Abstract
Diastole is the sequence of physiological events that occur in the heart during ventricular filling and principally depends on myocardial relaxation and chamber stiffness. Abnormal diastolic function is related to many cardiovascular disease processes and is predictive of health outcomes, but its genetic architecture is largely unknown. Here, we use machine-learning cardiac motion analysis to measure diastolic functional traits in 39,559 participants of the UK Biobank and perform a genome-wide association study. We identified nine significant, independent loci near genes that are associated with maintaining sarcomeric function under biomechanical stress and genes implicated in the development of cardiomyopathy. Age, sex and diabetes were independent predictors of diastolic function and we found a causal relationship between genetically determined ventricular stiffness and incident heart failure. Our results provide insights into the genetic and environmental factors influencing diastolic function that are relevant for identifying causal relationships and potential tractable targets.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Diastole is not a passive phase of the cardiac cycle, but is a complex sequence of inter-related physiological processes dependent on myocardial relaxation, stiffness and recoil, which are modulated by loading conditions, heart rate and contractile function. Diastolic function therefore plays a central role in determining left ventricular filling and stroke volume with dysfunction shown to be a predictor of major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality1. Decline in diastolic function is also a hallmark of cardiac aging, which occurs through multiple profibrotic and energetic pathways2,3. While several candidate genes have been implicated in various systolic function phenotypes through genome-wide association studies (GWASs)4,5, the genetic architecture of diastolic function and causal associations with disease are largely unknown. Efforts to better define the molecular mechanisms of diastolic dysfunction could enable the development of innovative therapies for many cardiovascular disease states.
Preclinical models of diastolic dysfunction are associated with alterations in left ventricular stiffness on atomic force microscopy that occur at the level of the cardiomyocyte sarcomere as well as due to extracellular matrix protein expansion6. Such tissue level changes can be assessed at macroscopic scale in human populations through analysis of diastolic mechanics. Here we use data from participants in the UK Biobank with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR)7 and apply deep-learning computer vision techniques for precision motion analysis to derive image-based phenotypes of diastolic function8,9. In a GWAS of diastolic traits we identify associated loci that map to genes involved in actin assembly, cardiac myocyte survival and heart failure phenotypes. We also describe the relationship between diastolic function and cardiovascular risk factors and identify potential causal relationships with disease through Mendelian randomization (MR).
Results
Study overview
We analyzed CMR data from 39,559 participants in the UK Biobank using machine-learning segmentation and motion tracking to measure three validated parameters of diastolic function: radial and longitudinal peak early diastolic strain rate (PDSRrr and PDSRll, respectively) (Fig. 1) and maximum body surface area-indexed left atrial volume (LAVmaxi)10. A flow chart of the analysis steps is depicted in Extended Data Fig 1. Baseline characteristics of the population are shown in Extended Data Fig. 2. For the GWAS, the population was partitioned into discovery and validation sets by the release of data tranches by UK Biobank. To assess the association between these diastolic function traits and other clinical measurements, we further considered a broad selection of 30 imaging and 110 non-imaging phenotypes that included biophysical data and circulating biomarkers (Supplementary Data 1). Independent GWASs were undertaken for each image-derived phenotype and heritability was estimated. We used a phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) to identify multiple phenotypes associated with a polygenic instrumental variable score (PIVS) for diastolic function. Potential causal associations were examined using two-sample MR. The results are reported in accordance with GWAS reporting guidelines and a checklist is provided in Supplementary Information.
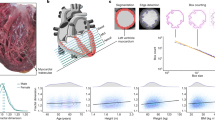
Motion analysis of CMR imaging performed on left ventricular short-axis cines. a, An example from one individual where deep-learning segmentation and image registration were used to determine the radial components of myocardial deformation. Data from the basal, midventricular and apical levels are shown at four representative phases from the 50 acquired. b, Radial strain and strain rate (first derivative of strain) for all UK Biobank participants (median and interquartile ranges, n = 39,559 individuals).
Imaging and non-imaging phenotype associations
Strain rates declined with age and were lower in men (P < 10−16 for both associations) (Fig. 2), but no univariable association was observed between age and LAVmaxi (Extended Data Fig. 3). Multiple linear regression analysis was used to develop a model for predicting each diastolic trait from demographic, hemodynamic and cardiovascular risk factors (Fig. 3a and Extended Data Fig. 4a). In this multivariable analysis, strain rate and left atrial volumes were negatively associated with age, male sex and pulse rate in the full model (P < 10−16 for all associations). Significant associations were also observed for body surface area (BSA) and systolic blood pressure (SBP). Diabetes also added significantly to the associations with the diastolic function traits in the model (PDSRll: P = 2.36 × 10−8; PDSRrr: P = 9.98 × 10−6; LAVmaxi: P = 1.04 × 10−3).
a,b, Scatter-plots of PDSRll (n = 38, 923) (a) and PDSRrr with age (n = 38, 700) (b) with density contours, linear model fit and marginal density plots. c,d, Violin plots of longitudinal (n = 38, 923) (c) and radial (n = 38, 700) (d) peak diastolic strain rate with sex; ****P < 10−16 (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Box plots show the median, hinges indicate interquartile range (IQR) and whiskers show 1.5 × IQR.
a, Multiple linear regression analysis of left ventricular PDSRll, PDSRrr and indexed LAVmaxi with age, sex, BSA, SBP, pulse rate and diabetes as predictors. All associations were significant after false discovery rate (FDR) correction. Data are presented as beta coefficient point estimates (95% CI). b, Circular plot visualization of the associations between the imaging (red, PDSRll, PDSRrr, global systolic radial strain (Err), global systolic longitudinal strain (Ell), ascending aortic (AAo) distensibility, descending aortic (DAo) distensibility, indexed left ventricular stroke volume (LVSVi), left ventricular cardiac index (LVCI), LAVmaxi, indexed right ventricular stroke volume (RVSVi) and right atrial ejection fraction (RAEF) and the non-imaging phenotypes (green for environmental; blue for biochemical). The strength of the connection between each pair is presented as a ribbon with a size proportional to the regression coefficient. All associations with a regression coefficient <0.3 are shown in faint colors (apart from the associations between PDSRll, PDSRrr and LAVmaxi and all other phenotypes). The coefficients for the associations of the circular plot are shown in Extended Data Fig. 4b. Standardized beta coefficients are shown with units in s.d. for each variable.
We investigated the association between image-derived measures of atrial, ventricular and aortic function with a broader range of non-imaging phenotypes using regularized regression analysis (Fig. 3b and Extended Data Figs. 4b and 5) (Supplementary Material).
C-reactive protein (CRP), a circulating biomarker of inflammation, showed a positive relationship with serum triglycerides, but we found no circulating biomarkers independently associated with diastolic function. We found that reduced peak diastolic strain rates were associated with reduced LAVmaxi. Left atrial function was related to indicators of right ventricular function emphasizing their functional interdependence11.
Genetic architecture of diastolic function traits
Genome-wide common and rare variant association analyses of diastolic function traits
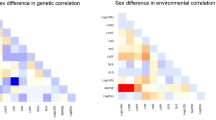
The single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based heritability (proportion of variance per trait explained by all considered SNPs) was 12% for PDSRll, 13% for PDSRrr and 21% for LAVmaxi. The observed genetic correlation between the diastolic function traits was 0.22 (standard error (SE) 0.07) between PDSRll and LAVmaxi, 0.12 (SE 0.08) between PDSRrr and LAVmaxi and 0.85 (SE 0.04) between PDSRll and PDSRrr.
In total, we identified nine independent loci from our GWAS analyses, five loci for PDSRrr, four for PDSRll and two for LAVmaxi (two loci are shared between PDSRrr and PDSRll). Within the discovery set, we identified five independent loci (one LAVmaxi; three PDSRrr; and one PDSRll) reaching genome-wide significance (P = 5 × 10−8; Supplementary Fig 3), which were also significant in the validation dataset also (P < 0.05/5). Considering the full dataset, the number of significant independent loci increased to nine with two additional loci associating with PDSRrr, one additional with LAVmaxi and one additional with PDSRll (Fig. 4).
a–c, Indexed LAVmaxi (a), PDSRll (b) and (PDSRrr (c) (full dataset). This figure shows the −log10(P value) on the y axis across all autosomal chromosomal positions (x axis) from BOLT-LMM. The dotted line indicates genome-wide significance (P = 5 × 10−8, n = 34,245). Significant loci are labeled by their likely causal gene and lead SNP (Table 1).
Variant annotation
Summary information for the nine loci identified using the full GWAS dataset and two predicted loss-of-function (LoF) variants are presented in Table 1 (further information is provided in Supplementary Material, Supplementary Fig. 5 and Supplementary Table 1). The closest gene to each locus is depicted, with further variants to gene mapping presented as the ‘likely gene’ given by evidence of a functional effect on a gene (Supplementary Material), additional heart-related phenotype associations or a previously reported mechanism linking the gene to diastolic function. Taking lead variants identified from GWAS and the LoF analysis, we were able to highlight several structural genes associated with diastolic function that also have a known role in myocardial contractility (such as TTN, PLN and GJA1) and in the functional maintenance and stress response of the cytoskeleton (such as FHOD3 and BAG3)12. Moreover, we were also able to identify a link between the NPR3 locus and left atrial volume. The signal colocalizes with a previously discovered association with blood pressure traits (systolic, diastolic and mean arterial blood pressure). The C-allele of the lead SNP (rs1173727) at this locus increases NPR3 expression and is associated with increased blood pressure and LAVmaxi and an increase in risk of heart failure (Supplementary Material). The NPR3 gene encodes the C-type natriuretic peptide receptor, which has a high drug tractability score (https://platform.opentargets.org/target/ENSG00000113389), making it a potential therapeutic target.
The relationship between common variants in NPR3 and genes encoding other proteins in the natriuretic peptide pathway with traits linked to the lead SNP (rs1173727) are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6 and an abridged version is provided in Extended Data Fig. 6.
Potential causes and consequences of diastolic function
Creation of polygenic instrumental variable scores (PIVS and PheWAS)
PIVSs for each diastolic function trait consisted of 20 SNPs for PDSRrr, 15 SNPs for PDSRll and 8 for LAVmaxi. The PIVS explained 1.5% of the variability of PDSRrr, 1.1 % of PDSRll and 0.2 % of LAVmaxi. There was good agreement between the distribution of the PIVS in the UK Biobank participants with and without CMR, indicating no systematic bias in genetic architecture (Supplementary Fig. 9). The Pearson correlation coefficient for the PIVS for PDSRll and PDSRrr was 0.35, whereas the correlation coefficient between LAVmaxi and PDSRll or PDSRrr, respectively was much lower (<0.01). PheWAS was undertaken and we considered traits that have been previously associated with cardiac phenotypes in the literature, but in addition included an unbiased selection of phenotypes for exploration. In total, we considered 71 quantitative phenotypes and 63 (binary) disease end points (Supplementary Data 1). Out of these, 31 phenotypes were significantly associated (Padj < 0.05) with at least one of the diastolic function PIVSs after leave-one-out cross-validation (Fig. 5). Some of the identified PheWAS associations are consistent with the phenotype correlation analysis (such as pulse rate and blood pressure). We also confirmed associations between diastolic function and previously reported biomarkers of heart failure (such as sex hormone binding globulin13 and insulin-like growth factor 1 (ref. 14)). Furthermore, we identified an association of PDSRrr to heart failure, cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy, implicating diastolic function in cardiovascular end points.
a, Quantitative traits that significantly associated with the PIVSs of diastolic function (beta coefficient point estimates standardized to change per 1 s.d. increase in diastolic function trait with 95% CI). b, Binary traits that significantly associated with the PIVSs of diastolic function. Point estimates are log(odds ratio) per 1 s.d. increase in diastolic function trait (95% CI). Detailed results, including numerical P values and 95% CI are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10. One unit change in the PIVS represents a change of 1 s.d. in the respective diastolic function trait. All dependent variables (traits) were standardized, representing the change in dependent variable s.d. for a 1 × s.d. change in the respective measurement. Associations not significant after multiple testing correction (conducted per PIVS) are displayed as gray bars. LDL, low-density lipoprotein; HDL. high-density lipoprotein; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 s; FVC, forced vital capacity; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; NS, non-significant. n = 449,263.
Mendelian randomization
Diastolic dysfunction is a substrate for the subsequent development of heart failure and, in observational studies, diabetes and hypertension are associated risk factors15. Here we used MR to identify potential causal relationships between diastolic function as an exposure and two key clinical outcomes (mixed-etiology heart failure and atrial fibrillation). We also assessed causal effects of biochemical, metabolic and hemodynamic exposures on diastolic function. These were chosen on the basis of clinical plausibility and the findings of the phenotype correlation analysis.
We tested a number of MR techniques, each addressing different assumptions and excluded potentially confounding instruments. A strong bi-directional causal relationship was observed between pulse rate and PDSRrr, PDSRll and LAVmaxi (Extended Data Fig. 7, Supplementary Figs. 12–14 and Supplementary Tables 2–4), consistent with findings from preclinical models16. Diastolic blood pressure was causally associated with PDSRrr and had a bi-directional association with PDSRll. SBP was causally associated PDSRll, but not PDSRrr. In addition, higher total peripheral resistance was strongly associated with higher PDSRll, PDSRrr and LAVmaxi, adding to the evidence implicating ventriculovascular coupling in the development of diastolic dysfunction17.
We also identified a potential causal relationship between lower PDSRrr (stiffer ventricle) and increased risk of heart failure (Supplementary Fig. 11), which was further corroborated using GWAS summary results18 from the HERMES consortium (Supplementary Table 5), a GWAS meta-analysis from 47,309 cases of heart failure and 930,014 controls. The magnitude of the effect observed in the MR analysis is consistent with the observational epidemiological estimate, derived from correlating PDSRrr with incident heart failure (Extended Data Fig. 7). We found no causal relationship between longitudinal PDSRll and heart failure and neither was one observed in our epidemiological analysis (Extended Data Fig. 7).
Diastolic dysfunction is frequently present in diabetic patients19; however, the effects are mostly mediated by an increased risk of coronary artery disease18. We found parameter estimates that support a causal relationship between diabetes as an exposure and diastolic function as an outcome, as well as a potential link with instruments for lipid profiles.
Last, we found a causal association between LAVmaxi and an outcome of atrial fibrillation20, but there was no evidence that ventricular stiffness also has a causal association.
Discussion
Diastole is a complex series of molecular, biophysical and electromechanical processes that initiate contractile deactivation and promote efficient ventricular filling. Impairment of these coordinated mechanisms may lead to diastolic dysfunction, which is associated with the presence of multiple cardiovascular risk factors leading to reduced quality of life and higher mortality21,22. Here, we used deep-learning cardiac motion analysis to perform the first reported GWAS of diastolic function traits with the aim of determining tractable causative mechanisms. We found that diastolic function was a heritable trait with associations in loci related to myofilament mechanics, protein synthesis during mechanical stress and regulation of cardiac contractility. Furthermore, we find a role for a gene implicated in endothelium-derived signaling in diastolic function that is a potential therapeutic target23. Last, through MR we observe a causal relationship between genetically determined diastolic function and heart failure outcomes.
A decline in diastolic function is a feature of the aging heart and we found that age was a strong independent predictor of diastolic function, with a greater decrease present in males. Outcome studies have suggested that this is a prognostically benign feature of healthy aging that is not related to adverse effects of cardiac senescence2,24,25. Changes in titin protein phosphorylation, myocardial redox state and impairment of nitric oxide signaling have been proposed as potential mechanisms26 and clinical studies indicate that age-related myocardial fibrosis, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and reduced microvascular density, may be a consequence rather than an initiating cause of diastolic dysfunction27. Non-invasive imaging biomarkers of fibrosis have also shown promise in identifying biologically relevant pathways for myocardial fibrosis in adult hearts28.
We found that diabetes was causally associated with impaired diastolic function after excluding potentially confounding instruments. In epidemiological analyses this relationship was independent of age, BSA and SBP. Increased myocardial stiffness is recognized as one of the earliest and potentially reversible, manifestations of myocardial dysfunction in diabetes29. Several underlying mechanisms related to insulin resistance have been proposed that include altered cardiac energetics and accumulation of advanced glycation end products that promote ventricular stiffness30. We also observed a unidirectional causal relationship between genetically determined diastolic function and an outcome of heart failure, as well as associations with cardiovascular end points and circulating biomarkers of heart failure through PheWAS. Longitudinal cohort studies have suggested that persistence or progression of diastolic dysfunction is a risk factor for subsequent heart failure15 and our findings suggest that ventricular stiffness is a substrate for the evolution of mixed-etiology heart failure. We also found a unidirectional causal association between left atrial volume and atrial fibrillation, suggesting that it is atrial remodeling that drives this arrhythmic outcome31. Lipid profiles are associated with adverse changes in cardiac structure and systolic function and our findings extend that causal association to diastolic traits32.
Our study provides insights into the biological basis of diastolic function with potential implications for therapy development. We identified common variants within genes implicated in cardiomyopathies (such as BAG3, FHOD3 and PLN), suggesting that sarcomere homeostasis during mechanical stress may affect diastolic function in both health and disease33. Phospholamban (PLN) is a key regulator of cardiac diastolic function, which modulates sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase activity34. Common variants in this gene are also associated with trabeculation, which has been implicated in promoting ventricular filling9. Speckle-tracking echocardiography of Pln knockout mice reveals alterations in longitudinal strain but not radial strain35, which is concordant with our observed associations with diastolic function and may relate to associated changes in ventricular geometry36. Although there is a genetic correlation between strain rate vectors, the majority of SNPs used as polygenic instruments were independent of each other for these traits. We also identified a potential therapeutic target through the association of variants at the locus of NPR3 influencing diastolic function and risk of heart failure. Previous studies have highlighted its role in blood pressure control37 and in mediating the cardioprotective effects of cardiomyocyte and fibroblast-released C-type natriuretic peptide23.
This analysis has some limitations. The UK Biobank is a large-cross-sectional study that is subject to selection bias and latent population stratification; however, risk factor associations seem to be broadly generalizable38. The population is predominantly European and further work is required to explore diastolic traits and outcomes in people of diverse ancestries. Echocardiography has been the cornerstone of assessing diastolic function by characterizing features of ventricular relaxation, stiffness and recoil39. However, feature-tracking CMR has excellent agreement with speckle-tracking echocardiography40 and invasive measures of diastolic function41. While analysis of myocardial deformation is performed throughout the cardiac cycle, the measures of early diastolic strain rate may not capture variation in active relaxation before ventricular filling. While the relationship between quantitative and dichotomous outcomes may be nonlinear, such a relationship has not been observed between other genetically driven diastolic traits and outcomes42.
In conclusion, we found that diastolic function is a heritable trait that is causally upstream of incident heart failure. Associated common variants are related to genes that maintain functional homeostasis under biomechanical stress. We also identify a gene encoding an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor as a potential therapeutic target for modulating aspects of diastolic function.
Methods
All analyses in this study are on GitHub at https://github.com/ImperialCollegeLondon/diastolic_genetics/43 and were conducted with R v.>3.6.0.
Participants
For the UK Biobank, approximately 500,000 community-dwelling participants aged 40–69 years were recruited across the United Kingdom between 2006 and 2010 (ref. 44). All participants provided written informed consent for participation in the study, which was also approved by the National Research Ethics Service (11/NW/0382). Our study was conducted under terms of access approval number 28807 and 40616. A range of available data were included in this study comprising genotyping arrays and whole-exome sequencing (WES), cardiac imaging, health-related diagnoses and biological samples.
There are 488,252 genotyped participants of which 200,640 have whole-exome sequencing. We partitioned 39,559 participants with both CMR imaging and genotyping array data into two tranches by date of release from the UK Biobank, providing a discovery dataset of 26,893 participants and a validation dataset of 12,666 participants.
Imaging protocol
A standardized CMR protocol was followed to assess cardiac structure and function using two-dimensional retrospectively gated cine imaging on a 1.5T magnet (Siemens Healthineers). A contiguous stack of images in the left ventricular short-axis plane from base to apex was acquired, with long-axis cine imaging in the two and four-chamber views. Each cine sequence had 50 cardiac phases with an acquired temporal resolution of 31 ms (ref. 7). Transverse cine imaging was also performed in the ascending and descending thoracic aorta. All imaging phenotypes used for the analysis underwent quality control assessment8. Participants also underwent a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram, which was automatically analyzed using proprietary software (CardioSoft, GE Healthcare).
Cardiac image analysis
Segmentation of the short-axis and long-axis cine images in UK Biobank was made using fully convolutional networks, a type of deep-learning neural network, which predict a pixel-wise image segmentation by applying a number of convolutional filters onto each input image for feature extraction and classification9. The accuracy of image segmentation on the UK Biobank dataset is equivalent to expert human readers45. End-diastolic volume, end-systolic volume, stroke volume and ejection fraction were determined for both ventricles. Left ventricular myocardial mass was calculated from the myocardial volume assuming a density of 1.05 g ml−1. Left atrial volume was calculated from the segmented images using the biplane area–length formula \(V=\frac{8}{3\pi }\times \frac{{A}_{2Ch}\times {A}_{4Ch}}{L}\), where A2Ch and A4Ch indicate the atrial area on the two and four-chamber cines, respectively and L indicates the longitudinal diameter averaged across two views. Measurements were indexed to BSA according to the Du Bois formula: 0.20247 × (weight0.425) × (height0.725), with weight in kg and height in meters. The heart was divided into 16 standardized anatomical segments, excluding the true apex, according to American Heart Association nomenclature46.
The aorta was segmented on the cine images using a spatiotemporal neural network47. The maximum and minimum cross-sectional areas were derived from the segmentation and distensibility calculated using estimates of central blood pressure obtained using peripheral pulse-wave analysis (Vicorder)8.
Motion tracking was performed on the cine images using nonrigid image registration between successive frames (in GitHub repository ukbb_cardiac)48,49. To reduce the accumulation of registration errors, motion tracking was performed in both forward and backward directions from the end-diastolic frame and an average displacement field calculated8. This motion field was then used to warp the segmentation contours from end-diastole onto successive adjacent frames. Circumferential (Ecc) and radial (Err) strains were calculated on the short-axis cines by the change in length of respective line segments (Fig. 1a) as \({E}_{dir}=\frac{{{\Delta }}{L}_{dir}}{{L}_{dir}}\), where dir represents the direction, Ldir the length of a line segment along this direction and ΔLdir its change over time. Motion tracking was also performed on the long-axis four-chamber cines to derive longitudinal (Ell) strain. Peak strain for each segment and global peak strain were then calculated (Fig. 1b). Strain was measured from slices acquired at basal, midventricular and apical levels. For comparison between each component absolute strain values are reported. Strain rate was estimated as the first derivative of strain and PDSRrr and PDSRll directions was detected using an algorithm to identify local maxima (in GitHub repository peak_detection) (Fig. 1c).
Non-imaging phenotypes
In total we consider 110 non-imaging cardiovascular-related phenotypes in UK Biobank participants for the phenotype regression analysis and the genetic analysis. These phenotypes contain information acquired by touch-screen questionnaire, interview, biophysical measurement, hospital episode statistics, primary care data and biochemical analysis of venous blood. Details of how each phenotype was acquired are available on the UK Biobank Showcase (http://biobank.ctsu.ox.ac.uk/crystal/). It should be noted that the biochemical markers used here were acquired at the initial assessment visit that preceded imaging assessment. Also of note, not all phenotypes were used in both the phenotype and the genetic analysis (such as due to lack of available data at the imaging visit). We refer to the Supplementary Material both for details on the definition of the considered phenotypes and for information on the inclusion of specific phenotypes for each analysis.
Statistical significance testing and multiplicity control
We considered a P value < 0.05 as significant in all phenotype analysis. Where not stated otherwise, we controlled the FDR with a Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment. Significance thresholds and decision criteria for GWAS significant loci and causality assessment (MR) are described in the respective sections and/or in the Supplementary Material.
Phenotype association analysis
Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± s.d.). Differences in continuous variables between groups were performed using a Student’s t-test. Univariable and multiple linear regression analysis was used to explore the phenotype relationship between each diastolic parameter and cardiovascular risk factors. To identify relationships between diastolic function and a broader range of imaging and non-imaging phenotypes, including circulating biomarkers, we used the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) with stability selection, to optimize the model coefficients. We then ran regression diagnostics on the model with the selected variables, to exclude a possible collinearity inappropriately influencing our model (Supplementary Material has details on the phenotype analysis and LASSO analysis procedure).
Genotyping and sample quality control
Genotyping of UK Biobank participants has been described elsewhere in detail50. Briefly, UK Biobank genotyping for 488,252 participants was performed on the UK BiLEVE or UK Biobank Axiom arrays. Imputation was based on the HaplotypeReference Consortium panel and the UK10K+1000 Genomes Project panel. In this study, UK Biobank Imputation V3 (in GRCh37 coordinates) were used. WES was performed on data released in 2020 collected from 200,640 UK Biobank participants51. The sequencing methods and variant calling procedures have been described in detail52. In the present study, genotypes in their released PLINK-format files are utilized and samples were restricted to the European population. Quality control of the genetic data was performed as recommended by UK Biobank (Supplementary Material provides details on the procedure and number of excluded samples).
GWAS analysis
For the genetic analysis, there were 34,242 participants of European ancestry (Supplementary Material describes criteria) providing a discovery dataset of 23,321 participants and a validation set of 10,924 participants. GWAS analyses for the three diastolic function traits and additional quantitative traits of interest (as described for the causality assessment) were performed with BOLT-LMM (v.2.3.2), which accounts for ancestral heterogeneity, unknown population structure and sample relatedness53,54. GWAS analyses were adjusted for imaging traits for the first ten genetic principal components, sex, age at time of MRI, the genotyping array and the MRI assessment center and for non-imaging quantitative traits for the first ten principal components, sex, age at measurement of the trait and the genotyping array. GWAS analyses for clinical end points of interest (binary end points) were conducted with PLINK2 and adjusted for the first ten principal components, sex, age at baseline and the genotyping array. Post-GWAS filtering removed any SNPs with a Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium P < 0.05 and MAF < 0.005.
Assessment of shared genetic architecture
For the assessment of shared genetic architecture between diastolic function traits, linkage disequilibrium (LD) score regression (LDSC (LD SCore) v.1.0.1, ref. 55) was used to obtain a genetic correlation score between each pair of traits.
Variant annotations
Lead variants for each locus were assigned causal genes, where possible, using a combination of variant annotations and additional functional genomic data sources (colocalization). Each lead variant was systematically tested for any evidence of functional consequence using variant effect predictor. In addition, QTL evidence was extensively searched using Open Targets Genetics56. Where eQTL data were available for the locus, the full summary statistics were downloaded to assess colocalization (Supplementary Material).
Variant effect predictor57 and LoF transcript effect estimator (LOFTEE)58 plugins were applied on all genomic variants of WES data. In the present study, we considered the genomic variants predicted by LOFTEE with high-confidence label ‘HC’, non-dubious (no ‘LoF flag’, such as variants that located in poorly conserved exons or splice variants that affect NAGNAG sites or non-canonical splice regions) and MAF < 0.05, as an LoF mutation.
LoF association analysis
An LoF carrier indicator was created for each WES sample and each of the human protein-coding genes based on the collapsed information of LoF annotations. An individual was considered as an LoF carrier of the gene if there was at least one LoF mutation (based on methods in the variant annotation section) and a non-carrier if there was none. We then conducted the association test between LoF carrier indicator and the three diastolic function imaging phenotypes. Linear regression was performed with the adjustment of sex, age at time of MRI and the top ten genetic principal components. The association results were further filtered as those with at least two carriers and the end point available. The association was considered significant after multiple testing correction at α = 0.05 (FDR, calculated for three diastolic function traits). We identified 18,660 participants with both WES data and CMR imaging data.
Polygenic instrumental variable scores
Candidate variants for PIVS for the three diastolic function traits (LAVmaxi, PDSRll and PDSRrr) were obtained based on the respective GWAS (full imaging cohort) results by performing clumping (PLINK 1.9) using an LD threshold of R2 = 0.1 (in a window of 1,000 kb) and considering all SNPs with P < 10−6. Unlike more traditional polygenic risk scores we do not use thousands of variants as instruments but aim to identify a set of instrumental variables that are minimally correlated. This comes with the price of a relatively small set of instruments that explains less variability of a trait, but can be used as proper instruments for the MR analysis. Candidate variants were included in multivariate linear modeling evaluated on the European subset of the full imaging cohort with the first ten genetic principal components, age at MRI, sex, genotyping array and the MRI center as additional covariates and the respective diastolic function trait as dependent variables. The diastolic function traits were scaled to 1 s.d. before the model estimation; therefore, a unit change in the PIVS score represents a change of 1 s.d. unit in the respective diastolic function trait. PIVS estimates per individual were then calculated by multiplying the observed genotype with the estimated beta from the multivariate linear model for each SNP and summing these values up. Missing genotypes were imputed using a mean imputation. The variance explained for the PIVS is measured by R2, estimated in a linear regression with the PIVS as the only variable and the respective diastolic function trait as an end point.
Next, we conducted a PheWAS using the obtained PIVS (see above and Supplementary Material for a full definition of included phenotypes in the PheWAS). Evaluation of the PIVS were performed in the European non-imaging cohort (an independent set of individuals compared to the PIVS construction set). Only results are shown that are significant after multiple testing correction at α = 0.05 (FDR, calculated per diastolic function trait) and, as a sensitivity analysis, for which all leave-one-SNP out cross validations analysis led to a significant result at α = 0.05 after multiple testing correction (FDR) for the number of considered phenotypes. The latter condition is supposed to exclude spurious results that are only driven by one single variant. Leave-one-SNP-out cross-validation is performed by excluding one SNP from the list of candidate variants, then re-estimating the PIVS and performing the PheWAS as described above. For the leave-one-SNP-out cross-validation, FDR adjustment is performed per combination of diastolic trait and phenotype, considering the number of included SNPs.
Mendelian randomization
For exploring the causes and consequences of diastolic function parameters, we used a bi-directional MR approach (two MR analyses are performed): first, an MR analysis using the first chosen trait as exposure is conducted and second an MR analysis using the selected second trait is run. By considering both results, evidence can be gathered for a one-directional causal relationship, a bi-directional causal relationship or no causal relationship at all. We performed this analysis taking into account one diastolic and one non-diastolic function trait and for that, we selected non-diastolic function traits of interest by taking into account the results from the observational correlation analysis and clinical expertise. This approach led to the consideration of six dichotomous risk factors associated with diastolic dysfunction, arteriosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, hypertension and diabetes, considering type I and type II separately. Further, we considered four physiological variables as potential causes or consequences of changes in diastolic function, as well as five quantitative lipid traits as surrogate for arteriosclerotic risks as a potential confounder source for changes in diastolic function. In total we analyzed 15 nondiastolic phenotypes and the 3 diastolic phenotypes in our MR.
We established a workflow for the MR analysis, which is briefly described in this section. Full details are provided in the Supplementary Material. Genetic instrumental variables were selected from the UK Biobank GWAS results generated, as described above, via clumping with PLINK 1.9 as described for the PIVS approach. The candidate SNP set before clumping was restricted to the intersection between the SNP sets of the pair of GWAS results (hypothesized causal trait GWAS and hypothesized consequence trait GWAS). A full list of the instrumental variables is contained in the Supplementary Table file SupplementaryTable_InstrumentalVariantsMR.xlsx.
We aimed to remove potential confounding instruments by two filtering steps. First, we ran phenotype association analysis to identify and remove instruments that associate significantly with any of the traits for arteriosclerosis, triglycerides, apolipoprotein B and LDL cholesterol. Second, we ran Steiger filtering to remove instruments with potential wrongly inferred causal directions.
All MR analysis are based on the point estimates and s.d. obtained from the respective GWAS. We follow a similar approach to van Oort et al.59 by using inverse-variance weighted method as the main analysis and applying several other MR methods for ensuring robustness of the obtained results as sensitivity analyses. We used weighted median-based methods, MR-PRESSO and MR-Egger. Consistent effect estimates across the different methods improves our confidence in a truly causal effect. We consider an association as ‘potentially causal’ if the main analysis indicates a causal relationship (P < 0.01), at least two of the sensitivity analyses indicate at least a suggestive causal relationship (P < 0.05) and none of the sensitivity analyses indicate associations with inconsistent effect directionality (none of the methods showed a suggestive association with conflicting directionality) (P < 0.05). No explicit multiplicity adjustment is performed for MR experiments. For ‘potential causal’ associations, we next conducted a supplementary sensitivity analysis using published GWAS results as described in the Supplementary Material, if published GWAS data were available.
All analysis, which involved diastolic and non-diastolic function traits, were conducted in a two-sample approach (the diastolic function trait GWAS was calculated in the full imaging cohort and the non-diastolic function trait GWAS was calculated in the non-imaging cohort).
For comparison of the effect estimates from the MR analysis to the observed correlation of diastolic function measurement and disease status, we restricted the analysis population to individuals who were disease-free at the CMR visit. We then fitted a logistic regression model by coding individuals who experienced a first event of the selected disease during follow-up time as 1 and event-free individuals during follow-up as 0. As covariates, we included age at CMR visit, sex, diabetes status, diastolic blood pressure and body mass index. Note that this analysis was only performed for relationships judged as potentially causal and involving a disease end point (and not a quantitative measurement such as pulse rate).
NPR3 pathway analysis
To increase our understanding of the association of NPR3 with LAVmaxi and to further characterize the role of natriuretic peptides, we looked for additional genetic associations within genes of the natriuretic peptide pathway (so in addition to NPR3–NPR1, NPR2, NPPA, NPPB and NPPC). We conducted GWAS using BOLT-LMM for all imaging traits listed in Extended Data Fig. 2 as described above, as well as any non-imaging traits associated with rs1173727 (the lead variant for NPR3) across the four loci (NPPA and NPPB share the same locus). The GWAS summary statistics were filtered to a 1-MB window around each gene (for NPPA/B, the gene used for centering was NPPA). Across these summary statistics, we performed clumping with a P value threshold of 10−5 and R2 < 0.1.
For the identified tag SNPs and associated variants in LD from the clumping analysis, we then tested which of these variants we could confidently link to the natriuretic gene in the locus. If any variant was classified as missense, we selected that variant directly. For eQTL variants, we used colocalization analysis to link these SNPS to the natriuretic genes in each locus. Relevant eQTL and protein QTL data were used (eQTL summary statistics were taken from eQTL catalog60 and protein QTL data were taken from Sun et al.61) and SNPs with only a clear association with the gene of interest and traits of interest were kept (P < 10−4 for association with gene or protein expression, P < 10−5 for association with the trait and H12 > 0.5 was used as a threshold for the colocalization analysis).
Hierarchical clustering was then performed on the \(-\log (P)\times \beta\) values with the β values aligned to have a negative sign on the DBP. Extended Data Fig. 6 shows all SNPs and traits with a genome-wide significant association. The SNPs and traits with suggestive associations (P < 10−5) are shown in the Supplementary Material (Supplementary Fig. 6).
Reporting Summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
All raw and derived data in this study are available from UK Biobank (http://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/). GWAS summary level data are publicly available through the GWAS catalog (accession numbers GCST90019012, GCST90019013 and GCST90019014 for left atrial volume, longitudinal peak diastolic strain rate and radial peak diastolic strain rate, respectively). eQTL data used for variant to gene mapping are available through eQTL catalog (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/eqtl/).
Code availability
The analysis code is freely available on GitHub43.
References
Ladeiras-Lopes, R., Araújo, M., Sampaio, F., Leite-Moreira, A. & Fontes-Carvalho, R. The impact of diastolic dysfunction as a predictor of cardiovascular events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 38, 789–804 (2019).
Shah, A. M. et al. Contemporary assessment of left ventricular diastolic function in older adults: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Circulation 135, 426–439 (2017).
Chiao, Y. A. & Rabinovitch, P. S. The aging heart. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 5, a025148 (2015).
Aung, N. et al. Genome-wide analysis of left ventricular image-derived phenotypes identifies fourteen loci associated with cardiac morphogenesis and heart failure development. Circulation 140, 1318–1330 (2019).
Wild, P. S. et al. Large-scale genome-wide analysis identifies genetic variants associated with cardiac structure and function. J. Clin. Invest. 127, 1798–1812 (2017).
Travers, J. G. et al. HDAC inhibition reverses preexisting diastolic dysfunction and blocks covert extracellular matrix remodeling. Circulation https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046462 (2021).
Petersen, S. E. et al. UK Biobank’s cardiovascular magnetic resonance protocol. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 18, 8 (2016).
Bai, W. et al. A population-based phenome-wide association study of cardiac and aortic structure and function. Nat. Med. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-1009-y (2020).
Meyer, H. V. et al. Genetic and functional insights into the fractal structure of the heart. Nature 584, 589–594 (2020).
Kermer, J. et al. Assessment of diastolic dysfunction: comparison of different cardiovascular magnetic resonance techniques. ESC Heart Fail. 7, 2637–2649 (2020).
Baroncini, L. A. V. et al. Echocardiographic correlation between right ventricular function and left atrial volume. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 112, 249–257 (2019).
Ushijima, T. et al. The actin-organizing formin protein Fhod3 is required for postnatal development and functional maintenance of the adult heart in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 148–162 (2018).
Pascual-Figal, D. A. et al. Sex hormone-binding globulin: a new marker of disease severity and prognosis in men with chronic heart failure. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 62, 1381–1387 (2009).
Barroso, M. C. et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor-1 and its binding protein-7: potential novel biomarkers for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 16, 1–9 (2016).
Kane, G. C. et al. Progression of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and risk of heart failure. JAMA 306, 856–863 (2011).
Reil, J.-C. et al. Heart rate reduction by If-inhibition improves vascular stiffness and left ventricular systolic and diastolic function in a mouse model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J. 34, 2839–2849 (2013).
O’Regan, D. P. Stiff arteries, stiff ventricles: correlation or causality in heart failure? Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 9, e005150 (2016).
Shah, S. et al. Genome-wide association and Mendelian randomisation analysis provide insights into the pathogenesis of heart failure. Nat. Commun. 11, 163 (2020).
Bouthoorn, S. et al. The prevalence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in men and women with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 15, 477–493 (2018).
Ahlberg, G. et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 18 novel loci associated with left atrial volume and function. Eur. Heart. J. 42, 4523–4534 (2021).
Reddy, Y. N., Carter, R. E., Obokata, M., Redfield, M. M. & Borlaug, B. A. A simple, evidence-based approach to help guide diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 138, 861–870 (2018).
Playford, D. et al. Diastolic dysfunction and mortality in 436 360 men and women: the National Echo Database Australia (NEDA). Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jeaa253 (2021).
Moyes, A. J. et al. C-type natriuretic peptide co-ordinates cardiac structure and function. Eur. Heart J. 41, 1006–1020 (2020).
van Grootel, R. W. J. et al. Influence of age and sex on left ventricular diastolic strain analysis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 35, 491–498 (2019).
Hung, C.-L. et al. Age- and sex-related influences on left ventricular mechanics in elderly individuals free of prevalent heart failure. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 10, e004510 (2017).
Borbély, A. et al. Cardiomyocyte stiffness in diastolic heart failure. Circulation 111, 774–781 (2005).
Campbell, D. J. et al. Diastolic dysfunction of aging is independent of myocardial structure but associated with plasma advanced glycation end-product levels. PLoS ONE 7, e49813 (2012).
Nauffal, V. et al. Genetics of myocardial interstitial fibrosis in the human heart and association with disease. Preprint at medRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.05.21265953 (2021).
Grandi, A. M. et al. Effect of glycemic control on left ventricular diastolic function in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Cardiol. 97, 71–76 (2006).
Fontes-Carvalho, R., Ladeiras-Lopes, R., Bettencourt, P., Leite-Moreira, A. & Azevedo, A. Diastolic dysfunction in the diabetic continuum: association with insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 14, 1–9 (2015).
Raisi-Estabragh, Z. et al. Left atrial structure and function are associated with cardiovascular outcomes independent of left ventricular measures: a UK Biobank CMR study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jeab266 (2021).
Aung, N. et al. The effect of blood lipids on the left ventricle: a Mendelian randomization study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 76, 2477–2488 (2020).
Harper, A. R. et al. Common genetic variants and modifiable risk factors underpin hypertrophic cardiomyopathy susceptibility and expressivity. Nat. Genet. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-00764-0 (2021).
Frank, K. F., Bölck, B., Erdmann, E. & Schwinger, R. H. Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase modulates cardiac contraction and relaxation. Cardiovasc. Res. 57, 20–27 (2003).
Chowdhury, S. A. et al. Modifications of sarcoplasmic reticulum function prevent progression of sarcomere-linked hypertrophic cardiomyopathy despite a persistent increase in myofilament calcium response. Front. Physiol. 11, 107 (2020).
Bonazzola, R. et al. in Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021, de Bruijne, M. et al. (eds) 699–708 (Springer International Publishing, 2021).
Surendran, P. et al. Trans-ancestry meta-analyses identify rare and common variants associated with blood pressure and hypertension. Nat. Genet. 48, 1151–1161 (2016).
Batty, G. D., Gale, C. R., Kivimäki, M., Deary, I. J. & Bell, S. Comparison of risk factor associations in UK Biobank against representative, general population-based studies with conventional response rates: prospective cohort study and individual participant meta-analysis. BMJ https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m131 (2020).
Nagueh, S. F. Left ventricular diastolic function: Understanding pathophysiology, diagnosis, and prognosis with echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 13, 228–244 (2020).
Onishi, T. et al. Global longitudinal strain and global circumferential strain by speckle-tracking echocardiography and feature-tracking cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: comparison with left ventricular ejection fraction. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 28, 587–596 (2015).
Ito, H. et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking for characterization of patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: correlation of global longitudinal strain with invasive diastolic functional indices. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 22, 1–11 (2020).
Arvanitis, M. et al. Linear and nonlinear Mendelian randomization analyses of the association between diastolic blood pressure and cardiovascular events. Circulation 143, 895–906 (2021).
Thanaj, M., Mielke, J., Bender, C., Zeng, L. & O’Regan, D. P. Genetic and environmental determinants of diastolic heart function. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4767044 (2022).
Sudlow, C. et al. UK Biobank: an open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 12, e1001779 (2015).
Bai, W. et al. Automated cardiovascular magnetic resonance image analysis with fully convolutional networks. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 20, 65 (2018).
Cerqueira Manuel, D. et al. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. Circulation 105, 539–542 (2002).
Bai, W. et al. in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. 586–594 (Springer, 2018).
Rueckert, D. et al. Nonrigid registration using free-form deformations: application to breast MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 18, 712–21 (1999).
Puyol-Antón, E. et al. Fully automated myocardial strain estimation from cine MRI using convolutional neural networks. In 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018) 1139–1143 (IEEE Computer Society, 2018).
Bycroft, C. et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 562, 203–209 (2018).
Szustakowski, J. D. et al. Advancing human genetics research and drug discovery through exome sequencing of the UK Biobank. Nat. Genet. 53, 942–948 (2021).
Van Hout, C. V. et al. Exome sequencing and characterization of 49,960 individuals in the UK Biobank. Nature 586, 749–756 (2020).
Loh, P.-R. et al. Efficient Bayesian mixed-model analysis increases association power in large cohorts. Nat. Genet. 47, 284 (2015).
Loh, P.-R., Kichaev, G., Gazal, S., Schoech, A. P. & Price, A. L. Mixed-model association for Biobank-scale datasets. Nat. Genet. 50, 906–908 (2018).
Bulik-Sullivan, B. K. et al. LD Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 47, 291–295 (2015).
Ghoussaini, M. et al. Open targets genetics: systematic identification of trait-associated genes using large-scale genetics and functional genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, D1311–D1320 (2021).
McLaren, W. et al. The Ensembl variant effect predictor. Genome Biol. 17, 122 (2016).
Karczewski, K. J. et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 581, 434–443 (2020).
van Oort, S., Beulens, J. W., van Ballegooijen, A. J., Burgess, S. & Larsson, S. C. Cardiovascular risk factors and lifestyle behaviours in relation to longevity: a Mendelian randomization study. J. Intern. Med. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13196 (2021).
Kerimov, N. et al. A compendium of uniformly processed human gene expression and splicing quantitative trait loci. Nat. Genet. 53, 1290–1299 (2021).
Sun, B. B. et al. Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome. Nature 558, 73–79 (2018).
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by Bayer AG; Medical Research Council (MC-A658-5QEB0); National Institute for Health Research Imperial College Biomedical Research Centre; British Heart Foundation (NH/17/1/32725, RG/19/6/34387, RE/18/4/34215); Wellcome Trust (107469/Z/15/Z); Academy of Medical Sciences (SGL015/1006); Mason Medical Research Trust grant; and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EP/P001009/1). H.V.M. also receives funding from the Simons Center for Quantitative Biology at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.T. and J.M. performed the formal analyses and co-wrote the paper; W.B., N.S., A.d.M. and D.R. performed the image analysis; K.A.M., J.S.W., H.V.M., L.Z., F.S., R.T.L. and C.B. performed or interpreted the genetic analyses; A.M. performed the GWAS; M.R.W. interpreted the pharmacology findings; D.F.F. and D.P.O. conceived the study, managed the project and revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J.M., L.Z., F.S., C.B., A.M. and D.F.F. are full-time employees of Bayer AG, Germany. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Cardiovascular Research thanks James Priest and the other, anonymous, reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Integrated supplementary information
Extended Data Fig. 1 A summary of the main steps in our analysis of the genetic and environmental determinants of diastolic heart function.
Flow chart of study design including image analysis, environmental associations and genetic studies. A summary of the main steps in our analysis of the genetic and environmental determinants of diastolic heart function.
Extended Data Fig. 2 Baseline characteristics of the UK Biobank participants in the study.
AAo, ascending aorta; CMR, cardiac magnetic resonance; DAo, descending aorta; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; LA, left atrium; LDL, low density lipoprotein; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.
Extended Data Fig. 3 Population left atrial data.
a) Scatterplots of indexed left atrial maximum volume (LAVmaxi) against age with density contours, linear model fit and marginal density plots. b) Violin plots of LAVmaxi by sex with boxplots showing the median, hinges indicating interquartile ranges (IQR) and whiskers 1.5 x IQR (n=38,046). Wilcoxon signed-rank test was not significant (NS).
Extended Data Fig. 4 Association between imaging and non-imaging phenotypes.
a) Bubble plot showing beta coefficients and b) negative logarithm of the P-values for multiple linear regression analysis between imaging and non-imaging phenotypes. The false discovery rate threshold is shown as a dashed line. c) A plot showing the coefficients for predictors in the LASSO regression model (training set, n=21,403; test set, n=10,217). AAo, ascending aorta; BSA, body surface area; DAo, descending aorta; Ell, longitudinal strain; Err, radial strain; LA, left atrium; LAVmaxi, indexed maximum left atrial volume; LAVmini, indexed minimum left atrial volume; LV, left ventricle; LVCI, left ventricular cardiac index; LVSI, indexed left ventricular stroke volume; PDSRll, longitudinal peak diastolic strain rate; PDSRrr, radial peak diastolic strain rate; RA, right atrium; RAEF, right atrial ejection fraction; RV, right ventricle; RVSVi, indexed right ventricular stroke volume; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Extended Data Fig. 5 Predictors of diastolic function.
a) Plot showing the covariates selected after stability selection as predictors of peak longitudinal strain rate (PDSRll). b) Plot showing the odds ratio of each of the three diastolic function parameters (PDSRll, peak radial diastolic strain rate, PDSRrr and indexed left atrial maximum volume, LAVmaxi) with all covariates using LASSO regression and 10-fold cross-validation. Red bars indicate variables selected after stability selection.
Extended Data Fig. 6 Natriuretic peptide pathway analyses.
Heatmap of associations with SNPs in genes of the natriuretic peptide pathway. All cardiac imaging traits and traits with a genome-wide significant association with rs1173727 (NPR3) were included. SNPs were included if they have a genome-wide significant association with one of these traits except height (height is an extremely polygenic trait with many genome-wide association signals). Values indicate -log10(P-value) of the association test (BOLT-LMM, linear mixed-model, 2-sided, not corrected for multiple comparisons), directionality is aligned to the beta values of the systolic blood pressure (sbp_adj) associations, and to the height associations if there is no significant blood pressure association. AAo, ascending aorta; DAo, descending aorta; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; Ecc, circumferential strain; EDV, end diastolic volume; EF, ejection fraction; Ell, longitudinal strain; Err, radial strain; ESV, end-systolic volume; FVC, forced vital capacity; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; LVM, left ventricular mass; PDSR, peak diastolic strain rate; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle, SBP, systolic blood pressure; SV, stroke volume.
Extended Data Fig. 7 Outcome association analysis.
(a) Comparison of association estimates for diastolic function traits, radial peak diastolic strain rate (PDSRrr), longitudinal peak diastolic strain rate (PDSRll) and indexed left atrial maximum volume (LAVmaxi), vs. heart failure risk across different approaches (Mendelian ramdomisation (MR) approach using HERMES for the heart failure risk estimates, incident heart failure based on observational data; see Methods for set of considered covariates). Displayed are Log(Odds ratios) with 95% confidence intervals. (b - d) Results of Mendelian randomization for PDSRrr, PDSRll and LAVmaxi. For sensitivity analysis several methods are used. We regard a causal relation as significant, if at least two of the methods report a suggestive connection (p<=0.05) with non-conflicting direction. P-values are shown without correction for multiple testing. MR-PRESSO is used to remove potential horizontal pleiotropy. If empty, no outlier variants were detected by MR-PRESSO and the estimate is equal to IVW.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary methods, Supplementary Figs. 1–14 and Supplementary Tables 1–5.
Supplementary Data 1
Disease definitions.
Supplementary Data 2
Instrumental variants.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Thanaj, M., Mielke, J., McGurk, K.A. et al. Genetic and environmental determinants of diastolic heart function. Nat Cardiovasc Res 1, 361–371 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44161-022-00048-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44161-022-00048-2
This article is cited by
-
APOE ε4 carriage associates with improved myocardial performance from adolescence to older age
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2024)
-
Genetic architecture of cardiac dynamic flow volumes
Nature Genetics (2024)
-
Environmental and genetic predictors of human cardiovascular ageing
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Genetic insights into cardiac relaxation and filling
Nature Cardiovascular Research (2022)