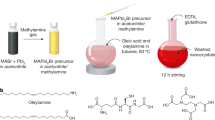
Abstract
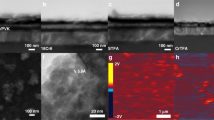
The colloidal synthesis of one-dimensional metal halide perovskite nanocrystals with precisely controlled diameter (D) and length (L) values is challenging due to the intrinsic structural symmetry and ionic crystal nature of the perovskites. This hinders investigation into their size- and shape-dependent properties and prevents their application. Here we report a general platform of cylindrical unimolecular nanoreactors to synthesize a library of one-dimensional perovskite nanorods (NRs) with tailored dimensions (D ≈ 7–16 nm; L ≈ 40–220 nm), compositions (all-inorganic perovskites; organic–inorganic perovskites; lead-free double perovskites) and enhanced colloidal, photo, polar-solvent and thermal stabilities. The dependence of the charge-carrier dynamics, photoluminescence quantum yield and optical anisotropy of the perovskite NRs on the diameter and length was examined. Decreasing the diameter yields opposite trends in the photoluminescence quantum yields and charge-carrier dynamics to that of increasing the length. In addition, enhanced structural anisotropy (that is, a higher aspect ratio of L/D) always increases the optical anisotropy of the perovskite NRs. By leveraging the cylindrical unimolecules as nanoreactors, a rich variety of uniform perovskite NRs with controllable dimensions, compositions and enhanced stabilities can be designed for use as building blocks for a variety of applications, such as in optoelectronic devices, catalysis and sensors.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data reported in this paper are available in the main text or the Supplementary Information. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Swarnkar, A. et al. Quantum dot-induced phase stabilization of α-CsPbI3 perovskite for high-efficiency photovoltaics. Science 354, 92–95 (2016).
Dong, Y. et al. Bipolar-shell resurfacing for blue LEDs based on strongly confined perovskite quantum dots. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 668–674 (2020).
Ma, X. et al. A flexible plasmonic-membrane-enhanced broadband tin-based perovskite photodetector. Nano Lett. 21, 9195–9202 (2021).
Shang, Q. et al. Role of the exciton–polariton in a continuous-wave optically pumped CsPbBr3 perovskite laser. Nano Lett. 20, 6636–6643 (2020).
Chen, Q. et al. All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators. Nature 561, 88–93 (2018).
Raja, S. N. et al. Encapsulation of perovskite nanocrystals into macroscale polymer matrices: enhanced stability and polarization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 35523–35533 (2016).
Li, Q., Yang, Y., Que, W. & Lian, T. Size- and morphology-dependent Auger recombination in CsPbBr3 perovskite two-dimensional nanoplatelets and one-dimensional nanorods. Nano Lett. 19, 5620–5627 (2019).
Zhang, C. et al. Metal halide perovskite nanorods: shape matters. Adv. Mater. 32, 2002736 (2020).
Dou, Y. et al. Lattice distortion in mixed-anion lead halide perovskite nanorods leads to their high fluorescence anisotropy. ACS Mater. Lett. 2, 814–820 (2020).
Wang, S. et al. Stable, strongly emitting cesium lead bromide perovskite nanorods with high optical gain enabled by an intermediate monomer reservoir synthetic strategy. Nano Lett. 19, 6315–6322 (2019).
Bera, S., Shyamal, S. & Pradhan, N. Chemically spiraling CsPbBr3 perovskite nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 14895–14906 (2021).
He, Y. et al. Dual-protected metal halide perovskite nanosheets with an enhanced set of stabilities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 7259–7266 (2021).
Huang, H. et al. Growth mechanism of strongly emitting CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals with a tunable bandgap. Nat. Commun. 8, 996 (2017).
Shamsi, J., Urban, A. S., Imran, M., De Trizio, L. & Manna, L. Metal halide perovskite nanocrystals: synthesis, post-synthesis modifications, and their optical properties. Chem. Rev. 119, 3296–3348 (2019).
Gao, M. et al. Scaling laws of exciton recombination kinetics in low dimensional halide perovskite nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 8871–8879 (2020).
Li, Y. et al. Using polar alcohols for the direct synthesis of cesium lead halide perovskite nanorods with anisotropic emission. ACS Nano 13, 8237–8245 (2019).
Yang, D. et al. Interfacial synthesis of monodisperse CsPbBr3 nanorods with tunable aspect ratio and clean surface for efficient light-emitting diode applications. Chem. Mater. 31, 1575–1583 (2019).
Wang, Y. et al. Reversible transformation between CsPbBr3 perovskite nanowires and nanorods with polarized optoelectronic properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2011251 (2021).
Akkerman, Q. A., Rainò, G., Kovalenko, M. V. & Manna, L. Genesis, challenges and opportunities for colloidal lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 17, 394–405 (2018).
Yoon, Y. J. et al. Enabling tailorable optical properties and markedly enhanced stability of perovskite quantum dots by permanently ligating with polymer hairs. Adv. Mater. 31, 1901602 (2019).
Roy, D., Semsarilar, M., Guthrie, J. T. & Perrier, S. Cellulose modification by polymer grafting: a review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 2046–2064 (2009).
Pang, X., He, Y., Jung, J. & Lin, Z. 1D nanocrystals with precisely controlled dimensions, compositions, and architectures. Science 353, 1268–1272 (2016).
Pang, X., Zhao, L., Han, W., Xin, X. & Lin, Z. A general and robust strategy for the synthesis of nearly monodisperse colloidal nanocrystals. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 426–431 (2013).
De Roo, J. et al. Highly dynamic ligand binding and light absorption coefficient of cesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano 10, 2071–2081 (2016).
Zhang, D., Eaton, S. W., Yu, Y., Dou, L. & Yang, P. Solution-phase synthesis of cesium lead halide perovskite nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 9230–9233 (2015).
Li, W. et al. Chemically diverse and multifunctional hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 16099 (2017).
Fan, Q. et al. Lead-free halide perovskite nanocrystals: crystal structures, synthesis, stabilities, and optical properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 1030–1046 (2020).
Shi, Y. et al. Noble-metal nanocrystals with controlled shapes for catalytic and electrocatalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 121, 649–735 (2020).
Liu, W. et al. Mn2+-doped lead halide perovskite nanocrystals with dual-color emission controlled by halide content. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 14954–14961 (2016).
Zhu, H. et al. One-dimensional highly-confined CsPbBr3 nanorods with enhanced stability: synthesis and spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 22, 8355–8362 (2022).
Lan, Y.-F. et al. Spectrally stable and efficient pure red CsPbI3 quantum dot light-emitting diodes enabled by sequential ligand post-treatment strategy. Nano Lett. 21, 8756–8763 (2021).
Pradhan, N. Do halide perovskites prefer a specific direction for forming one-dimensional nanostructures? ACS Energy Lett. 7, 150–153 (2021).
Protesescu, L. et al. Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, and I): novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut. Nano Lett. 15, 3692–3696 (2015).
Krieg, F. et al. Monodisperse long-chain sulfobetaine-capped CsPbBr3 nanocrystals and their superfluorescent assemblies. ACS Cent. Sci. 7, 135–144 (2020).
Shinde, A., Gahlaut, R. & Mahamuni, S. Low-temperature photoluminescence studies of CsPbBr3 quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 14872–14878 (2017).
Hintermayr, V. A. et al. Tuning the optical properties of perovskite nanoplatelets through composition and thickness by ligand-assisted exfoliation. Adv. Mater. 28, 9478–9485 (2016).
Bohn, B. J. et al. Boosting tunable blue luminescence of halide perovskite nanoplatelets through postsynthetic surface trap repair. Nano Lett. 18, 5231–5238 (2018).
Rabouw, F. T. et al. Delayed exciton emission and its relation to blinking in CdSe quantum dots. Nano Lett. 15, 7718–7725 (2015).
Shabaev, A. & Efros, A. L. 1D exciton spectroscopy of semiconductor nanorods. Nano Lett. 4, 1821–1825 (2004).
Planelles, J., Rajadell, F. & Climente, J. I. Electronic origin of linearly polarized emission in CdSe/CdS dot-in-rod heterostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 27724–27730 (2016).
Liu, Z. et al. Ligand mediated transformation of cesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals to lead depleted Cs4PbBr6 nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 5309–5312 (2017).
Diroll, B. T., Zhou, H. & Schaller, R. D. Low-temperature absorption, photoluminescence, and lifetime of CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1800945 (2018).
He, Y. et al. Unconventional route to dual-shelled organolead halide perovskite nanocrystals with controlled dimensions, surface chemistry, and stabilities. Sci. Adv. 5, eaax4424 (2019).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the following funding: Air Force Office of Scientific Research grant FA9550-19-1-0317 (Z.L.), National Science Foundation grant DMR 1903990 and CHE 1903957 (Z.L.) and National Science Foundation grant CHE 2004080 (T.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.L. conceived the idea and supervised the work. S.L., M.Z., S.H., M.T. and W.C. carried out the experiments. S.L., M.Z., S.H., M.T., W.C., T.L. and Z.L. analysed and discussed the data and results. Z.L. and S.L. wrote the original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Synthesis thanks Qiao Zhang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary handling editor: Alexandra Groves, in collaboration with the Nature Synthesis team.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Materials and additional experimental method, Discussion, Figs. 1–26 and Tables 1–4.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 5
Normalized PL decay data, averaged PL lifetime data and absolute PLQY data.
Source Data Fig. 6
Data reflecting evolution of the PL peak positions or intensities for the perovskite NRs under different conditions.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, S., Zhang, M., He, S. et al. Metal halide perovskite nanorods with tailored dimensions, compositions and stabilities. Nat. Synth 2, 719–728 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-023-00307-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-023-00307-5
This article is cited by
-
Recent Advances in Patterning Strategies for Full-Color Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes
Nano-Micro Letters (2024)
-
The reformation of catalyst: From a trial-and-error synthesis to rational design
Nano Research (2024)