Abstract
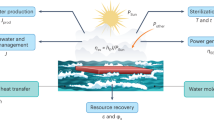
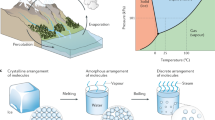
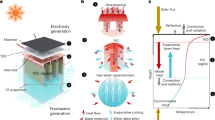
Solar desalination holds great promise for addressing global water scarcity and reducing carbon footprints. In recent years, thermally localized solar interfacial desalination processes have attracted much attention due to their efficient water evaporation potential. Previous efforts have focused on developing novel photothermal materials and optimizing thermal management to increase system evaporation rates. However, the water production rate of a desalination device is mainly independent of its evaporator performance, which makes it challenging to translate improved system evaporation rates into actual water production rates. This Review discusses the significance of steam condensation in promoting water production and emphasizes the importance of latent heat recovery. We highlight the industrial design of the desalination system, application scenarios, current limitations and potential costs. Furthermore, we present the potential of hybrid drive solutions for the future design of interference-resistant, fast-response, all-weather desalination systems. This Review aims to provide guidance for the development of high-performance solar desalination integrated devices and their large-scale industrial applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$99.00 per year
only $8.25 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
New water and climate coalition launched ahead of World Water Day. WMO https://public.wmo.int/en/media/press-release/new-water-and-climate-coalition-launched-ahead-of-world-water-day (2021).
He, C. et al. Future global urban water scarcity and potential solutions. Nat. Commun. 12, 4667 (2021).
Wang, X. et al. Solar steam-driven membrane filtration for high flux water purification. Nat. Water 1, 391–398 (2023).
Zheng, Y. et al. Large-scale solar-thermal desalination. Joule 5, 1971–1986 (2021).
Menon, A. K. et al. Enhanced solar evaporation using a photothermal umbrella for wastewater management. Nat. Sustain. 3, 144–151 (2020).
Hofste, R. W. et al. Aqueduct 3.0: Updated Decision-Relevant Global Water Risk Indicators (World Resources Institute, 2019); https://www.wri.org/publication/aqueduct-30
GDP per capita (current US$). World Bank https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.CD?end=2019&start=1960&view=chart (2023).
Solar resource maps of world: global horizontal irradiation. Solargis https://solargis.com/maps-and-gis-data/download/world (2023).
Zhang, L. et al. Passive, high-efficiency thermally-localized solar desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 1771–1793 (2021).
Kabeel, A. E. & El-Agouz, S. A. Review of researches and developments on solar stills. Desalination 276, 1–12 (2011).
Al-Karaghouli, A. & Kazmerski, L. L. Energy consumption and water production cost of conventional and renewable-energy-powered desalination processes. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 24, 343–356 (2013).
Wang, F. et al. A high-performing single-stage invert-structured solar water purifier through enhanced absorption and condensation. Joule 5, 1602–1612 (2021).
Ghasemi, H. et al. Solar steam generation by heat localization. Nat. Commun. 5, 4449 (2014).
Tao, P. et al. Solar-driven interfacial evaporation. Nat. Energy 3, 1031–1041 (2018).
Xu, N. et al. Mushrooms as efficient solar steam-generation devices. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606762 (2017).
Zhang, L. et al. Modeling and performance analysis of high-efficiency thermally-localized multistage solar stills. Appl. Energy 266, 114864 (2020).
Chen, C. et al. Challenges and opportunities for solar evaporation. Joule 3, 683–718 (2019).
Zhao, F. et al. Materials for solar-powered water evaporation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 5, 388–401 (2020).
Thoai, D. N. et al. Review on the recent development and applications of three dimensional (3D) photothermal materials for solar evaporators. J. Clean. Prod. 293, 126122 (2021).
Gao, M. et al. Solar absorber material and system designs for photothermal water vaporization towards clean water and energy production. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 841–864 (2019).
Dang, C. et al. A multichannel photothermal rod for antigravity water transportation and high-flux solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 10, 18116–18125 (2022).
Li, J. et al. Over 10 kg m−2 h−1 evaporation rate enabled by a 3D interconnected porous carbon foam. Joule 4, 928–937 (2020).
Xu, K. et al. Salt mitigation strategies of solar-driven interfacial desalination. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2007855 (2020).
Liu, G. et al. Salt-rejecting solar interfacial evaporation. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2, 100310 (2021).
Dang, C. et al. Ultra salt-resistant solar desalination system via large-scale easy assembly of microstructural units. Energy Environ. Sci. 15, 5404–5414 (2022).
Zhou, L. et al. The revival of thermal utilization from the Sun: interfacial solar vapor generation. Natl Sci. Rev. 6, 562–578 (2019).
Ni, G. et al. Steam generation under one sun enabled by a floating structure with thermal concentration. Nat. Energy 1, 2016126 (2016).
Li, X. et al. Measuring conversion efficiency of solar vapor generation. Joule 3, 1798–1803 (2019).
Li, R., Wang, W., Shi, Y., Wang, C. T. & Wang, P. Advanced material design and engineering for water-based evaporative cooling. Adv. Mater. 13, e2209460 (2023).
Li, X. et al. Enhancement of interfacial solar vapor generation by environmental energy. Joule 2, 1331–1338 (2018).
Song, H. et al. Cold vapor generation beyond the input solar energy limit. Adv. Sci. 5, 1800222 (2018).
Zhao, G. et al. Engineering high-tortuosity 3D gradient structure and CFD-assisted multifield analysis for solar interfacial evaporation. Small 27, e2305855 (2023).
Yang, Z. et al. Optimized water supply in a solar evaporator for simultaneous freshwater production and salt recycle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 13047–13055 (2023).
Dang, C. et al. Design of solar evaporator with well-aligned and multi-scale fluid channels based on convection tuning for stable and efficient brine desalination. Desalination 550, 116408 (2023).
Liu, Z. et al. Continuously producing watersteam and concentrated brine from seawater by hanging photothermal fabrics under sunlight. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1905485 (2019).
Liu, Z. et al. Hierarchical photothermal fabrics with low evaporation enthalpy as heliotropic evaporators for efficient, continuous, salt-free desalination. ACS Nano 15, 13007–13018 (2021).
Zhang, C. et al. Designing a next generation solar crystallizer for real seawater brine treatment with zero liquid discharge. Nat. Commun. 12, 998 (2021).
Dang, C. et al. Industrial pathways to lithium extraction from seawater: challenges and perspectives. Nano Res. Energy 2, e9120059 (2023).
Hao, X. et al. Multifunctional solar water harvester with high transport selectivity and fouling rejection capacity. Nat. Water https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-023-00152-y (2023).
Wang, S. et al. Boosting clean water evaporation and sustainable water treatment by photothermally induced artificial system. J. Mater. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-09029-7 (2023).
Zhao, L. et al. A passive high-temperature high-pressure solar steam generator for medical sterilization. Joule 4, 2733–2745 (2020).
Xu, N. et al. Synergistic tandem solar electricity-water generators. Joule 4, 347–358 (2020).
Wang, W. et al. Integrated solar-driven PV cooling and seawater desalination with zero liquid discharge. Joule 5, 1873–1887 (2021).
Xu, Z. et al. Solar evaporation with solute replacement towards real-world applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 16, 5325–5338 (2023).
Wu, S. L. et al. Suspended membrane evaporators integrating environmental and solar evaporation for oily wastewater purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 39513–39522 (2021).
Zhang, Z. et al. Improving solar vapor generation by eliminating the boundary layer inhibition effect of evaporator pores. ACS Energy Lett. 8, 2276–2283 (2023).
Yang, H. et al. High freshwater flux solar desalination via a 3D plasmonic evaporator with an efficient heat-mass evaporation interface. Adv. Mater. 35, e2304699 (2023).
Yang, B. et al. Flatband λ-Ti3O5 towards extraordinary solar steam generation. Nature 622, 499–506 (2023).
Wu, S.-L. et al. Solar-driven evaporators for water treatment: challenges and opportunities. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 7, 24–39 (2021).
Irshad, M. S. et al. Advances of 2D-enabled photothermal materials in hybrid solar-driven interfacial evaporation systems toward water-fuel-energy crisis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2304936 (2023).
Cui, X. et al. Photothermal nanomaterials: a powerful light-to-heat converter. Chem. Rev. 123, 6891–6952 (2023).
Liu, S. et al. Understanding interfacial properties for enhanced solar evaporation devices: from geometrical to physical interfaces. ACS Energy Lett. 8, 1680–1687 (2023).
Yin, Q. et al. The emerging development of solar evaporators in materials and structures. Chemosphere 289, 133210 (2021).
Zhang, Y. et al. Structure architecting for salt-rejecting solar interfacial desalination to achieve high-performance evaporation with in situ energy generation. Adv. Sci. 7, 1903478 (2020).
Ying, P. et al. Band gap engineering in an efficient solar-driven interfacial evaporation system. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 32880–32887 (2020).
Sharshir, S. W. et al. New hydrogel materials for improving solar water evaporation, desalination and wastewater treatment: a review. Desalination 491, 114564 (2020).
Li, X., Zhu, B. & Zhu, J. Graphene oxide based materials for desalination. Carbon 146, 320–328 (2019).
Zhu, L. et al. Solar-driven photothermal nanostructured materials designs and prerequisites for evaporation and catalysis applications. Mater. Horiz. 5, 323–343 (2018).
Pang, Y. et al. Solar-thermal water evaporation: a review. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 437–456 (2020).
Cao, S. et al. Advances in solar evaporator materials for freshwater generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 24092–24123 (2019).
Ding, T. et al. Hybrid solar-driven interfacial evaporation systems: Beyond water production towards high solar energy utilization. Mater. Today 42, 178–191 (2021).
Guan, W. et al. Carbon materials for solar water evaporation and desalination. Small 17, e2007176 (2021).
Meng, F. et al. Nano/microstructured materials for solar-driven interfacial evaporators towards water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 13746–13769 (2021).
Liu, H. et al. Bioinspired self-standing, self-floating 3D solar evaporators breaking the trade-off between salt cycle and heat localization for continuous seawater desalination. Adv. Mater. 35, e2301596 (2023).
Yang, H. C. et al. Membranes in solar-driven evaporation: design principles and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2304580 (2023).
Li, T. et al. Scalable and highly efficient mesoporous wood-based solar steam generation device: localized heat, rapid water transport. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1707134 (2018).
Xu, Y. et al. A facile approach to fabricate sustainable and large-scale photothermal polydopamine-coated cotton fabrics for efficient interfacial solar steam generation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 61, 18109–18120 (2022).
Li, C. et al. A covalent organic framework/graphene dual-region hydrogel for enhanced solar-driven water generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 3083–3090 (2022).
Abdoul-Carime, H. et al. Velocity of a molecule evaporated from a water nanodroplet: Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics versus non-ergodic events. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 14685–14689 (2015).
Kudo, K. et al. Structural changes of water in poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel during dehydration. J. Chem. Phys. 140, 044909 (2014).
Miyazaki, M. et al. Infrared spectroscopic evidence for protonated water clusters forming nanoscale cages. Science 304, 1134–1137 (2004).
Xingyi, Z. et al. Architecting highly hydratable polymer networks to tune the water state for solar water purification. Sci. Adv. 5, eaaw5484 (2019).
Zhao, F. et al. Highly efficient solar vapour generation via hierarchically nanostructured gels. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 489–495 (2018).
Liu, Y. et al. A bioinspired, reusable, paper-based system for high-performance large-scale evaporation. Adv. Mater. 27, 2768–2774 (2015).
Xu, W. et al. Efficient water transport and solar steam generation via radially, hierarchically structured aerogels. ACS Nano 13, 7930–7938 (2019).
Wang, C., Xu, K., Shi, G. & Wei, D. Water skin effect and arched double-sided evaporation for boosting all-weather high salinity desalination. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2300134 (2023).
Ni, G. et al. A salt-rejecting floating solar still for low-cost desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 1510–1519 (2018).
Xia, Y. et al. Spatially isolating salt crystallisation from water evaporation for continuous solar steam generation and salt harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 1840–1847 (2019).
Wu, L. et al. Highly efficient three-dimensional solar evaporator for high salinity desalination by localized crystallization. Nat. Commun. 11, 521 (2020).
Xu, N. et al. A scalable fish-school inspired self-assembled particle system for solar-powered water-solute separation. Natl Sci. Rev. 8, nwab065 (2021).
Xia, Y. et al. A self-rotating solar evaporator for continuous and efficient desalination of hypersaline brine. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 16212–16217 (2020).
Chen, X. et al. Sustainable off-grid desalination of hypersaline waters using Janus wood evaporators. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 5347–5357 (2021).
Yao, H. et al. Janus-interface engineering boosting solar steam towards high-efficiency water collection. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 5330–5338 (2021).
Hu, R. et al. A Janus evaporator with low tortuosity for long-term solar desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 15333–15340 (2019).
Zhao, W. et al. Hierarchically designed salt-resistant solar evaporator based on Donnan effect for stable and high-performance brine treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2100025 (2021).
Kuang, Y. et al. A high-performance self-regenerating solar evaporator for continuous water desalination. Adv. Mater. 31, e1900498 (2019).
Su, X. et al. Setaria viridis-inspired hydrogels with multilevel structures for efficient all-day fresh water harvesting. J. Mater. Chem. A 11, 7702–7710 (2023).
Patel, S. K. et al. The relative insignificance of advanced materials in enhancing the energy efficiency of desalination technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 1694–1710 (2020).
Zhang, S. et al. The effect of surface-free energy and microstructure on the condensation mechanism of water vapor. Prog. Nat. Sci. 33, 37–46 (2023).
Durán, I. R. & Laroche, G. Current trends, challenges, and perspectives of anti-fogging technology: surface and material design, fabrication strategies, and beyond. Prog. Mater Sci. 99, 106–186 (2019).
Li, X., Li, B., Li, Y. & Sun, J. Nonfluorinated, transparent, and spontaneous self-healing superhydrophobic coatings enabled by supramolecular polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 404, 126504 (2021).
Xu, Z. et al. Ultrahigh-efficiency desalination via a thermally-localized multistage solar still. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 830–839 (2020).
Vaartstra, G. et al. Capillary-fed, thin film evaporation devices. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 130901 (2020).
Narayanan, S. et al. A thermophysical battery for storage-based climate control. Appl. Energy 189, 31–43 (2017).
Zhou, X. et al. Solar water evaporation toward water purification and beyond. ACS Mater. Lett. 3, 1112–1129 (2021).
Wang, W. et al. Simultaneous production of fresh water and electricity via multistage solar photovoltaic membrane distillation. Nat. Commun. 10, 3012 (2019).
Chiavazzo, E. et al. Passive solar high-yield seawater desalination by modular and low-cost distillation. Nat. Sustain. 1, 763–772 (2018).
Wang, H. et al. Simultaneous solar steam and electricity generation from synergistic salinity-temperature gradient. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2100481 (2021).
Xue, G. et al. Water-evaporation-induced electricity with nanostructured carbon materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 317–321 (2017).
Zhang, Y. et al. Manipulating unidirectional fluid transportation to drive sustainable solar water extraction and brine-drenching induced energy generation. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 4891–4902 (2020).
Zuo, K. et al. Multifunctional nanocoated membranes for high-rate electrothermal desalination of hypersaline waters. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 1025–1032 (2020).
Huang, C. H. et al. Tailoring of a piezo-photo-thermal solar evaporator for simultaneous steam and power generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2010422 (2021).
Li, L. et al. Highly salt-resistant and all-weather solar-driven interfacial evaporators with photothermal and electrothermal effects based on Janus graphene@silicone sponges. Nano Energy 81, 105682 (2021).
Wang, M. et al. Aramid-based aerogels for driving water evaporation through both photo-thermal and electro-thermal effects. J. Mater. Chem. A 11, 7711–7723 (2023).
Average monthly residential cost of water in the U.S. from 2010 to 2019. Statista https://www.statista.com/statistics/720418/average-monthly-cost-of-water-in-the-us/ (2023).
Kabeel, A. E. Performance of solar still with a concave wick evaporation surface. Energy 34, 1504–1509 (2009).
Geng, Y. et al. Bioinspired fractal design of waste biomass-derived solar-thermal materials for highly efficient solar evaporation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2007648 (2020).
Interagency Working Group on Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases, United States Government. Technical Update of the Social Cost of Carbon for Regulatory Impact Analysis-under Executive Order 12866 (Environmental Protection Agency, 2013); https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2016-12/documents/sc_co2_tsd_august_2016.pdf
Zhu, B. et al. Solar-driven watersteam/brine production and brine-driven electricity generation by photothermal fabric coupled with osmotic membrane. Nano Energy 117, 108844 (2023).
Niu, R. et al. Bio-inspired sandwich-structured all-day-round solar evaporator for synergistic clean water and electricity generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2302451 (2023).
He, N. et al. Ionization engineering of hydrogels enables highly efficient salt-impeded solar evaporation and night-time electricity harvesting. Nanomicro Lett. 16, 8 (2023).
Deng, W. et al. Capillary front broadening for water-evaporation-induced electricity of one kilovolt. Energy Environ. Sci. 16, 4442–4452 (2023).
Zhang, L. et al. Hydrophobic light-to-heat conversion membranes with self-healing ability for interfacial solar heating. Adv. Mater. 27, 4889–4894 (2015).
Velmurugan, V. et al. Single basin solar still with fin for enhancing productivity. Energy Convers. Manage. 49, 2602–2608 (2008).
Zou, M. et al. 3D printing a biomimetic bridge-arch solar evaporator for eliminating salt accumulation with desalination and agricultural applications. Adv. Mater. 33, e2102443 (2021).
Cao, P. et al. Gradient heating effect modulated by hydrophobic/hydrophilic carbon nanotube network structures for ultrafast solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 19109–19116 (2021).
Ni, F. et al. Micro-/macroscopically synergetic control of switchable 2D/3D photothermal water purification enabled by robust, portable, and cost-effective cellulose papers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 15498–15506 (2019).
Wang, W. et al. Solar seawater distillation by flexible and fully passive multistage membrane distillation. Nano Lett. 21, 5068–5074 (2021).
Zhu, L. et al. Self-contained monolithic carbon sponges for solar-driven interfacial water evaporation distillation and electricity generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702149 (2018).
Li, R. et al. An integrated solar-driven system produces electricity with fresh water and crops in arid regions. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 3, 100781 (2022).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFB3803502), National Natural Science Foundation of China (52103076), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Graduate Student Innovation Fund of Donghua University (CUSF-DH-D-2023001), special fund of Beijing Key Laboratory of Indoor Air Quality Evaluation and Control (No. BZ0344KF21-02), and State Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and Power Equipment (EIPE22203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Water thanks Hao-Cheng Yang, and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, C., Cao, Y., Nie, H. et al. Structure integration and architecture of solar-driven interfacial desalination from miniaturization designs to industrial applications. Nat Water 2, 115–126 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-024-00200-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-024-00200-1
This article is cited by
-
Structural integration of solar desalination system
Science China Materials (2024)