Abstract
To extend the Moore’s law in 5 nm node, a large number of two dimensional (2D) materials and devices have been researched, among which the ‘cold’ metals 2H MS2 (M = Nb, Ta) with unique band structures are expected to achieve the sub-60 mVdec−1 subthreshold swing (SS). We explored the electronic properties and ballistic quantum transport performance of ‘cold’ metals and the corresponding MOSFETs with idealized structures. The studied ‘cold’ metal field-effect transistors (CM-FETs) based on the ‘cold’ metals are capable to fulfill the high-performance (HP) and low-dissipation (LP) goals simultaneously, as required by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). Moreover, gaps of ‘cold’ metals CM-FETs also demonstrate negative differential resistance (NDR) property, allowing us to further extend the use of CM-FETs. Owing to the wide transmission path in the broken gap structure of NbS2/MoS2 heterojunction, the 4110 μAμm−1 peak current, several orders of magnitude higher than the typical tunneling diode, is achieved by NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET. The largest peak-valley ratio (PVR) 1.1×106 is obtained by TaS2/MoS2 CM-FET with VGS = −1 V at room temperature. Our results claim that the superior on-state current, SS, cut-off frequency and NDR effect can be obtained by CM-FETs simultaneously. The study of CM-FETs provides a practicable solution for state-of-the-art logic device in sub 5 nm node for both more Moore roadmap and more than Moore roadmap applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The Moore’s law now faces the bottleneck due to the short channel effect of Si-based metal-oxide-semiconductor field field-effect transistors (MOSFET)1,2. Considering the prospect of integrated circuits (ICs), two main technology roadmaps have been put forward by the industry field, namely more Moore roadmap and more than Moore roadmap3,4. The more Moore roadmap aims to pursue the device scaling complying with the Moore’s law3, while the more than Moore technology focuses on improving the functionality of ICs, such as combining digital electronics with devices such as radio frequency (RF), power devices and sensors4. In the more Moore field, unlike the thickness-dependent mobility of Si and Ge channels, two dimensional (2D) materials not only have atomically thin channel thickness which is beneficial for the gate control, but also maintain promising carrier mobility5,6,7,8. Previous works have proven that devices using 2D materials are capable to fulfill the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS) requirements9 even with nanometer-scale gate length10,11,12,13,14. Recently, the transistor channel length has already scaled down to 5 nm node15. How to further decrease the power consumption and sustain the Moore’s law is a task of top priority. Various novel transistors such as Fin filed-effect-transistors (FinFETs)16, fully depleted silicon on insulator (FDSOI) transistors17, tunneling FET (TFETs)18,19 and negative capacitance (NC) transistors20,21 have been put forward. Apart from novel device configurations, looking for new materials is an alternative approach to sustain the Moore’s law. Recently, cold-source FETs (CS-FETs) have been proposed to achieve sub-60 mVdec−1 subthreshold swing (SS), which can be realized by using materials with desired density of state (DOS) such as Dirac materials22, appropriately doped semiconductors23,24 and materials with gaps near the Fermi level (εF)25. Compared with the complex heterostructure of Dirac source materials or appropriately doped semiconductors, the ‘cold’ metal 2H MS2 (M = Nb, Ta) with gaps close to the εF, equivalent to a naturally p-doped or n-doped semiconductor, would be an ideal solution to fulfill the steep slope of SS25. The unique band structure allows the ‘cold’ metal MOSFET (CM-FET) to filter the transmission of high-energy carriers in the subthreshold region and reach sub-60 mVdec−1 SS22. Another cornerstone is that the ‘cold’ metal monolayer 2H NbS2 and TaS2 have been successfully synthesized26,27 and served as the injection source in the heterojunction transistors28, which solids the way for the research of ‘cold’ metal heterojunctions and transistors.
In this work, we conduct a comprehensive electronic and transport calculation of ‘cold’ metals (NbS2 and TaS2) and their devices with transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) channels. The SS of CM-FETs successfully breakthrough the 60 mVdec−1 thermionic limit at room temperature. In terms of more Moore field (to extend the Moore’s law), CM-FETs are capable to fulfill the on-state current, power consumption and cut-off frequency (fT) requirements of both ITRS high performance (HP) and low dissipation (LP) goals. Apart from the favorable performance against ITRS goals, the CM-FETs with unique band structures of ‘cold’ metals can successfully achieve the negative differential resistance (NDR) effect, which can be further exploited in multifunctional ICs. Owing to the wide transmission path in the broken gap characters of MS2/MoS2 heterojunctions, the peak current is several orders of magnitude higher than the typical tunneling diodes29,30, with the mechanism shown in Supplementary Fig. 1. The benchmarking 4110 μAμm−1 peak current and 1.1×106 peak-valley ratio (PVR) are achieved by NbS2/MoS2 and TaS2/MoS2 CM-FETs, respectively. The results demontrated that the superior Ion, SS, fT and NDR effect are obtained by our CM-FETs simultaneously, which provides a feasible method for the development of state-of-the-art logic devices beyond the Moore’s law.
Results and discussion
The performance of CM-FETs against the ITRS goals
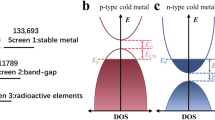
The calculated lattice constants of monolayer 2H NbS2 and TaS2 are a1 = 3.36 Å and a2 = 3.31 Å respectively, which is in agreement with previous results of lattice constants28,31. The band structures and DOS of 2H NbS2 and TaS2 are shown in Fig. 1. Energy gaps occur above (ECG) and below (EVG) the εF of ‘cold’ metals. The NbS2 and TaS2 can thus be considered as heavily p-doped or n-doped semiconductors and used as the injection source of a transistor. Considering the DOS between the εF and EVG is higher than the DOS above the εF, the ‘cold’ metal is more suitable to serve as the source electrode in a p-type transistor. Previous work presented that MX2 CM-FETs with 10 nm gate length have successfully reached the sub-60 mVdec−1 SS at room temperature25. To illustrate the mechanism of superior SS, schematic energy band diagram comparing with the p-type conventional MOSFET and CM-FET in off-state are shown in Fig. 1(c, d). In terms of the conventional p-type MOSFET in Fig. 1c, the DOS of source electrode varies inversely with the energy. In the off-state, electrons have a long thermal due to the thermal Boltzmann distribution (n(E) = D(E)f(E)), leading to the 60 mVdec−1 limit on SS. Unlike the n(E) of normal source having a long thermal tail, the thermal tail of ‘cold’ metal source below εS is filtered by the D(E) around EVG22. The current of cold metal device is calculated by the Landauer–Bűttiker formula32,
where T(E) is the transmission coefficient, fS and fD are the Fermi-Dirac distribution functions for source and drain electrodes, εS and εD are the Fermi levels of source and drain electrodes, respectively. In formula (1) the current is proportional with the DOS. The n(E) of ‘cold’ metal source, steeper than the f(E), decreases super-exponentially with the decreasing of energy, which allows the CM-FET to achieve the sub-60 mVdec−1 SS. Meanwhile, electrons localized around the εS permit a large on-state current. The schematic energy band diagrams of the CM-FET corresponding to the on-state and the off-state are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2. As the transistor channel length scales down, it is of interest to investigate whether the superior SS can be maintained in the sub-5 nm node CM-FETs.
a, b Band structures of monolayer metallic 2H MS2 (M = Nb, Ta). The green dash lines in band structures represent the Fermi level. The energy gaps in the conduction band (ECG) and valence band (EVG) are labelled. c, d The schematic DOS, carrier density (n(E)) and energy band diagrams of the (c) conventional MOSFET and (d) CM-FET. εS and εD represent the Fermi level of source and drain, respectively. ΦB is the channel barrier height. The width of arrows represents the magnitude of currents, and the number of balls represent the carrier density for transmission. The black curves in n(E) represent the Fermi-Dirac distribution.
The schematic view of MS2/TMDs CM-FET and the corresponding I-V curves are shown in Fig. 2. The source and drain electrodes are using ‘cold’ metal and p-doped TMD materials, respectively, and the heterojunction of ‘cold’metal and TMD materials is shown in Supplementary Fig. 3. The p-type doping concentration of source is 3×1013 cm−2. The gate length of CM-FET is 5 nm. The source and drain length is 1 nm. The bias voltage is 0.64 V. The gate oxide is SiO2 and the equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) is 0.41 nm based on the ITRS standards in 20139. Considering the top contact configuration in Fig. 2a is more feasible than the edge contact configuration shown in Supplementary Fig. 4, we only calculate the performance of top contact CM-FETs here. I-V curves and performance benchmark of edge contact CM-FETs are shown in Supplementary Fig. 4 and Supplementary Fig. 5, respectively. On-state current (Ion) is obtained by the corresponding on-state gate voltage (VGS(on)). The VGS(on) is defined as VGS(on) = VGS(off) + Vdd, where VGS(off) is the off-state gate voltage defined by ITRS standards in 20139. Vdd is the bias voltage applied between the source and drain electrodes, fixed at 0.64 V in our work. We observed that SS of CM-FETs significantly outperforms that of heavily p-doped TMD MOSFETs. Among these studied CM-FETs, NbS2 CM-FETs exhibit lower SS because the EVG is close to the εF, while TaS2 CM-FETs deliver larger currents owing to the wide transmission path between the EVG and εF as shown in Fig. 1b. The most favorable SS (45 mVdec−1) and Ion (2643 μAμm−1) achieved by NbS2/MoSe2 and TaS2/ MoS2 CM-FETs, respectively prove the analysis above. The CM-FET with smaller bais Vdd = 0.05 V is shown in Supplementary Fig. 6. Compared with the I-V curves of Vdd = 0.64 V, the current of Vdd = 0.05 V is obviously degraded due to the small bias voltage. The largest Ion of 53 μAμm−1 is achieved by TaS2/ MoS2 CM-FETs. The SS of CM-FET is slightly improved compared with that of Vdd = 0.64 V, with the smallest SS of 45 mVdec−1 achieved by NbS2/MoSe2 CM-FETs. The performance of CM-FET compared with IRDS 2018 requirements is summarized in Supplementary Table 133. The top contact CM-FETs with smaller SS and Ion than that of edge contact CM-FETs (data shown in Supplementary Fig. 4 and Supplementary Fig. 5) indicates that barriers of top contact devices interacted by the van der Waals force is higher than that of edge contact configurations. So, with the extreme low SS, the CMFET proposed in this work can fully sustain the more Moore roadmap in the 5 nm nodes.
To present a panoramic performance analysis of CM-FETs in 5 nm node, Ion and SS of our work compared with previous work are shown in Fig. 334,35,36,37,38,39,40,41. The Ion of CM-FETs ranges from 693 μAμm−1 to 2643 μAμm−1 and TaS2/MoS2 CM-FET with largest Ion is about three times higher than that of ITRS HP goals. The Ion performance is only inferior to the monolayer arsenene and antimonene MOSFETs (Ion of 3200 μAμm−1 and 2980 μAμm−1, respectively) and comparable with the black phosphorus (BP) MOSFET with 1994 μAμm−1 Ion. As is known, the BP is limited to the poor air-stability42. The superior Ion of arsenene and antimonene MOSFETs benefits from the ideal heavily doped source/drain electrodes34. As for SS, the performance of CM-FETs is overall superior to previous results in Fig. 3. Especially, the NbS2/MoSe2 and TaS2/MoSe2 CM-FETs even achieve the low SS of 45 and 47 mVdec−1, respectively at room temperature. In Fig. 3c we plot the power dissipation (PDP) and cut-off frequency (fT). PDP is a decisive parameter for low dissipation applications, defined as \({{{\mathrm{PDP}}}} = V_{{{{\mathrm{DS}}}}}(Q_{{{{\mathrm{on}}}}} - Q_{{{{\mathrm{off}}}}})/w\), where Qon and Qoff are the total charge of the channel in on-state and off-state, respectively. w is the channel width. The PDP values of CM-FETs vary from 0.144 to 0.197 fJum−1, obviously lower than the ITRS requirement of 0.24 fJum−1, showing a desired gate control capability. fT is a relevant factor for radio frequency devices, obtained by \(f_{{{\mathrm{T}}}} = g_{{{\mathrm{m}}}}/(2\pi C_{{{{\mathrm{total}}}}})\), where gm is the transconductance of MOSFETs, defined as \(g_{{{\mathrm{m}}}} = I_{{{{\mathrm{DS}}}}}/V_{{{{\mathrm{GS}}}}}\). Ctotal is the sum of gate capacitance CG and fringing capacitance (Cf). Based on the ITRS standard, the gate-to-source/drain overlapped parasitic capacitance and Miller effect are all included in the Cf that is assumed as twice of the CG. CG is the gate capacitance, defined as \(C_{{{\mathrm{G}}}} = \partial Q_{{{{\mathrm{ch}}}}}/\partial V_{{{{\mathrm{GS}}}}}\), where Qch is the charge in gate electrode region. fT of NbS2/MoS2 and TaS2/MoS2 in Fig. 3c reach the THz level, indicating that our CM-FETs are competent to be applied into radio frequency circuits43. Hence, the air-stability and excellent performance totally strengthen the competitive advantage of CM-FETs among these low-dimensional material MOSFETs as listed in Fig. 3.
a HP goal and (b) LP goal of MOSFETs, respectively. The other data are extracted from the arsenene34, antimonene34, BP35, Te36, GeSe37, silicane38, AsP39, Si nanowire (NW)40 and carbon nanotube (CNT)41. c The fT and PDP of CM-FETs compare with ITRS goals. The Ion of ITRS HP and LP is set to 900 μAμm−1 and 295 μAμm−1, respectively. The ITRS PDP is set as 0.24 fJμm−1.
To better understand the mechanism of extreme low (sub-60 mVdec−1) SS achieved by the CM-FETs, we take the NbS2/MoSe2 CM-FET as an example to plot the projected local density of states (PLDOS) in Fig. 4. The SS ranges from 45 mVdec−1 to 59 mVdec−1 with VGS increasing from −0.2 V to 0 V in Fig. 4a. The PLDOS in Fig. 4b and c represents the switching process of the device. At VGS = −0.2 V, the ΦB is small. Thermal emission current can directly transport through the channel region. With the increasing of VGS, ΦB and EVG are overlapped. Therefore, the current is only tunneling around the top of EVG, so the transmission efficiency, T(E), around the εS decreases rapidly compared with its counterpart in Fig. 4b.
The NDR effect of CM-FETs
The device structure and simulation methods for NDR effect is the same as the 2.1 section. Apart from the superior Ion and SS, CM-FETs are demonstrate the NDR effect, Based on the PLDOS in Fig. 4, the ‘cold’ metal source can form the type-III band alignment with the heavily p-doped MoS2. I-V curves of NbS2/MoS2 and TaS2/MoS2 CM-FETs under various VGS are shown in Fig. 5. Results claim that the NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET tends to deliver a large peak current from 1791 μAμm−1 to 4110 μAμm−1, while the large peak-valley ratio (PVR) is ready to be obtained by the TaS2/MoS2 CM-FET with the detailed values labelled in Fig. 5. The NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET has the largest peak current 4110 μAμm−1 at VGS = −2V. The largest PVR of 1.1×106 is achieved by the TaS2/MoS2 CM-FET at VGS = −1V, several orders of magnitude higher than the mainstream reports, which will be discussed later. It is noteworthy that the VGS plays an important role in controlling the peak current and peak-valley ratio (PVR). The peak current varies inversely with the VGS, while the PVR is proportional with the VGS.
a, b The I-V curves of NbS2/MoS2 and TaS2/MoS2 CM-FETs. PVR labelled in (a, b) is the ratio of the peak current and valley current. (c) Energy band diagrams under different bias voltages (VDS) at VGS = -1 V. The pink areas in (c) represent gaps of NbS2/MoS2 heterojunction. The εS and εD are the Fermi level of source and drain, respectively. The width of red arrows represents the magnitude of currents.
We plot the energy band diagrams at VGS = −1V in Fig. 5c to analyze the NDR mechanism in the NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET. The I-IV in Fig. 5c represent the energy band diagrams under various bias voltages (VDS). Notably, unlike the conventional type-III band alignment NDR device with a narrow transmission path between the broken gap44,45, the wide transmission path, as shown in Supplementary Fig. 7, allows the CM-FET to achieve a larger current, which is desirable for the extremely high PVR. Considering the εS is already tuned to the valence band maximum (VBM) of MoS2 with 0.2 V VDS, the current reaches the peak point. With the increasing of VDS, the current comes to the valley point, because the transmission is blocked by the overlapped gaps of NbS2 and MoS2. As the VDS further increases, the current starts to rise with a transmission path appearing below the VBM of MoS2. It can be concluded that the width of energy window between the εD and VBM of MoS2 is a key factor for the peak current. Considering lower VGS corresponds to a wider transmission path as shown in Supplementary Fig. 7, the peak current is inversely proportional with the VGS. In terms of the PVR, with the decreasing of VGS, a larger VDS is needed to shift the gap of MoS2 and reach valley point. The εD in valley point is even close to the VBM of NbS2, which leads to more efficient transmission through the VBM of MoS2 and a larger valley current. Hence, the PVR is proportional with the VGS.
Furthermore, to analyze the relationship between temperature and NDR effect, I-V curves of NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET with VGS = −1V at various temperature are shown in Fig. 6. The corresponding analysis of TaS2/MoS2 CM-FET is shown in Supplementary Fig. 8. Encouragingly, the NDR effect is improved with the decreasing of temperature. As temperature decreases in Fig. 6b, the peak current increases, while the valley current decreases. Consequently, the PVR(peak current) increases from 549(989 μAμm−1) to 2.3×106(1070 μAμm−1) with temperature decreasing from 300 K to 100 K. Based on Eq. (2), the current is mainly contributed by transmission between the εS and εD of device. As temperature decreases in Fig. 6f, the Fermi-Dirac distribution near the εF becomes sharp. Thus, the weight of current contributed by the transmission between εS and εD is even higher, while the weight of transmission below the εS and above the εD becomes lower. In terms of peak current in Fig. 6d, there is large T(E) around the εS. On the contrary, the T(E) of valley current between εS and εD is really flat. As a result, the valley current is proportional with the temperature and peak current varies inversely with the temperature. These results claim that the NDR performance of NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET is immune to the temperature oscillation, which enables the NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET adapt to more complex working environment.
a I-V curves of the NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET at various temperature from 100 K to 300 K. b Enlarged views of I-V curves at peak point and valley point under different temperature. Ipeak and Ivalley represent the peak current and the valley current. c The PVR as a function of temperature from 100 K to 300 K. d, e The transmission spectrum of NbS2/MoS2 MOSFET at peak point and valley point, respectively. The εS and εD are the Fermi level of NbS2 and MoS2, respectively. The magnitude of T(E) indicates the transmission efficiency of carriers. f Fermi-Dirac distribution at different temperature.
Apart from the temperature effect, PVR and peak current are regarded as two decisive factors for practical applications. The NDR performance of NbS2/MoS2 and TaS2/MoS2 CM-FETs compared with previous results is summarized in Fig. 744,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52. To deliver a fair comparison, the device width is normalized to 10μm for both our devices and data from previous reports. The PVR of NbS2/MoS2 CM-FET is only inferior to the MoS2/WSe2 and BP/Al2O3/BP heterojunction NDR devices. However, the poor air-stability of BP and the small peak current of MoS2/WSe2 NDR device hinder their practical application. Compared with previous results superior in either PVR or peak current, the NDR devices in our work are fully capable to achieve both large PVR and peak current simultaneously. Especially, the peak currents in this work are several orders of magnitude higher than previous work in Fig. 7. The large peak current not only improves the noise margin ability of NDR devices and relevant circuits, but also increases the output power and enhances the stability of oscillation circuits. With the large peak current and PVR, NbS2/MoS2 and TaS2/MoS2 CM-FETs are suitable for the MVL system and multifunctional device in more than Moore field.
In summary, we present a comprehensive electronic and transport calculation of nanoscale CM-FETs based on the ‘cold’ metal NbS2 and TaS2 heterojunctions. The Ion of CM-FETs with 5 nm channel length can achieve ITRS HP and LP goals simultaneously to further sustain the more Moore roadmap, which are rarely fulfilled in previous work because of the contradictory requirements of HP (high drain current) and LP (small SS). The dilemma is successfully solved by the superior switching performance of ‘cold’ metals and the favorable mobility of 2D TMDs. The extreme low SS of 45 and 47 mVdec−1 is obtained for NbS2/MoSe2 and TaS2/MoSe2 CM-FETs, respectively In terms of NDR effect in more than Moore field, our results claim that the large peak current and PVR can be both achieved by NbS2/MoS2 and TaS2/MoS2 CM-FETs, owing to the wide broken gap feature. We find that the peak currents and PVR can be effectively controlled by the gate voltage and immune to the temperature influence. The recording 4110 μAμm−1 peak current and 1.1×106 PVR are achieved by NbS2/MoS2 and TaS2/MoS2 CM-FETs, respectively. The results prove that ‘cold’ metal materials are competitive candidates for multifunctional logic devices and can be employed into the MVL system and radiofrequency circuits.
Methods
Calculation method
We calculated the electronic and transport properties of ‘cold’ metal MS2 and their devices with TMD channels based on density functional theory (DFT) and non-equilibrium Green function (NEGF) with Atomsitix Tool Kit 2020 package53. The exchange correlation was the Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) functional of generalized gradient approximation (GGA). All simulations are conducted with the Pseudo Dojo pseudopotential and DFT-D3 van der Waals correction54. A 80-Hartree cut-off energy was adopted. Monkhorst-Pack grids used for the transport calculation sampling the 8×1×163 k point meshes. To avoid the interaction from adjacent layers, a 30 Å vacuum was applied to the device for transport calculations. The other basic settings refer to our previous work55,56,57. In ATK platform, the transmission is calculated by the non-equilibrium Green’s function (NEGF) method. The key quantity to calculate is the retarded Green’s function matrix G(E), which can be described as58
where E is the energy. S and H are the overlap and Hamiltonian matrices, respectively. \(\sum ^S(E)\) and \(\sum ^D(E)\) are self-energy of source and drain electrodes, respectively. The transmission coeffcient T(E) at given energy E is represented by59
where G(E) and \(G^{\dagger} (E)\) are the retard and advanced Green’s functions, respectively. \(\Gamma _{S/D}(E)\) is the level broadening source/drain electrodes, defined as \(\Gamma _{S/D}(E) = i[\mathop{\sum}\limits_{S/D}(E) - \mathop{\sum}\limits_{S/D}(E)]\).
The carrier density can be included into the Poisson equation to renew the electrostatic potential through60
where φ(r) is the electrostatic potential. e is the unit charge. ε0 is the vacuum permittivity. n(r) is the valence electron density. Then the self-consistent iteration procedure is constructed between the Schrodinger and Poisson equations.
Accuracy verification
To confirm the accuracy of our simulation, We compared the simulated single gate monolayer MoS2 MOSFET with the experimental results in Supplementary Fig. 961. The detailed parameters of experimental and simulated monolayer MoS2 MOSFET are shown in Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Table 3, respectively. The simulated SS of 209 mVdec−1 is in good agreement with the experimental one of 208 mVdec−1 in the MoS2 MOSFET. Such an agreement validates the reliability of our simulations. The Poisson–Schrodinger solver is shown in Supplementary Fig. 10. To illustrate the SS improved by the 2D material MOSFETs compared with the Si-based MOSFETs, the schematic view of Si-based MOSFET, simulated I-V curves and PLDOS compared with monolayer MoS2 MOSFET are shown in Supplementary Fig. 11, Supplementary Fig. 12 and Supplementary Fig. 13, respectively. The simulated parameters are summarized in Supplementary Table 4.
Data availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Code availability
The codes that are necessary to reproduce the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Chau, R., Doyle, B., Datta, S., Kavalieros, J. & Zhang, K. Integrated nanoelectronics for the future. Nat. Mater. 6, 810–812 (2007).
Lv, Y. W., Qin, W. J., Wang, C. L., Liao, L. & Liu, X. Q. Recent advances in low‐dimensional heterojunction‐based tunnel field effect transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 5, 1800569 (2019).
Badaroglu, M. et al. In 2014 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD). 147–152 (IEEE).
Arden, W. et al. More-than-Moore White Paper. https://www.seas.upenn.edu/~ese570/spring2015/IRC-ITRS-MtM-v2%203.pdf (2010).
Akinwande, D. et al. Graphene and two-dimensional materials for silicon technology. Nature 573, 507–518 (2019).
Liu, Y. et al. Promises and prospects of two-dimensional transistors. Nature 591, 43–53 (2021).
Liu, Y., Duan, X. D., Huang, Y. & Duan, X. F. Two-dimensional transistors beyond graphene and TMDCs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 6388–6409 (2018).
Song, C. et al. Growth and interlayer engineering of 2D layered semiconductors for future electronics. ACS Nano 14, 16266–16300 (2020).
International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (2013 edition) http://www.itrs2.net/2013-itrs.html (2013).
Franklin, A. D. et al. Sub-10 nm carbon nanotube transistor. Nano Lett. 12, 758–762 (2012).
Hammam, A. M., Schmidt, M. E., Muruganathan, M., Suzuki, S. & Mizuta, H. Sub-10 nm graphene nano-ribbon tunnel field-effect transistor. Carbon 126, 588–593 (2018).
Nourbakhsh, A. et al. MoS2 field-effect transistor with sub-10 nm channel length. Nano Lett. 16, 7798–7806 (2016).
Xu, K. et al. Sub-10 nm nanopattern architecture for 2D material field-effect transistors. Nano Lett. 17, 1065–1070 (2017).
Wang, X. R. et al. Room-temperature all-semiconducting sub-10-nm graphene nanoribbon field-effect transistors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 206803 (2008).
Yeap, G. et al. In 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM). 36.37. 31-36.37. 34 (IEEE).
Hisamoto, D. et al. FinFET - A self-aligned double-gate MOSFET scalable to 20 nm. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 47, 2320–2325 (2000).
Carter, R. et al. In 2016 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM). 2.2. 1-2.2. 4 (IEEE).
Ionescu, A. M. & Riel, H. Tunnel field-effect transistors as energy-efficient electronic switches. Nature 479, 329–337 (2011).
Lu, H. & Seabaugh, A. Tunnel field-effect transistors: State-of-the-art. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2, 44–49 (2014).
Si, M. et al. Steep-slope hysteresis-free negative capacitance MoS2 transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 24 (2018).
Wang, X. W. et al. Van der Waals negative capacitance transistors. Nat. Commun. 10, 1–8 (2019).
Qiu, C. G. et al. Dirac-source field-effect transistors as energy-efficient, high-performance electronic switches. Science 361, 387–392 (2018).
Liu, F. et al. Dirac electrons at the source: breaking the 60-mV/decade switching limit. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65, 2736–2743 (2018).
Liu, F. et al. In 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM). 33.32. 31-33.32. 34 (IEEE).
Liu, F. Switching at less than 60 mv/decade with a “cold” metal as the injection source. Phys. Rev. Appl. 13, 064037 (2020).
Coleman, J. N. et al. Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science 331, 568–571 (2011).
Wu, J. J. et al. Acid-assisted exfoliation toward metallic sub-nanopore TaS2 monolayer with high volumetric capacitance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 493–498 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Edge‐epitaxial growth of 2D NbS2‐WS2 lateral metal‐semiconductor heterostructures. Adv. Mater. 30, 1803665 (2018).
Paletti, P., Yue, R., Hinkle, C., Fullerton-Shirey, S. K. & Seabaugh, A. Two-dimensional electric-double-layer Esaki diode. npj 2D Mater. Appl 3, 1–7 (2019).
Schmid, H., Bessire, C., Björk, M. T., Schenk, A. & Riel, H. Silicon nanowire Esaki diodes. Nano Lett. 12, 699–703 (2012).
Hall, J. et al. Environmental control of charge density wave order in monolayer 2H-TaS2. ACS Nano 13, 10210–10220 (2019).
Datta, S. Quantum transport: atom to transistor. (Cambridge university press, 2005).
International Roadmap for Devices and Systems (IRDS™) 2018 Edition, https://irds.ieee.org/editions/2018 (2018).
Pizzi, G. et al. Performance of arsenene and antimonene double-gate MOSFETs from first principles. Nat. Commun. 7, 12585 (2016).
Quhe, R. et al. Can a black phosphorus Schottky barrier transistor be good enough? ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 3959–3966 (2017).
Yan, J. H. et al. Excellent device performance of sub‐5‐nm monolayer tellurene transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 5, 1900226 (2019).
Guo, Y. et al. Sub-5 nm monolayer germanium selenide (GeSe) MOSFETs: towards a high performance and stable device. Nanoscale 12, 15443–15452 (2020).
Pan, Y. Y. et al. Sub-5-nm monolayer silicane transistor: a first-principles quantum transport simulation. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 024016 (2020).
Zhou, W. H. et al. Anisotropic in-plane ballistic transport in monolayer black arsenic-phosphorus FETs. Adv. Electron. Mater. 6, 201901281 (2020).
Lee, H. et al. In 2006 Symposium on VLSI Technology, 2006. Digest of Technical Papers. 58–59 (IEEE).
Qiu, C. G. et al. Scaling carbon nanotube complementary transistors to 5-nm gate lengths. Science 355, 271–276 (2017).
Zhou, Q. H., Chen, Q., Tong, Y. L. & Wang, J. L. Light‐induced ambient degradation of few‐layer black phosphorus: mechanism and protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 11437–11441 (2016).
Wang, H. et al. Black phosphorus radio-frequency transistors. Nano Lett. 14, 6424–6429 (2014).
Shim, J. et al. Phosphorene/rhenium disulfide heterojunction-based negative differential resistance device for multi-valued logic. Nat. Commun. 7, 1–8 (2016).
Roy, T. et al. Dual-gated MoS2/WSe2 van der Waals tunnel diodes and transistors. ACS Nano 9, 2071–2079 (2015).
Zhang, P. et al. Strong room-temperature negative transconductance in an axial Si/Ge hetero-nanowire tunneling field-effect transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 062106 (2014).
Yan, R. S. et al. Esaki diodes in van der Waals heterojunctions with broken-gap energy band alignment. Nano Lett. 15, 5791–5798 (2015).
Xiong, X. et al. A transverse tunnelling field-effect transistor made from a van der Waals heterostructure. Nat. Electron. 3, 106–112 (2020).
Perrin, M. L. et al. Large negative differential conductance in single-molecule break junctions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 830–834 (2014).
Lin, Y. C. et al. Atomically thin resonant tunnel diodes built from synthetic van der Waals heterostructures. Nat. Commun. 6, 1–6 (2015).
Britnell, L. et al. Resonant tunnelling and negative differential conductance in graphene transistors. Nat. Commun. 4, 1–5 (2013).
Burg, G. W. et al. Coherent interlayer tunneling and negative differential resistance with high current density in double bilayer graphene–WSe2 heterostructures. Nano Lett. 17, 3919–3925 (2017).
Smidstrup, S. et al. QuantumATK: an integrated platform of electronic and atomic-scale modelling tools. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 32, 015901 (2019).
van Setten, M. J. et al. The PseudoDojo: training and grading a 85 element optimized norm-conserving pseudopotential table. Comput. Phys. Commun. 226, 39–54 (2018).
Yin, Y. H. et al. Anisotropic transport property of antimonene MOSFETs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 22378–22386 (2020).
Yin, Y. H. et al. Tellurium nanowire gate-all-around MOSFETs for sub-5 nm applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 3387–3396 (2021).
Zhao, J. L. et al. Two-dimensional gallium oxide monolayer for gas-sensing application. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12, 5813–5820 (2021).
Brandbyge, M., Mozos, J. L., Ordejon, P., Taylor, J. & Stokbro, K. Density-functional method for nonequilibrium electron transport. Phys. Rev. B 65, 165401 (2002).
NEGF: Device Calculators, https://docs.quantumatk.com/manual/NEGFDevice.html (2015).
HartreePotential, https://docs.quantumatk.com/manual/Types/HartreePotential/HartreePotential.html#hartreepotential-hartree-and-electrostatic (2014).
Xie, L. et al. Graphene‐contacted ultrashort channel monolayer MoS2 transistors. Adv. Mater. 29, 1702522 (2017).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Wuhan University. Authors acknowledge the financial support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the funding from EPSRC grant EP/P005152/1. The numerical calculations in this work is conducted on the supercomputing system in the Supercomputing Center of Wuhan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.G. and Z.Z. conceived the project. Y.Y., S.C. and Y. G. performed the simulation. The results were analyzed and discussed by Y.Y., Z.Z., and J.R. Y.Y., Z.Z. and Y.G. wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Y., Zhang, Z., Shao, C. et al. Computational study of transition metal dichalcogenide cold source MOSFETs with sub-60 mV per decade and negative differential resistance effect. npj 2D Mater Appl 6, 55 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41699-022-00332-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41699-022-00332-6
This article is cited by
-
The rise of semi-metal electronics
Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering (2024)