Abstract
Low handgrip strength and increased arterial stiffness are both associated with poor health outcomes, but evidence on the relationship between handgrip strength and arterial stiffness is limited. In this cross-sectional analysis of combined baseline datasets from the LipidCardio and Berlin Aging Study II cohorts we aimed to examine whether handgrip strength (HGS) is associated with arterial stiffness. 1511 participants with a median age of 68.56 (IQR 63.13–73.08) years were included. Arterial stiffness was assessed by aortal pulse wave velocity (PWV) with the Mobil-O-Graph device. Handgrip strength was assessed with a handheld dynamometer.
The mean HGS was 39.05 ± 9.07 kg in men and 26.20 ± 7.47 kg in women. According to multivariable linear regression analysis per 5 kg decrease in handgrip strength there was a mean increase in PWV of 0.08 m/s after adjustment for the confounders age, sex, coronary artery disease, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, cohort, and smoking. Thus, there was evidence that low handgrip strength and increased arterial stiffness go hand in hand. Arterial stiffness can possibly create the missing link between low handgrip strength and increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Causality and direction of causality remain to be determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Understanding the relationship between aging and cardiovascular disease (CVD) is becoming increasingly important in the light of aging populations around the world, leading to a steep increase in age-related morbidity1. Aging occurs at varying rates and is a heterogeneous process2. Some individuals exhibit typical age-associated conditions and deficits early, whereas others never develop certain symptoms and markers of aging. There may be a discrepancy between an individual’s chronological and biological ages3. An individual’s biological age can be estimated using biomarkers. Handgrip strength, as a surrogate measure of overall muscular strength, is an attractive candidate biomarker of aging since handgrip strength is easily accessible and measuring grip strength is simple and inexpensive.
Low handgrip strength is associated with a whole range of poor health outcomes, including incident CVD, and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), but also frailty, impaired quality of life, longer hospital stays, disability, cognitive impairment, decrease in renal function, respiratory and cancer outcomes, and premature mortality, respectively4,5,6,7,8,9,10.
The mechanisms underlying the association between handgrip strength and cardiovascular disease, among others, remain unclear. Although not immediately obvious, skeletal muscle and the vascular system are closely connected; a bi-directional relationship can be assumed11. Skeletal muscle has broad physiological and functional roles. While the obvious role is to enable body movements, skeletal muscle is also the primary location of protein storage within the body, the primary glucose consumer, and important in metabolic conditions such as diabetes12. Therefore, healthy muscles require, among other things, an adequate supply of nutrients. There is convincing evidence demonstrating an association between vascular function and skeletal muscle health13. Both quantitative and qualitative changes in the microvasculature may contribute to reduced muscle mass and function. E.g. it has been suggested that endothelial dysfunction may result in reduced flow due to microvascular dysfunction, and reduced microcirculation may lead to muscle fiber atrophy14.
Furthermore accumulating evidence supports coronary microvascular dysfunction as an important component of the explanation for myocardial ischemia and its relation to adverse outcomes15. By analogy, it would be conceivable that microvascular dysfunction also plays a major role in skeletal muscular dysfunction (reduced strength and loss of skeletal muscle mass, altered metabolism, e.g. development of insulin resistance)16,17.
Recently, some studies suggested that endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness might mediate the association between muscle strength and cardiovascular events18. Arterial stiffening—i.e. the loss of the arteries’ or the aorta’s elastic properties—is a feature of physiological vascular aging, but may be accelerated in a variety of pathological conditions19.
Arterial stiffness can be assessed by measurement of pulse wave velocity (PWV), being considered the gold standard parameter of non-invasively measured arterial stiffness5,20. Numerous publications including meta-analyses and systematic reviews have shown associations of pathological arterial stiffness with aging, cognitive decline cardiovascular disease, and traditional and novel CV risk factors17,21,22,23,24,25. As with handgrip strength, PWV is highly predictive for cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality24,26,27.
The current evidence regarding the association between pulse wave velocity or arterial stiffness and muscular strength, respectively is scarce and conflicting: recently the Wakayama Study showed in community-dwelling older adults (72 ± 5 years) without manifest cardiovascular disease that HGS progressively decreased with an increase in brachial-ankle PWV (baPWV) level7.
Another study performed in 1002 Chinese community dwelling adults aged ≥ 65 years showed that PWV was significantly associated with handgrip strength, but only in men, while another study was not able to replicate the finding of handgrip strength being associated with PWV in hypertensive patients28,29.
Since evidence on the relationship between handgrip strength and arterial stiffness is limited and in parts inconclusive, the aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between handgrip strength and arterial stiffness, both in a cardiovascular high-risk sample of patients and in an above-average healthy sample of community-dwelling adults. We hypothesized that lower handgrip strength would be associated with higher arterial stiffness.
Methods
Population and design
A cross-sectional study was conducted. We combined baseline data from two cohort studies, the LipidCardio and the Berlin Aging Study II (BASE-II).
The LipidCardio cohort is a cohort of 1005 consecutive patients (70.9 ± 11.1 years) recruited on the occasion of elective coronary angiography at a single large academic center (Department of Cardiology, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin) during 2016–201830. Patients aged 18 years and older undergoing cardiac catheterization due to (suspected) chronic coronary syndromes, except those with troponin-positive acute coronary syndromes (ACS), were eligible for inclusion. Participation rate was particularly high (> 95%).
All participants gave written informed consent at the time of enrolment. Patients unable to provide informed consent were excluded from the study. The study was approved by the ethics committee at Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin (approval number: EA1/135/16).
The population-based sample of the Berlin Aging Study II (BASE-II) has been described previously in detail31,32. Briefly, BASE-II was recruited as a convenience sample from the greater Berlin metropolitan area. In 2009–2014, 2171 participants (~ 75% aged 60–85 years and ~ 25% aged 20–35 years) were enrolled in the medical part of the study. All participants gave written informed consent, and the study was approved by the Ethics Committee at Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin (EA2/029/09). Of course, generalizability was an issue, which has been dealt with in depth elsewhere33.
Both studies were performed in compliance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki on Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects, and the manuscript was prepared in compliance with the STrenghtening the Reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE)-Statement34.
The LipidCardio study was implemented by the same team of researchers, who had implemented the BASE-II study before. Both studies used the same standard operating procedures (SOP), instruments, and questionnaires, thus reliability within the pooled data set was given.
In both cohorts only in random subsamples PWV measurements had been performed (LipidCardio N = 598 out of total 1005, and BASE-II N = 913 out of total 2171), resulting in a sample size of 1511.
Pulse wave velocity (PWV)
PWV is generally accepted as the most simple, non-invasive, robust, and reproducible method to assess arterial function35. It is defined as the time difference between the start of the forward - pulse wave and the beginning of the reflected wave. PWV in m/s was measured with the Mobil-O-Graph, I.E.M. Germany, a non-invasive oscillometric device, by trained study personnel and according to manufacturer’s instructions. Measurements were performed in a sitting position and relaxed atmosphere36. With an upper arm pressure sleeve and oscillometric recording of the A. brachialis waveform and pulse pressure arterial stiffness indices were measured shape and amplitude of central PWV and central (aortic) blood pressure were reconstructed via a mathematical transfer function. For data quality assurance only measurements with good or very good quality were used based on the standard deviation of pulse wave recording for a period of 8 s. PWV was used as a continuous variable in most analyses, and also recoded into a binary variable using 11 m/s as cutoff, which corresponded to the fifth quintile. An accepted threshold for end-organ damage is 10–12 m/s37.
Handgrip strength
Handgrip strength was measured by trained study personnel with a Smedley dynamometer, according to a standard operating procedure (participants either standing or seated, the elbow by their side and flexed to right angles, and a neutral wrist position). Three measurements were made from both hands of each participant. We used only the maximum value obtained from any hand (maximum handgrip strength). Tertiles of HGS were obtained separately for both sexes and low handgrip strength was defined as handgrip below the lowest tertile.
Furthermore HGS as the main exposure variable was divided into 5 kg intervals, and also was recoded into a binary variable (probable sarcopenic vs. normal) according to the EWGSOP2 sarcopenia cut-off points38,39.
Covariables
Blood pressure was measured with an Omron oszillometric device on both arms. For assessment of confounding and effect modification blood pressure was categorized into 5 levels (lowest to 99 mmHg, 100–129 mmHg, 130–149 mmHg, 150–170 mmHg, and greater than 170 mmHg), and age was categorized into 20–40 years, 40–60 years, 60–70 years, 70–80 years, and 80–100 years.
Height and weight were either measured (in BASE-II) or taken over from participants’ records (in LipidCardio). Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters and categorized into < 25 kg/m2, 25–30 kg/m2, and > 30 kg/m2; waist and hip circumferences were measured in light clothes.
Information on current smoking status was sampled during structured interviews, and coded into yes/no.
Classification of coronary artery disease status was based on an up-to-date coronary angiogram in the LipidCardio study, while in BASE-II it was based on self-reported history of CAD or review of medical records provided by the participants.
Statistics
There were only a few missing values in the combined dataset (less than 5% of the total number of cases per variable).
The outcome of interest was pulse wave velocity (PWV). We treated PWV mainly as a continuous variable, and for some analyses also as binary variable (increased vs. normal PWV). The exposure of interest was handgrip strength, Firstly, we treated grip strength as a continuous variable and calculated coefficients for 5 kg change (increase or decrease) in hand grip strength. We also calculated coefficients for sex specific tertile cut-off points of grip strength in order to facilitate comparability with previous studies, which have used these categories.
Moreover, we did analyses using a sex specific HGS cut-off point for probable sarcopenia as recommended by the EWGSOP2 sarcopenia guidelines38,39.
Descriptive statistics were used to describe the pooled study population. Univariable analyses were conducted using all data available. Associations of variables with the outcome of interest (PWV) were examined using linear regression (Table 2), and associations with the main exposure of interest (low handgrip) were calculated using cross-tabulations and crude odds ratios (Table 3), and the chi square test of independence was used to assess statistical significance.
All covariables were tested for confounding and effect modification by calculating stratum-specific estimates for each level of the potential confounder and comparing Mantel-Haenzsel odds ratios to the crude odds ratio.
We computed multivariable linear regression analyses to further examine the relationship between handgrip strength with pulse wave velocity taking confounding into account. We calculated multivariable-adjusted coefficients (ß) for 5 kg increase in handgrip strength including all above-mentioned covariables.
We also performed stratified analyses (by sex, age-group, and cohort) and used the likelihood ratio test (LRT) for interaction to test for evidence of interaction between the main exposure of interest and sex, age, and cohort.
Results
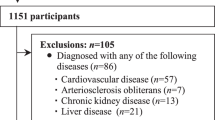
Altogether, 1511 participants from the LipidCardio Study (n = 598) and the Berlin Aging Study II (BASE-II, n = 913), who had HGS and PWV measurements at baseline, have been included in this cross-sectional analysis (Fig. 1).
The median age was 68.56 (interquartile range, IQR 63.13–73.08 years. 954 (63.1%) participants were men.
The mean handgrip strength in men was 39.1 ± 9.1 kg, and one third had a handgrip strength of less than 35 kg. In women, the mean handgrip strength was 26.2 ± 7.5 kg, and one third had a HGS lower than 23 kg. Table 1 shows participant characteristics according to sex and handgrip strength tertiles. Participants with low HGS (below the first tertile) were significantly older than participants in the middle group and those with high HGS. They were less likely current smokers and had the highest prevalence of CAD. They had a higher blood pressure than participants in the other two tertile groups; BMI was similar. Not least, those with low HGS showed the highest PWV.
HGS and PWV showed a moderate negative correlation both in men (r = − 0.405, p < 0.001) and women (r = − 0.499, p < 0.001). According to linear regression analysis, per 5 kg decrease in handgrip strength PWV increased on average by 0.30 m/s (ß = − 0.30, 95% CI − 0.35 to − 0.25, p < 0.001, Table 2), or by about 1 m/s per tertile decrease of handgrip strength, which is also evident from Table 1.
133 (8.8%) participants were probable sarcopenic according to the EWGSOP2 HGS cut-off points39. The prevalence of probable sarcopenia increased stepwise with increasing age (< 60 years: 2.0%, 60–70 years: 3.8%, 70–80 years: 8.3%, > 80 years: 47.8%).
Unadjusted, probable sarcopenic participants had on average a 2.06 m/s higher PWV than non-sarcopenic individuals (ß = 2.06, 95% CI 1.69—2.43, p < 0.001).
In addition to the association between handgrip strength and PWV the univariable analyses performed showed that PWV was positively associated with age, male sex, body mass index, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diagnosis of CAD (Table 2), while low HGS was significantly associated with (increasing) age, being overweight, high SBP and a CAD diagnosis (Table 3).
The results of the multivariable analyses of the association between HGS and PWV are shown in Table 4. Controlling for age, sex, BMI, smoking, CAD, blood pressure, and cohort, the association between HGS and pulse wave velocity was attenuated, but still per 5 kg decrease in handgrip strength there was a mean increase in PWV of 0.08 m/s. Given a mean difference of 18 kg between participants in the lowest and the highest HGS tertile this makes a clinically relevant difference of 1.31 m/s in PWV (Table 4).
The effect did not differ significantly by age-group, even if the data showed a trend towards an increasing effect with increasing age. The effect was more pronounced in men compared to women (Table 4).
Moreover, when we examined the relationship between HGS and PWV in the two genuine cohorts separately, the univariate analyses provided consistent evidence that PWV increased with decreasing handgrip strength (LipidCardio: ß = − 0.33, 95% CI − 0.39 to − 0.26; BASE-II: − 0.16, 95% CI − 0.23 to − 0.09), and also after controlling for important confounders there was evidence of an independent association between handgrip strength and pulse wave velocity in both cohorts (BASE-II: ß = − 0.06, 95% CI − 0.11 to − 0.02, p = 0.002, LipidCardio: ß = − 0.09, 95% CI − 0.14 to − 0.05, p < 0.001; Table 4).
Discussion
The principal finding of this study was that low handgrip strength (HGS) was associated with increased pulse wave velocity, i.e. arterial stiffness, across a wide age range, and irrespective of age, sex, and cardiovascular comorbidity.
It has been shown before that increased PWV is predictive for adverse (cardiovascular) outcomes40. The observed 1.31 m/s difference in PWV between individuals with low and high handgrip strength can be translated into a more than 15% increased risk of CV events, more than 15% higher CV mortality, and more than 15% increased all-cause mortality, which underlines that the relationships investigated here are clinically relevant41.
As to the explicit association between pulse wave velocity or arterial stiffness and muscular strength there has been only scarce and conflicting evidence so far: Consistent with our findings, a recent analysis of the Wakayama Study showed in community-dwelling older adults (72 ± 5 years) without manifest cardiovascular disease that HGS progressively decreased with an increase in brachial-ankle PWV (baPWV) level7. They could also show that baPWV was significantly and independently associated with appendicular skeletal mass.
Another study performed in 1002 Chinese community dwelling adults aged ≥ 65 years showed that baPWV was significantly associated with handgrip strength, but only in men (OR 1.23, 95% CI 1.07–1.42, p < 0.01), whereas there was only weak evidence in women (p = 0.07)28.
Accordingly, although we were able to show that the association existed consistently in both sexes, it was much less pronounced in women than in men (Table 4).
In contrast, a small study from Brazil was not able to replicate the finding of handgrip strength being associated with PWV in hypertensive patients29.
Of note, we could show the association between handgrip strength and pulse wave velocity in both genuine cohorts, in BASE-II, which is convenience sample of community-dwelling older adults whose participants were positively selected regarding health and education, and in LipidCardio, a cohort of patients enriched with manifest cardiovascular disease30,31.
Furthermore, our observation is coherent with findings from a steadily growing body of evidence linking low handgrip strength with manifest and preclinical CVD, incident cardiovascular events, cardiovascular mortality, and all-cause mortality, among others, as well as some few studies suggesting an association between low handgrip strength and endothelial dysfunction42,43,44. Of note, these associations have been shown consistently in diverse populations—in the general population, as well as in patients with chronic kidney disease, hypertensive individuals, diabetics, elderly individuals, individuals with CV-disease—and across ethnies24,42,44,45.
Likewise, by analogy, several studies have established links between sarcopenia on the one hand and CVD, manifest or preclinical atherosclerosis, and arterial stiffness on the other hand45,46.
Yet, low handgrip strength should not be equated with sarcopenia. Individuals with low muscle strength can be regarded as probable cases of sarcopenia. According to the operational definition diagnosis of sarcopenia has to be confirmed by additional documentation of low muscle quantity or quality38,39. The EWGSOP2 sarcopenia cut-off points for low strength by grip strength are < 27 kg in men and < 16 kg in women39. Sarcopenia is highly prevalent in older adults general population. In this pooled data set 9.0% of men and 8.4% of women (total 8.8%, n = 133) were probable sarcopenic cases according to the EWGSOP2 sarcopenia cut-off points. Thus the majority of participants in the lowest tertile group (men: ≤ 35 kg, women: ≤ 23 kg, n = 523) were not probable sarcopenic. Indeed, in the present study probable sarcopenic participants had on average a 2.06 m/s higher PWV than non-sarcopenic individuals according to crude analyses (ß = 2.06, 95% CI 1.69—2.43, p < 0.001), and 0.38 m/s controlling for sex, age, BMI, smoking, SBP, CAD, and cohort (ß = 0.38, 95% CI 0.26–0.50).
What remains to be elucidated is the question of causality and the involved pathophysiological mechanisms. There are a number of puzzle pieces already available: Low muscle strength, muscle mass reduction, and sarcopenia on the one hand, and arterial stiffness on the other hand share some common assumed underlying pathomechanisms that include alterations in endocrine, metabolic, inflammatory, and immunologic systems47,48. Common pathophysiologic changes including elevated levels of C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, D-dimer, factor VIII, and insulin resistance have been subsumed as inflammaging, and may be involved in the development of clinical syndromes such as sarcopenia and the frailty phenotype, alterations in markers of CVD such as arterial stiffness and finally CVD and CV events itself24,49,50. For example, an analysis from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA) found that higher handgrip strength is associated with lower levels of inflammation at 8-year follow-up, and inflammatory markers partly explained the association between handgrip strength and mortality51,52.
Likewise, circulating markers of oxidative stress have been shown to be independently associated with both handgrip strength and sarcopenia, and related to CVD risk53,54.
The present study adds to the existing evidence, suggesting that arterial stiffness might be an important intermediate step between muscle strength and CV disease and mortality.
Still, reverse causation is not ruled out. Indeed, it would be conceivable that those with low handgrip strength have subclinical, incipient cardiovascular disease responsible for the lower muscle strength and for the seemingly prospective relation of HGS with CV disease and mortality.
As is commonly accepted, an individual’s chronological age can be quite different from his or her biological age. Although there is no exact definition and measure for biological age, individuals of the same chronological age may vary in their “biological aging”, i.e. rate of declining integrity of multiple organ systems. Individuals who are aging more rapidly are typically less physically able, with greater cognitive decline and brain aging, lower self- reported health, and looking older2. Biological age is commonly used as a relative measure indicating whether the body is functioning better or worse than suggested by the chronological age55,56.
Given that both HGS and PWV are candidate markers of biological age, it would also be possible that there is not a unilateral or bilateral causal relationship between vascular aging and muscle mass decline, but they are associated simply because they measure the same trait. Our results and the above-mentioned findings of others suggest that low handgrip strength and arterial stiffness commonly go hand in hand.
Arterial stiffness has been established as an independent risk marker for cardiovascular disease, and well reflects the dissociation between chronological and biological age of large arteries. The concept of Early Vascular Ageing (EVA) has been suggested to identify individuals whose vessels prematurely show alterations typically found in more advanced chronological age57. These may be due to lifestyle (e.g. sedentary, no sports, smoking), high blood pressure, hypercholesterolemia, genetics, amongst others.
Likewise, handgrip strength declines with increasing age, and is widely used as simple and robust marker of biological age58. The PURE study suggested that simply measuring one’s handgrip strength could be a good way to assess biological age18.
PWV has not been widely integrated into the clinical routine yet, despite the intriguing additional information it provides. This study underlines that HGS is very well suited as a clinical risk marker. The test-retest reliability is excellent59. Since we may well infer from low HGS that PWV may be high—only 5.4% in the highest handgrip strength tertile had a high PWV > 11 m/s, compared to 39.4% in the lowest tertile—and measurement of HGS is done in a few seconds and inexpensive, it may be the ideal screening tool. In a similar vein, handgrip strength has been shown to correlate well with European System for Cardiac Operative Risk Evaluation (EuroSCORE) values60.
Of course, given the high interest in predicting biological age the most precisely possible, both markers HGS and PWV are candidates to be integrated in multimarker scores61.
Handgrip strength is inversely associated with PWV. While both are inexpensive and easy to measure, measurement of HGS is yet easier, quicker and less error-prone, and is highly reproducible. It is at least as effective in predicting adverse outcomes as PWV. Both seem to be suited for early identification of accelerated aging—even before chronic disease becomes established—offering opportunities for prevention. Therefore, adoption of HGS into clinical setting to identify or screen for individuals at greatest risk for future CV outcomes is appealing.
Furthermore, arterial stiffness may help explain the relationship between HGS and CVD. Not least it is conceivable that targeted interventions following a diagnosis of low HGS would be capable to improve arterial compliance.
Strengths and limitations
In addition to the already mentioned aspects our study has several limitations.
We used aortal PWV (aPWV), which is the gold standard measure of arterial stiffness. Recently, criticism of cuff-based, or algorithm-based devices like the Mobil-O-Graph, which has been used in this study, has been expressed. It is being criticized that the estimation of PWV is largely dependent on age and blood pressure, thus arguably providing no extra information62,63.
On the other hand, there is good evidence that the Mobil-O-Graph provides similar results as devices noninvasively measuring cf-PWV, and shows good correlation with invasive aortic PWV64,65,66.
While we cannot prove or disprove the issues raised with the present work, we however, believe that the potential issues do not compromise our study.
Further limitations of our study include the observational nature and cross-sectional design of this study, which does not allow us to make conclusions on the causal role of muscular strength in arterial stiffness and cardiovascular disease, or vice versa. Conclusions on temporality are impossible, and residual confounding cannot be excluded. The observed association between handgrip strength and arterial stiffness may be causal, due to (unmeasured) confounding, or due to reverse-causation, i.e. reflecting early manifestation of underlying disease processes. Indeed, mendelian randomization analyses could not show that muscular strength is predictive for mortality risk, or cardiovascular events8.
Furthermore, the possibility of bias, both selection and information bias must be considered:
BASE-II is a convenience sample, whose participants were positively selected regarding education and health31. On the other hand, for the LipidCardio study, consecutive patients of a tertiary cardiology center, who all underwent coronary angiography, have been recruited30. Thus there is potential for selection bias, while the direction of bias is unpredictable.
As to the generalizability of the results, given the fact that the association was observed in two very different samples, we believe that the finding may well apply to the population of older adults with Caucasian ancestry in comparable living conditions in Central Europe.
Conclusion
Handgrip strength was inversely associated with PWV, indicating that low handgrip strength and increased arterial stiffness go hand in hand. Arterial stiffness can possibly create the missing link between low handgrip strength and increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Data availability
Data can be requested from the steering committees of the Berlin Aging Study II and the LipidCardio Study. Further Information can be found under https://www.base2.mpg.de/en.
References
Wang, H. et al. Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: a comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 396, 1160–1203 (2020).
Belsky, D. W. et al. Quantification of biological aging in young adults. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 112, E4104–E4110 (2015).
Jackson, S. H. D., Weale, M. R. & Weale, R. A. Biological age—what is it and can it be measured?. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 36, 103–115 (2003).
Bohannon, R. W. Hand-grip dynamometry predicts future outcomes in aging adults. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 31, 3–10 (2008).
Izzo, J. L. Jr. & Shykoff, B. E. Arterial stiffness: clinical relevance, measurement, and treatment. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2(29–34), 37–40 (2001).
Celis-Morales, C. A. et al. Associations of grip strength with cardiovascular, respiratory, and cancer outcomes and all cause mortality: prospective cohort study of half a million UK Biobank participants. BMJ 361, k1651 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Muscle mass reduction, low muscle strength, and their combination are associated with arterial stiffness in community-dwelling elderly population: the Wakayama study. J. Hum. Hypertens. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0355-z (2020).
Willems, S. M. et al. Large-scale GWAS identifies multiple loci for hand grip strength providing biological insights into muscular fitness. Nat. Commun. 8, 16015 (2017).
García-Peña, C. et al. Handgrip strength predicts functional decline at discharge in hospitalized male elderly: a hospital cohort study. PLoS ONE 8, e69849 (2013).
Musalek, C. & Kirchengast, S. Grip strength as an indicator of health-related quality of life in old age: a pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121447 (2017).
Groen, B. B. L. et al. Skeletal muscle capillary density and microvascular function are compromised with aging and type 2 diabetes. J. Appl. Physiol. 116, 998–1005 (2014).
Mesinovic, J., Zengin, A., De Courten, B., Ebeling, P. R. & Scott, D. Sarcopenia and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a bidirectional relationship. Diabetes. Metab. Syndr. Obes. 12, 1057–1072 (2019).
Dvoretskiy, S. et al. Exploring the association between vascular dysfunction and skeletal muscle mass strength and function in healthy adults: a systematic review. Nutrients https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030715 (2020).
Weibel, E. R., Taylor, C. R. & Hoppeler, H. The concept of symmorphosis: a testable hypothesis of structure-function relationship. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 10357–10361 (1991).
Vancheri, F., Longo, G., Vancheri, S. & Henein, M. Coronary microvascular dysfunction. J. Clin. Med. Res. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092880 (2020).
Park, K. E. & Pepine, C. J. Microvascular dysfunction: What have we learned from WISE?. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 9, 1491–1494 (2011).
Rensma, S. P. et al. Associations of arterial stiffness with cognitive performance, and the role of microvascular dysfunction: the maastricht study. Hypertension 75, 1607–1614 (2020).
Leong, D. P. et al. Prognostic value of grip strength: findings from the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study. Lancet 386, 266–273 (2015).
Lyle, A. N. & Raaz, U. Killing me unsoftly: causes and mechanisms of arterial stiffness. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 37, e1–e11 (2017).
Laurent, S. et al. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur. Heart. J. 27, 2588–2605 (2006).
Safar, M. E. & Lacolley, P. Disturbance of macro- and microcirculation: relations with pulse pressure and cardiac organ damage. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 293, H1-7 (2007).
Oliver, J. J. & Webb, D. J. Noninvasive assessment of arterial stiffness and risk of atherosclerotic events. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 554–566 (2003).
Baulmann, J., Homsi, R., Un, S., Vetter, H. & Düsing, R. Mengden T [Arterial stiffness in arterial hypertension. A new risk factor for left ventricular hypertrophy and cardiac insufficiency?]. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 129, 447–452 (2004).
Orkaby, A. R. et al. Cross-sectional association of frailty and arterial stiffness in community-dwelling older adults: the framingham heart study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 74, 373–379 (2019).
Fesler, P., Safar, M. E., du Cailar, G., Ribstein, J. & Mimran, A. Pulse pressure is an independent determinant of renal function decline during treatment of essential hypertension. J. Hypertens. 25, 1915–1920 (2007).
Willum-Hansen, T. et al. Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation 113, 664–670 (2006).
Ben-Shlomo, Y. et al. Aortic pulse wave velocity improves cardiovascular event prediction: an individual participant meta-analysis of prospective observational data from 17,635 subjects. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63, 636–646 (2014).
Zhang, L. et al. A cross-sectional study of the association between arterial stiffness and sarcopenia in chinese community-dwelling elderly using the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia Criteria. J. Nutr. Health. Aging. 23, 195–201 (2019).
de Lima-Junior, D. et al. Association between handgrip strength and vascular function in patients with hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 41, 692–695 (2019).
König, M. et al. Cohort profile: role of lipoproteins in cardiovascular disease-the LipidCardio study. BMJ Open. 9, e030097 (2019).
Bertram, L. et al. Cohort profile: The Berlin Aging Study II (BASE-II). Int. J. Epidemiol. 43, 703–712 (2014).
Gerstorf, D. et al. Editorial. Gerontology 62, 311–315 (2016).
Sassenroth, D., Kroh, M. & Wagner, G. G. Selectivity processes in and weights for the Berlin Aging Study II (Base-II). SSRN J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2365707 (2013).
von Elm, E. et al. STROBE statement: checklist of items that should be included in reports of observational studies1 (©STROBE Initiative). Int. J. Public Health https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-007-0239-9 (2008).
Papaioannou, T. G. et al. The influence of resting heart rate on pulse wave velocity measurement is mediated by blood pressure and depends on aortic stiffness levels: insights from the Corinthia study. Physiol. Meas. 40, 055005 (2019).
Van Bortel, L. M. et al. Clinical applications of arterial stiffness, Task Force III: recommendations for user procedures. Am. J. Hypertens. 15, 445–452 (2002).
Mancia, G. et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J. Hypertens. 31, 1281–1357 (2013).
Dodds, R. M. et al. Grip strength across the life course: normative data from twelve British studies. PLoS ONE 9, e113637 (2014).
Cruz-Jentoft, A. J. et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 48, 16–31 (2019).
Sequí-Domínguez, I. et al. Accuracy of pulse wave velocity predicting cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. Res. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072080 (2020).
Vlachopoulos, C., Aznaouridis, K. & Stefanadis, C. Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 55, 1318–1327 (2010).
Dos Santos, M. R. et al. Sarcopenia and endothelial function in patients with chronic heart failure: results from the studies investigating comorbidities aggravating heart failure (SICA-HF). J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 18, 240–245 (2017).
Yamanashi, H. et al. Association between atherosclerosis and handgrip strength in non-hypertensive populations in India and Japan. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 18, 1071–1078 (2018).
Peterson, M. D. et al. Low normalized grip strength is a biomarker for cardiometabolic disease and physical disabilities among US and Chinese adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 72, 1525–1531 (2017).
Sampaio, R. A. C. et al. Arterial stiffness is associated with low skeletal muscle mass in Japanese community-dwelling older adults: Arterial stiffness and low SMI in older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 14, 109–114 (2014).
Kirkham, F. A., Bunting, E., Fantin, F., Zamboni, M. & Rajkumar, C. Independent association between cardio–ankle vascular index and sarcopenia in older UK adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 67, 317–322 (2019).
Ochi, M. et al. Arterial stiffness is associated with low thigh muscle mass in middle-aged to elderly men. Atherosclerosis 212, 327–332 (2010).
Buchmann, N., Spira, D., König, M., Demuth, I. & Steinhagen-Thiessen, E. Frailty and the metabolic syndrome: results of the Berlin Aging Study II (BASE-II). J. Frailty. Aging. 8, 169–175 (2019).
Dalle, S., Rossmeislova, L. & Koppo, K. The role of inflammation in age-related sarcopenia. Front. Physiol. 8, 1045 (2017).
Müller-Werdan, U., Nuding, S. & Ost, M. Assessing inflammageing. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 20, 346–348 (2017).
Smith, L., Yang, L. & Hamer, M. Handgrip strength, inflammatory markers, and mortality. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 29, 1190–1196 (2019).
Goldeck, D. et al. No strong correlations between serum cytokine levels, CMV serostatus and hand-grip strength in older subjects in the Berlin BASE-II cohort. Biogerontology 17, 189–198 (2016).
Bellanti, F. et al. Oxidative stress is increased in sarcopenia and associated with cardiovascular disease risk in sarcopenic obesity. Maturitas 109, 6–12 (2018).
Howard, C. et al. Oxidative protein damage is associated with poor grip strength among older women living in the community. J. Appl. Physiol. 103, 17–20 (2007).
Lin, H. et al. Whole blood gene expression associated with clinical biological age. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 74, 81–88 (2019).
Murabito, J. M. et al. Measures of biologic age in a community sample predict mortality and age-related disease: the framingham offspring study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 73, 757–762 (2018).
Cunha, P. G., Boutouyrie, P., Nilsson, P. M. & Laurent, S. Early vascular ageing (EVA): definitions and clinical applicability. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 13, 8–15 (2017).
Koopman, J. J. E., van Bodegom, D., van Heemst, D. & Westendorp, R. G. J. Handgrip strength, ageing and mortality in rural Africa. Age Ageing. 44, 465–470 (2015).
Bohannon, R. W. Test-retest reliability of measurements of hand-grip strength obtained by dynamometry from older adults: a systematic review of research in the PubMed database. J. Frailty. Aging. 6, 83–87 (2017).
Perry, I. S., Pinto, L. C., da Silva, T. K., Vieira, S. R. R. & Souza, G. C. Handgrip strength in preoperative elective cardiac surgery patients and association with body composition and surgical risk. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 34, 760–766 (2019).
Jylhävä, J., Pedersen, N. L. & Hägg, S. Biological Age Predictors . EBioMedicine 21, 29–36 (2017).
Schwartz, J. E., Feig, P. U. & Izzo, J. L. Jr. Pulse wave velocities derived from cuff ambulatory pulse wave analysis. Hypertension 74, 111–116 (2019).
Salvi, P. et al. Noninvasive estimation of aortic stiffness through different approaches. Hypertension 74, 117–129 (2019).
Weber, T., Wassertheurer, S., Hametner, B., Parragh, S. & Eber, B. Noninvasive methods to assess pulse wave velocity: comparison with the invasive gold standard and relationship with organ damage. J. Hypertens. 33, 1023–1031 (2015).
Reshetnik, A., Gohlisch, C., Tölle, M., Zidek, W. & Van Der Giet, M. Oscillometric assessment of arterial stiffness in everyday clinical practice. Hypertens. Res. 40, 140–145 (2017).
Kusunoki, H. et al. Associations between arterial stiffness indices and chronic kidney disease categories in essential hypertensive patients. Am. J. Hypertens. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpaa163 (2020).
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. The LipidCardio study was partly funded by the Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH. The provided support was exclusively financial, with no influence on study design, data collection and analysis, nor the decision to publish, nor the preparation of this manuscript. The BASE-II research project (Principle-Investigators: Lars Bertram, Ilja Demuth, Denis Gerstorf, Ulman Lindenberger, Graham Pawelec, Elisabeth Steinhagen-Thiessen, and Gert G. Wagner) was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, BMBF) under Grant Nos.: #16SV5536K, #16SV5537, #16SV5538, #16SV5837, #01UW0808, 01GL1716A and 01GL1716B. The provided support was exclusively financial, with no influence on study design, data collection and analysis, nor the decision to publish, nor the preparation of this manuscript. Additional funding was provided by the Max Planck Institute for Human Development, Berlin, Germany. Contributions (e.g., equipment, logistics, personnel) were made from each of the other participating sites.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.K. conceived of the presented idea. M.K. developed the theory and analysed the data, and wrote the manuscript with support from I.D., who also verified the analytical methods. N.B. and D.S. made substantial contributions to the acquisition of data, they participated in revising the article critically for important intellectual content; U.S. participated in revising the article critically for important intellectual content, and encouraged M.K. to investigate gender specific aspects. E.S.T. and I.D. made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, and interpretation of data. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. All authors gave final approval of the version to be submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
König, M., Buchmann, N., Seeland, U. et al. Low muscle strength and increased arterial stiffness go hand in hand. Sci Rep 11, 2906 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81084-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81084-z
This article is cited by
-
Hand grip strength as a proposed new vital sign of health: a narrative review of evidences
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition (2024)
-
Handgrip strength is inversely associated with augmentation index in patients with type 2 diabetes
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Associations of cardiorespiratory fitness, body composition, and blood pressure with arterial stiffness in adolescent, young adult, and middle-aged women
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
The influence of cardiovascular risk factors on near-infrared spectroscopy-derived muscle oxygen saturation during exercise recovery in older adults
Sport Sciences for Health (2022)
-
Exposure to mixture of heavy metals and muscle strength in children and adolescents: a population-based study
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.