Abstract
The Caucasus region is key for understanding early human dispersal and evolution in Eurasia, and characterizing the environmental contrast between Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene is crucial for investigating human adaptation strategies to large climatic shifts. However, a paucity of high-resolution paleoclimate records leave this context largely unknown for early human populations in the Caucasus region. Based on our model-proxy comparison of high- and low-resolution records of 24 stalagmites from three caves, we find spatially distinct changes in vegetation and seasonality of precipitation, especially under glacial conditions. Supported by modern oxygen-isotope data and climate modeling, we identify a supraregional cold-season temperature control for oxygen isotopes in Black Sea speleothems, which previously had been interpreted as a local moisture-source signal. Carbon-isotope and trace-element data further suggest disproportionate changes in vegetation cover and soil dynamics at high altitudes, which would have resulted in a reduction but not a disappearance of human refugia during the Last Glacial Maximum, relative to the current interglacial. Our findings imply that abrupt climatic pressures from harsh conditions were overcome by adaptive strategies in the past.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Located at the crossroads between the Mediterranean, Europe, and Asia, the Caucasus long served as a natural passage, the so-called Trans-Caucasian corridor that facilitated hominin expansion from the Levant into the rest of Eurasia during the Pleistocene. Yet, the pressure imposed by past climate change on the expansion and development of anatomically modern humans in this region remains to be elucidated. While archaeological records provide some baseline information of past climate variability, the paucity of high-resolution paleoclimate records in the Caucasus region strongly limits our understanding of how anatomically modern human groups adapted to major climatic changes. This lack of paleoclimate reconstructions is especially critical for the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM; ~ 21,000 years ago), a time when parts of the Caucasus likely served as a refuge habitat that facilitated population and repopulation of Eurasia1,2,3,4. Identifying the nature and extent of climate and environmental change as a result of LGM cooling and warming during the following deglaciation into the Holocene is crucial for understanding historical and current human resilience in this region.
In most locations across the Caucasus region, there is a break in the archeological record during the LGM; however, several sites do suggest continued occupation5,6,7. One hypothesis to explain this pattern suggests the presence of low-altitude refugia sheltering human groups during otherwise harsh LGM climatic conditions6. It remains unclear whether discontinuities in cave occupation during the LGM reflect absence of humans in the region or site-specific formation and taphonomic processes. Elevation likely had an impact on subsistence strategies, with high-altitude locations being used less often, while lower elevation sites being occupied more densely influenced by seasonal accessibility of migratory herds. During the Late Glacial, a new industry emerged in the region5,8,9, which could imply the arrival of new groups or adaptation techniques tailored to mitigate changing environmental and climatic conditions. These developments underscore the need for a more detailed interpretive framework from paleoclimatic archives that can inform regional-scale environmental changes at different elevations, supporting our understanding of human migration in this region.
So far, the limited paleoclimate data available suggested substantial drying during the LGM10,11, accompanied by substantially lower Black Sea levels of up to −145 m11,12,13,14,15. Similar results are found in a speleothem record from northeastern Turkey, which reveals a fourfold reduction in growth rates during the LGM compared to the Holocene16, and speleothem records from Romania17 also suggesting strong regional drying at the start of the LGM followed by a growth interruption at ~ 21,000 years BP. These proxy observations are challenged by the recent PMIP4-CMIP6 model ensemble that suggests a fairly small reduction in precipitation18 in this region, especially when compared to contemporary central European climate. Here we hypothesize that the impact of LGM climate was spatially diverse in the Caucasus, with elevation being a potential factor. Thus, proxy records reflecting past precipitation from both lowland and high-altitude settings, covering the LGM and Holocene, are required to understand the full effect of climate changes on anatomically modern humans development across the wider Caucasus region. Here, we present three cave records from Abkhazia, western South Caucasus, covering the LGM to present, and compare one high- and two low-altitude multi-proxy records (δ18O, δ13C, Sr/Ca, S/Ca) to investigate the effects of LGM climate on local vegetation and habitability. We find that LGM drying was much more pronounced at the high-altitude site, compared to the lowland sites. Based on abnormally high δ18O, δ13C, and dead carbon fraction, we conclude that during the LGM, high-altitude speleothem formation proceeded largely through pyrite oxidation in the bedrock (sulfuric-acid dissolution) rather than soil-CO2 contributions to the epikarst (carbonic-acid dissolution). Also reflected in our speleothem δ18O records is a pan-regional climatic signal controlled by a mixture of cold-season temperature variability and synoptic-scale circulation dynamics, rather than a direct moisture-source control from the Black Sea itself, as previously interpreted.
Local climatic and hydrological regime
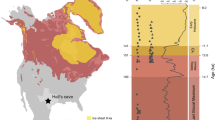
Sarma Cave is located in the Arabika karst plateau in Abkhazia, western South Caucasus, near the eastern seaboard of the Black Sea (43.39 °N, 40.37 °E, Fig. 1). With 1830 m depth, Sarma Cave is the 3rd deepest recorded cave in the world, and its main entrance is located at 2150 m above mean sea level, thus representing the high-altitude setting. The climate on the Arabika plateau is classified as humid continental mild summer, wet all year/subarctic with cool summer, wet all year (Dfb/Dfc), with dry summers and substantial winter precipitation, whereas the coastal climate is temperate oceanic climate (Cfb)19. The greater alpine region of Abkhazia is moist, maritime, subtropical and receives between 2500–3000 mm of precipitation annually, compared to ~1500 mm in the coastal zone; the mean annual air temperature is ~6 °C at Sarma Cave, compared to ~15 °C in the coastal zone (Fig. S1)20,21. Soil cover on the plateau, well above the ~1700 m tree line, is poorly developed and patchy, reflecting the harsh alpine climate conditions22. Cave air temperature stabilizes near the collection site (~200 m depth) at around 4 °C23,24. Sarma Cave receives most of its infiltration from snowmelt, although short but intense flooding events occur during summer storms. Infiltration of summer rainfall is reduced by high evaporation rates and has a smaller contribution to drip water compared to spring meltwater derived from winter snow (Fig. S1e). We thus interpret the hydrological proxy reconstructions from Sarma Cave to be indicative primarily of winter precipitation and climate variability of the Caucasus region (Figs. S1 and S2).
Map showing streamlines of the mean wind field at 200 hPa from the ERA5 dataset covering 1970 to 202266. Zoomed in map shows the locations of archeological sites as purple dots (KC (Korotkaya Cave), AK (Akhshtyrskaya Cave), A3 (Aghitu 3 Cave), SC (Satsurblia Cave), MC (Mezmaiskaya Cave), and WC (western Caucasus including: Dzudzuana, Bondi, Ortvale and Kotias Klde). Cave sites used for paleoclimate studies are shown as orange hexagons: SAR (Sarma Cave), ABR (Abrskil Cave), and NA (Novoafonskaya Cave).
To investigate the spatial paleoenvironmental changes and test how potential refugia developed over time, we add data from two well-monitored lowland caves in Abkhazia (Fig. 1): Novoafonskaya (New Athos) Cave (43.09°N 40.81°E; 220 m a.s.l.) and Abrskil (Otapskaya) Cave (42.92°N 41.55°E; 225 m a.s.l.). Reported cave air temperatures and relative humidity range from 12 to 14.5 °C and 98 to 100%25, consistent with our ongoing monitoring. Based on a survey of regional weather stations (Figs. S1), we estimate that monthly temperature is 8.5–12.5 °C warmer at the lowland sites (10.4 °C warmer annually) compared to the Sarma Cave entrance. Correcting for potential evapotranspiration (P–PET26), the winter half-year (October–March) precipitation contributes up to ~76% of infiltrating water at all three caves sites, from which we infer that cold-season precipitation and climate should similarly dominate the paleoclimatic signal in lowland sites. This conclusion is supported by δ18O measurements of dripwater in Sofular, Novoafonskaya, and Abrskil caves, whose mean values fall within 0.05‰, 0.08‰, and 0.43‰ respectively, of modeled dripwater δ18O using a P–PET correction (see Table S1 and Fig. S3, and Supplementary Discussion 2). Modeled dripwater δ18O in Sarma Cave further agrees with observed δ18O in speleothem calcite, assuming equilibrium precipitation (Fig. S1e and Table S1;26). The proxy bias toward cold-season precipitation is important, because climatic and environmental changes during the LGM winter would likely have a greater impact on human habitability of the region. While LGM changes in seasonality could result in a weakened infiltration cold-season bias, our estimates that ~76% of water infiltrates during the winter half-year is supported by a simulated LGM climatology27.
Controls on meteoric δ 18O in Abkhazia
To understand the climatic significance of temporal variations in δ18O at our cave sites, we investigated links between local monthly δ18O in precipitation (δ18OP) from the Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation/Rivers (GNIP/GNIR)28, and atmospheric data using the IsoGSM2 and National Centers for Environmental Prediction/National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCEP/NCAR) reanalysis datasets, over the common period of 1979–2016 C.E29,30. Monthly δ18OP exhibits a significant (p < 0.001) positive correlation with temperature from October to April that is strongest in March (r = 0.62), whereas any ‘temperature effect’ on warm-season δ18OP is likely obscured by terrestrial moisture recycling. Winter (December to February (DJF)) δ18OP is strongly controlled by a mid-tropospheric dipole between the study site and the northeast Atlantic Ocean (Fig. 2). This dipole broadly mimics and overlaps with the East Atlantic/West Russia pattern31, a blocking feature32 whose positive phase is characterized by positive 500 hPa geopotential height anomalies over the eastern Atlantic Ocean and negative anomalies over western Russia. Monthly temperature along the eastern Black Sea coast is strongly anticorrelated with the East Atlantic/West Russia index at both low- and high-altitude stations (Fig. S2). This observation indicates enhanced northwesterly circulation towards our cave sites during positive East Atlantic/West Russia phases, resulting in lower temperatures and negative δ18OP anomalies, while the opposite is true for enhanced southwesterly circulation.
Gridded correlation between (a) winter (DJF) and (b) summer (JJA) δ18OP at Sarma Cave and 500-hPa Geopotential height (NCEP/NCAR reanalysis30). Monthly δ18OP values are taken from the IsoGSM2 dataset29, with means plotted in Fig. S1d. Dashed and dotted lines indicate areas of 95% and 99% statistical significance, respectively. δ18OP exhibits a strong correlation with the mid-tropospheric dipole in winter, but not summer.
Thus, two cold-season temperature controls on Sarma δ18OP should be considered in paleoclimate interpretations: First, Rayleigh distillation along moisture trajectories is enhanced at lower regional temperature, resulting in lower δ18OP, and vice versa. Second, the relative contribution of moisture from the North Atlantic and Mediterranean basins, driven by the frequency of circulation modes (Fig. S2; primarily the East Atlantic/West Russia), alters δ18OP at our cave sites. Because the East Atlantic/West Russia pattern emanates from Rossby wave propagation across western Eurasia and is sensitive to upstream meridional dipoles such as the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO)31, persistent shifts in jet stream position and/or baroclinic forcing via sea surface temperatures (SST) or sea ice dynamics in the North Atlantic sector are plausibly recorded as long-term variations in Sarma Cave δ18OC.
Results
Speleothem δ 18O records from Abkhazia
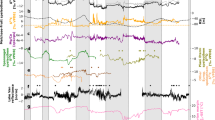
Stalagmite SAR-12-1, collected 100 m below surface in Sarma Cave, is ca. 18 cm long and consists of yellowish-brown calcite (Fig. 3b). U/Th dating reveals that the sample grew between ca. 22.4 ka BP and 3 ka BP (Fig. 3a and Table S3). A hiatus is visible in the lower section, confirmed by the U/Th dating, which separates the LGM section from the Holocene growth interval. The older part of SAR-12-1 was deposited between 22.4 and 20.9 ka BP (i.e., during the LGM), while the section above the hiatus spans a 5.5 ka long interval from Early to Late Holocene (ca. 8.5 to 3 ka BP) (Fig. 3). The U/Th dates indicate that the growth rate (ca. 25 µm/year) did not differ strongly between LGM and Holocene. In addition to the high-resolution proxy time series (δ18O, δ13C, Sr/Ca, S/Ca) from Sarma Cave, we report single-point stable isotope (δ18O and δ13C) analyses of 23 U/Th dated microcores (see “Methods” section) from Novoafonskaya and Abrskil cave stalagmites, which collectively span from 32.4 ka to 0 (Table S4).
LGM δ18O values of SAR-12-1 range from −9.6‰ to −11.8‰ (Fig. 3c), which is lower than during the Holocene, when δ18O values range between −8.0‰ and −10.8‰ and gradually increase towards a maximum value of −8‰ at ca. 3 ka BP. These trends are corroborated by Novoafonskaya and Abrskil δ18O data (Fig. 4), which range from −12.9‰ at 26 ka to −8.3‰ in the late Holocene. Holocene values between the alpine and lowland sites are unexpectedly similar, given that meteoric δ18OP at Sarma Cave should be >2‰ lower compared to Novoafonskaya and Abrskil, due to the difference in elevation (assuming a 2.15‰/km lapse rate28). Apparently, that altitudinal difference is offset by enhanced fractionation during calcite precipitation associated with the ~9 °C lower cave air temperature observed at Sarma Cave (Table S1). Modern δ18OC values in Novoafonskaya and Abrskil caves, however, are within uncertainty of equilibrium values predicted from observed dripwater δ18O and temperature33 (Fig. S3). We thus conclude that SAR-12-1 stalagmite captures a long-term δ18OP and climatic signal. Unless the local lapse rate deviates from that of the wider Western Caucasus region28, this signal was modified systematically by internal cave processes such as Prior Carbonate Precipitation (PCP) and kinetic effects known to increase δ18O fractionation between the dripwater and stalagmite carbonate34,35.
Carbon (a) and oxygen (b) isotope records of SAR (Sarma, highland), ABR, and NA caves (lowland). Gray lines indicate winter (DJF) precipitation (a) and winter (DJF) temperature (b) simulated by CESM transient model outputs. Dots show individual samples from NA and ABR caves (U/Th age and mean of duplicate isotope measurements) including 2-σ age uncertainties (black lines), whereas line plots show time series for each isotope record. The gray line in b shows the oxygen-isotope data from Sofular Cave36 (SC). c Transient simulations of δ18O in precipitation based on iTRACE62 and iCESM52 at Sarma cave. MRI-CGCM327 monthly mean change in temperature (d) and precipitation (e) between LGM and PI simulations. f MRI-CGCM3 LGM–PI anomalies in wintertime (DJF) atmospheric structure. Color shading shows the gridded difference in DJF 500-hPa geopotential height between LGM and PI simulations. Dashed and dotted lines are the same as those in Fig. 2a, outlining the modern correlation to a mid-tropospheric dipole that influences δ18OP at our cave sites.
All our Abkhazian datasets are broadly coherent with the δ18O timeseries from Sofular Cave on the southern Black Sea coast of Turkey36 (Fig. 4). However, we find several deviations among the records: For example, the sign-reversal of the isotopic offset between Sarma and Sofular speleothems during the LGM, for which Sarma speleothem δ18O is systematically higher by 1–2‰. Higher LGM values cannot feasibly be attributed to a change in moisture source, since they are not observed in Novoafonskaya and Abrskil data, which are instead similar to those at Sofular Cave. To explain this discrepancy, we consider (1) substantial changes in the LGM climatology on the Arabika Plateau, and/or (2) enhanced PCP in Sarma Cave, relative to the lowland sites. The MRI-CGCM3 simulation shows regional LGM cooling of 3.6 °C (mean annual surface air temperature; Fig. 4d), within uncertainty of the PMIP4 ensemble18. More importantly the winter (DJF) anomaly is substantially larger than for summer (June to August (JJA)), i.e., 4.8 °C vs. 1.1 °C, and is associated with a nearly 50% reduction in DJF precipitation (Fig. 4e). Such a shift in the seasonality in precipitation (along with cooler summers) would enhance the relative contribution of summer precipitation to groundwater infiltration, thereby increasing the δ18O in dripwater. The modeled reduction in DJF precipitation may also have been exacerbated at high elevation, where modern mean winter temperature is already near −5 °C21,22. To isolate the potential influence from disproportionate changes in monthly T and P between the LGM and preindustrial (PI) climatologies, we recalculated the P–PET correction used to construct the isotope climatology at Sarma Cave (Fig. S1) by referencing the monthly LGM–PI anomalies shown in Fig. 4d–e. With all other factors held constant, the effect of drier winters from LGM cooling should result in a + 0.42‰ shift in dripwater δ18O. Even if the seasonality shift were isolated to the Arabika Plateau, it could not plausibly account for the +1.5‰ anomaly in Sarma, relative to Novoafonskaya, Abrskil, and Sofular caves. Thus, we suspect PCP to play a major role and explore Sr/Ca and S/Ca ratios obtained by µ-XRF mapping in combination with δ13C to constrain the influence of PCP on speleothem δ18O in Sarma Cave, which we deem the most likely source of the observed discrepancy between low and high-altitude caves.
Local hydroclimate proxy data from Sarma Cave
Our local hydroclimate proxies, Sr/Ca and S/Ca ratios (expressed as X/Ca x 103) and carbon isotopes (δ13C), show similar trends with higher values during the LGM and lower values during the Holocene. Relatively high Sr/Ca ratios occur during the LGM that vary between 5.6 and 10.1 while Sr/Ca values are lower and more stable (between 5.5 and 8 × 103; Fig. 3c) in the Holocene. Similarly, S/Ca × 103 ratios are much higher during the LGM, with values ranging from 1.1 to 4.4 × 103, whereas values are constantly low (ca. 1.5 ×103) during the Holocene (Fig. 3c). The trace-element pattern is very similar to the δ13C record, which shows δ13C values ranging from 3.1‰ to −4.3‰ (mean around 0.6‰) during the LGM and much more stable values ranging from −3.3‰ to −5.0‰ (mean of −3.7‰) for the Holocene.
High δ13C values, mostly above 0‰, during the LGM suggest minimal or absent influence of biogenic soil CO2. Increasing δ13C with altitude can reflect sparser vegetation cover and/or soil thickness34. The soil above Sarma Cave is poorly developed today and higher speleothem δ13C values likely indicate even more thinning of the soil layer and ceased soil biological activity. Climate model simulations suggest low regional temperatures of ca. −10 to −4 °C during the LGM compared to present and decreases in precipitation making it likely that biological activity was reduced or absent during the LGM leading to high speleothem δ13C34. However, speleothem formation required low pH waters in order to dissolve carbonate host rock. Studies from caves in the Alps at similar altitudes37 suggest that pyrite oxidation in the karst produces sulfuric acid leading to carbonate dissolution. Similar observations have been made in parts of the Greater Caucasus region38, which should also apply to the Upper Jurassic limestone flysch hosting Sarma Cave. Pyrite oxidation releases sulfur which can be incorporated in the speleothem and, thus, we interpret the elevated S/Ca values (LGM relative to Holocene) as higher amounts of pyrite oxidation. Further evidence for reduced biological CO2 at our cave site is given by two radiocarbon dates, which suggest a dead carbon fraction of ~ 60% in the Holocene and 95% during the LGM (Table S3). A dead carbon fraction close to 100% during the LGM indicates that nearly all carbon incorporated in the stalagmite originated from the host rock. For the Holocene, a dead carbon fraction of ~ 60% indicates that carbonate dissolution is the result of both, pyrite oxidation and presence of organic matter, which is also corroborated by lower mean δ13C values in the Holocene39. Additionally, we find a significant positive correlation between δ18O and δ13C (r = 0.54, p-value < 0.001) and between Sr/Ca and S/Ca (r = 0.91, p-value < 0.001) in SAR-12-1 during the LGM, but not for the Holocene. We observe that temporal trends for all four proxies are similar during the LGM, in particular, between the local proxy records (δ13C, Sr/Ca, and S/Ca). However, uncertainties in sampling depth and the large discrepancy in sampling resolution preclude a meaningful calculation of statistical confidence for this apparent correlation. It should also be noted here that radiocarbon dating is applied to estimate the dead carbon fraction in SAR-12-1, the dates are not used for age determination. Using radiocarbon dating for age determination in speleothems is highly complex and can only yield useful results when the samples meet specific requirements40.
Nevertheless, these similarities suggest that one mechanism is primarily responsible for changes during the LGM in all four proxies. Sr/Ca is usually interpreted as reflecting changes in PCP, where enhanced or longer duration of PCP leads to higher Sr/Ca values and vice versa41,42,43. These PCP-induced changes in Sr/Ca can be associated with simultaneous increases in oxygen and/or carbon isotope values34,35,44, thus, can explain the speleothem proxy pattern observed in the LGM. During the Holocene, the co-variability of the proxies decreases, potentially indicating a reduction or absence of PCP during this time.
Discussion
Revisiting precipitation δ 18O as recorded by speleothems in the Caucasus/Black Sea region
Based on our model-proxy data comparison (Figs. 4b and S3), we find that Abkhazian stalagmite δ18O documents a pan-regional climate signal, governed principally by winter temperature effects and shifts in the general circulation pattern (Fig. 4). The close relationship between modeled DJF temperature and speleothem δ18O in both Sofular and our Abkahzian cave records suggest that winter temperature was a key control on δ18O variability in this region over orbital timescales. For the LGM, most δ18O records based on marine sediments from the Mediterranean and the northern Atlantic show increased values compared to the Holocene, similar to model simulations (Figs. S4 and S6). However, our δ18O records from Abkhazia exhibit the opposite trend, with lower stalagmite δ18O values during the LGM compared to the Holocene; a trend also observed at Sofular Cave36 (Fig. S6). The decline in δ18O values of Black Sea water during the LGM has been explained by the broken connection to the Mediterranean Sea via the Bosphorus sill, along with increased meltwater influx into the Black Sea and lower δ18O of riverine inputs from northern Eurasia45,46. This process led to decreased Black Sea water δ18O values45,46 and indirectly influenced the long-term δ18O trend at Sofular Cave36,47. We emphasize, however, that the Black Sea speleothem δ18O records are strongly consistent with those from central Europe17,48 and the Ural Mountains49, which encompass the Black Sea watershed and are interpreted to reflect cold-season air temperature. The combined moisture-source and temperature effects on continental precipitation over Europe are thus imprinted on speleothem δ18O in the Black Sea region, both directly via delivery of North Atlantic moisture or indirectly via evaporation from the Black Sea, which receives predominantly cold-season runoff from continental Europe. These moisture source dynamics are not yet captured in current simulations, and the model-proxy discrepancy presented here provides a key test to refine those in future.
Further, we find some evidence that the Black Sea δ18O did not ubiquitously or uniformly influence δ18OP at all four cave sites across the LGM–Holocene transition. Holocene δ18O values in SAR-12-1 are systematically more negative by ca. 1–2‰ than Sofular δ18O values. This observed offset is predicted by our modeling of dripwater at each site (Fig. S3), but the magnitude of the offset between Sarma and Sofular δ18O values increases from the Middle to the Late Holocene. By itself, a widening offset could be explained by a site-specific change in the isotopic signal at Sarma Cave or a temporal change in lapse rate. However, neither factor explains how Novoafonskaya and Abrskil δ18O values could exhibit the same Mid-Holocene offset, despite that they replicate Late and Early Holocene, as well as LGM Sofular δ18O values (Fig. 4b). These patterns suggest that instead, moisture source dynamics could have evolved differently between the southern and eastern Black Sea sites, possibly as a function of westerly circulation driven by orbital forcing. For example, an increase in the frequency of northwesterly winter air masses during the Mid-Holocene (analogous to persistent NAO- or SCAN+ conditions) would explain both enhanced rainfall over northwestern Turkey/East Mediterranean Sea47 and enhanced delivery of 18O-depleted North Atlantic-derived moisture delivered to the Western Caucasus (Fig. 4f). This interpretation is consistent with relatively low Mid-Holocene δ18O values at Kinderlinskaya Cave, Russia49. We hypothesize that the gradient between coeval δ18O series from each region provides information to constrain westerly wind dynamics over continental Eurasia. Our results provide a novel interpretation of δ18O in rainfall recorded in paleoclimate records in this region and highlight that δ18O records capture a pan-regional signal beyond changes in the oxygen-isotope composition of the Black Sea.
While all speleothem δ18O records exhibit relatively low δ18O values in the LGM, reflecting low temperatures compared to the Holocene, LGM δ18O values in the Sofular, Novoafonskaya and Abrskil records have almost no offset, as observed similarly in Late Holocene values. These similarities between lowland δ18O records during the LGM and Late Holocene, combined with LGM climate model simulations compared to PI, show that the East Atlantic/West Russia pattern likely dominated the atmospheric circulation in this region during the LGM (Fig. 4b, f). Thus, we propose that while air temperature was much lower than today during the LGM, the general circulation patterns likely resembled those of today.
Paleoclimatic context of human occupation and expansion through the Western Caucasus
A key question in human evolution relates to the mechanisms which drove the global expansion of early Homo from Africa to the subsequent population of Eurasia. The Caucasus being a fluid region of intensive human migrations and climate fluctuations over the Pleistocene is a relevant model to generate a mechanistic understanding of human dispersal patterns and strategies as well as human response to climatic shifts and resulting changes in the environment. Here, we present reconstructions of local past climate and vegetation in Abkhazian to elucidate environmental conditions during this key period of human evolution.
Supported by the trace-element record, we interpret δ13C as reflective of soil thickness, microbial activity, and vegetation cover, which collectively modulate the contribution of soil-respired CO2 to carbonate dissolution in the epikarst34. δ13C values are nearly constant from 8.5 to 3 ka BP, without any major shifts (Fig. 3c), suggesting a stable soil thickness and no large changes in vegetation cover. Precipitation reconstructions from the Southern Caucasus, based on pollen data50, suggest that annual and summer precipitation show similar trends to our δ13C record, with constant values from 9 ka BP on. Indeed, the Holocene onset in growth at Sarma Cave coincides with a major increase in annual precipitation and increased cold season temperatures recorded in the Southern Caucasus50,51. Model and proxy data52,53 further suggest that the Late Glacial was characterized by even colder temperatures than the LGM (Fig. S4). While we have no certainty about the hiatus observed in our Sarma Cave record, it may be related to freezing of the soil, preventing water from entering the cave. However, a comparison with other paleoclimate reconstructions in the wider region is difficult, because of the seasonal biases in archives54, e.g. reconstructions from lake Van are biased towards spring/summer moisture, whereas Sarma Cave primarily reflects a winter signal.
The much higher LGM δ13C values at Sarma Cave are essentially equal to that of the Jurassic bedrock, which combined with a dead carbon fraction of ~95% suggests minimal to no presence of active soils and vegetation – i.e., a carbon pool derived almost entirely from inorganic carbonate bedrock. During the LGM, the Sarma Cave record thus indicates very dry and potentially cold conditions, with negligible or absent soil cover, most likely unsuitable for plant growth, even meadows (Fig. 4a). Holocene δ13C values and radiocarbon results on the other hand, reflect atmospheric and soil-carbon contributions of ~35%, consistent with the modern meadow landscape and thin, unfrozen soils. Carbon-isotope data from Abrskil and Novoafonskaya caves do not follow this trend; instead, values are relatively low (ca. −9‰) and remain similar during the LGM and Holocene (Fig. 4a), suggesting no major changes in soil cover and vegetation over this time period. Our records thus indicate that low-altitude regions in Abkhazia were hydroclimatically and ecologically stable from LGM to Holocene and provided a favorable stable microenvironment enabling species to persist during these climatic extremes. This interpretation is also supported by modeling of summer-green tree refugia during the LGM4. A distinct characteristic of the pockets of relatively stable warm climate is the presence of Colchic and Hyrcanian forests, which provided a habitat for Tertiary relict plants and animals55,56,57. Sporadically dispersed patches of mesophilic Cenozoic plants currently observed between the Caspian and Black seas58, support our findings and suggest the existence of multiple spatially confined refugia during the LGM. Furthermore, rich zooarchaeological records of the region indicate that the onset of the LGM did not cause a major turnover in faunal diversity further supporting the refugia hypothesis. Local Upper Paleolithic sequences have many temporal and spatial gaps, reflecting a hiatus in human occupation during the LGM. Yet, both sides of the Greater Caucasus were repopulated as early as ca. 20 ka6, suggesting that anatomically modern humans likely survived these harsh climate conditions and quickly repopulated the region. Our proxy records give evidence that humans could have retreated into coastal, low-altitude refugia when climate conditions became less favorable.
Here, we compare LGM climatic conditions at the Abkhazian coast and the Arabika plateau, which are the most extreme endmembers for low and high-altitude sites. While it is unlikely that anatomically modern human groups lived in shelters directly on top of the Arabika plateau, we use our comparison to show that there is a disproportional change in LGM climate in high-altitude locations, which is not pronounced at the coastal sites. We provide insights into the effects of large-scale climate shifts on local hydrology and vegetation and highlight that migration may have had a crucial role in sheltering animal and human groups in the Caucasus region during the LGM.
Materials and methods
230Th (U/Th) dating
All 230Th dating was performed at the Isotope Laboratory of Xi’an Jiaotong University (China) using a multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (MC–ICP–MS) (Thermo-Finnigan Neptune-plus). We used standard chemistry procedures to separate uranium and thorium for dating. A triple-spike (229Th–233U–236U) isotope dilution method was employed to correct for instrumental fractionation and determine U/Th isotopic ratios and concentrations. The instrumentation, standardization, and half-lives are reported in Cheng et al. (2013)59. Uncertainties in U/Th isotopic data were calculated offline at the 2σ level, including corrections for blanks, multiplier dark noise, abundance sensitivity, and contents of the same nuclides in spike solution. Corrected 230Th ages assume an initial 230Th/232Th atomic ratio of 4.4 ± 2.2 × 10−6, the value for material at secular equilibrium with a bulk earth 232Th/238U value of 3.8.
Radiocarbon dating
Two samples (~20 mg) were drilled with a Dremel and the powder samples were leached to reduce weight by 50% with diluted HCl prior to hydrolysis, which was performed with 85% phosphoric acid. Sample preparation backgrounds have been subtracted, based on measurements of 14C-free calcite. Radiocarbon concentrations are given as fractions of the Modern standard, Δ14C, and conventional radiocarbon age, following the conventions of Stuiver and Polach (1977)60. All results have been corrected for isotopic fractionation60. Measurements were performed at the Keck Carbon Cycle Accelerator Mass Spectrometer Facility at the University of California, Irvine.
SAR-12 proxy record
Seven subsamples from SAR-12-1 were analyzed for U/Th dating. For δ18O and δ13C measurements, 288 powder samples were manually drilled every 0.1 mm to 1.0 mm and analyzed on a IsoPrime 100 mass spectrometer equipped with a Multi-Prep device at the Institute of Earth Environment of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The external analytical uncertainty of the stable isotope analysis is ca. 0.08‰ for both, δ18O and δ13C. Micro-X-ray fluorescence (μXRF) mapping with a 50 µm resolution was acquired using a Bruker M4 Tornado μXRF scanner at the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences. Element intensity records of S, Ca, and Sr (in counts per second, cps) were retrieved from the element maps and reported as Sr/Ca and S/Ca ratios from this stalagmite.
The age model for the proxy record of SAR-12-1 was calculated in COPRA, using 2000 Monte-Carlo simulations to account for age uncertainties61.
Sampling of Novoafonskaya and Abrskil caves
Preliminary fieldwork conducted in August 2019 sought to constrain the range of speleothem growth within Novoafonskaya and Abrskil caves, along with their suitability to paleoclimate reconstruction. Because both caves are highly touristic and important to the local economy, we avoided the removal of in situ stalagmites that might alter cave aesthetics. Instead, we employed a minimally invasive technique to recover 150–250 mg of calcite powder from a suite of stalagmite cores for U-Th dating and stable-isotope analysis. For sampling, a 2-mm drill bit was used to bore either vertically or horizontally toward the growth axis (when practical, top and bottom samples were taken from single stalagmites). For top samples, the outer ~1 mm of material was discarded to minimize environmental contamination; for bottom samples, material from the flank of the stalagmite was discarded to avoid mixing of layers and potential disequilibrium effects. Drill bits were also washed thoroughly between sampling to minimize cross contamination. Once the powder was collected, the 2-mm hole was plugged with clay to conceal it.
Of all stalagmites sampled, a total of 35 calcite powders from 23 individual stalagmites yielded 230Th ages from the LGM to Present and are reported here (Table S2). Three samples are excluded from this table due to exceptionally high 232Th concentrations. Several of the reported samples yielded 230Th/232Th ratios <50 (Table S4), which likely was influenced by the incorporation of cave water during sampling. Although uncertainties from detrital-Th corrections are higher than acceptable for precise age modeling, they are inconsequential to our interpretations herein.
Each calcite powder was then analyzed in duplicate for δ18O and δ13C on a Thermo-Scientific MAT-253-plus mass spectrometer coupled with an on-line carbonate preparation device (Kiel-IV) at the Isotope Laboratory, Xi’an Jiaotong University (China). Values were corrected to in-house and external standards, from which the external analytical uncertainty of δ13C and δ18O was determined to be 0.08 and 0.10‰, respectively. We report the mean and standard deviation of duplicate analyses in Table S4.
Climate model simulations and δ 18O calculation
In order to identify underlying drivers of δ18O variability in the Caucasus region we employ the output of several models and experiments. However, we do not perform any of the experiments in this study and, thus, we refer the reader to the previous studies for a full description of the experimental setups. We chose the model output based on suitability, resolution, and available variables.
Firstly, we use data produced by Timmerman et al., 2022, using the Community Earth System Model (CESM), version 1.2, which is forced by time-varying greenhouse gasses, ice sheets and insolation conditions to understand the impacts of changes in seasonal precipitation and temperature. Second, we compare our proxy data to output from two transient isotope-enabled models (iTRACE62 and iCESM52). iTRACE is a water isotope–enabled transient simulation covering the last deglaciation between 20 and 11 kyrs BP (50). iTRACE simulations are performed in iCESM1.363, which encompasses the Community Atmosphere Model version 1.3 (CAM5.3), the Parallel Ocean Program version 2 (POP2), the Los Alamos Sea Ice Model version 4 (CICE4), and the Community Land Model version 4 (CLM4). The iCESM data from Osman et al., 202152 is based on the isotope-enabled Community Earth System Model, versions 1.2 and 1.3 (iCESM1.2 and iCESM1.3), and paleoclimate data assimilation. For validation, we also show data from the Transient Climate of the Last 21,000 Years Simulation (TraCE-21ka)64 and ECBilt-CLIO65.
Data availability
All data are available in the main text, the supplementary materials or online at: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10152032. The climate model output used in this study can be accessed at: TraCE21ka: https://www.earthsystemgrid.org/project/trace.html. iTRACE: https://www.earthsystemgrid.org/dataset/ucar.cgd.ccsm4.iTRACE.html. ECBilt-CLIO: http://apdrc.soest.hawaii.edu/datadoc/ecbilt-clio-control.php. IsoGSM2: http://isotope.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~kei/tmp/isogsm2/. CESM: https://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/cesm2
Change history
26 March 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-024-01328-4
References
Bar-Yosef, O., Belfer-Cohen, A. & Adler, D. S. The implications of the Middle-Upper Paleolithic chronological boundary in the Caucasus to Eurasian prehistory. Anthropol. 44, 49–60 (2006).
Belmaker, M., Bar-Yosef, O., Belfer-Cohen, A., Meshveliani, T. & Jakeli, N. The environment in the Caucasus in the Upper Paleolithic (Late Pleistocene): evidence from the small mammals from Dzudzuana cave, Georgia. Quat. Int. 425, 4–15 (2016).
Antonosyan, M. et al. Ancient DNA shows high faunal diversity in the Lesser Caucasus during the Late Pleistocene. Quat. Sci. Rev. 219, 102–111 (2019).
Arpe, K., Leroy, S. A. G. & Mikolajewicz, U. A comparison of climate simulations for the last glacial maximum with three different versions of the ECHAM model and implications for summer-green tree refugia. Clim. Past 7, 91–114 (2011).
Meshveliani, T. et al. Mesolithic hunters at Kotias Klde, western Georgia: preliminary results. Paléorient 33, 47–58 (2007).
Golovanova, L. V., Doronicheva, E. V., Doronichev, V. B., Tselmovich, V. A. & Shirobokov, I. G. Impact of climatic stresses and volcanism on the tendencies of the cultural process in the North Caucasus during the late pleistocene. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 57, 781–802 (2021).
Doronichev, V. B. & Golovanova, L. Environment, Culture And Subsistence Of Humans In The Caucasus Between 40,000 And 10,000 Years Ago (Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2019).
Kot, M. et al. Filling the gaps: late upper palaeolithic settlement in Gvardjilas Klde, Georgia. Quat. Int. 587, 384–399 (2021).
Montoya, C. et al. The Upper Palaeolithic site of Kalavan 1 (Armenia): an epigravettian settlement in the lesser caucasus. J. Hum. Evol. 65, 621–640 (2013).
Wegwerth, A. et al. Black Sea temperature response to glacial millennial‐scale climate variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 8147–8154 (2015).
Constantinescu, A. M. et al. Evolution of the Danube deep-sea fan since the last glacial maximum: new insights into Black Sea water-level fluctuations. Mar. Geol. 367, 50–68 (2015).
Lericolais, G. et al. Assessment of Black Sea water-level fluctuations since the Last Glacial Maximum. Geol. Geoarchaeol. Black Sea Reg. Beyond Flood Hypothesis 473, 33 (2011).
Yanchilina, A. G. et al. Compilation of geophysical, geochronological, and geochemical evidence indicates a rapid Mediterranean-derived submergence of the Black Sea’s shelf and subsequent substantial salinification in the early Holocene. Mar. Geol. 383, 14–34 (2017).
Lambeck, K. & Purcell, A. Sea-level change in the Mediterranean Sea since the LGM: model predictions for tectonically stable areas. Quat. Sci. Rev. 24, 1969–1988 (2005).
Ion, G., Briceag, A., Vasiliu, D., Lupaşcu, N. & Melinte-Dobrinescu, M. A multiproxy reconstruction of the Late Pleistocene-Holocene paleoenvironment: New insights from the NW Black Sea. Mar. Geol. 443, 106648 (2022).
Rowe, P. J. et al. Speleothem isotopic evidence of winter rainfall variability in northeast Turkey between 77 and 6 ka. Quat. Sci. Rev. 45, 60–72 (2012).
Constantin, S., Bojar, A. V., Lauritzen, S.-E. & Lundberg, J. Holocene and Late Pleistocene climate in the sub-Mediterranean continental environment: a speleothem record from Poleva Cave (Southern Carpathians, Romania). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 243, 322–338 (2007).
Kageyama, M. et al. The PMIP4 Last Glacial Maximum experiments: preliminary results and comparison with the PMIP3 simulations. Clim. Past 17, 1065–1089 (2021).
Peel, M. C., Finlayson, B. L. & McMahon, T. A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 11, 1633–1644 (2007).
Gulia, V. O., Orlovskaya, T. V., Adzinba, Z. I. & Chitanava, S. M. Physical features of abkhazia (Report 1) (in Russian). Int. J. Appl. Fundam. Res. 11, 35–38 (2014).
Bondyrev, I. V., Davitashvili, Z. V. & Singh, V. P. The Geography Of Georgia: Problems And Perspectives (Springer, 2015).
Mavlyudov, B. R. & Kadebskaya, O. I. Ice Caves. 529–610 (Elsevier, 2018).
Safina, I. R., Balmochniykh, E. S., Bezkorovaynaya, I. N., and Khizhnyak, S. V. Ecology, Environment, and Human Health: XXI Century, p. 73–75. (Krasnoyarsk State Agrarian University, 2014).
Balmochniykh, E. S. & Bezkorovaynaya, I. N. Ratio of allochthonous and autochthonous microbiota in cold karst caves of the Western Caucasus: examples from Sarma and Troika caves (in Russian). in International Conference of Students, Doctoral Candidates, and Young Researchers ‘Freedom Avenue-2015’, Sib, (Siberian Federal University, 2015).
Mikhalenko, V., Kozachek, A. & Ekba, J. A. Transformation of the initial isotopic composition of precipitation in caves of the south-western Caucasus. Geogr. Environ. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 8, 4–12 (2015).
Thornthwaite, C. W. An approach toward a rational classification of Climate. Geogr. Rev. 38, 55–94 (1948).
Yukimoto, S. et al. A new global climate model of the Meteorological Research Institute: MRI-CGCM3—Model. description and basic performance—. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn Ser. II 90, 23–64 (2012).
Zakharov, E. V., Kimber, V. B., Rezvan, V. D., Tokarev, I. V. & Mavlyudov, B. R. Results of isotopic investigations in 2013–2016 on karst areas of Sochinskiy speleological region (Western Caucasus) (in Russian). Vopr. Geogr. Problems Geogr. 147, 57–87 (2018).
Yoshimura, K., Kanamitsu, M., Noone, D. & Oki, T. Historical isotope simulation using reanalysis atmospheric data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 113, D19108 (2008).
Kalnay, E. et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 77, 437–472 (1996).
Lim, Y.-K. The East Atlantic/West Russia (EA/WR) teleconnection in the North Atlantic: climate impact and relation to Rossby wave propagation. Clim. Dyn. 44, 3211–3222 (2015).
Perşoiu, A., Ionita, M. & Weiss, H. Atmospheric blocking induced by the strengthened Siberian High led to drying in west Asia during the 4.2 ka BP event–a hypothesis. Clim. Past 15, 781–793 (2019).
Tremaine, D. M., Froelich, P. N. & Wang, Y. Speleothem calcite farmed in situ: Modern calibration of δ18O and δ13C paleoclimate proxies in a continuously-monitored natural cave system. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 75, 4929–4950 (2011).
Fohlmeister, J. et al. Main controls on the stable carbon isotope composition of speleothems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 279, 67–87 (2020).
Deininger, M. et al. Are oxygen isotope fractionation factors between calcite and water derived from speleothems systematically biased due to prior calcite precipitation (PCP)? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 305, 212–227 (2021).
Fleitmann, D. et al. Timing and climatic impact of Greenland interstadials recorded in stalagmites from northern Turkey. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, (2009).
Spötl, C., Fohlmeister, J., Cheng, H. & Boch, R. Modern aragonite formation at near-freezing conditions in an alpine cave, Carnic Alps, Austria. Chem. Geol. 435, 60–70 (2016).
Chervyatsova, O. Y. et al. Sulfuric acid speleogenesis in the North Caucasus: Sharo-Argun valley Caves (Chechen Republic, Russia). Geomorphology 369, 107346 (2020).
Bajo, P. et al. Stalagmite carbon isotopes and dead carbon proportion (DCP) in a near-closed-system situation: an interplay between sulphuric and carbonic acid dissolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 210, 208–227 (2017).
Lechleitner, F. A. et al. A novel approach for construction of radiocarbon-based chronologies for speleothems. Quat. Geochronol. 35, 54–66 (2016).
Johnson, K. R., Hu, C., Belshaw, N. S. & Henderson, G. M. Seasonal trace-element and stable-isotope variations in a Chinese speleothem: The potential for high-resolution paleomonsoon reconstruction. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 244, 394–407 (2006).
Sinclair, D. J. et al. Magnesium and strontium systematics in tropical speleothems from the Western Pacific. Chem. Geol. 294, 1–17 (2012).
Wassenburg, J. A. et al. Determination of aragonite trace element distribution coefficients from speleothem calcite-aragonite transitions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 190, 347–367 (2016).
Wolf, A. et al. Deciphering local and regional hydroclimate resolves contradicting evidence on the Asian monsoon evolution. Nat. Commun. 14, 5697 (2023).
Wegwerth, A., Plessen, B., Kleinhanns, I. C. & Arz, H. W. Black Sea hydroclimate and coupled hydrology was strongly controlled by high-latitude glacial climate dynamics. Commun. Earth Environ. 2, 1–8 (2021).
Bahr, A., Arz, H. W., Lamy, F. & Wefer, G. Late glacial to Holocene paleoenvironmental evolution of the Black Sea, reconstructed with stable oxygen isotope records obtained on ostracod shells. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 241, 863–875 (2006).
Göktürk, O. M. et al. Climate on the southern Black Sea coast during the Holocene: implications from the Sofular Cave record. Quat. Sci. Rev. 30, 2433–2445 (2011).
Warken, S. F. et al. Reconstruction of late Holocene autumn/winter precipitation variability in SW Romania from a high-resolution speleothem trace element record. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 499, 122–133 (2018).
Baker, J. L., Lachniet, M. S., Chervyatsova, O., Asmerom, Y. & Polyak, V. J. Holocene warming in western continental Eurasia driven by glacial retreat and greenhouse forcing. Nat. Geosci. 10, 430–435 (2017).
Cromartie, A. et al. The vegetation, climate, and fire history of a mountain steppe: a holocene reconstruction from the South Caucasus, Shenkani, Armenia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 246, 106485 (2020).
Joannin, S. et al. Vegetation, fire and climate history of the Lesser Caucasus: a new Holocene record from Zarishat fen (Armenia). J. Quat. Sci. 29, 70–82 (2014).
Osman, M. B. et al. Globally resolved surface temperatures since the Last Glacial Maximum. Nature 599, 239–244 (2021).
Timmermann, A. et al. Climate effects on archaic human habitats and species successions. Nature 604, 495–501 (2022).
Kwiecien, O. et al. What we talk about when we talk about seasonality – a transdisciplinary review. Earth-Science Rev. 225, 103843 (2022).
Denk, T., Frotzler, N. & Davitashvili, N. Vegetational patterns and distribution of relict taxa in humid temperate forests and wetlands of Georgia (Transcaucasia). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 72, 287–332 (2001).
Ramezani, E., Mohadjer, Marvie, Knapp, M. R., Ahmadi, H.-D. & Joosten, H. H. The late-Holocene vegetation history of the Central Caspian (Hyrcanian) forests of northern Iran. The Holocene 18, 307–321 (2008).
Tarkhnishvili, D., Gavashelishvili, A. & Mumladze, L. Palaeoclimatic models help to understand current distribution of Caucasian forest species. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 105, 231–248 (2012).
Mulkidjanyan, Y. I. Relic islands of the mesothermophilic flora of the Caucasus between Colchis and Hyrkanika. Flora and vegetation of the Armenian flora. Proc. Bot. Inst. Armen. 63, 16–18 (1967).
Cheng, H. et al. Improvements in 230Th dating, 230Th and 234U half-life values, and U-Th isotopic measurements by multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 371, 82–91 (2013).
Stuiver, M. & Polach, H. A. Discussion reporting of 14C data. Radiocarbon 19, 355–363 (1977).
Breitenbach, S. F. M. et al. Constructing proxy records from age models (COPRA). Clim. Past 8, 1765–1779 (2012).
He, C. et al. Hydroclimate footprint of pan-Asian monsoon water isotope during the last deglaciation. Sci. Adv. 7, eabe2611 (2021).
Brady, E. et al. The connected isotopic water cycle in the Community Earth System Model version 1. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 11, 2547–2566 (2019).
Liu, Z. et al. Transient simulation of last deglaciation with a new mechanism for Bølling-Allerød warming. Science (80-.) 325, 310–314 (2009).
Opsteegh, J. D., Haarsma, R. J., Selten, F. M. & Kattenberg, A. ECBILT: A dynamic alternative to mixed boundary conditions in ocean models. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 50, 348–367 (1998).
Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). ERA5: Fifth generation of ECMWF atmospheric reanalyses of the global climate. Copernicus Climate Change Service Climate Data Store (CDS) (2020).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Kei Yoshimura and Jiaoyang Ruan for their help in accessing IsoGSM2 and CESM data. Russian weather-station data were accessed from http://meteo.ru (July 2022). Funding was awarded as follows: National Natural Science Foundation of China, NSFC 41888101 (J.L.B. and H.C.), NSFC 42050410316 (J.L.B. and H.C.), National Natural Science Foundation of China, 42130503 (Y.C.), and the U.S. Fulbright Scholar program (J.L.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sample collection: A.O., J.L.B., O.Y.C., Y.V.D., and R.S.D. U/Th dating: J.L.B., Y.C., and H.C. Radiocarbon dating: A.W. and K.R.J. µ-XRF: R.T. IRMS: Y.C., S.F.M.B., O.K., and J.L.B. Modeling output: J.L.B., A.W., and Y.V.D. Figures: A.W. and J.L.B. Writing: A.W., J.L.B., V.S., J.M., M.A., N.A., and S.F.M.B.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Ola Kwiecien is an Editorial Board Member for Communications Earth and Environment, but was not involved in the editorial review of, nor the decision to publish this article.
Peer review
Peer review information
Communications Earth & Environment thanks Suzanne Leroy, Ran Feng and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editor: Aliénor Lavergne. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wolf, A., Baker, J.L., Tjallingii, R. et al. Western Caucasus regional hydroclimate controlled by cold-season temperature variability since the Last Glacial Maximum. Commun Earth Environ 5, 66 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-023-01151-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-023-01151-3
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.