Abstract
Coralligenous assemblages are among the most species-rich and vulnerable habitats of the Mediterranean Sea. Nevertheless, data on connectivity patterns on species inhabiting these habitats, crucial to define management and protection priorities, are largely lacking. Moreover, unreliable species-level taxonomy can confound ecological studies and mislead management strategies. In the northwestern Mediterranean two Parazoanthus axinellae morphotypes differing in size, color and preferred substrate are found in sympatry. In this study, we used COI and ITS sequence polymorphism to assess (1) the genetic divergence between the two morphotypes, (2) their connectivity patterns and (3) their phylogenetic position within the Parazoanthidae. Specimens of P. axinellae were sampled in 11 locations along the northwestern Mediterranean; in 6 locations, samples of the two morphotypes were collected in sympatry. Small genetic diversity and structure were found within morphotypes, while marked and consistent differentiation was detected between them. Moreover, the less widespread morphotype appeared to be closer to Pacific species as P. juanfernandezii and P. elongatus. Our findings confirmed the limited knowledge on Parazoanthus species complex, and how this gap can have important implication for the conservation strategies of this widespread and valuable genus in the Mediterranean Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Biogenic reefs are made by calcareous encrusting algae and animals that change the geological primary habitat on which they settled through superimposition of their skeletons. They are among the most productive and diverse benthic ecosystems, providing habitat, feeding grounds, recruitment and nursery areas for a variety of invertebrate and vertebrate species1.
In the Mediterranean Sea, the main biogenic reefs are the coralligenous reefs. They are among the most important Mediterranean ecosystems due to the high diversity of species and ecological processes that they support1,2. These complex habitats are threatened by several human activities (e.g. recreational fishing and trawling, sediment deposition, anchorage, diving), which lead to their fragmentation and loss3,4.
Monitoring spatio-temporal changes in species composition is crucial to quantify human-induced biodiversity loss and habitat fragmentation, but the absence of clear taxonomic identifiers to distinguish between species makes this a challenging task.
Many relevant coralligenous taxa (e.g. Porifera, Echinodermata, Cnidaria) lack diagnostic morphological characteristics, and therefore these groups are recognized as taxonomically problematic, in particular at lower taxonomic levels5. Moreover, in these species, with high morphological plasticity6, some characters such as shape and coloration might not be reliable for species delimitation. It happened that morphospecies have turned out to be a single morphologically variable species7,8,9, and, conversely, what was thought to be multiple growth forms of a single species turned out to be a complex of species10,11.
The presence of species complexes in the sea can confound ecological studies and mislead management strategies. For example, connectivity patterns12 may be erroneously inferred when cryptic species are ignored13,14, which may provide biased conclusions about the overall capacity of the studied populations to resist stress15. To disclose cryptic species before estimating gene flow and indeed evaluate connectivity among populations, we should (1) use more than one independent molecular marker, (2) sample individuals all along the distributional range of the investigated species, and (3) sample closely related taxonomic species to understand the spectrum of population to species divergence13.
To our knowledge, three species of Parazoanthus exist along the Mediterranean and North-East Atlantic coasts: Parazoanthus axinellae (Schmidt, 1862), P. anguicomus (Norman, 1869) and another Parazoanthidae yet to be described in the Macaronesian waters16. In the Mediterranean Sea, Parazoanthus axinellae (Cnidaria, Hexacorallia, Zoantharia) species complex17 is one of the most common cnidarians inhabiting coralligenous assemblages. The simplicity of the zoanthid body plan makes morphology-based species identification quite challenging. Numerous morphological identification criteria have been used to identify phylogenetic signal ranging from colour, sphincter muscle anatomy18, tentacles number19, type and distribution of nematocysts20. In addition, differences in substrate preference, overall ecology17, biochemical profiles21,22,23 and sequence divergence using various gene markers were also proposed as zoanthid identification criteria24,25,26. Original species descriptions were thereby based on different traits depending on the authors27. Due to the aforementioned lack of morphological characters to identify zoanthids, a comprehensive taxonomic identification of the P. axinellae species complex is still missing (but see17 for a detailed description of P. axinellae species complex). Historically, there were four described subspecies of P. axinellae: P. axinellae mülleri Pax, 1957, common across the whole Mediterranean coastline; P. axinellae liguricus Pax, 1937, in the Ligurian Sea; P. axinellae brevitentacularis in the Gulf of Lion and P. axinellae adriaticus Pax, 1937 in the Adriatic Sea28,29,30. However, the morphological descriptions of these four subspecies are quite imprecise and overlapping, and clear diagnostic characters to discriminate them are still lacking. Recently, Ocana et al.17 stated that these four subspecies can be grouped in two morphotypes based on their chemical profiles31 and ecological requirement17. These two morphotypes live in sympatry in the northwestern Mediterranean29. One of them displays an elongated trunk, longer and thinner tentacles, and a light yellow color. This morphotype (“Morphotype 1” in17, “Slender” in31; Fig. 1a) is found across the whole Mediterranean, including the Adriatic Sea, and could correspond to the descriptions of the two subspecies P. axinellae mülleri and P. axinellae adriaticus (Fig. 1a). A more pronounced orange color, and shorter and thicker trunk and tentacles characterize the second morphotype (Morphotype 2 in17, “Stocky” in31; Fig. 1b). This form is restricted to the north-western Mediterranean and could correspond to P. axinellae brevitentacularis and P. axinellae liguricus (Fig. 1b). On top of their morphological differences, the “Slender” form is mainly characterized by an epibiotic lifestyle on the sponges of the genus Axinella, while the “Stocky” form lives primarily on the rocky substratum32 and has never been observed on Axinella spp17.
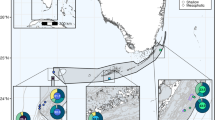
(a) “Slender” morphotype of Parazoanthus axinellae (Photo: A. Villamor); (b) “Stocky” morphotype of Parazoanthus axinellae, secca del Tinetto, Portovenere, Italy (Photo: A. Villamor); (c) map of the sampling sites where the colonies of P. axinellae were collected. Yellow dots represent samples of “Slender” morphotype; orange dots represent samples of “Stocky” morphotype, The map was created with the free software QGIS (https://qgis.osgeo.org/es/site/) and edited in Adobe Photoshop version 14.2.1 (www.adobe.com) for this study.
In the present study, we aim to describe the patterns of diversity and connectivity for populations of the two Parazoanthus axinellae morphotypes along the Northwestern Mediterranean and the Adriatic Sea. Specifically, we use mitochondrial (COI) and nuclear (ITS) sequences polymorphism to asses: (1) the genetic diversity and structure among populations within and between morphotypes and (2) phylogeny and differentiation in the Parazoanthidae Family.
Results
Genetic diversity and structure among P. axinellae populations
A total of 322 sequences of 402 bp of COI were obtained (Table 1), and 5 polymorphic sites and 7 haplotypes were detected. Haplotype and nucleotide diversity were low within all the localities. The “Slender” and the “Stocky” morphotypes showed 3 (I, IV, VI) and 4 (II, III, V, VII) different haplotypes, respectively (Fig. 2, Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Table S1). The unrooted haplotype network exhibited two star-like patterns (haplogroups: “Slender” and “Stocky”) connected by 1 mutational step. The two haplogroups were surrounded by private and low frequency haplotypes differing in 1 bp (Fig. 2, Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Table S1).
Haplotype network analysis for COI (above) and ITS (below) gene markers in Parazoanthus axinellae species complex. Haplotype network was built in Rstudio version 1.1.453 (https://rstudio.com/) with an R package pegas (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pegas/index.html), using an infinite site model based on Hamming distances of DNA sequences. Each haplotype is presented as a separate pie chart, and size of the pie charts directly correlates to the number of individuals within the haplotype. Pie chart colors for geographic location were chosen to intuitively associate the reader to Parazoanthus axinellae morphotypes, with orange tones being attributed to the “Stocky” morphotype, and yellow and grey tones to the “Slender” morphotype. Distances between haplotypes correspond to the genetic differentiation observed for each of the markers, and each mutation between the haplotypes is shown as a hyphen. Alluvial diagrams were made using an online platform RAWGraphs (https://rawgraphs.io/) to further clarify haplotype-morphotype assignments, and final graph modifications were done in Inkscape version 0.92.4 (https://inkscape.org/it/).
As for the ITS fragment, a total of 20 haplotypes were obtained from 232 sequences (698 bp) and “Stocky” and “Slender” morphotypes were differentiated by a minimum number of 68 mutation steps (between haplotypes II and VI) (Fig. 2, Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Table S2). The two morphotypes showed different ITS haplotypes, with the exception of 9 individuals sampled in Olbia, West Tyrrhenian Sea (codes SRY and SRO) that shared the same haplotype with the morphologically distinct phenotype. In particular, 5 “Stocky” individuals at Olbia (code SRO) had the identical ITS sequence with the haplotype IV (mostly composed out of “Slender” individuals), and 4 specimens with the “Slender” phenotype (code SRY) shared the same sequence with haplotype I, composed mostly of “Stocky” Parazoanthus specimens (see Fig. 2, Supplementary Figure S1).
Genetic differentiation (pairwise ΦST values) between populations ranged between 0 and 1 for both markers (See Supplementary Table S3, Supplementary Table S4; Supplementary Figure S2, Supplementary Figure S3). The lowest differentiation values corresponded to the comparisons between populations of the same morphotype, whereas the highest differentiation values occurred between populations of different morphotypes. Significant differentiation was also detected (for ITS) between populations within the “Stocky” morphotype, in particular between population pairs Banyuls-sur-Mer/Alassio and Porto Venere/Portofino/Giannutri (ΦST BAO versus PVO = 0.60; ΦST BAO versus PFO = 0.70; ΦST ALO versus PVO = 0.37; ΦST ALO versus PFO = 0.35; ΦST BAO versus GIO = 0.99; ΦST ALO versus GIO = 0.58) (Supplementary Table S4 Supplementary Figure S3). The samples from Olbia (SRY and SRO codes) showed a specific pattern of genetic differentiation, with ITS haplotypes being intermixed within morphotypes, as previously elaborated.
The Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA) between groups of samples according to morphotype and biogeographic areas showed that for the “Slender” morphotype most variability is explained by differences between all populations (COI: 81.79%, P < 0.01; ITS: 68.87%, P < 0.01; Table 2). For the “Stocky” morphotype, the same is true according to COI, but ITS shows some variability related to the biogeographic pattern (Table 2).
AMOVA between the two groups defined by the morphotype attributed most of the variation to the differences between morphotypes for both markers (COI: 96.62%, P < 0.01; ITS: 89.52%, P < 0.01; Table 2).
Neutrality tests showed no departure from neutrality according to COI in both morphotypes, but a positive and significant departure according to Fu and Li test33 for the ITS marker in both morphotypes (1.77, P < 0.02 for the “Slender”; and 2.28 P < 0.02 for the “Stocky”), which might indicate a decrease in population size and/or balancing selection acting in this marker. Mismatch distributions in both markers showed a bimodal distribution34, but the observed distributions were not statistically different from those expected under a sudden expansion model (COI: SSD = 0.15 P value = 0.047; rg = 0.48 P value = 0.05; ITS: SSD = 0.09 P value = 0.22; rg = 0.30 P value = 0.42). Two genetic pools were observed; one is corresponding to a recent expansion and a second one with older demographic history. These two genetic pools are more similar according to COI, but very distant according to ITS (Supplementary Figure S4, Supplementary Figure S5).
Phylogeny and differentiation within Family Parazoanthidae
Haplotype function from pegas35 dereplicated identical sequences into a total number of 16 (COI) and 38 (ITS) haplotypes within Parazoanthidae family (sequences from our study + those retrieved from GenBank) (Supplementary Table S5, Supplementary Table S6). These haplotypes were reconstructed from 344 (COI) and 275 (ITS) same-length sequences (474 and 734 nucleotides for COI and ITS genes) and were used for Maximum Likelihood (ML) treebuilding.
Likelihood ratio test (performed with modelTest function in phangorn R package), based on minimum AICc values, identified HKY + I and HKY + G + I models as best nucleotide evolution models for COI and ITS markers, respectively. The Maximum Likelihood trees were reconstructed for each marker using F81 nucleotide substitution model as this was the most similar model to HKY + I and HKY + G + I available in phangorn R package.
Although indels in ITS gene marker created large gaps, the overall network topology and the number of mutation steps between species did not vary greatly between the different MAFFT alignments performed (only one result is shown). Moreover, the phylogenetic trees with MAFFT alignment (without gap removal) and with MAFFT alignment + GBlock gap removal also give similar topology. We only show results for P. axinellae + Genbank ITS sequences aligned in MAFFT using L-INS-i algorithm with 1,000 iterations, and with Gblock gap removal parameters set to: b1 = 0.8, b2 = 0.9, b4 = 2, b5 = "h".
Bayesian Inference and maximum likelihood trees reflected the same topology for both COI and ITS genes but with different statistical support. It is interesting to note that various haplotypes in both markers shared the same sequence across more than one species. Particularly for COI gene, this was the case for haplotypes I (ANG, PAR and “Slender” P. axinellae), and V (ALI and “Stocky” P. axinellae), whereas for ITS marker this occurred only in haplotype VI (ELO and JUA). Overall “Stocky” and Slender” morphotypes cluster in two well-separated clades (although with low bootstrap support). In the “Stocky” clade all the “Stocky” morphotype haplotypes showed high similarity with P. elongatus (COI and ITS), and P. juanfernandezii (ITS), both species from the southeastern Pacific. The “Slender” morphotypes grouped with P. anguicomus (COI and ITS) from the eastern Atlantic, P. parasiticus (COI), P. swiftii (COI) both Caribbean species and P. aliceae (COI) from the Azores Archipelago (Fig. 3). Finally, it is interesting to note that despite clear genetic differences between the studies morphotypes, certain individuals sampled in Olbia, West Tyrrhenian Sea (codes SRY and SRO) shared the same sequence for ITS marker with the morphologically distinct phenotype (Fig. 3).
Phylogenetic trees and clustering dendrograms based on COI (above) and ITS (below) gene markers between 16 (COI) and 38 (ITS) haplotypes within Parazoanthidae family, respectively. Identical sequences were dereplicated into haplotypes and are presented on the tree nodes in roman numerals. For ITS the phylogentic tree using the MAFFT + GBlock alignment is shown. Bayesian posterior probability (on the left) and Maximum Likelihood (ML) bootstrap support based on 1,000 iterations (on the right) are shown on tree branches with a cutoff value of p = 50 (%). Inferior support values were considered as unresolved. Clustering dendrograms were reconstructed for each gene marker in RAWGraphs (https://rawgraphs.io/) and added as extensions onto tree nodes to further clarify haplotype/sequence assignments. Clustering dendrograms hierarchically consist out of 2 levels for sequences downloaded from GenBank (Species code, Number of sequences) and 3 levels for samples sampled in our study (Morphotype Color, Sampling Location, Number of sequences). Sequences originating from our samples are colored in yellow and orange for “Slender” and “Stocky” morphotypes, respectively, while all sequences downloaded from GenBank are in grey. Codes are as follows for Parazoanthus sp. sequences from NCBI: ALI—Parazoanthus aliceae, NE Atlantic; ANG—Parazoanthus anguicomus, NE Atlantic; BEC—Bergia catenularis, Carribean Sea; BEP—Bergia puertoricense, Carribean Sea; CAP—Parazoanthus capensis, Port Elizabeth, South Africa; DAR—Parazoanthus darwini, Galapagos islands; ELO—Parazoanthus elongatus, multiple localities; GRA—Hydrozoanthus gracilis, multiple localities; JUA—Parazoanthus juanfernandezii, South Pacific; MES—Mesozoanthus fossii, South Pacific; PAX—Parazoanthus axinellae, multiple localities; PAR—Umimayanthus parasiticus, Caribbean Sea; SAV—Savalia savaglia, Gran Canaria (Spain); SWI—Parazoanthus swiftii, multiple localities; TUN—Hydrozoanthus tunicans, multiple localities. Codes for individuals of P. axinellae species complex sampled in our study are as follows: ALO—(Orange), East Ligurian Sea, Alassio; ALY—(Yellow), East Ligurian Sea, Alassio; BAO—(Orange), Gulf of Lions, Banyuls-sur-Mer; BAY—(Yellow), Gulf of Lions, Banyuls-sur-Mer; CAM—(Yellow), East Tyrrhenian Sea, Campania; CHI—(Yellow), North East Adriatic Sea, Chioggia; GIA—(Yellow), North Tyrrhenian Sea, Giannutri; GIO—(Orange), North Tyrrhenian Sea, Giannutri; PFO—(Orange), Central Ligurian Sea, Portofino; PFY—(Yellow), Central Ligurian Sea, Portofino; PUG—(Yellow), Ionian Sea, Gallipoli; PVO—(Orange), South Ligurian Sea, Porto Venere; PVY—(Yellow), South Ligurian Sea, Porto Venere; ROV—(Yellow), North West Adriatic Sea, Rovigno; SRO—(Orange), West Tyrrhenian Sea, Olbia; SRY—(Yellow), West Tyrrhenian Sea, Olbia; TRE—(Yellow), South Adriatic Sea, Tremiti.
Discussion
In the present study we evidenced for the first time that (1) the two Mediterranean morphotypes of Parazoanthus axinellae differ more between them that in comparison to other allopatric zoanthid species and (2) that the “Slender” morphotype is characterized by a lower genetic differentiation among populations compared to the “Stocky” morphotype.
COI and ITS evidenced clear genetic isolation between the two morphotypes. Differences in chemical profiles31 and in morphological features17 between the two morphotypes are consistent with our results, suggesting that the Parazoanthus axinellae species complex includes two different taxa. Both COI and ITS haplotype networks showed the presence of two highly abundant haplotypes surrounded by low frequency haplotypes that clearly discriminate the two morphotypes. This low variability can be explained by the geographical distribution of the morphotypes. In fact, the “Slender” morphotype is widespread all along the Mediterranean Sea while the “Stocky” morphotype17 has a more restricted distribution. Although we cannot discard the existence of more populations of the “Stocky” morphotype in other unsampled areas of the Atlantic Ocean, information on the geographic distribution of this species in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean is scarce and refers only to the “Slender” morphotype (Boavida J., personal communication). The widespread distribution of the “Slender” morphotype can also explain the low genetic structuring observed among populations.
Despite the limited geographical distribution compared to the “Slender” morphotype, the “Stocky” morphotype shows genetic structure between northeastern Tyrrhenian populations (Portovenere, Portofino, and Giannutri) and the northwestern ones (Banyuls -sur -mer and Alassio) with a break around Portofino. Portofino area represents a barrier to gene flow for several species of sessile invertebrates (Corallium rubrum36; Paramuricea clavata37; Patella caerulea38) related to the presence of a large‐scale separation of currents that occurs in the region39. Biological and reproductive characteristics of the species can also contribute to explain the observed pattern. Pax and Muller40 found hermaphroditic colonies of P. axinellae in the Adriatic Sea, while observed that colonies of P. axinellae from the British Isles (North Atlantic) are gonochoric41. Moreover, Previati et al.42 observed that the “Stocky” morphotype collected in the Ligurian Sea, where the two morphotypes live in sympatry, exhibited both asexual and sexual reproduction (Cerrano C. personal communication). Although not much information is available on the ecological and biological traits of this morphotype, it seems to be defined by a lower dispersal capacity compared to the “Slender” morphotype in this area.
Sardinia samples (codes SRY and SRO) present an intermediate pattern of differentiation, with some samples from both “Slender” and “Stocky” morphs sharing the same sequence with the morphologically distinct phenotype. These identities on ITS-rDNA sequences were already observed within another genus within Parazoanthidae (Antipathozoanthus43). These Authors found that, despite being highly variable compared to mitochondrial markers (due to presence of indels), ITS marker can leave some uncertainties regarding the specific status of different morphotypes. ITS markers are therefore unable to fully resolve the phylogenetic relationships of this group43, which coincides with what was already described for other groups of cnidarians (for instance Eunicella9,44). Hypervariable ITS sequences can lead to alignment challenges (difference in both length and nucleotide identity), and intragenomic variation, that are widely acknowledged as being the primary obstacles to successfully using these sequences in phylogenetic inference in Zoanthidea45. These difficulties stress the need to increase the number of analyzed individuals to detect even small differences that can unlock the relationships among species, particularly in Zoanthidae phylogenetic studies46.
Despite these molecular issues, from the phylogenetic point of view, our results are in accordance with the latest accepted phylogeny of Parazoanthidae24,25 suggesting paraphyly of the genus Parazoanthus. As observed previously by46, the “Slender” P. axinellae is genetically similar to P. anguicomus and, to a lesser extent, to the Atlantic-Caribbean counterparts such as Parazoanthus capensis47. These are Atlantic species which are able to colonize sponges just like P. axinellae, but do not depend on such associations to survive46. The “Stocky” morphotype showed a genetic similarity with the shallow Pacific water P. elongatus, P. juanfernandezii24,46,47,48 and with the deep Atlantic P. aliceae sp. n.24. All these species are mainly found on rocks rather than on sponges, similarly to the “Stocky” morphotype, and conversely to the “Slender” morphotype. However, despite consistency between our molecular results with those by other Authors24,43, genetic data should be taken with caution since discrepancies between genetic and morphological data were already documented. From a morphological point of view, P. elongatus and P. aliceae sp. n. are quite different from the P. axinellae species complex, and do not seem to share similar morphological features, which contradicts the low COI and ITS gene divergence we observed. Specifically, Ocaña and Brito16 recently evidenced that Parazoanthus elongatus from Chile, should be placed into a different genus based on morphological data (e.g. the absence of special spirulae, the scarce presence of mineral particles in the ectoderm, and the large spirulae found in tentacles). This confirms once more that uncovering the origin of the “Stocky” morph in the western Mediterranean is a challenge. Future research using an integrative taxonomy approach13 could complement the results of the present study regarding the status of the Mediterranean Parazoanthus genus. In fact taxonomy using only molecular tools should not be a replacement of classical taxonomy, but findings derived from one approach should be used as a driver for further investigation for the other. A multidisciplinary approach should include (1) reproductive biology of both morphotypes in sympatry, (2) field experiments to evaluate substrate specificity26, (3) studies of chemodiversity49, (4) naturalistic studies16 and (5) more variable molecular markers (e.g. RAD sequencing50; Terzin et al. unpublished) and/or sequencing of the complete mitochondrial genome51.
The results of this work stress the importance of studies on species delimitation and connectivity for the implementation of effective plans for the conservation of coralligenous species. In fact, other studies have observed that in closely related species, with similar biological features, differences in the phylogeographic patterns can occur10,52. Finally, our results highlight occurence of hidden diversity within the flag-genus Parazoanthus, even in well-studied geographical areas, calling for a carefull taxonomic reevaluation of other key-species of the fragile endemic Mediterranean coralligenous ecosystem53.
Methods
The original observation of the occurrence of two clearly distinguishable morphotypes of Parazoanthus was done by SCUBA diving in Portofino where, during the same dive, the “Slender” morphotype was observed in the deeper and in the shallower layers of a cliff, while the “Stocky” morphotype was found at an intermediate depth. Based on these preliminary results we developed a sampling design at a Mediterranean scale identifying sites where the occurrence on Parazoanthus was recorded (Fig. 1c). We identified 11 locations, and in six of them both morphotypes occurred in sympatry (Table 1). In each location up to 30 polyps per morphotype of Parazoanthus were collected by SCUBA diving, keeping a minimum distance of 2 m between polyps to avoid sampling of clones.
All samples were immediately fixed in 80% ethanol and refrigerated at 4ºC.
DNA was extracted from single polyps using EuroClone EuroGold tissue DNA mini kit. Mitochondrial COI fragment was amplified using species-specific designed primers COIpaxFwd (sequence 5′–3′: CGGTATGATAGGAACAGC), and COIpaxRev (sequence5′-3′:CGGGGTCAAAGAAGGTAGTG). A fragment of the nuclear DNA including 18S, ITS-1, 5,8Sa, ITS-2, and 28S (hereafter ITS) was amplified using zoanthid-specific primers described in54. PCR was performed in a final volume of 25 µl per sample and included: 5 µl GoTaq Flexi Buffer 1x (Promega), 4 µl MgCl 25 mM, 0.5 µl dNTPs 10 mM, 0.5 µl of each primer (10 mM), and one unit of GO Taq G2 Flexi DNA polymerase (Promega) and filled with nuclease free water to reach the volume. Amplifications were conducted on a GeneAmp 2,700 thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems) under the following conditions: a hold at 94° C for 3′ followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 45″, annealing at a primer specific temperature (59 °C for COI and 50° C for ITS) for 1′ and extension at 72 °C for 2′, finishing with a final extension at 72° for 7′.
PCR products were checked in 1.5% agarose gel stained with Gelred (BIOTIUM) 1% after a 20′ 120 V electrophoresis. They were then sent to Macrogen Europe Inc. for purification and sequencing.
Field and experimental protocols were approved by the University of Bologna, Italy and were performed in accordance with its relevant guidelines and regulations. No permit was required for the collection of the species.
Data analysis
Sequence quality check and alignment
Each sequence was checked for quality in MEGA v.6 and good quality sequences were aligned using MAFFT (Multiple Alignment using Fast Fourier Transform)55 through phyloch R package56 (see below for more detail).
Genetic diversity and structure among Parazoanthus axinellae samples
The number of haplotypes (H) and haplotype and nucleotide diversity (Hd and π respectively), were calculated for each sample and marker in DNAsp57. Haplotype networks for COI and ITS markers were built using pegas R package35 in Rstudio (Version 1.1.453)58. Haplotypes were reconstructed with haploNet function using an infinite site model based on Hamming distances of DNA sequences. As there was an overlap between genetically approximate haplotypes on the Fig. 2 (in particular for the ITS gene), alluvial diagrams were created using an online platform RAWGraphs59 to better clarify Morphotype/Haplotype/Sampling locations correlations, and Inkscape (version 0.92.4) was used to integrate the plots and finalize graph compilation.
A Minimum Spanning Tree was computed as in60 to infer links between the most similar haplotypes based on a previously computed distance matrix, and to visualize the number of mutations between them. This was done by performing a Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) analysis on Hamming distances computed between haplotypes, using the show.mutation = T option to show the number of mismatches between linked haplotypes. The results were presented as a two-dimensional MDS plot.
Genetic differentiation between samples (with morphs from the same locality treated as different populations) was estimated using Φ statistics (ΦST based on haplotype frequencies and molecular divergence) and its significance determined using a permutation test (10,000 permutations) for each marker in Arlequin v. 3.561. Significance values were corrected for multiple comparisons following FDR correction method62.
Hierarchical Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA) was carried out for each marker using (1) morphotype as grouping factor (two levels: “Slender” and ”Stocky”) and (2) biogeographic areas as grouping factor38: Gulf of Lion and Ligurian Sea (Banyuls-sur-Mer, Alassio, Portofino and Porto Venere), Tyrrhenian Sea (Giannutri, Olbia and Napoli), Ionian and South Adriatic (Gallipoli and Tremiti), and North Adriatic (Chioggia and Rovinj).
To study the demographic history of the two morphotypes Fu and Li33 and Tajima63′s neutrality tests were performed in DNAsp for each locus and morphotype across the study area. Subsequently, the demographic history was also assessed by performing a mismatch distribution analysis, in which the frequencies of pairwise nucleotide differences between individuals were compared with the expected values under a sudden expansion model34 using Arlequin. The best fit was tested by evaluating both the sum of squared deviation (SSD) and the Harpending’s raggedness (HRI) indexes with a total of 1,000 permutations.
Phylogeny and differentiation within Family Parazoanthidae
We retrieved COI and ITS sequences belonging to the family Parazoanthidae from Genbank. Full details on the species, accession numbers, approximate geographic origin, and original reference are given in Supplementary Table S7 for each marker.
We decided to perform all downstream analyses at the taxonomic level of family due to large uncertainties regarding the phylogeny and systematics within Parazoanthidae at lower taxonomic categories, which led to significant and recent taxonomic modifications for these cnidarians (e.g.25,64). For each marker, the retrieved sequences were aligned together with our sequences using multiple sequence aligner MAFFT v7.310 (Multiple Alignment using Fast Fourier Transform)55 through phyloch R package56. P. axinellae + Genbank COI sequences were aligned with default parameters, whereas L-INS-i algorithm with 1,000 iterations (iterative refinement method incorporating local pairwise alignment information) was used to align P. axinellae + Genbank ITS sequences due to a presence of gaps between individuals showing high sequence divergence.
Gblocks Version 0.91b65 was then ran from R to exclude gaps between highly divergent sequences, with parameters finally set to: b1 = 0.8 (the minimum number of sequences for a conserved position), b2 = 0.9, (the minimum number of sequences for a flank position), b4 = 2, (the minimum length of a block, default 2) and b5 = "h", to remove gaps present in > 50% of individuals.
Likelihood ratio test was performed with modelTest function in phangorn66,67 to decide on the model of nucleotide evolution that best fits COI and ITS markers, and the best nucleotide substitution model was identified based on minimum AICc values for each marker separately.
Then, Bayesian inference (BI) in MrBayes v. 3.2.668 and Maximum Likelihood (ML) trees with UPGMA algorithm and clustering dendrograms were used to resolve phylogenetic situation of P. axinellae species complex within Parazoanthidae family based on COI and ITS gene markers. Distance matrices were calculated using the suggested F81 nucleotide substitution model and Maximum Likelihood (ML) trees with 1,000 bootstrap iterations were estimated from the obtained distance matrices using the UPGMA algorithm. This was done in phangorn66,67 by computing the likelihood of a given tree with the function pml(), and with the function optim.pml(), which was used to optimize tree topology and branch length for F81 model of nucleotide evolution. Tree plotting was done using plotBS function, with haplotypes presented on the tree nodes in roman numerals, and bootstrap support values (based on 1,000 iterations) shown on tree branches with a cutoff value of p = 50 (%). To further clarify “haplotype-sampling location” associations, clustering dendrograms were reconstructed for each gene marker in RAWGraphs59 and combined with ML trees in Inkscape (version 0.92.4). Hierarchically, the clustering dendrograms are composed out of 2 levels for sequences downloaded from GenBank (Species code, Number of sequences) and 3 levels for individuals sampled in our study (Morphotype Color, Sampling Location, Number of sequences). Sequences originating from our samples were colored in yellow and orange for “Slender” and “Stocky” morphotypes, respectively, while all sequences downloaded from GenBank are in grey.
Data availability
The dataset and the R codes supporting the conclusions of this article are available in fasta format as additional files in the Supplementary information.
References
Ingrosso, G. et al. Mediterranean bioconstructions along the Italian coast. Adv. Mar. Biol. 79, 61–136 (2018).
Giakoumi, S. et al. Ecoregion-based conservation planning in the mediterranean: dealing with large-scale heterogeneity. PLoS ONE 8, e76449 (2013).
Coll, M. et al. The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: estimates, patterns, and threats. PLoS ONE 5, e11842 (2010).
Airoldi, L. & Beck, M. W. Loss, status and trends for coastal marine habitats of Europe. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 45, 345–405 (2007).
Knowlton, N. Molecular genetic analyses of species boundaries in the sea. Hydrobiologia 420, 73–90 (2000).
Todd, P. A. Morphological plasticity in scleractinian corals. Biol. Rev. 83, 315–337 (2008).
Stefani, F. et al. Comparison of morphological and genetic analyses reveals cryptic divergence and morphological plasticity in Stylophora (Cnidaria, Scleractinia). Coral Reefs 30, 1033–1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-011-0797-4 (2011).
Pinzon, J. H. et al. Blind to morphology: genetics identifies several widespread ecologically common species and few endemics among Indo-Pacific cauliflower corals (Pocillopora, Scleractinia). J. Biogeogr. 40, 1595–1608 (2013).
Costantini, F., Gori, A., Lopez-gonzález, P. & Bramanti, L. Limited genetic connectivity between gorgonian morphotypes along a depth Gradient. PLoS ONE 11, 50–55. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160678 (2016).
Boissin, E., Egea, E., Féral, J. P. & Chenuil, A. Contrasting population genetic structures in Amphipholis squamata, a complex of brooding, self-reproducing sister species sharing life history traits. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 539, 165–177 (2015).
Fukami, H. et al. Geographic differences in species boundaries among members of the Montastraea annularis complex based on molecular and morphological markers. Evolution 58, 324–337 (2004).
Costantini, F., Ferrario, F. & Abbiati, M. Chasing genetic structure in coralligenous reef invertebrates: patterns, criticalities and conservation issues. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–12 (2018).
Pante, E. et al. Species are hypotheses: avoid connectivity assessments based on pillars of sand. Mol. Ecol. 24, 525–544 (2015).
Chenuil, A., Cahill, A. E., Délémontey, N., Du Salliant du Luc, E. & Fanton, H. Problems and questions posed by cryptic species. a framework to guide future studies. In From Assessing to Conserving Biodiversity. History. Philosophy and Theory of the Life Sciences (eds Casetta, E. et al.) 77–106 (Springer, New York, 2019).
Cowen, R. K. Population connectivity in marine systems. Oceanography 20, 14–21 (2007).
Ocaña, O. & Brito, A. Zoanthids parasitizing Anthozoa: taxonomy, ecology and morphological evolution by genomes acquisition. Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. 30, 103–134 (2018).
Ocaña, O. et al. Parazoanthus axinellae: a species complex showing different ecological requierements. Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. XXXI, 1–24 (2019).
Lwowsky, F. F. Revision der Gattung Sidisia Gray (Epizoanthus auct.). Ein Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Zoanthiden. Zool. Jahrbücher, Abteilung für Syst. Ökologie und Geogr. der Tiere 34, 557–614 (1913).
Herberts, C. Contribution a l’etude biologique de quelques zoantharies tempérés et tropicaux II. Relations entre la reproduction sexue ´e, la corissance somatique et le bourgeonnement. Tethys 4, 961–968 (1972).
Ryland, J. S. & Lancaster, J. E. A review of zoanthid nematocyst types and their population structure. Hydrobiologia 530, 179 (2004).
Cariello, L., Crescenzi, S., Prota, G. & Zanetti, L. Methylation of zoanthoxanthins. Tetrahedon 30, 3611–3614 (1974).
Cariello, L., Crescenzi, S., Prota, G. & Zanetti, L. Zoanthoxanthins of a new structural type from Epizoanthus arenaceus (Zoantharia). Tetrahedon 30, 9191–4196 (1974).
Cariello, L. et al. Zoanthoxanthin, a natural 1,2,5,7-tetrazacyclopent[f]-azulene from Parazoanthus axinellae. Tetrahedon 30, 3281–3287 (1974).
Carreiro-Silva, M. et al. Zoantharians (Hexacorallia: Zoantharia) associated with cold-water corals in the azores region: New species and associations in the deep sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 4, 88 (2017).
Montenegro, J., Low, M. E. Y. & Reimer, J. D. The resurrection of the genus Bergia (Anthozoa, Zoantharia, Parazoanthidae). Syst. Biodivers. 14, 63–73 (2016).
Sinniger, F., Montoya-Burgos, J., Chevaldonné, P. & Pawlowski, J. Phylogeny of the order Zoantharia (Anthozoa, Hexacorallia) based on the mitochondrial ribosomal genes. Mar. Biol. 147, 1121–1128 (2005).
Sinniger, F., Reimer, J. D. & Pawlowski, J. Potential of DNA Sequences to Identify Zoanthids (Cnidaria: Zoantharia). Zoolog. Sci. 25, 1253–1260 (2008).
Pax, F. Die Zoanthanen des Golfes von Neapel. Pubbl. della Stn. Zool. di Napoli 30, 309–329 (1957).
Gili, J. M., Pages, F. & Barange, M. Zoantharios (Cnidaria, Anthozoa) de la costa y de la plataforma continental catalanas (Mediterraneo Occidental). Misc. Zool. 11, 13–24 (1987).
Abel, E. F. Zur Kenntnis der mannen Höhlenfauna unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Anthozoen. Pubbl. della Stn. Zool. di Napoli 30, 1–94 (1959).
Cachet, N. et al. Metabolomic profiling reveals deep chemical divergence between two morphotypes of the zoanthid Parazoanthus axinellae. Sci. Rep. 5, 8282 (2015).
Cerrano, C., Totti, C., Sponga, F. & Bavestrello, G. Summer disease in Parazoanthus axinellae (Schmidt, 1862) (Cnidaria, Zoanthidea). Ital. J. Zool. 73, 355–361 (2006).
Fu, Y.-X. & Li, W.-H. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations. Genetics 133, 693–770 (1993).
Rogers, A. R. & Harpending, H. Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9, 552–569 (1992).
Paradis, E. Pegas: An R package for population genetics with an integrated-modular approach. Bioinformatics 26, 419–420 (2010).
Costantini, F., Fauvelot, C. & Abbiati, M. Fine-scale genetic structuring in Corallium rubrum: evidence of inbreeding and limited effective larval dispersal. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 340, 109–119 (2007).
Mokhtar-Jamaï, K. et al. From global to local genetic structuring in the red gorgonian Paramuricea clavata: the interplay between oceanographic conditions and limited larval dispersal. Mol. Ecol. 20, 3291–3305 (2011).
Villamor, A., Costantini, F. & Abbiati, M. Multilocus phylogeography of Patella caerulea (Linnaeus, 1758) reveals contrasting connectivity patterns across the Eastern-Western Mediterranean transition. J. Biogeogr. 45, 1301–1312 (2018).
Rossi, V., Ser-Giacomi, E., Lõpez, C. & Hernández-García, E. Hydrodynamic provinces and oceanic connectivity from a transport network help designing marine reserves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 2883–2891 (2014).
Pax, F. & Muller, I. Die Anthozoenfauna der Adria. Fauna Flora Adriat. 3, 1–343 (1962).
Ryland, J. S. Reproduction in Zoanthidea (Anthozoa: Hexacorallia). Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 31, 177–188 (1997).
Previati, M., Palma, M., Bavestrello, G., Falugi, C. & Cerrano, C. Reproductive biology of Parazoanthus axinellae (Schmidt, 1862) and Savalia savaglia (Bertoloni, 1819) (Cnidaria, Zoantharia) from the NW Mediterranean coast. Mar. Ecol. 31, 555–565 (2010).
Sinniger, F., Reimer, J. D. & Pawlowski, J. The Parazoanthidae (Hexacorallia: Zoantharia) DNA taxonomy: description of two new genera. Mar. Biodivers. 40, 57–70 (2010).
Aurelle, D. et al. Fuzzy species limits in Mediterranean gorgonians (Cnidaria, Octocorallia): inferences on speciation processes. Zool. Scr. 46, 767–778 (2017).
Swain, T. D. Revisiting the phylogeny of Zoanthidea (Cnidaria: Anthozoa): staggered alignment of hypervariable sequences improves species tree inference. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 118, 1–12 (2018).
Sinniger, F. & Häussermann, V. Zoanthids (Cnidaria: Hexacorallia: Zoantharia) from shallow waters of the southern Chilean fjord region, with descriptions of a new genus and two new species. Org. Divers. Evol. 9, 23–36 (2009).
Jaramillo, K. B. et al. Assessing the zoantharian diversity of the Tropical Eastern Pacific through an integrative approach. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–15 (2018).
Swain, T. D. Evolutionary transitions in symbioses: dramatic reductions in bathymetric and geographic ranges of Zoanthidea coincide with loss of symbioses with invertebrates. Mol. Ecol. 19, 2587–2598 (2010).
Samorì, C., Costantini, F., Galletti, P., Tagliavini, E. & Abbiati, M. Inter- and intraspecific variability of nitrogenated compounds in gorgonian corals via application of a fast one-step analytical protocol. Chem. Biodivers. 15, e1700449 (2018).
Pante, E. et al. Use of RAD sequencing for delimiting species. Heredity 14, 450–459. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2014.105 (2014).
Poliseno, A. et al. Evolutionary implications of analyses of complete mitochondrial genomes across order Zoantharia (Cnidaria: Hexacorallia). J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 10, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/jzs.12380 (2020).
Taboada, S. & Pérez-Portela, R. Contrasted phylogeographic patterns on mitochondrial DNA of shallow and deep brittle stars across the Atlantic-Mediterranean area. Sci. Rep. 6, 32425 (2016).
Cerrano, C., Milanese, M. & Ponti, M. Diving for science-science for diving: volunteer scuba divers support science and conservation in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 27, 303–323 (2017).
Swain, T. D. Phylogeny-based species delimitations and the evolution of host associations in symbiotic zoanthids (Anthozoa, Zoanthidea) of the wider Caribbean region. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 156, 223–238 (2009).
Katoh, K., Rozewicki, J. & Yamada, K. MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 20, 1160–1166 (2017).
Heibl, C. PHYLOCH: R language tree plotting tools and interfaces to diverse phylogenetic software packages. http://www.christophheibl.de/Rpackages.html (2008).
Librado, P. & Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25, 1451–1452 (2009).
Team, R. C. R: a language and environment for statistical computing (2018).
Mauri, M., Elli, T., Caviglia, G., Uboldi, G. & Azzi, M. RAWGraphs: a visualisation platform to create open outputs. ACM Int. Conf. Proceeding Ser. Part F1313 (2017).
Paradis, E. Analysis of haplotype networks: The randomized minimum spanning tree method. Methods Ecol. Evol. 9, 1308–1317 (2018).
Excoffier, L. & Lischer, H. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 10, 564–567 (2010).
Narum, S. R. Beyond Bonferroni: less conservative analyses for conservation genetics. Conserv. Genet. 7, 783–787 (2006).
Tajima, F. Statistical methods for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphisms. Genetics 123, 585–595 (1989).
Montenegro, J., Sinniger, F. & Reimer, J. D. Unexpected diversity and new species in the sponge-Parazoanthidae association in southern Japan. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 89, 73–90 (2015).
Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 17, 540–552 (2000).
Schliep, K. Phangorn: phylogenetic analysis in R. Bioinformatics 27, 592–593 (2011).
Schliep, K., Potts, A., Morrison, D. & Grimm, G. Intertwining phylogenetic trees and networks. Methods Ecol. Evol. 8, 212–1220 (2017).
Ronquist, F. et al. MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 61, 539–542 (2012).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to F. Barbieri, G. Bavestrello, L. Benedetti Cecchi, F. Mastrototaro, L Pezzolesi, L. Piazzi, M. Ponti, R. Sandulli for providing samples and S. Tasselli, for helping with lab work. We thank V. Crobe for her precious help on the last version of the manuscript. We really thank Dott. Oscar Ocaña (Museo del Mar de Ceuta), Dott. Alfredo Rosas (Granada University) and the Editor Dr Sergio Stefanni whose comments improved the manuscript. This study is part of the Prin 2010-2011 (MIUR) project on “Coastal bioconstructions: structure, function and management” and the Prin 2015 (MIUR) prot. 2015J922E4 project on “Resistance and resilience of Adriatic mesophotic biogenic habitats to human and climate change threats”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.V., F.C., M.A. performed the sampling design and fieldwork activities; L.S. analyzed the samples in the laboratory; A.V., F.C. and M.T. analyzed the data; all the authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript and revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Villamor, A., Signorini, L.F., Costantini, F. et al. Evidence of genetic isolation between two Mediterranean morphotypes of Parazoanthus axinellae. Sci Rep 10, 13938 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70770-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70770-z
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.