Abstract
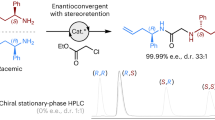
Typical methods for the synthesis of P-stereogenic allenylphosphine derivatives depend on chirality transfer from P-stereogenic substrates and require multiple synthetic steps. Now we report a Ni-catalysed enantioselective propargylic substitution reaction for the synthesis of P-stereogenic allenylphosphine derivatives from propargylic carbonates and secondary phosphines. Using in situ generated secondary phosphines, after a reduction of the corresponding phosphine oxides, a wide range of allenylphosphine derivatives with a P-stereogenic centre were synthesized with a high enantiocontrol (up to 97% e.e.). The method was also applied to the enantioconvergent synthesis of the P,axial-stereogenic 1,3-disubstituted allenylphosphines, using secondary propargylic carbonates as substrates with excellent enantio- and diastereocontrol (up to 97% e.e. and 14:1 d.r.) without the need for racemization or symmetrization of the secondary propargylic carbonates. The chiral phosphine products were readily incorporated into transition metal complexes with retention of stereopurity. Experimental and computational mechanistic studies suggest that the process proceeds through an enantioconvergent reaction mechanism, which gives enantioenriched phosphine products from a racemic mixture of secondary propargylic carbonates.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available in the manuscript or the Supplementary materials. Crystallographic data for the structures reported in this article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, under deposition numbers CCDC 2079669 (3av), 2079668 (3a-Ir) and 2071745 (Ni-PH). Copies of the data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/.
References
Ma, S. Some typical advances in the synthetic applications of allenes. Chem. Rev. 105, 2829–2872 (2005).
Liu, L., Ward, R. M. & Schomaker, J. M. Mechanistic aspects and synthetic applications of radical additions to allenes. Chem. Rev. 119, 12422–12490 (2019).
Swamy, K. C. K., Anitha, M., Debnath, S. & Shankar, M. Reactivity of allenylphosphonates/allenylphosphine oxides—some new addition/cycloaddition and cyclization pathways. Pure Appl. Chem. 91, 773–784 (2019).
Nicolaou, K. C., Maligres, P., Shin, J., De Leon, E. & Rideout, D. DNA-cleavage and antitumor activity of designed molecules with conjugated phosphine oxide–allene–ene–yne functionalities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 7825–7826 (1990).
Gangadhararao, G., Kotikalapudi, R., Nagarjuna Reddy, M. & Swamy, K. C. K. Allenylphosphine oxides as simple scaffolds for phosphinoylindoles and phosphinoylisocoumarins. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 10, 996–1005 (2014).
Nishimura, T., Hirabayashi, S., Yasuhara, Y. & Hayashi, T. Rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric hydroarylation of diphenylphosphinylallenes with arylboronic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 2556–2557 (2006).
Yu, F., Lian, X. & Ma, S. Pd-catalyzed regio- and stereoselective cyclization−Heck reaction of monoesters of 1,2-allenyl phosphonic acids with alkenes. Org. Lett. 9, 1703–1706 (2007).
Wei, K., Luo, K., Liu, F., Wu, L. & Wu, L.-Z. Visible-light-driven selective alkenyl C–P bond cleavage of allenylphosphine oxides. Org. Lett. 21, 1994–1998 (2019).
Mao, M., Zhang, L., Chen, Y.-Z., Zhu, J. & Wu, L. Palladium-catalyzed coupling of allenylphosphine oxides with N-tosylhydrazones toward phosphinyl [3]dendralenes. ACS Catal. 7, 181–185 (2017).
Ma, S., Guo, H. & Yu, F. Palladium(0)-catalyzed highly regio- and stereoselective addition of organoboronic acids with 1,2-allenylphosphonates forming tri- or tetrasubstituted 1(E)-alkenylphosphonates. J. Org. Chem. 71, 6634–6636 (2006).
Kumar, N. N. B., Reddy, M. N. & Swamy, K. C. K. Reactivity of allenylphosphonates toward salicylaldehydes and activated phenols: facile synthesis of chromenes and substituted butadienes. J. Org. Chem. 74, 5395–5404 (2009).
Kawamoto, T., Hirabayashi, S., Guo, X.-X., Nishimura, T. & Hayashi, T. Rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric hydroalkoxylation and hydrosulfenylation of diphenylphosphinylallenes. Chem. Commun. 2009, 3528–3530 (2009).
Gu, Y., Hama, T. & Hammond, G. B. Diastereoselective synthesis of cyclic α-fluoromethylidenephosphonates using α-fluoroallenephosphonate as dienophile. Chem. Commun. 2000, 395–396 (2000).
Chen, Y.-Z., Zhang, L., Lu, A.-M., Yang, F. & Wu, L. α-Allenyl ethers as starting materials for palladium catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura couplings of allenylphosphine oxides with arylboronic acids. J. Org. Chem. 80, 673–680 (2015).
Deng, H. et al. Palladium-catalyzed stereospecific C–P coupling toward diverse PN-heterocycles. Chem 8, 1–11 (2022).
Hu, G. et al. Copper-catalyzed direct coupling of unprotected propargylic alcohols with P(O)H compounds: access to allenylphosphoryl compounds under ligand- and base-free conditions. Org. Lett. 18, 6066–6069 (2016).
Yang, C. H. et al. Direct access to allenylphosphine oxides via a metal free coupling of propargylic substrates with P(O)H compounds. Org. Lett. 21, 9438–9441 (2019).
Qiu, M. R. et al. Stereoselective preparation of P,axial-stereogenic allenyl bisphosphine oxides via chirality-transfer. Org. Biomol. Chem. 18, 3017–3021 (2020).
Kalek, M. & Stawinski, J. Novel, stereoselective and stereospecific synthesis of allenylphosphonates and related compounds via palladium-catalyzed propargylic substitution. Adv. Synth. Catal. 353, 1741–1755 (2011).
Kalek, M., Johansson, T., Jezowska, M. & Stawinski, J. Palladium-catalyzed propargylic substitution with phosphorus nucleophiles: efficient, stereoselective synthesis of allenylphosphonates and related compounds. Org. Lett. 12, 4702–4704 (2010).
Guo, H., Fan, Y. C., Sun, Z., Wu, Y. & Kwon, O. Phosphine organocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 118, 10049–10293 (2018).
Fu, W. & Tang, W. Chiral monophosphorus ligands for asymmetric catalytic reactions. ACS Catal. 6, 4814–4858 (2016).
Ye, X., Peng, L., Bao, X., Tan, C.-H. & Wang, H. Recent developments in highly efficient construction of P-stereogenic centers. Green Synth. Catal. 2, 6–18 (2021).
Xu, G., Senanayake, C. H. & Tang, W. P-chiral phosphorus ligands based on a 2,3-dihydrobenzo[d][1,3]oxaphosphole motif for asymmetric catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 52, 1101–1112 (2019).
Tang, W. & Zhang, X. New chiral phosphorus ligands for enantioselective hydrogenation. Chem. Rev. 103, 3029–3070 (2003).
Imamoto, T. Searching for practically useful P-chirogenic phosphine ligands. Chem. Rec. 16, 2659–2673 (2016).
Dutartre, M., Bayardon, J. & Jugé, S. Applications and stereoselective syntheses of P-chirogenic phosphorus compounds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 5771–5794 (2016).
Anderson, B. J., Glueck, D. S., Dipasquale, A. G. & Rheingold, A. L. Substrate and catalyst screening in platinum-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of bis(secondary) phosphines. Synthesis of an enantiomerically pure C2-symmetric diphosphine. Organometallics 27, 4992–5001 (2008).
Scriban, C. & Glueck, D. S. Platinum-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of secondary phosphines: enantioselective synthesis of P-stereogenic phosphines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 2788–2789 (2006).
Chapp, T. W., Glueck, D. S., Golen, J. A., Moore, C. E. & Rheingold, A. L. Platinum-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of bis(isitylphosphino)ethane: stereoselectivity reversal in successive formation of two P−C bonds. Organometallics 29, 378–388 (2010).
Scriban, C., Glueck, D. S., Golen, J. A. & Rheingold, A. L. Platinum-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of a secondary phosphine: mechanism and origin of enantioselectivity. Organometallics 26, 1788–1800 (2007).
Li, C., Li, W., Xu, S. & Duan, W. Pd-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of methylphenylphosphine with alkyl halides for the synthesis of P-stereogenic compounds. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 33, 799 (2013).
Chapp, T. W., Schoenfeld, A. J. & Glueck, D. S. Effects of linker length on the rate and selectivity of platinum-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of the bis(isitylphosphino)alkanes IsHP(CH2)nPHIs (Is = 2,4,6-(i-Pr)3C6H2, n = 1−5). Organometallics 29, 2465–2473 (2010).
Anderson, B. J., Reynolds, S. C., Guino-O, M. A., Xu, Z. & Glueck, D. S. Effect of linker length on selectivity and cooperative reactivity in platinum-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of bis(phenylphosphino)alkanes. ACS Catal. 6, 8106–8114 (2016).
Chan, V. S., Chiu, M., Bergman, R. G. & Toste, F. D. Development of ruthenium catalysts for the enantioselective synthesis of P-stereogenic phosphines via nucleophilic phosphido intermediates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 6021–6032 (2009).
Zhang, S., Xiao, J.-Z., Li, Y.-B., Shi, C.-Y. & Yin, L. Copper(I)-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of unsymmetrical secondary phosphines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 9912–9921 (2021).
Gibbons, S. K., Xu, Z., Hughes, R. P., Glueck, D. S. & Rheingold, A. L. Chiral bis(phospholane) PCP pincer complexes: synthesis, structure, and nickel-catalyzed asymmetric phosphine alkylation. Organometallics 37, 2159–2166 (2018).
Chan, V. S., Stewart, I. C., Bergman, R. G. & Toste, F. D. Asymmetric catalytic synthesis of P-stereogenic phosphines via a nucleophilic ruthenium phosphido complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 2786–2787 (2006).
Korff, C. & Helmchen, G. Preparation of chiral triarylphosphines by Pd-catalysed asymmetric P–C cross-coupling. Chem. Commun. 2004, 530–531 (2004).
Anderson, B. J. et al. Platinum-catalyzed enantioselective tandem alkylation/arylation of primary phosphines. Asymmetric synthesis of P-stereogenic 1-phosphaacenaphthenes. Org. Lett. 10, 4425–4428 (2008).
Blank, N. F. et al. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric phosphination. Scope, mechanism, and origin of enantioselectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 6847–6858 (2007).
Moncarz, J. R., Laritcheva, N. F. & Glueck, D. S. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric phosphination: enantioselective synthesis of a P-chirogenic phosphine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 13356–13357 (2002).
Brunker, T. J., Anderson, B. J., Blank, N. F., Glueck, D. S. & Rheingold, A. L. Enantioselective synthesis of P-stereogenic benzophospholanes via palladium-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization. Org. Lett. 9, 1109–1112 (2007).
Yue, W. J., Xiao, J. Z., Zhang, S. & Yin, L. Rapid synthesis of chiral 1,2‐bisphosphine derivatives through copper(I)‐catalyzed asymmetric conjugate hydrophosphination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 7057–7062 (2020).
Scriban, C., Kovacik, I. & Glueck, D. S. A protic additive suppresses formation of byproducts in platinum-catalyzed hydrophosphination of activated olefins. Evidence for P−C and C−C bond formation by Michael addition. Organometallics 24, 4871–4874 (2005).
Song, Y.-C., Dai, G.-F., Xiao, F. & Duan, W.-L. Palladium-catalyzed enantioselective hydrophosphination of enones for the synthesis of chiral P,N-compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 57, 2990–2993 (2016).
Huang, Y., Pullarkat, S. A., Li, Y. & Leung, P.-H. Palladacycle-catalyzed asymmetric hydrophosphination of enones for synthesis of C*- and P*-chiral tertiary phosphines. Inorg. Chem. 51, 2533–2540 (2012).
Li, Y.-B., Tian, H. & Yin, L. Copper(I)-catalyzed asymmetric 1,4-conjugate hydrophosphination of α,β-unsaturated amides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 20098–20106 (2020).
Teo, R. H. X., Chen, H. J., Li, Y., Pullarkat, S. A. & Leung, P. H. Asymmetric catalytic 1,2-dihydrophosphination of secondary 1,2-diphosphines—direct access to free P*‐ and P*,C*‐diphosphines. Adv. Synth. Catal. 362, 2373–2378 (2020).
Huang, Y., Li, Y., Leung, P.-H. & Hayashi, T. Asymmetric synthesis of P-stereogenic diarylphosphinites by palladium-catalyzed enantioselective addition of diarylphosphines to benzoquinones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4865–4868 (2014).
Liu, X.-T. et al. Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrophosphination of unactivated alkynes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 11309–11316 (2021).
Zhang, Y., He, H., Wang, Q. & Cai, Q. Asymmetric synthesis of chiral P-stereogenic triaryl phosphine oxides via Pd-catalyzed kinetic arylation of diaryl phosphine oxides. Tetrahedron Lett. 57, 5308–5311 (2016).
Qiu, H., Dai, Q., He, J., Li, W. & Zhang, J. Access to P-chiral sec- and tert-phosphine oxides enabled by Le-Phos-catalyzed asymmetric kinetic resolution. Chem. Sci. 11, 9983–9988 (2020).
Liu, X.-T., Zhang, Y.-Q., Han, X.-Y., Sun, S.-P. & Zhang, Q.-W. Ni-catalyzed asymmetric allylation of secondary phosphine oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 16584–16589 (2019).
Dai, Q., Liu, L., Qian, Y., Li, W. & Zhang, J. Construction of P-chiral alkenylphosphine oxides through highly chemo-, regio-, and enantioselective hydrophosphinylation of alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 20645–20650 (2020).
Dai, Q., Li, W., Li, Z. & Zhang, J. P-chiral phosphines enabled by palladium/Xiao-Phos-catalyzed asymmetric P–C cross-coupling of secondary phosphine oxides and aryl bromides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 20556–20564 (2019).
Beaud, R., Phipps, R. J. & Gaunt, M. J. Enantioselective Cu-catalyzed arylation of secondary phosphine oxides with diaryliodonium salts toward the synthesis of P-chiral phosphines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 13183–13186 (2016).
Zhang, Q., Liu, X.-T., Wu, Y. & Zhang, Q.-W. Ni-catalyzed enantioselective allylic alkylation of H-phosphinates. Org. Lett. 23, 8683–8687 (2021).
Dai, Q., Liu, L. & Zhang, J. Palladium/Xiao-Phos-catalyzed kinetic resolution of sec-phosphine oxides by P-benzylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 27247–27252 (2021).
Wu, Z.-H. et al. Cobalt-catalysed asymmetric addition and alkylation of secondary phosphine oxides for the synthesis of P-stereogenic compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 27241–27246 (2021).
Glueck, D. S. Applications of 31P NMR spectroscopy in development of M(Duphos)-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of P-stereogenic phosphines (M = Pt or Pd). Coord. Chem. Rev. 252, 2171–2179 (2008).
Glueck, D. S. Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of P-stereogenic phosphines: beyond precious metals. Synlett 32, 875–884 (2020).
Gibbons, S. K. et al. Diastereoselective coordination of P-stereogenic secondary phosphines in copper(I) chiral bis(phosphine) complexes: structure, dynamics, and generation of phosphido complexes. Inorg. Chem. 58, 8854–8865 (2019).
Scriban, C., Glueck, D. S., Dipasquale, A. G. & Rheingold, A. L. Chiral platinum Duphos terminal phosphido complexes: synthesis, structure, phosphido transfer, and ligand behavior. Organometallics 25, 5435–5448 (2006).
Paris, S. I., Petersen, J. L., Hey-Hawkins, E. & Jensen, M. P. Spectroscopic characterization of primary and secondary phosphine ligation on ruthenium(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 45, 5561–5567 (2006).
Nell, B. P. & Tyler, D. R. Synthesis, reactivity, and coordination chemistry of secondary phosphines. Coord. Chem. Rev. 279, 23–42 (2014).
Chang, X., Zhang, J., Peng, L. & Guo, C. Collective synthesis of acetylenic pharmaceuticals via enantioselective nickel/Lewis acid-catalyzed propargylic alkylation. Nat. Commun. 12, 299 (2021).
Peng, L., He, Z., Xu, X. & Guo, C. Cooperative Ni/Cu-catalyzed asymmetric propargylic alkylation of aldimine esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 14270–14274 (2020).
Xu, X., Peng, L., Chang, X. & Guo, C. Ni/chiral sodium carboxylate dual catalyzed asymmetric O-propargylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 21048–21055 (2021).
Cherney, A. H., Kadunce, N. T. & Reisman, S. E. Enantioselective and enantiospecific transition-metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organometallic reagents to construct C–C bonds. Chem. Rev. 115, 9587–9652 (2015).
Watanabe, K. et al. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric propargylic amination of propargylic carbonates bearing an internal alkyne group. Org. Lett. 20, 5448–5451 (2018).
Tsuji, H., Shimizu, Y., Miyazaki, Y. & Kawatsura, M. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric propargylic amination of propargylic carbonates with aniline derivatives. Chem. Lett. 50, 1002–1005 (2021).
Smith, S. W. & Fu, G. C. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric cross-couplings of racemic propargylic halides with arylzinc reagents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 12645–12647 (2008).
Bhat, V., Welin, E. R., Guo, X. & Stoltz, B. M. Advances in stereoconvergent catalysis from 2005 to 2015: transition-metal-mediated stereoablative reactions, dynamic kinetic resolutions, and dynamic kinetic asymmetric transformations. Chem. Rev. 117, 4528–4561 (2017).
Shao, X. B., Zhang, Z., Li, Q. H. & Zhao, Z. G. Synthesis of multi-substituted allenes from organoalane reagents and propargyl esters by using a nickel catalyst. Org. Biomol. Chem. 16, 4797–4806 (2018).
Li, Q. & Gau, H. Synthesis of allenes via nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of propargylic bromides with Grignard reagents. Synlett 23, 747–750 (2012).
Li, Q.-H., Liao, J.-W., Huang, Y.-L., Chiang, R.-T. & Gau, H.-M. Nickel-catalyzed substitution reactions of propargyl halides with organotitanium reagents. Org. Biomol. Chem. 12, 7634–7642 (2014).
Xu, Y., Yi, H. & Oestreich, M. Enantioconvergent and regioselective synthesis of allenylsilanes by nickel-catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) cross-coupling starting from racemic α-silylated propargylic bromides. Organometallics 40, 2194–2197 (2021).
Huo, H., Gorsline, B. J. & Fu, G. C. Catalyst-controlled doubly enantioconvergent coupling of racemic alkyl nucleophiles and electrophiles. Science 367, 559–564 (2020).
Ito, H., Kunii, S. & Sawamura, M. Direct enantio-convergent transformation of racemic substrates without racemization or symmetrization. Nat. Chem. 2, 972–976 (2010).
Imamoto, T. et al. Synthesis and reactions of optically active phosphine-boranes. Heteroatom Chem. 3, 563–575 (1992).
Cruchter, T. & Larionov, V. A. Asymmetric catalysis with octahedral stereogenic-at-metal complexes featuring chiral ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 376, 95–113 (2018).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0702001), NSFC (22071224, 21901235), USTC (KY2060000143) and USTC Research Funds of the Double First-Class Initiative (YD2060002010). The numerical calculations in this paper weere done on the supercomputing system in the Supercomputing Center of University of Science and Technology of China. Y. Shao of Lanzhou University is acknowledged for refinement of the XRD data of compounds 3a-Ir and Ni-PH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.-H.W. carried out the experimental and data-analysis work. Y.W. carried out the computational studies. H.-T.W., P.-J.Q. and W.-N.L. performed the synthesis of the substrates. Q.-W.Z. designed the reaction, directed the project and wrote the paper with feedback from all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Synthesis thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editor: Thomas West, in collaboration with the Nature Synthesis team.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Table 1, Figs, 1–8, detailed experimental data and copies of NMR spectrum and HPLC chromatography.
Supplementary Data 1
X-ray crystallographic data for compound 3a-Ir. CCDC 2079668.
Supplementary Data 2
X-ray crystallographic data for compound 3av. CCDC 2079669.
Supplementary Data 3
X-ray crystallographic data for compound Ni-PH. CCDC 2071745.
Supplementary Data 4
.xyz file of computed structures.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, WH., Wu, Y., Wang, HT. et al. Enantioselective synthesis of P-stereogenic allenylphosphines through Ni-catalysed propargylic substitution. Nat. Synth 1, 738–747 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-022-00123-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-022-00123-3