Abstract
This study presents a comprehensive study of the genetic bases controlling variation in the rice ionome employing genome-wide association studies (GWAS) with a diverse panel of indica accessions, each genotyped with 5.2 million markers. GWAS was performed for twelve elements including B, Ca, Co, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, P, and Zn and four agronomic traits including days to 50% flowering, grain yield, plant height and thousand grain weight. GWAS identified 128 loci associated with the grain elements and 57 associated with the agronomic traits. There were sixteen co-localization regions containing QTL for two or more traits. Fourteen grain element quantitative trait loci were stable across growing environments, which can be strong candidates to be used in marker-assisted selection to improve the concentrations of nutritive elements in rice grain. Potential candidate genes were revealed including OsNAS3 linked to the locus that controls the variation of Zn and Co concentrations. The effects of starch synthesis and grain filling on multiple grain elements were elucidated through the likely involvement of OsSUS1 and OsGSSB1 genes. Overall, our study provides crucial insights into the genetic basis of ionomic variations in rice and will facilitate improvement in breeding for trace mineral content.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a major staple food for over half of the world’s population and is a major source of nutrition, although in the form that most consumers eat (white, polished rice), it contains only small amounts of micronutrients1. A reliance on rice in the diet, coupled with limited diversity of nutrient-rich foods can lead to malnutrition2, with an estimated two billion people suffering from Fe deficiency3 and 1.5 billion from Zn deficiency4. Fe and Zn are responsible for 2.4% and 1.9%, respectively, of the total global burden of disease5.
To combat these deficiencies, various interventions have been used by the nutrition and public health community including supplementation, fortification and in more recent years, biofortification1. Both supplementation and fortification can be expensive as they require suitable infrastructure and networks to deliver the nutrient rich product. Biofortification relies on the delivery of Fe- and Zn-dense crops via various strategies, including plant breeding and fertilizer applications6,7,8 and is considered a longer-term sustainable approach where farmers can keep back nutrient-dense seed for subsequent plantings.
Worldwide, the biofortification strategy has led to 300 biofortified varieties being approved for release, in over 40 developing countries9 and this includes Zn biofortified rice with moderate levels of Zn, indicating the need for further improvement. The development of Fe-dense rice has not been a target for conventional plant breeding due to insufficient variation for Fe within germplasm, which would not allow for sufficient genetic improvement to have a significant biological effect in humans. The strategy for breeding Fe-dense rice is through a transgenic route, with the overexpression of nicotianamine synthase genes showing significant promise in delivering Fe to deficient communities9,10.
Conventional breeding for Zn-dense rice is challenging. While sufficient variation for Zn exists in the germplasm and this allows for a breeding strategy to be undertaken, there is moderate heritability11 and therefore stability of the Zn-dense trait across environments is a major challenge. Understanding of the various environmental factors and genes impacting on the scavenging of Zn from the root rhizosphere and the short/long distance transport routes to the developing caryopsis has come a long way12,13,14 but there remain major gaps in our understanding and this confounds selection of stable parents. The introduction of stable genetic markers would be advantageous to accelerate development of Zn-dense rice.
GWAS is a powerful tool to study the molecular basis for phenotypic diversity in rice. Compared with conventional biparental population linkage mapping, GWAS has two outstanding advantages: (i) the rice varieties/accessions used in GWAS panels often contain much more genetic diversity and (ii) GWAS can take full advantage of numerous ancient recombination events resulting in higher mapping resolution15. Over the last decades, studies using GWAS platforms have successfully dissected the genetic bases of several complex traits in major crops, such as flowering time and yield-related traits16,17,18. There have also been studies investigating the genetics controlling the element accumulation in rice grain resulting in the identification of significantly associated loci and putative casual genes11,19,20,21. Examples of the identified genes include the OsHMA3 transporter gene controlling the translocation of Cd from the roots to the shoots22 and the molybdate transporter OsMOT1 gene controlling molybdenum concentration in both straw and grain23.
Many factors can affect the efficacy of GWAS such as population structure, sample size and marker density. The rice diversity panel used in this study consisted of 233 Oryza sativa subsp. indica genotypes. This panel was developed at the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Philippines for the Phenomics of Rice Adaptation and Yield potential (PRAY) project as a part of the Global Rice Phenotyping Network (http://ricephenonetwork.IR.org/diversity‐panels/pray‐diversity‐panel). The panel represented the diversity within the indica sub-species covering improved and traditional varieties across subtropical and tropical regions around the world24. Previously, this panel was used in GWAS studies for various traits including grain quality, panicle architecture, root plasticity, grain yield and yield-related traits24,25,26,27,28. This panel was initially genotyped with 700,000 SNPs29 and in the latest restatement, 5.2 million biallelic SNPs have been imputed on this panel by comparing the 700,000 SNPs with whole-genome sequence data of the 3000 sequenced rice cultivars30. The imputed high-density SNP set aimed to increase the signal strength of the marker–trait associations (MTA) and improve the mapping resolution.
In this study, we investigated the performance of twelve elements in brown rice grain of the diversity panel grown in four environments. GWAS were carried out to identify significant association loci that were stably expressed in the multiple environments. Subsequently, multiple potential causal candidate genes were identified and a genetic mechanism underlying the correlations among different trace minerals were proposed. Favourable alleles and candidate genes for improved micronutrient nutrition, especially for zinc, were identified that could be used in rice biofortification programs.
Results
Genotypic markers and population structure
The number of independent markers in the indica accessions was estimated to be 6591. Using this figure in a Bonferroni correction gave a corrected significance threshold of p < 7.59 × 10–6 (= 0.05/6591) or a − log10(p) > 5.12 for use in declaration of significant MTA.
Population structure within the panel was examined using principal component analysis. The first PC (PC1) was sufficient to discriminate indica from aus and japonica accessions (Fig. 1). PC2 and PC3 further separated indica accessions into three distinct groups. Wang et al.30 termed the three indica sub-populations IND1, IND2 and IND3 with their origins mapped broadly to China (1); Indonesia and the Philippines (2); and India and Pakistan (3). The principal component analysis identified 17 non-indica accessions in the population, consistent with allocations made by Wang et al.30. Non-indica accessions were removed from this study. The first 2 PCs were used as covariates for association analyses due to their representation of real indica sub-populations.
Population structure in PRAY Indica panel indicated by principal component analysis. Principal component analysis was performed in genotypic data in Plink, which separate different subpopulations identified by Wang, et al.30. PC1 vs PC2 (A) separates Indica accessions from Japonica; PC2 v PC3 (B) separates Indica subpopulations.
Phenotypic variation and trait heritability
The concentrations of 12 element (B, Ca, Co, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, P and Zn) of the brown rice grain from the panel and their broad-sense heritability values are presented in Table 1. The scale of ionomic variation depends on both the element and the growing environment (Table 1, Fig. 2). Amongst the 12 elements, the lowest variation in concentrations were found with the three macronutrients: K, Mg and P (coefficient variation (CV) ranging from 6 to 10%), followed by Ca, Fe, Mn and Zn (CV ranging from 12 to 19%). The largest variations were found with the five elements: B, Co, Cu, Mo and Na (CV ranging from 19 to 51%). The agronomic traits including days to 50% flowering (DF), grain yield (GY), plant height (PH) and thousand grain weight (TGW) were also included in Table 1. Amongst these traits, GY (CV ranging from 25 to 50%) varied considerably more than the other three traits: PH, DF and TGW (CV ranging from 12 to 22%).
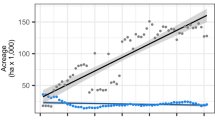
The growing environment had significant effects on all measured traits (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05) (Table 1). GY was significantly different between all four environments. The highest GY was observed at PR12, approximately 1.6-, 2.4- and 3.7-fold higher than those at PR13, IR13 and IR12, respectively. The panel grown in the wet season (IR12) had significantly taller plants and longer DF than those grown in the dry seasons.
The highest yielding environment (PR12) had the lowest concentrations of 11 elements; all except for Co. On the contrary, the third highest yielding environment (IR13) had the highest concentrations of 10 elements (all except for Mg and Zn). The grain Zn concentration had the exact reverse ranking of the GY, with the highest concentration was from IR12, followed by IR13, PR13 and PR12.
The broad-sense heritability values for all the traits ranged from 26 to 90%. High heritabilities (> 70%) were observed for the nine grain elements (Ca, Co, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, P and Zn) and the two agronomic traits (DF and PH). The three grain elements (B, Cu and Na) and GY were estimated to have low to moderate heritabilities (26–55%).
Correlations between traits and environments
Significant correlations between all four environments were observed for 10 elements (all except for B and Cu) and PH (p < 0.01, r: 0.25–0.93) (Supplementary Table S1). The group that had consistently high correlation coefficients (r > 0.5) between all environments included Ca, Mo, Mn, K and PH. For GY, significant correlations were found for the panel grown at the same site; between IR12 and IR13 (r: 0.36) and between PR12 and PR13 (r: 0.41). For DF, high correlations (r: 0.85–0.87) were found between the three dry seasons (IR13, PR12 and PR13).
Trait-wise correlation analysis within each environment reveals that the concentrations of the five elements; Zn, Fe, K, Mg, P were significantly correlated with each other in all environments (p < 0.05) (Supplementary Table S2). Of the five elements, P concentration consistently had the highest correlation coefficients with the other four elements in all environments: Zn and P (r: 0.45–0.57), Fe and P (0.41–0.59), K and P (0.60–0.74) and Mg and P (r: 0.73–0.89). These five elements also had strong correlations to the other elements including Cu (3/4 environments), Mn (3/4), Mo and Co (2/4).
Significant correlations were also observed between element concentrations and the other traits within each environment (Supplementary Table S2). Specifically, GY was negatively correlated with the grain Zn, Fe, K, Mg and P concentrations in all environments, with the Cu, Mn, Mo and Na concentrations in three and with B, Ca and Co in two environments. PH had positive correlations with the Ca, Co, K, Mg, Na, P and Zn concentrations in two or more environments and negative correlations to Cu and Mo concentrations in three environments. DF had negative correlations six elements: namely Ca, Co, Cu, Fe, Mg, P in two or more environments.
The correlations between developmental and agronomic traits differed markedly between the growing environments. GY was positively correlated to DF and PH in two seasons (PR12 and PR13) and negative correlated with PH in one (IR13). PH and DF had only one significant correlation in the wet growing season IR12 (r:0.58).
Detection of stable and environment-specific QTL
GWAS was performed separately for each environment and identified 128 QTL for grain element concentrations and 57 QTL for agronomic traits (Supplementary Tables S3 and S4).
QTL associated with grain elements
The QTL identified for grain elements were distributed on all chromosomes (Supplementary Table S3). The highest number of QTL was detected for Mo (22 QTL), followed by B, Co, Fe, K, Mn, Na and Zn (10–19 QTL, each) and Ca, Cu, Mg and P (3–5 QTL, each). Environment-wise, the highest numbers of QTL were detected for the two dry growing seasons IR13 and PR13 (45 and 43 QTL, respectively), followed by PR12 (35 QTL) and IR12 (25 QTL).
Of the grain element QTL, 14 were consistently identified in two or more environments (Table 2). There was one QTL that was common in all four environments; namely qZn7.2, three QTL stable in three environments (qCo7.1, qK6.1 and qZn7.2) and ten QTL common in two environments (qB7.1, qCa3.1, qCa12.2, qCo8.1, qFe1.2, qMo3.3, qMo8.1, qMo10.2, qNa1.2, qNa11.5). Elements having multiple stable QTL were Ca, Co, K, Mo, Na, Zn while Cu, Mg, Mn and P had no stable QTL.
The proportions of phenotypic variation explained (PVE) by these QTL ranged from 3.6 to 15.7% (Supplementary Table S3). The QTL having the largest proportion of PVE in each environment were: qB4.3, qMn9.1 and qCu1.1 (11.8%, 10.5% and 10.2%, respectively) in IR12; qB7.1, qCu4.1 and qFe7.2 (11.5%, 10.4% and 10.1%, respectively) in IR13; qCo8.1, qB2.1 and qMo8.1 (15.7%, 10.9% and 9.9%, respectively) in PR12; qCo8.1, qMg3.1 and qMo8.1 (12.4%, 10.3% and 10.1%, respectively) in PR13.
Combined effect of the QTL for grain Zn concentration
A total 13 QTL identified for Zn concentration in four environments (Fig. 3, Supplementary Table S3). The combined QTL effects explained for approximately 19.7–32.1% of the variation in Zn concentration in each environment. The highest additive effects in each environment were 7.3 mg kg−1 (qZn7.2 in IR12), 5.4 mg kg−1 (qZn6.1 in IR13), 4.0 mg kg−1 (qZn7.3 in PR12) and 4.3 mg kg−1 (qZn1.1 in PR13). In all of those cases, high Zn was associated with the minor alleles (6–8% allele frequency). Two of the QTL (qZn7.2 and qZn7.3) were stable across three and four growing environments, respectively.
Manhattan plots (left) and QQ plots (right) showing results of association analysis for zinc concentration in 2012 IRRI wet season (IRRI 12 Wet Zn), 2013 IRRI dry season (IRRI 13 Dry Zn), 2012 PhilRice dry season (PR 12 Dry Zn) and 2013 PhilRice dry season (PR 12 Dry Zn). The orange line indicates a significance threshold of − log10(p) > 5.12.
Haplotypes for the four environment Zn QTL (qZn7.2) were further examined (Fig. 4). Ten haplotypes were identified in the panel (Fig. 4). The H40 haplotype was associated with high Zn (30.5 mg kg−1). Meanwhile, the most common haplotypes in qZn7.2 was H1 associated with low Zn (21.2 mg kg−1).
Haplotype analysis of OsNAS3 (a candidate gene under four- environment Zn QTL qZn7.2, including 1.5 kb upstream from start codon. Top: boxplot of grain zinc concentration associated with each haplotype. Middle: SNP analysis of the same region for homozygous haplotypes, ordered by mean grain zinc concentration. Zero and one indicate allele status at each position. Asterisks indicate alleles found exclusively in the top four Zn haplotypes. Bottom: boxplots showing grain Zn concentration associated with each genotype for SNPs unique to high Zn haplotypes.
QTL for agronomic traits
The QTL detected for and the four agronomic traits were distributed on all chromosomes: nine for DF, seven for GY, 28 for PH and twelve for TGW (Supplementary Table S4, Supplementary Fig. S1). The PVE by these QTL ranged from 2.9 to 14.7%. The QTL that explained the largest proportions of the PVE for each agronomic trait (with corresponding additive effects) were: qDF2.2 (14.7%; 9.7 days), qGY12.2 (7.2%, 150.3 kg ha−1), qPH1.12 (12.8%; 49.3 mm), and qTGW7.4 (7.7%; 4.3 mg).
Thirteen QTLs were consistently identified in two or more environments: one for DF (qDF6.1) eight for PH (qPH1.1, qPH1.2, qPH1.4, qPH1.10, qPH1.11, qPH1.12, qPH1.13 and qPH1.14) and four for TGW (qTGW4.1, qTGW6.1, qTGW7.3 and qTGW12.1). The QTL detected for GY, in contrast were only detected in single environments: two in IR13 and five in PR13.
Co-localisation of QTL
Co-localization among QTL for different traits were detected chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 (Table 3). As expected, some highly correlated traits showed QTL that were co-located or in close proximity (within 100 kb). For examples, Zn had one common QTL with Cu on chr 1 and one with Mg on chr 3. Na and K shared a common QTL on chr 2, P and K shared one on chr 1.
All agronomic traits had co-located QTL with those of the grain elements (Table 3). DF shared a common QTL with K and Mn (chr 2). GY had co-located QTL with Mo (chr 10). TGW shared a common QTL with B, Ca, Co and Mo (chr 3). The QTL for PH were co-localized with those for Co, Cu, K, Mg, Na, P and Zn on chr 1 and 8.
The two genomic regions that harboured the highest number of QTL were on chrs 3 and 8 (Table 3). The region around 15.9–16.6 Mb on chr 3 contained QTL controlling five elements: B, Ca, Co, Mn and Mo (qB3.1, qCa3.1, qCo3.1, qMn3.1, qMo3.2) and TGW (qTGW3.2). On chr 8, the region between (19.6–20.6 Mb) had the QTL controlling the concentrations of Co, Mg, Na and PH (qCo8.2, qMg8.1, qNa8.1, qPH8.1).
Candidate genes
The physical positions of trait-associated markers were used to locate genes that were either linked to or in close proximity (within 300 kb) of the most significant SNPs. Supplementary Table S5 lists the potential candidate genes linked to the stable QTL (over three or more environments) and the major QTL clusters (on chrs 3 and 8). There were three main groups: (i) genes involved in metal transportation processes such as Zinc transporter (ZIP2), High-affinity potassium transporters (HKT1, HKT9), Nicotianamine synthase 3 (NAS3), Heavy-metal transport/detoxification, heavy-metal ATPase; (ii) genes controlling grain development such as Sucrose synthase (SUS1), Granule-bound starch synthase 1 (GBSS1), grain size (GS3) and (iii) genes controlling plant phenology such as Flowering-time locus (FLT7), Heading response regulator, senescence protein, No apical meristem protein (NAC factor).
Discussion
Phenotypic variation
The control of macro- and micro-nutrient homeostasis in plants have been extensively studied, however the loci that control natural ionomic variations in the grain are still largely undetermined in rice31,32,33. GWAS has been a powerful to dissect complex traits in plants31, however there are several factors that can limit the success of using GWAS to study the rice ionomes. These limiting factors include the relatively little variation in plant elemental concentrations and the often-substantial environmental effect34,35. In plant the transport and homeostasis of essential mineral nutrients are highly regulated processes as they require adequate levels of these essential nutrients for their growth and reproduction, while at the same time excess accumulation can also be detrimental to cell growth36.
The rice panel used in this study represents an excellent resource for genetic diversity covering a wide geographical and ecological variation in rice germplasm25,26,30. This diversity promising a large number of haplotypes is advantageous, however the effects of population structure need to be accounted for, in this case through a mixed model approach. The high density of SNPs (∼ 17 SNPs per kb on average) in our GWAS panel also facilitates high-resolution mapping with the loci were generally obtained within ∼ 100 kb, much higher than those obtained using linkage mapping approach37. This high resolution makes it possible to identify plausible candidate genes for a number of loci identified by GWAS using the information about the functional gene annotation or their orthologous genes in other plant species38,39.
The group of elements that showed relatively low levels of variation for the grain element concentrations consisted of four essential macronutrients (K, Mg, P, Ca) and four essential micronutrients (Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn) (Table 1, Fig. 2). These results indicate that the homeostasis of these elements is under relatively tight regulation. Previous research has shown that plants have evolved regulatory mechanisms to control the internal fluctuation of the essential nutrients to maintain their concentrations within narrow ranges for optimal growth, development and seed production40,41. Significantly larger variations were found for the concentration of the second group consisting of the three essential micronutrients B, Co and Mo and Na (Na is a functional but nonessential element42). It is likely that the elements in the second group were under less pressure to regulate their concentrations (unless they approach toxicity levels), thus having more relaxed control mechanisms. The differences in these control mechanisms exist not only among genotypes, they can also vary temporally and spatially within a given plant. Because this regulatory variability exists, it would appear that enhancing the micronutrient density of edible plant components through the manipulation of physiological processes is an achievable goal. The high heritability values of the nine grain elements also indicate that the contribution of genotypic variance to the total phenotypic variance was significant for these traits. Similar results were reported in previous studies11,43,44. Thus, direct selection for these elements may be a practical approach for trait improvement.
Our study shows significant variations in agronomic and grain element traits between four growing environments (Table 1). The most substantial differences were observed between the wet and the dry seasons and this might be because the wet season generally had lower temperature and higher rainfall during the period of vegetative and reproductive growth stages (Supplementary Table S6). These factors have been shown to influence flowering time in cereals45, which in turn would affect grain yield and grain nutrient levels46,47. The differences in soil chemistry, soil moisture and field management (including fertiliser application) (Supplementary Table S6) might also be the attributing factors to the variation between experimental sites.
Trait correlation and QTL clusters
All twelve element concentrations in the grain were negatively correlated with grain yield in at least two environments using the Spearman’s rank correlation method (Supplementary Table S2). Six elements including Fe, K, Mg, Na, P and Zn had negative correlations with grain yield in all four environments and the highest correlation coefficients were found with Fe, Mg and P (r: − 0.39 to − 0.52). The negative correlations between grain yield and grain element concentrations are not uncommon in rice and have been reported in past studies for K, Mg, Mn, P, and Zn11,20. This likely reflects the dilution effects of increasing grain mass on the elemental concentrations. Minimizing the effect of grain yield for genetic mapping may be a required corrective measure in determining the genetics controlling this element accumulation in the grain, which would benefit breeding for rice lines with high nutrient concentrations. In our study, despite having strong negative correlations with all elements, grain yield had only one co-located QTL with Mo concentration on chr 10 (16.8 Mb) in one environment (PR13). This suggests that selection to enhance these grain elements at the identified loci is not likely to incur a yield penalty.
PH had consistent positive correlations with Co, Ca K and Zn; negative correlations with Cu and Mo and no correlations with Fe or Mn in three or more environments. As expected, PH QTL were located with those of Co, Ca, Na and Zn on chr 1 and 8. In theory, a taller plant will have more biomass and hence is able to accumulate higher levels of minerals during vegetative growth, which then becomes a larger source for remobilization of the stored minerals from leaves when they senesce at grain filling48,49.
Strong positive correlations between Co, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, and P were observed in three or more environments. This could be explained by an overlap in mechanisms to uptake and transport these elements within the plant. There have been several studies that reported correlations between different trace minerals21,44,50 and between essential minerals and toxic elements21. Genetic mapping has also been attempted to elucidate the genetic basis underlying these correlations in rice and other cereals51,52,53. Previous studies suggested that gene pleiotropy and QTL co-localization played a role in the correlations among trace minerals21,44,51. Similarly, several correlated traits were associated with the same QTLs either in the same or in a different environment in this study (Table 3). The results confirm that there is a highly complex genetic network controlling grain nutrition levels at multiple loci19,54,55. The co-localisations of Cu–Zn (chr 1), Co–Zn (chr 7), K–P (chr 1), K–Na (chr 2), K–Mn (chr 2) QTL support the possibility of simultaneous improvement of these elements in rice grain. Fe and Zn have been targeted for biofortification for decades56,57 and it is beneficial to explore the possibility to expand to other essential nutrients.
Despite of their strong correlations, P did not share any common QTL with either Zn, Fe or Mg. Thus, the selection for increasing the element concentrations of those at the loci is not likely to increase P concentration, which is desirable in relations to Zn and/or Fe bioavailability. In mature grain, P is mainly stored as phytate (myo-inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate, InsP6), which has the ability to complex Zn and Fe forming insoluble complexes that cannot be digested or absorbed by humans58.
Two genomic regions contained the most QTL for element concentration on chrs 3 and 8 (Table 3). The region around 15.9–16.6 Mb on chr 3 harboured the QTL controlling five elements: B, Ca, Co, Mn and Mo (qB3.1, qCa3.1, qCo3.1, qMn3.1, qMo3.2) and TGW (qTGW3.1). Previous studies have also reported the association of this region with several grain element concentrations including Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, P and Zn as well as grain length, thousand grain weight, grain yield and heading date20,34,43,59. There has not been any report of the QTL controlling B, Ca or Co concentration in this genomic region to date. On chr 8, the region between 19.6 and 20.6 Mb harboured the QTL controlling the concentrations of Co, Mg, Na and PH (qCo8.2, qMg8.1, qNa8.1, and qPH8.1). This region was also found to be associated with traits including Cd, Cu and Zn concentrations in the grain, Cu and Mg concentrations in the leaf, photosynthetic ability and plant height in previous studies20,34,59,60. This is the first time that a QTL for the grain Co and Na concentrations is being reported in this region. Overall, the two genomic regions on chr 3 and 8 that were associated with multiple elements could lead to the possibility for improvement of multiple nutrients simultaneously in rice breeding. However, grain yield and other developmental traits have also been mapped to the three regions in previous studies, suggesting that selection for higher grain nutrition may incur yield penalty and should be taken into consideration.
Stable QTL
For QTLs to be highly effective within breeding programs, they must explain a significant proportion of the variation and be stable across environments and populations31. The stability of the QTL in our study was investigated over four environments. Among the QTL detected for grain elements, qZn7.2 associated with Zn concentration on chr 7 was consistent in all four environments. The QTL with consensus in three environments were qCo7.1 and qK6.1, associated with Co and K concentrations, respectively in three dry growing seasons. The two-environment QTL were found for eight traits including B, Ca, Co, Fe, K, Mo, Na and Zn concentrations. Interestingly, the four-environmental qZn7.2 and the three-environmental qCo7.1 were co-located on chr 7 (~ 29.26 Mb). The QTL accounted for approximately 5–8% and 4–6% of the variation in Zn and Co concentrations, respectively. The alleles associated with increased Zn and Co concentrations were present in less than 20% of the panel accessions indicating this was a rare allele, probably originating from an uncommon genetic pool. Not only was this QTL highly stable in our study, but it has also been identified in different genetic backgrounds. For example, significant QTL for grain Zn and Fe concentrations were reported in this genomic region on chr 7 (~ 29 Mb) in a Multi-parent Advanced Generation Intercross (MAGIC) population43 and a mapping population consisting of F6 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from the cross Madhukar × Swarna55. Thus, our results reinforce the significance of the loci in controlling grain Zn density and affirm its potential as a strong target for Zn biofortification. Other traits that have been linked to this genomic region were grain inorganic P concentration52 and heading date61 which may have to be taken into account for breeding purposes.
The three-environment QTL qK6.1 was located on the top of chr 6. This genomic region also harboured QTL for K, Cu and Zn concentrations and heading date in previous studies11,20,62. There has not been any QTL for grain yield reported in either of the genomic regions on chr 6 and 7 indicating that they are promising targets for improving Zn, Co and/or K concentration without yield penalty.
There was no stable QTL detected for grain yield or Cu, Mg, Mn and P concentrations. This is likely attributed to the large effect of the environmental conditions on the traits. For example, factors such as temperature, rainfall and/or soil chemistry could influence the bioavailability of these ions from the soil, which in turn affecting the mechanisms that plants would take for uptake, long-distance transport and remobilization34,63. Our results show significant environmental effects on the genetics controlling grain nutrient levels, which have also been reported in previous studies in wheat and rice34,64. Although consensus QTL can generally be considered as more favourable for marker-assisted selection, some QTL detected in one environment may lead to important discoveries.
Key candidate genes underlying the QTL clusters on chromosomes 3 and 8
Underlying the QTL clusters, there were key genes that control plant phenology, grain development and metal transportation (Table 4 and Supplementary Table S5). Three genes involved in the processes of starch synthesis and grain filling were linked to the QTL cluster on chr 3. These genes were SUS1 (Os03g0401300), GS3 (Os03g0407400) and GS5 (Os03g0393300). SUS1 (linked to qCo3.1) encodes a sucrose synthase (Sucrose-UDP glucosyltransferase) responsible for the biosynthesis of starch within the endosperm. Overexpression of this gene in transgenic rice lines led to increased GY (per plant) and TGW65. GS3 (linked to qCa3.2 and qTGW3.1) and GS5 (linked to qMo3.2) encode a transmembrane protein and a putative serine carboxypeptidase, respectively66,67. Natural variations in either of these genes were found to play important roles in regulating grain filling and final grain size and weight67,68,69. The results indicate a link between the processes of starch synthesis/grain filling and grain element accumulation. The transfer route of micronutrients (such as Fe and Zn) into the grain is thought to be similar to that of sucrose70,71. In transgenic wheat lines overexpressing a sucrose transporter gene, there was an increase in grain yield as well as a 20–40% increase in grain Fe and Zn concentrations78. The functionality of those genes in relation to controlling grain nutrient elements such as Ca, Co and Mo in rice, will require further studies to elucidate.
On chr 8, the gene Os08g0430500 codes for a 14-3-3 protein (Florigen receptor) involved in controlling flowering time in rice72. Flowering, grain filling and whole-plant senescence are processes that are highly important in determining grain weight, yield and quality parameters such as grain protein content (GPC) and grain micronutrient including Fe, Mn and Zn levels in cereals46,47.
Metal transporter genes were linked to the QTL clusters on both chrs 3 and 8. On chr 3, two genes, Os03g0411800 (OsZIP2) and Os03g0412300 (a heavy metal transport/detoxification) were located within the QTL for Ca concentration and TGW. On chr 8, the gene Os08g0422200 (linked to qPH8.3 and qCo8.2) codes for a Cation efflux protein, namely MTP12 (Metal tolerance protein). All of the three transporters have broad substrate transport activity (transporting Zn2+, Cd2+ Co2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Mn2+, Ni2+)73,74,75, which may explain their involvement with the transport of multiple elements under the QTL clusters. The ZIP transporter family mostly mediates metal ions influx to the cytoplasm of root cells and some members (OsZIP1, 2, 4, 5, 7, and 8) were highly induced by Zn deficiency73,76. The Cation efflux protein family is involved mainly in the compartmentation of metal ions into organelles such as vacuoles at high concentrations77. Mineral uptake and transportation in rice has been revealed being a complex process that involved the combined actions of several transporter genes78,79. The genes being identified in this study would be potential candidates for further studies to improve essential nutrients in the rice grain.
Key candidate genes underlying the stable QTL on chromosomes 6 and 7
Located within the markers flanking the four-environment QTL for Zn (qZn7.2), there was a prominent potential candidate gene OsNAS3 (Os07g0689600) coding for nicotianamine synthase 3 (Table 4). Nicotianamine synthase (NAS) is the enzyme responsible for production of nicotianamine (NA), a metal chelator for the internal transport of diverse metals, including Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn80. In rice, NA bound to Zn in phloem is supposed to avoid Zn immobilization in the alkaline conditions of the phloem sap, thus playing a vital role in intercellular and long-distance transport of Zn to maintain Zn homeostasis in plants48,81. Rice possesses three NAS genes, namely OsNAS1-382. Overexpression of each NAS gene led to significant increases of Fe and Zn levels in the rice grain83,84 implying that they can all be targets for improving Zn and Fe concentrations in rice grain. The fact that NAS3 gene was linked to the stable Zn and Co QTL implies the important roles of the phloem transport processes for Zn and possibly also for Co from vegetative tissues into the grain. The presence of SNPs specific to high Zn haplotypes within the OsNAS3 promoter43 suggests that the effect of qZn-7.2 may be achieved through modulating expression of this gene.
On chr 6, there was one gene coding for granule-bound starch synthase GBSS1 (Os06g0133000) located within the three-environment QTL qK6.1. This enzyme is involved in starch synthesis during grain filling, specifically being responsible for the synthesis of amylose and building the final structure of amylopectin85. Similar to the cases of SUS1 (on chr 3), the results here propose an important relationship between the processes of starch synthesis/grain filling and nutrient upload into the grain.
In conclusion, the rice diversity panel used in this study proved to be a useful resource for association mapping of rice grain nutrition with significant variation observed and QTL detected for all traits. Co-localizations of QTL for multiple grain element concentrations was found, and particularly those on chrs 3 and 8 open the opportunity for enhancing multi elements simultaneously. Consistent QTL across environments were identified, particularly the four-environment QTL for Zn (qZn7.2). This QTL had been reported previously, indicating its stability in different genetic backgrounds, and is a strong candidate for being used in breeding for higher Zn concentration. Multiple candidate genes were identified, which can potentially play various roles in controlling mineral accumulations in rice grain including NAS3, SUS1 and GBSS1. Further gene functionality studies would be helpful to validate the significance of the candidate genes in breeding for higher micronutrient content in rice grains.
Materials and methods
Plant material and field trial
Field trials were planted at two sites in the Philippines: (i) IRRI (14° 15′ N 121° 27′ E) during the 2012 wet season and 2013 dry season and (ii) PhilRice (15° 67′ N 120° 89′ E) during the 2012 and 2013 dry seasons. The wet season was sown in June and the dry season was in January each year. Each field trial comprised three replicates planted in a randomized complete block design. The accessions were sown at the same time and grouped by previously estimated heading date and plant height to facilitate measurements. Detailed description of the experimental design, watering and fertiliser regime, disease and weed management are included in Supplementary Table S6.
Phenotyping
At maturity, plants of from the middle two rows (excluding the border rows) were harvested to assess yield (14% moisture) and thousand grain weight (TGW) following standard procedure85. Days to flowering (DF) was assessed as the interval between the date of sowing and the date when panicles of 50% of plants per plot were fully exerted. Plant height (PH) was measured from the base of the root–shoot junction to the tip of the flag leaf, which was manually straightened to be aligned with the culm.
Grain nutrient analysis
Representative samples of about 250 g of mature grains collected from each plot were analysed for grain nutrient concentration at the Flinders Analytical Laboratory (Flinders University, Australia). The twelve grain elements being analysed included boron (B), calcium (Ca), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), sodium (Na), phosphorus (P) and zinc (Zn). Approximately 0.3 g of each grain sample (oven dried at 80 °C for 4 h) was digested with a closed tube acid digestion as described86. Grain element concentrations were determined using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS 7500x; Agilent, Santa Clara, CA) following the method described in Ref.87. A blank and a certified reference material (CRM; NIST 1567a wheat flour) were included in each digestion batch for quality assurance. The element concentrations were expressed on a dry weight basis. Contamination with soil was monitored by analysis for aluminium and titanium.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted by using R statistical software (ver. 3.6.0) and Genstat1888. The non-linear correlation between all traits was determined within each seasonal dataset using the Spearman rank correlation method as implemented in the corr.test function from the psych package89. The significance of the correlations was determined with two-sided test of the correlations against 0 at a probability of 0.05. The means of different seasons were compared using one-way ANOVA at a 0.05 level of probability. The frequency distributions of grain mineral concentrations and TGW were demonstrated using Histogram.
Genotypic data, population structure and linkage disequilibrium
Genotypic data describing 5.2 million biallelic SNPs in a rice reference panel covers 233 genotypes from the PRAY Indica panel30 and was used in this current study. The number of independent markers in the genotypic data was estimated according to the autocorrelation method described by Sobota et al.89. Briefly, genotypic data was split by chromosome and recoded to represent the number of minor alleles at each locus for each individual. An autoregressive model was fit to each individual to estimate the number of independent markers. This number was averaged for each chromosome and the final number of independent markers derived by summing all chromosomes.
Principal component analysis was conducted using PLINK 1.990 to identify population substructure and identify non-Indica individuals.
A kinship matrix was constructed using the IBS model in emmax91 to describe cryptic relatedness in the population.
GWAS
Normality of phenotypic distribution was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test implemented in R (R Core Team 2018) using a significance threshold of p < 0.05. Where possible, phenotypes found not to be normally distributed were transformed to normality using the following transformations: square root, cube root, natural log, inverse cube root, inverse square root, inverse. GWAS were performed for all transformations up to and including the first to be normally distributed.
GWAS were performed utilising a mixed linear model (MLM) in emmax, incorporating kinship plus up to two principal components to account for population structure.
In the mixed model, principal components and family kinship were included
where Y represents the vector of phenotype, X represents the vector of SNPs, Q is the PCA matrix and K is the relative kinship matrix. Xα and Qβ are the fixed effects, and Kμ and e represent random effects. The Q and K matrices help to reduce the spurious false positive associations. Correction for population structure (Q) substantially reduces the false positives but it sometimes eliminates true positive associations due to overcorrection. Therefore, the optimal number of principal components was estimated for each trait before incorporating them for MLM tests, based on the forward model selection method using the Bayesian information criterion. This method helps to control both false-positive and -negative associations more effectively although it cannot eliminate both completely.
The lambda genomic inflation factor was determined for each association analysis using the regression method of the estlambda function from the GenABEL R package92. In comparing multiple association models applied to a single trait, an inflation factor closest to one signified the best analysis.
A significance threshold α = 0.05 was used for association mapping, but was adjusted using the Bonferroni approach considering the estimated number of independent markers:
where α is the unadjusted significance threshold and n is the number of independent markers in the population.
Quantitative trait loci (QTLs), regions containing SNPs associated with phenotypes, were defined as described by McCouch et al.29. A QTL was defined as any region containing one SNP with − log10(p) > − log10 (αadj) flanked by markers with − log10 (p) > 4 on each side and within 100 kb.
Candidate gene and haplotype analysis
The physical locations of SNPs were identified based on the Rice Annotation version of 7.0 of variety Nipponbare from Michigan State University. Considering that the LD decay distance in XI accessions is about 100 kb93, significant SNPs located to a region of less than 100 kb were treated as one locus. The annotations of genes located within LD blocks were obtained from the Os-Nipponbare-Reference-IRGSP-1.0 rice genome database (https://rapdb.dna.affrc.go.jp/download/irgsp1.html).
Haplotype analysis of candidate genes plus 1.5 kb upstream was performed in R using the imputed SNP dataset.
Trait heritability
Trait heritability and genotype × environment interactions were investigated using additive main effects and multiplicative interactions (AMMI) model in GenStat88. The computed variance components were used to estimate broad-sense heritability across the four environments tested using the formula described by Velu et al.94:
where H2 is the broad-sense heritability, σg2 is the genotypic variance, σge2 is the genotype × environment variance, and σe2 is the residual error variance for r replicates and l locations.
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that the experimental research and field studies on plants in this study including the collection of plant material comply with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation.
Abbreviations
- AM:
-
Association mapping
- B:
-
Boron
- Ca:
-
Calcium
- Chr:
-
Chromosome
- Co:
-
Cobalt
- Cu:
-
Copper
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- DF:
-
Days to 50% flowering
- Fe:
-
Iron
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association study
- GY:
-
Grain yield
- ICP-MS:
-
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
- IRRI:
-
International Rice Research Institute
- K:
-
Potassium
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- Mg:
-
Magnesium
- MLM:
-
Mixed-linear model
- Mn:
-
Manganese
- Mo:
-
Molybdenum
- MTA:
-
Marker-trait association
- Na:
-
Sodium
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PH:
-
Plant height
- PRAY:
-
Phenomics of rice adaptation and yield
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- TGW:
-
Thousand grain weight
- Zn:
-
Zinc
References
Bouis, H. E. & Welch, R. M. Biofortification-a sustainable agricultural strategy for reducing micronutrient malnutrition in the Global South. Crop Sci. 50, S-20-S-32. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2009.09.0531 (2010).
White, P. J. & Broadley, M. R. Biofortification of crops with seven mineral elements often lacking in human diets—iron, zinc, copper, calcium, magnesium, selenium and iodine. New Phytol. 182, 49–84 (2009).
Zimmermann, M. B. & Hurrell, R. F. Nutritional iron deficiency. Lancet 370, 511–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61235-5 (2007).
Smith, M. R. & Myers, S. S. Impact of anthropogenic CO2 emissions on global human nutrition. Nat. Clim. Change 8, 834–839. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-018-0253-3 (2018).
Rodgers, A. et al. Distribution of major health risks: findings from the global burden of disease study. PLoS Med. 1, e27. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0010027 (2004).
Cakmak, I. & Kutman, U. Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: A review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 69, 172–180 (2018).
Welch, R. M. & Graham, R. D. Breeding for micronutrients in staple food crops from a human nutrition perspective. J. Exp. Bot. 55, 353–364. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh064 (2004).
Zhang, G.-M. et al. Joint exploration of favorable haplotypes for mineral concentrations in milled grains of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00447 (2018).
Van Der Straeten, D. et al. Multiplying the efficiency and impact of biofortification through metabolic engineering. Nat. Commun. 11, 1–10 (2020).
Trijatmiko, K. R. et al. Biofortified indica rice attains iron and zinc nutrition dietary targets in the field. Sci. Rep. 6, 19792. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19792 (2016).
Descalsota-Empleo, G. I. et al. Genetic mapping of QTL for agronomic traits and grain mineral elements in rice. Crop J. 7, 560–572 (2019).
Clemens, S. et al. A transporter in the endoplasmic reticulum of Schizosaccharomyces pombe cells mediates zinc storage and differentially affects transition metal tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 18215–18221. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M201031200 (2002).
Palmgren, M. G. et al. Zinc biofortification of cereals: Problems and solutions. Trends Plant Sci. 13, 464–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.06.005 (2008).
White, P. J. & Broadley, M. R. Physiological limits to zinc biofortification of edible crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2, 80 (2011).
Wang, Q., Tang, J., Han, B. & Huang, X. Advances in genome-wide association studies of complex traits in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 133, 1415–1425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03473-3 (2020).
Begum, H. et al. Genome-wide association mapping for yield and other agronomic traits in an elite breeding population of tropical rice (Oryza sativa). PLoS One 10, e0119873 (2015).
Huang, X. et al. Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat. Genet. 44, 32 (2012).
Kadam, N. N., Struik, P. C., Rebolledo, M. C., Yin, X. & Jagadish, S. K. Genome-wide association reveals novel genomic loci controlling rice grain yield and its component traits under water-deficit stress during the reproductive stage. J. Exp. Bot. 69, 4017–4032 (2018).
Bollinedi, H. et al. Genome-wide association study reveals novel marker-trait associations (MTAs) governing the localization of Fe and Zn in the rice grain. Front. Genet. 11, 213 (2020).
Norton, G. J. et al. Genetic mapping of the rice ionome in leaves and grain: Identification of QTLs for 17 elements including arsenic, cadmium, iron and selenium. Plant Soil 329, 139–153 (2010).
Zhang, M. et al. Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci associated with concentrations of 16 elements in unmilled rice grain. Theor. Appl. Genet. 127, 137–165 (2014).
Ueno, D. et al. Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 16500–16505 (2010).
Wang, C. et al. Genetic mapping of ionomic quantitative trait loci in rice grain and straw reveals OsMOT1; 1 as the putative causal gene for a molybdenum QTL qMo8. Mol. Genet. Genom. 295, 391–407 (2020).
Rebolledo, M. C. et al. Combining image analysis, genome wide association studies and different field trials to reveal stable genetic regions related to panicle architecture and the number of spikelets per panicle in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 7, 1384 (2016).
Kadam, N. N. et al. Genetic control of plasticity in root morphology and anatomy of rice in response to water deficit. Plant Physiol. 174, 2302–2315 (2017).
Kikuchi, S. et al. Genome-wide association mapping for phenotypic plasticity in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 40, 1565–1575 (2017).
Melandri, G. et al. Association mapping and genetic dissection of drought-induced canopy temperature differences in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 71, 1614–1627 (2020).
Qiu, X. et al. Genome-wide association study of grain appearance and milling quality in a worldwide collection of indica rice germplasm. PLoS One 10, e0145577 (2015).
McCouch, S. R. et al. Open access resources for genome-wide association mapping in rice. Nat. Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10532 (2016).
Wang, D. R. et al. An imputation platform to enhance integration of rice genetic resources. Nat. Commun. 9, 3519. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05538-1 (2018).
Collard, B. C., Jahufer, M., Brouwer, J. & Pang, E. An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142, 169–196 (2005).
Grotz, N. & Guerinot, M. L. Molecular aspects of Cu, Fe and Zn homeostasis in plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1763, 595–608 (2006).
Kawakami, Y. & Bhullar, N. K. Molecular processes in iron and zinc homeostasis and their modulation for biofortification in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 60, 1181–1198 (2018).
Norton, G. J. et al. Genome wide association mapping of grain arsenic, copper, molybdenum and zinc in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown at four international field sites. PLoS One 9, e89685 (2014).
Wang, P., Yamaji, N., Inoue, K., Mochida, K. & Ma, J. F. Plastic transport systems of rice for mineral elements in response to diverse soil environmental changes. New Phytol. 226, 156–169 (2020).
Grusak, M. A., Pearson, J. N. & Marentes, E. The physiology of micronutrient homeostasis in field crops. Field Crop Res. 60, 41–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(98)00132-4 (1999).
Si, L. et al. OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice. Nat. Genet. 48, 447–456 (2016).
Huang, X. & Han, B. Natural variations and genome-wide association studies in crop plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 65, 531–551 (2014).
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project & Sasaki, T. The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436, 793–800. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03895 (2005).
Castro, P. H., Lilay, G. H. & Assunção, A. G. L. Chapter 1 - Regulation of micronutrient homeostasis and deficiency response in plants. In Plant Micronutrient Use Efficiency (eds Mohammad, A. H. et al.) 1–15 (Academic Press, 2018).
Walker, E. L. & Waters, B. M. The role of transition metal homeostasis in plant seed development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 14, 318–324 (2011).
Subbarao, G., Ito, O., Berry, W. & Wheeler, R. Sodium—A functional plant nutrient. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 22, 391–416 (2003).
Descalsota, G. I. L. et al. Genome-wide association mapping in a rice MAGIC plus population detects QTLs and genes useful for biofortification. Front. Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01347 (2018).
Nawaz, Z. et al. Genome-wide association mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for contents of eight elements in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 63, 8008–8016 (2015).
Distelfeld, A., Li, C. & Dubcovsky, J. Regulation of flowering in temperate cereals. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12, 178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2008.12.010 (2009).
Distelfeld, A., Avni, R. & Fischer, A. M. Senescence, nutrient remobilization, and yield in wheat and barley. J. Exp. Bot. 65, 3783–3798 (2014).
Uauy, C., Distelfeld, A., Fahima, T., Blechl, A. & Dubcovsky, J. A NAC gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc, and iron content in wheat. Science 314, 1298–1301 (2006).
Nishiyama, R., Tanoi, K., Yanagisawa, S. & Yoneyama, T. Quantification of zinc transport via the phloem to the grain in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.) at early grain-filling by a combination of mathematical modeling and 65Zn tracing. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 59, 750–755. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2013.819774 (2013).
Sperotto, R. A. Zn/Fe remobilization from vegetative tissues to rice seeds: Should I stay or should I go? Ask Zn/Fe supply!. Front. Plant Sci. 4, 464 (2013).
Yu, Y.-H. et al. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for contents of macro-and microelements in milled rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 63, 7813–7818 (2015).
Cu, S. T. et al. Genetic dissection of zinc, iron, copper, manganese and phosphorus in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain and rachis at two developmental stages. Plant Sci. 291, 110338 (2020).
Stangoulis, J. C. R., Huynh, B.-L., Welch, R. M., Choi, E.-Y. & Graham, R. D. Quantitative trait loci for phytate in rice grain and their relationship with grain micronutrient content. Euphytica 154, 289–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9211-7 (2007).
Wu, D. et al. High-resolution genome-wide association study pinpoints metal transporter and chelator genes involved in the genetic control of element levels in maize grain. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 11, jkab059 (2021).
Agarwal, S., Tripura Venkata, V. G. N., Kotla, A., Mangrauthia, S. K. & Neelamraju, S. Expression patterns of QTL based and other candidate genes in Madhukar×Swarna RILs with contrasting levels of iron and zinc in unpolished rice grains. Gene 546, 430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.05.069 (2014).
Anuradha, K. et al. Mapping QTLs and candidate genes for iron and zinc concentration in unpolished rice of Madhukar × Swarna RILs. Gene 508, 233–240 (2012).
Connorton, J. M. & Balk, J. Iron biofortification of staple crops: Lessons and challenges in plant genetics. Plant Cell Physiol. 60, 1447–1456 (2019).
Nakandalage, N. et al. Improving rice zinc biofortification success rates through genetic and crop management approaches in a changing environment. Front. Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00764 (2016).
Gibson, R. S., Raboy, V. & King, J. C. Implications of phytate in plant-based foods for iron and zinc bioavailability, setting dietary requirements, and formulating programs and policies. Nutr. Rev. 76, 793–804 (2018).
Tan, Y., Zhou, J., Wang, J. & Sun, L. The genetic architecture for phenotypic plasticity of the rice grain ionome. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 12 (2020).
Thomson, M. et al. Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor. Appl. Genet. 107, 479–493 (2003).
Ishimaru, K. et al. Toward the mapping of physiological and agronomic characters on a rice function map: QTL analysis and comparison between QTLs and expressed sequence tags. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102, 793–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220000467 (2001).
Wang, Y. et al. Identify QTLs and candidate genes underlying source-, sink-, and grain yield-related traits in rice by integrated analysis of bi-parental and natural populations. PLoS One 15, e0237774 (2020).
Norton, G. J. et al. Genetic loci regulating arsenic content in rice grains when grown flooded or under alternative wetting and drying irrigation. Rice 12, 54 (2019).
Alomari, D. Z. et al. Identifying candidate genes for enhancing grain Zn concentration in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 1313 (2018).
Fan, C. et al. Sucrose synthase enhances hull size and grain weight by regulating cell division and starch accumulation in transgenic rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 4971 (2019).
Fan, C. et al. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor. Appl. Genet. 112, 1164–1171 (2006).
Li, Y. et al. Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Genet. 43, 1266–1269 (2011).
Mao, H. et al. Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 19579–19584 (2010).
Xu, C. et al. Differential expression of GS5 regulates grain size in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 66, 2611–2623 (2015).
Pearson, J., Rengel, Z., Jenner, C. F. & Graham, R. D. Transport of zinc and manganese to developing wheat grains. Physiol. Plant. 95, 449–455 (1995).
Saalbach, I. et al. Increased grain yield and micronutrient concentration in transgenic winter wheat by ectopic expression of a barley sucrose transporter. J. Cereal Sci. 60, 75–81 (2014).
Taoka, K.-I. et al. 14-3-3 proteins act as intracellular receptors for rice Hd3a florigen. Nature 476, 332–335 (2011).
Guerinot, M. L. The ZIP family of metal transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 1465, 190–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2736(00)00138-3 (2000).
Ricachenevsky, F. K., Menguer, P. K., Sperotto, R. A., Williams, L. E. & Fett, J. P. Roles of plant metal tolerance proteins (MTP) in metal storage and potential use in biofortification strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 4, 144 (2013).
Gustin, J. L., Zanis, M. J. & Salt, D. E. Structure and evolution of the plant cation diffusion facilitator family of ion transporters. BMC Evol. Biol. 11, 1–13 (2011).
Tiong, J. et al. Increased expression of six ZIP family genes by zinc (Zn) deficiency is associated with enhanced uptake and root-to-shoot translocation of Zn in barley (Hordeum vulgare). New Phytol. 207, 1097–1109 (2015).
Ricachenevsky, F., Menguer, P., Sperotto, R., Williams, L. & Fett, J. Roles of plant metal tolerance proteins (MTP) in metal storage and potential use in biofortification strategies. Front. Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00144 (2013).
Sasaki, A., Yamaji, N. & Ma, J. F. Transporters involved in mineral nutrient uptake in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 67, 3645–3653 (2016).
Waters, B. M. & Sankaran, R. P. Moving micronutrients from the soil to the seeds: genes and physiological processes from a biofortification perspective. Plant Sci. 180, 562–574 (2011).
Takahashi, M. et al. Role of nicotianamine in the intracellular delivery of metals and plant reproductive development. Plant Cell 15, 1263–1280 (2003).
Nishiyama, R., Kato, M., Nagata, S., Yanagisawa, S. & Yoneyama, T. Identification of Zn–Nicotianamine and Fe–2′-Deoxymugineic Acid in the phloem sap from rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 53, 381–390. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcr188 (2012).
Inoue, H. et al. Identification and localisation of the rice nicotianamine aminotransferase gene OsNAAT1 expression suggests the site of phytosiderophore synthesis in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 66, 193–203 (2008).
Johnson, A. A. et al. Constitutive overexpression of the OsNAS gene family reveals single-gene strategies for effective iron-and zinc-biofortification of rice endosperm. PLoS One 6, e24476 (2011).
Nozoye, T. The Nicotianamine synthase gene is a useful candidate for improving the nutritional qualities and Fe-deficiency tolerance of various crops. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 340. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00340 (2018).
Hanashiro, I. et al. Granule-bound starch synthase I is responsible for biosynthesis of extra-long unit chains of amylopectin in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 49, 925–933 (2008).
Wheal, M. S., Fowles, T. O. & Palmer, L. T. A cost-effective acid digestion method using closed polypropylene tubes for inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis of plant essential elements. Anal. Methods 3, 2854–2863. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1AY05430A (2011).
Palmer, L. & Stangoulis, J. Changes in the elemental and metabolite profile of wheat phloem sap during grain filling indicate a dynamic between plant maturity and time of day. Metabolites 8, 53 (2018).
VSN International. Genstat for Windows, 18th ed. (VSN International, 2015).
Sobota, R. S. et al. Addressing population-specific multiple testing burdens in genetic association studies. Ann. Hum. Genet. 79, 136–147 (2015).
Chang, C. C. et al. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13742-015-0047-8 (2015).
Kang, H. M. et al. Variance component model to account for sample structure in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 42, 348 (2010).
Aulchenko, Y. S., Ripke, S., Isaacs, A. & van Duijn, C. M. GenABEL: An R library for genome-wide association analysis. Bioinformatics 23, 1294–1296. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm108 (2007).
Zhou, H. et al. Genome-wide association analyses reveal the genetic basis of stigma exsertion in rice. Mol. Plant 10, 634–644 (2017).
Velu, G. et al. Genetic dissection of grain zinc concentration in spring wheat for mainstreaming biofortification in CIMMYT wheat breeding. Sci. Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31951-z (2018).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the field teams at IRRI and PhilRice in the Philippines for their field trial management; Dr Diane Wang for her assistance with the marker imputation works. Thank you also to the Plant Nutrition team at Flinders University, Australia for their assistance with sample preparation and analysis. We also acknowledge the GRiSP (Global Rice Science Partnerships; now renamed to RICE CRP consortium) for establishing the PRAY Global Phenotyping Network. This study was made possible with financial support from HarvestPlus. HarvestPlus’ principal donors are the UK Government; the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation; the US Government’s Feed the Future initiative; Global Affair Canada; the European Commission; the Children’s Investment Fund Foundation, and donors to the CGIAR Research Program on Agriculture for Nutrition and Health (A4NH). HarvestPlus is also supported by the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.T.C. and N.I.W. carried out data analyses, performed genetic mapping, wrote and edited the manuscript. M.D. and J.P.: oversaw field trial design and management and reviewed the manuscript. J.S.: supervised sample collection, preparation and analyses, reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Cu, S.T., Warnock, N.I., Pasuquin, J. et al. A high-resolution genome-wide association study of the grain ionome and agronomic traits in rice Oryza sativa subsp. indica. Sci Rep 11, 19230 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98573-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98573-w
This article is cited by
-
Improving the metal composition of plants for reduced Cd and increased Zn content: molecular mechanisms and genetic regulations
Cereal Research Communications (2023)
-
Genomic prediction of zinc-biofortification potential in rice gene bank accessions
Theoretical and Applied Genetics (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.