane coatings, Plasma Process. Polym. 8, 305–315 (2011)
Miljkovic, N., Enright, R. & Wang, E. N. Modeling and optimization of superhydrophobic condensation. J. Heat Transfer 135, 111004 (2013)
Yi, J. W. et al. Long-lasting hydrophilicity on nanostructured Si-incorporated diamond-like carbon films. Langmuir 26, 17203–17209 (2010)
Tricoli, A., Righettoni, M. & Pratsinis, S. E. Anti-fogging nanofibrous SiO2 and nanostructured SiO2-TiO2 films made by rapid flame deposition in situ annealing. Langmuir 25, 12578–12585 (2009)
Chen, Y. et al. Transparent superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic coatings for self-cleaning and anti-fogging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 033701 (2012)
Hofsäss, H. et al. The role of phase separation for self-organized surface pattern formation by ion beam erosion and metal atom co-deposition. Appl. Phys. A 111, 653–664 (2013)
El-Atwani, O. et al. Nanopatterning of metal-coated silicon surfaces via ion beam irradiation: Real time x-ray studies reveal the effect of silicide bonding. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 124305 (2013)
Yoo, J. et al. RIE texturing optimization for thin c-Si solar cells in SF6/O2 plasma. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 125205 (2008)
Patankar, N. A. Supernucleating surfaces for nucleate boiling and dropwise condensation heat transfer. Soft Matter 6, 1613–1620 (2010)
Landheer, D. et al. Formation of high-quality nitrided silicon dioxide films using electron-cyclotron resonance chemical vapor deposition with nitrous oxide and silane. J. Electrochem. Soc. 143, 1681–1684 (1996)
Her, E. K. et al. Superhydrophobic transparent surface of nanostructured poly(methyl methacrylate) enhanced by a hydrolysis reaction. Plasma Process. Polym. 10, 481–488 (2013)
Cha, S.-C. et al. Thermal stability of superhydrophobic, nanostructured surfaces. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 391, 152–157 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the KIST internal project, the Global Excellent Technology Innovation R&D Program under the Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MKE), the Republic of Korea and Project No. 10040003 funded by the MKE. This work was also funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (R11-2005-065, OKH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.Y., K.H.O. and M.W.M. planned the study. E.Y., H.L., S.C.K. and K.H.O. performed material fabrication and some of the characterization steps. E.Y., S.C.K., H.L. and K.H.O. carried out the wetting-related experiments and TEM analysis. E.Y., S.C.K., K.H.O. and M.W.M analyzed the experimental data and results. E.Y., M.W.M. and K.H.O. wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed and commented on the manuscript and provided feedback.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder in order to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, E., Kim, SC., Lee, H. et al. Extreme wettability of nanostructured glass fabricated by non-lithographic, anisotropic etching. Sci Rep 5, 9362 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09362
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09362
This article is cited by
-
Flexibly designable wettability gradient for passive control of fluid motion via physical surface modification
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Femtosecond laser hierarchical surface restructuring for next generation neural interfacing electrodes and microelectrode arrays
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Approaches to design a surface with tunable wettability: a review on surface properties
Journal of Materials Science (2021)
-
Lubricant-infused directly engraved nano-microstructures for mechanically durable endoscope lens with anti-biofouling and anti-fogging properties
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Quantitative measurements of nanoparticle layer thicknesses near the contact line region after droplet drying-out
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.