Abstract
Entomopathogenic fungi utilize specific secondary metabolites to defend against insect immunity, thereby enabling colonization of their specific hosts. We are particularly interested in the polyketide synthesis gene pks15, which is involved in metabolite production, and its role in fungal virulence. Targeted disruption of pks15 followed by genetic complementation with a functional copy of the gene would allow for functional characterization of this secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene. Using a Beauveria bassiana ∆pks15 mutant previously disrupted by a bialophos-resistance (bar) cassette, we report here an in-cis complementation at bar cassette using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. A bar-specific short guide RNA was used to target and cause a double-strand break in bar, and a donor DNA carrying a wild-type copy of pks15 was co-transformed with the guide RNA. Isolate G6 of ∆pks15 complemented with pks15 was obtained and verified by PCR, Southern analyses and DNA sequencing. Compared to ∆pks15 which showed a marked reduction in sporulation and insect virulence, the complementation in G6 restored with insect virulence, sporulation and conidial germination to wild-type levels. Atomic force and scanning electron microscopy revealed that G6 and wild-type conidial wall surfaces possessed the characteristic rodlet bundles and rough surface while ∆pks15 walls lacked the bundles and were relatively smoother. Conidia of ∆pks15 were larger and more elongated than that of G6 and the wild type, indicating changes in their cell wall organization. Our data indicate that PKS15 and its metabolite are likely not only important for fungal virulence and asexual reproduction, but also cell wall formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Beauveria bassiana, an entomopathogenic fungus, has a broad host spectrum and is considered to have high potential for insect biocontrol in agriculture. While B. bassiana can cause mycosis in several insect species1,2, insect killing is fairly slow due to several limiting factors, particularly in the field. The fungus is also vulnerable to environmental stress factors such as UV radiation, high temperature and drought3. A better understanding of the biological and physiological characteristics of this entomopathogen should allow us to improve its virulence and stress tolerance.
Secondary metabolites are abundant in entomopathogenic fungi and include polyketides, nonribosomal peptides, terpenes and alkaloids that play important roles in various aspects of the fungal life cycle. B. bassiana BCC2660, a widely used biocontrol fungus in Thailand, has 12 polyketide synthase (PKS) genes in its genome4. Two PKS genes, pks15 and pks14, have crucial roles in virulence against insects, as previously demonstrated by targeted gene deletion4,5. The pks15 mutant exhibits loss in phagocytic survival ability, a phenotype likely associated with changes in the cell wall, the outermost layer of fungal conidia. Unfortunately, little is known regarding the relationship between polyketides and the fungal wall. In a few reports, melanin, the metabolite of a non-reducing PKS and other enzymes in melanin biosynthetic pathway, has been found in the cell walls of Aspergillus fumigatus6, Colletotrichum lagenarium7, Neurospora crassa8 and Pestalotiopsis microspora9. The P. microsopora PKS1 is also important for wall integrity and conidial germination in this endophytic fungus9. In addition, the green pigment citreoisocoumarin, synthesized by a non-reducing PKS, is present in the cell wall of mature A. nidulans conidia10,11. To the best of our knowledge, however, no report thus far has identified a role for a reducing PKS in modulating the fungal wall.
Previously, using a gene knock-out approach, we found that insect virulence of the B. bassiana pks15 deletion mutant was considerably reduced4. Furthermore, our preliminary observation suggested that the spore wall surface of Δpks15 was noticeably different from that of the wild type. In this study, we have set out to investigate whether PKS15 has impact on the fungal wall by performing genetic complementation of Δpks15 by CRISPR/Cas9 to verify the role of PKS15 in cell wall formation.
So far, there have been a few reports on B. bassiana genome editing of using the CRISPR/Cas9 approach. This clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat sequence (CRISPR)/Cas9 system has been developed to perform genome editing in various microorganisms12. This system consists of two components: the Cas9 endonuclease and a single chimeric guide RNA (sgRNA) containing 20-nucleotides matching the target DNA region followed by protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). Base pairing of the sgRNA and the target DNA results in recruitment of Cas9 to generate a specific double-strand break (DSB)13. DSBs can be repaired by either error-free homologous recombination called homology-directed repair (HDR) in the presence of a donor DNA or error-prone repair via non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ). The latter usually leads to a small insertion or deletion in the target sequence, resulting in gene mutation.
Here, we employed CRISPR/Cas9 with HDR to obtain a complemented isolate of B. bassiana Δpks15 with a functional pks15. The complemented isolate was verified by PCR and Southern analyses and examined various phenotypes, namely sporulation, germination, We report the impact of PKS15 in the cell wall formation in this study.
Results
Directed mutagenesis of the bar cassette in the Δpks15 mutant efficiently driven by NHEJ repair
To study the function of PKS15 in B. bassiana BCC 2660, we were interested in generating a PKS15-complemented ∆pks15 mutant by CRISPR/Cas9. However, the CRISPR/Cas9 vector used in this study was previously developed for Aspergillus aculeatus13, so we first tested this vector for its ability to mediate targeted genome editing in the B. bassiana BCC 2660 ∆pks15 mutant. The sgRNA target site was designed based on the nucleotide sequence of the bar cassette previously inserted within pks15 to disrupt gene expression4. A list of candidate bar protospacer sequences was generated using a web-based sgRNA analysis tool (https://bioinfo.imtech.res.in/manojk/gecrispr/index.php). The sequence with the lowest likelihood of off-target binding was selected.
Construction of the bar-targeting vector, pCas9sgBar, was performed by introducing the protospacer into the CRISPR/Cas9 backbone vector via USER cloning13. DNA sequencing was used to verify sequence integrity and the correct sequential order of pCas9sgBar elements. The elements of pCas9sgBar are shown in Supplemental Fig. S1. The vector pCas9sgBar was then transformed into the pks15 mutant using PEG-mediated protoplast transformation. Transformants were first screened for hygromycin resistance conferred by pCas9sgBar. Additionally, as the bar cassette enables growth on medium supplemented with glufosinate4, hygromycin-resistant transformants were subsequently screened for the inability to grow in the presence of glufosinate, which would indicate successful mutation of the bar cassette. Among 50 hygromycin-resistant transformants, two clones, namely A26 and C1, had lost glufosinate resistance (data not shown). Single spore isolation was performed to purify those mutants, and those isolates were again verified for hygromycin resistance and glufosinate sensitivity.
To determine the sequence of bar in A26 and C1, their bar fragments were amplified with a pair of bar-specific primers, cloned into the TA cloning vector pCR 2.1, and submitted for DNA sequencing. Sequencing results showed that clones A26 and C1 both had a one-base insertion in the bar cassette (Table 1). These genome alterations resulted in a frameshift mutation in bar, changing their amino acid sequences. The CRISPR/Cas9 system, therefore, can mediate targeted gene editing in B. bassiana BCC 2660.
In-cis genetic complementation of Δpks15 using CRISPR/Cas9
In addition to directed mutagenesis, the CRISPR/Cas9 system has the potential to mediate targeted genetic complementation via HDR. In Δpks15, the bar cassette has been integrated in pks15, thereby disrupting gene function4. To further verify the role of pks15 in the fungus, a circular DNA donor pCR-PKS15-1k, which has a 1.0 kb pks15 sequence serving as arms for homologous recombination, was co-transformed with pCas9sgBar into ∆pks15 for homologous replacement of bar (Fig. 1a).
(a) A schematic diagram of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in the ∆pks15 mutant by targeting the selection marker gene bar that was used to disrupt pks15. An in-cis complementation of the ∆pks15 mutant was performed by homologous recombination with a wild-type copy of pks15 using the donor DNA pCR-PKS15-1K. Molecular analysis of the pks15 locus of transformants G1, G2 and G6 (from genetic complementation of ∆pks15) was compared to those for the wild type (WT) and Δpks15 using PCR (b, c) and Southern (d) analyses. Primers used for PCR and their locations are shown in (a). (b) PCR amplification with primers PKS15-minus-895F and PKS15-2200R primer. (c) PCR amplifications with primers Bar100F and PKS15-1182R, and PKS15-StartF and Bar360R. (d) Southern blotting results for Δpks15, the complemented isolate G6.6 and the wild type. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI and hybridized with a pks15-specific probe, shown in (a).
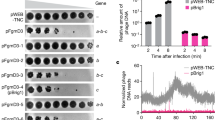
In the genetic complementation of ∆pks15, three transformants (G1, G2 and G6) grew on medium supplemented with hygromycin, but failed to grow on the glufosinate-supplemented one. This indicated the hygromycin resistance and glufosinate sensitivity of the aforementioned transformants (Fig. 2a). We performed molecular analysis of the pks15 locus in transformants G1, G2 and G6 by PCR amplification, in comparison to that of the wild type and Δpks15. The primers’ locations are mapped in Fig. 1a. G6 gave an amplification product of 3.2 kb similar to the wild-type amplicon, whereas G1 and G2 did not (Fig. 1b, left panel). The transformant G6, identified as a complemented isolate of Δpks15, was selected for further experiments and subjected to single spore isolation. It should be noted that, although we did not obtain a high number of transformants in our complementation experiment, one out of three (33%) had correctly repaired the pks15 locus. This recombination frequency is markedly higher than those of homologous recombination performed by conventional, non-CRISPR methods in various B. bassiana strains. For instance, 7–13% recombination was observed for strain Bb006214 and 7–25% for our BCC 2660 strain4,5. After single spore isolation, all ten isolates were re-checked for hygromycin and glufosinate resistance as described above. Three single spore isolates, G6.1, G6.3 and G6.6, were randomly selected for PCR analysis. Those three isolates gave products of similar size as the wild type (Fig. 1a, right panel). Furthermore, we checked for the presence of bar cassette using the bar-specific primers. The pks15 mutant was the only one able to produce bar-derived PCR products, whereas isolates G6.1, 6.3, 6.6 and the wild type did not (Fig. 1c). Southern hybridization also showed that isolate G6.6 had a hybridized band similar to that of the wild type and noticeably shorter than that of Δpks15 (Fig. 1d). The PCR and Southern hybridization data confirmed that the bar cassette had been removed in the complemented isolate G6. Lastly, for the molecular analysis of the pks15 locus, DNA sequencing demonstrated the sequence integrity of pks15 in G6.6, being identical to that of the wild type (Supplemental Fig. S2). Together, these results indicated that replacement of the bar cassette with a wild-type copy of pks15 via CRISPR/Cas9-induced HDR was successful in this entomopathogenic fungus.
(a) Growth of the B. bassiana wild type (WT), Δpks15 and transformants G1, G2 and G6 (from genetic complementation of ∆pks15) on PDA with/without hygromycin B or on a minimal medium containing glufosinate. The three isolates G1, G2 and G6 were resistant to hygromycin B but became sensitive to glufosinate. (b) Virulence against beet armyworm larvae determined by cumulative insect mortalities (%) caused by the B. bassiana wild type, Δpks15 and complemented isolate G6 using a low-dose inoculum (1 × 105 conidia ml−1). Saline was used as the control. (c) Phagocytic assay using the soil amoeba A. castellanii. Mortality rates (%) of the amoebae (A) after incubation with blastospores of the B. bassiana wild type, ∆pks15 and the complemented isolate G6 and S. cerevisiae cells (control). Data shown are mean ± S.E.M. Asterisks indicate statistical significance between the wild type or the complemented isolate G6 and Δpks15 (Student’s t test: *p < 0.05; **< 0.01). (d) Light micrographs of amoebae (A) after incubation with blastospores of the B. bassiana wild type, ∆pks15 and G6 and S. cerevisiae cells for 24 h. The wild type and G6 grew to generate hyphae at this early time point. Bars, 10 µm.
Restoration of wild-type levels of sporulation and germination in the complemented isolate
The sporulation assay has shown that Δpks15 produced significantly fewer conidia and blastospores than the wild type, as we previously reported4. In this study, the complemented isolate G6 restored sporulation, with an increase in the percentage of conidia (37–88%) and blastospores (30–98%) compared to Δpks15, relative to wild-type levels (Table 2). Conidial germination was also restored from 34% in Δpks15 to 77% in the complemented isolate G6 (Table 2).
Restoration of insect virulence and phagocytic survival ability of the complemented isolate
Virulence against the beet armyworm was determined by inoculating low doses (300 conidia) of the wild type, Δpks15 or the complemented isolate G6 into larvae. Mortality data showed that the complemented isolate G6 resulted in similar insect mortalities to that of wild type over the observation period (Fig. 2b). On day 4 post-injection, mycosis and insect death were clearly observed in the worms inoculated by the wild type and the complemented isolate G6, resulting in 30% and 56% mortality, respectively (Fig. 2b). On the other hand, insect larvae injected with Δpks15 exhibited only 10% insect mortality at the same time point. At the end of experiment (day 7 post-injection), the mortality rate of worms inoculated with the wild type and complemented isolate G6 was at 95%, whereas Δpks15-associated mortality was at 60%. The mean lethal time (LT50) of insect larvae injected with the wild type, Δpks15 and complemented isolate G6 was 4.09, 4.71 and 3.95 days, respectively. Thus, the complemented isolate G6 was capable of killing larvae at a rate similar to that of the wild type. These data indicated that the impaired insect virulence of Δpks15 could be restored by complementation with a wild-type copy of pks15, thus further cementing a role for pks15 in insect virulence.
We previously investigated whether PKS15 mediated the first line of insect host defense by assessing the ability of the wild type and Δpks15 in escaping phagocytosis using the soil-dwelling amoeba Acanthamoeba castellanii as a model of study. We found that phagocytic survival was impaired in Δpks15 compared to the wild type4. Here, we studied G6 in a similar assay and conducted microscopy to monitor amoeboid mortality. Similar to the previous result, several blastospores of Δpks15 were engulfed and lysed by the amoeba, whereas most wild-type and G6 blastospores escaped from phagocytosis (Fig. 2d). These blastospores then propagated extensively and switched to a vegetative phase, eventually leading to amoeboid death. Our quantitative data showed that co-culture of wild-type and G6 blastospores with phagocytic amoeba resulted in 40–50% amoeba mortality, while only ~ 20% mortality was seen for Δpks15 at 48 and 72 h after mixing (Fig. 2c). This indicated that the ability of the complemented isolate G6 to counteract with phagocytosis was restored to wild-type levels.
PKS15 is involved in cell wall formation
Since the cell wall is the outermost part of the cell which actively interacts with the surrounding cells, we thus explored the cell wall surface characteristics in the wild type, pks15 mutant and G6. We performed a series of comparative analyses on cell wall characterization used scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to determine the cellular characteristics of conidia used in the insect bioassay and blastospores. The appearance of rodlet bundles on the cell wall surface was the most striking difference seen with the conidia of the wild type and G6 compared to Δpks15 (Fig. 3). Wild-type and G6 conidia had rough wall surfaces and smaller sizes, while mutant conidia had smoother surfaces and larger sizes. Size measurements derived from the scanning electron micrographs indicated that Δpks15 conidia were significantly larger in width, length and size (area) than the wild type and G6 (Fig. 3a,b). The average size of Δpks15 conidia was 1.65 × 2.09 μm (width and length) compared to 1.52 × 1.78 and 1.44 × 1.77 μm for the wild type and G6, respectively (Fig. 3b). The Δpks15 conidia appeared as an ellipse-like shape, compared to circular forms seen for the other two strains.
(a) Scanning electron micrographs (SEMs) of conidia from the wild type (WT), Δpks15 and the complemented isolate G6. It is noted that wild-type and G6 conidia have characteristic rodlet bundles on the wall surface but the pks15 mutant lacks these bundles. Also, this Δpks15 conidium, as a representative of most of the mutant conidia, is larger and more elongated than that of the wild type and G6. Bars, 500 nm. (b) Measurement of width, length and area of conidia from the three strains, as analyzed from the electron micrographs taken. Data shown are mean ± S.E.M. Asterisks indicate statistical significance between the wild type or the complemented isolate G6 and Δpks15 (Student’s t test: *p < 0.05). (c) SEMs of blastospores from WT, Δpks15 and G6. Bars, 1 µm.
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was also performed to visualize conidial wall surface. It revealed a dramatic difference between the wild type and the complemented isolate G6 and that of Δpks15, with wild-type and G6 walls clearly possessing characteristic rodlet bundles, whereas Δpks15 walls lacked such a feature (Fig. 4). However, the arrangement of bundles in the wild type appeared to be more uniform throughout the conidial surface than that of G6, which revealed a few bulges on the surface. The typical bundles disappeared or drastically reduced in size in the Δpks15 conidial surface, with rodlets barely visible. Quantitative analysis of the rodlets showed that the wild type and G6 had similar average numbers of rodlets in each bundle (6.7 ± 1.4 and 6.1 ± 1.3, respectively).
Atomic force micrographs of conidial surfaces from the wild type (WT), Δpks15 and the complemented isolate G6. Amplitude images are shown. Rodlet bundles were found on the surface of wild-type and G6 conidia, but not detected for Δpks15. Bars, 500 and 100 nm for upper and lower panels, respectively.
Lastly, we examined differences in cell wall carbohydrate characteristics by staining conidia and blastospores with concanavalin A, which binds to α-glucan and α-mannan, and calcofluor white, which binds to chitin. Concanavalin A-stained Δpks15 conidia, and blastospores to a lesser extent, exhibited brighter staining patterns compared to wild-type and G6 blastospores under identical staining and microscopic protocols (Figs. 5a, 6a). In contrast, the calcofluor-stained wild type, Δpks15 and G6 conidia (Fig. 5a) as well as blastospores (data not shown) displayed similar fluorescence intensity.
Size and shape of fluorescently-stained conidia in the wild type (WT), Δpks15 and the complemented isolate G6. (a) Calcofluor- and FITC-tagged concanavalin A staining (upper and lower panels). Bars, 5 μm. (b) Distribution of sizes in the conidial populations of the wild type, Δpks15 and G6 from a single representative experiment. (c) Frequency of conidial sizes for each of the three strains. Size data were from three independent experiments. (d) Distribution of shapes in the conidial populations of wild type, Δpks15 and G6 from a single representative experiment. Shape factor (circularity) was determined using the NIS-Elements D software. A shape factor of 1.0 indicates a circle, whereas a shape factor less than 1.0 indicates an ellipse. (e) Frequency of conidial shapes for each of the three strains. Data shown are mean ± s.e.m. Asterisks indicate statistical significance between the wild type or the complemented isolate G6 and Δpks15 (Student’s t-test: *p < 0.05; **< 0.01).
Size and shape of fluorescently-stained blastospores in the wild type (WT), Δpks15 and the complemented isolate G6. (a) FITC-tagged concanavalin A staining. Bars, 5 μm. (b) Frequency of blastospore sizes for each of the three strains. (c) Frequency of blastospore elongation for each of the three strains. Data shown are mean ± S.E.M. Asterisks indicate statistical significance between the wild type or the complemented isolate G6 and Δpks15 (Student’s t-test: *p < 0.05; ns not significant).
We also determined the size and cell characteristics of stained conidia and blastospores. From 2D images, overall conidial size (areas in 2D) of Δpks15 was larger than that of the wild type and complemented isolate G6 (Fig. 5b,c), similar to SEM analysis results. In the wild type and complemented isolate G6, more than 88% of conidia were smaller than 6.0 µm2. In contrast, the ratio of Δpks15 conidia with areas less than to greater than 6.0 µm2 was 55:45. A number of Δpks15 conidia were bigger than 10 µm2, which is unusual and strikingly larger than typical B. bassiana conidia. We then applied the shape factor (circularity) feature in the NIS-Elements D software version 5.10 (Nikon, USA) with the formula [Shape Factor = 4 π (Area)/(Perimeter)2] to analyze conidia shapes. Nearly 40% of the Δpks15 conidial population had an elliptical shape rather than the circular form mostly seen with the wild type and G6 (Fig. 5d,e).
Comparisons of blastospore shapes and sizes did not reveal as large a difference among the three strains. The Δpks15 blastospores were noticeably smaller than the wild type and G6, however. When blastospores were classified as either smaller or larger than 15.0 μm2, Δpks15 blastospores exhibited a 70:30 ratio compared to 76:24 and 80:20 for the wild type and G6, respectively (Fig. 6b). Nonetheless, the differences were not statistically different (p > 0.05). With respect to the shape of blastospores, we assessed their elongation values using the formula [Elongation = MaxFeret/MinFeret]. The Δpks15 blastspores were more elongated than that of the wild type and G6, with nearly all (90%) Δpks15 blastospores being more elongated (elongation value of > 2.0) compared to 67–76% for wild type and G6 blastsopores (Fig. 6b). In contrast, only 10% of Δpks15 blastspores were less elongated (elongation value of < 2.0), compared to 33% and 24% for the wild type and G6 (Fig. 6c), respectively.
Discussion
In our previous report, the gene pks15 was observed to be expressed in almost all culture conditions tested for B. bassiana15, including potato dextrose broth (PDB) (where conidia are produced) and Sabouraud dextrose broth supplemented with 1% yeast extract (SDY) (where in vitro blastospores are formed). We thus hypothesized that PKS15 could be important for fungal growth and development. Indeed, PKS15 is necessary for the formation of conidia and blastospores in this fungus4. SEM and AFM examination of B. bassiana conidia in the current study revealed a remarkable difference in the cell walls, with conidial wall surfaces in the wild type and complemented isolate G6 appearing rough and possessing fascicle bundles of the wall rodlet layer. In contrast, the pks15 mutant’s conidial wall surface was noticeably smoother and completely lacked the bundles. Since the rodlet bundle is mainly composed of hydrophobin in B. Bassiana16, PKS15 could be linked to the presence or assembly of hydrophobin in the cell wall. Nevertheless, the pks15 mutant is not entirely similar to the hydrophobin mutants Δhyd1 and Δhyd1Δhyd2. These two mutants exhibit increased conidial germination compared to the wild type16. In contrast, a noticeably lower percentage of Δpks15 conidia germinate compared to the wild type4. Thus, there could be other components in the cell wall or within the cell that are mediated by PKS15 functions.
Wall carbohydrate staining indicated that there was a marked difference in the fluorescence intensity of concanavalin A staining between the wild type and G6 on the one hand and Δpks15 on the other. This suggests an alteration of mannan and glucan (substrates of concanavalin A binding) organization in the wall of the pks15 mutant. Alternatively, it is possible that target substrates could be more accessible to the corresponding dyes in Δpks15 compared to the wild type and G6 due to the lack of rodlet bundles in Δpks15. Furthermore, the size and shape of the stained conidia were apparently affected by pks15 disruption. Here, we revealed that Δpks15 conidia were significantly larger and more elongated than the wild type and G6. The Δpks15 blastospores were also more elongated. Together, our wall analysis data showed that pks15 disruption results in changes in the spore wall architecture, including rodlet bundle formation and spore size and shape, leading us to surmise that PKS15 could be directly or indirectly involved in cell wall formation. This impact is significant, as the spore wall acts as a rigid frame that predetermines the size and shape of a fungal cell.
Generally, fungal walls are composed of chitin, β-1,3-glucan, β-1,6-glucan, glycoprotein, mannoprotein, and galactomannoprotein17,18, which could influence binding to host receptors and immune invasion19,20. For instance, Candida albicans mannoproteins21, Paecilomyces farinosus galactomannan22,23 and Nomuraea rileyi galactose induce opsonization of fungal cells by insect hosts. Changes in the wall surface may therefore affect host–pathogen interactions, as seen when the loss of chitin and β-1,3 glucan increases the ability of fungal cells to escape insect immune responses24. In mycobacteria, the type I polyketide synthase gene pks13 is important for biosynthesis of mycolic acid, a major wall component of such pathogenic bacteria, and its deletion results in a change in the cell envelope structure25. Mycolic acid-containing glycolipids are also important for virulence in mice26. These observations further support the concept that pks15 plays a role in cell wall formation and subsequently affects virulence in insect hosts.
There are a few cases where fungal polyketides have been associated with insect virulence, sporulation or cell wall formation. For insect virulence, the red pigment oosporein has been reported to be important for B. bassiana virulence against insects, with the authors noting the effects of oosporein on host immunity modulation27 and limiting bacterial growth after host death28. The ΔpksA mutant of the saprophytic fungus Aspergillus parasiticus, which is deficient in biosynthesis of dothistromin (a polyketide structurally related to aflatoxin), was also reported to have reduced sporulation29. Notably, sporulation rates were only a third that of the A. parasiticus wild type, similar to the sporulation impairment seen for B. bassiana Δpks15. In two ascomycetes, Sordaria macrospora and Neurospora crassa, mutants lacking the putative dehydrogenase gene fbm1, which is in a polyketide biosynthesis cluster, were impaired in sexual development, particularly in perithecia formation30. In our current study, the role of PKS15 in cell wall integrity was clearly demonstrated by targeted gene disruption4 and genetic complementation. We therefore hypothesize that PKS15 and its metabolite might have a mechanistic role in cellular signaling during developmental processes, including sporulation, germination and spore wall formation, some of which clearly affect insect virulence. Alternatively, the PKS15 metabolite could directly be a spore wall component. Nonetheless, these two possibilities remain hypothetical and require further experimental proof. While involvement of non-reducing PKSs in cell wall formation have been reported6,7,8,9,10,31. Our study is the first to report a role for a reducing PKS in cell wall formation. Cell wall alteration seen for Δpks15 could account for the impaired phagocytic survival and consequently affect virulence against insects.
CRISPR/Cas9 has recently become one of the most popular molecular tools for genome editing due to its extraordinary capability for modifying genomes of various organisms. However, application of CRISPR/Cas9 editing to filamentous fungi such as B. bassiana is still in a preliminary stage. To our knowledge, there is only one prior study using CRISPR/Cas9 for genome editing in B. bassiana32. Here, we expand the great potential of CRISPR/Cas9 in fungal molecular genetic research by performing an in-cis genetic complementation of Δpks15 in B. bassiana using this technique. Interestingly, we successfully used a CRISPR/Cas9 vector previously developed for A. Aculeatus13 without any modification, despite the phylogenetic distance between A. aculeatus and B. bassiana and the rare occurrence of homologous recombination in filamentous fungi. This success may also be attributed to consideration of circumstances affecting CRISPR/Cas9-driven HDR, as DNA donor characteristics such as DNA form (circular versus linear) and arm sizes affect the repair success rate. For instance, as linear DNA donors are prone to degradation and are considered less efficient than circular DNA donors33, we used a circular DNA donor as the template for HDR. In contrast, attempts with linear donor DNA of similar length were unsuccessful in driving HDR in this fungus (unpublished data). We also used longer flanking regions to increase the efficiency of homologous recombination, as arms 1 kb or longer on either side of a target gene are generally used to facilitate successful recombination in filamentous fungi34. Our study demonstrated that a 600-bp arm was also sufficient to mediate HDR in B. bassiana. This finding is in agreement with a previous report that successfully used 250-bp arms for homologous recombination via CRISPR/Cas932. Our study therefore supports the use of CRISPR/Cas9 as a powerful tool for site-specific mutagenesis and genetic complementation in this fungal entomopathogen.
Methods
Strains, culture conditions and genomic DNA preparation
Beauveria bassiana strain BCC 2660 was obtained from Thailand’s BIOTEC Culture Collection, and the pks15 mutant was previously generated to contain a disruption in pks15, rendering the PKS gene nonfunctional4. The two strains were grown on half-strength potato dextrose agar (PDA; Difco, USA) at 25 °C for 5–7 days for the production of conidia. To produce blastospores, fungal conidia were inoculated in Sabouraud dextrose broth (Difco) supplemented with 1% yeast extract (SDY), and shaken at 150 rpm, 25 °C for 2 days. Escherichia coli strain DH5α was employed for plasmid propagation. For genomic DNA preparation, all fungal strains were grown in SDY as described above. All the cells were collected by centrifugation at 7,500 × g and fungal genomic DNA was extracted as previously described7.
Acanthamoeba castellanii, obtained from the Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand, was grown in peptone-yeast extract-glucose (PYG) broth as previously described4.
General molecular methods
Standard molecular techniques were performed35 for plasmid purification, restriction enzyme analysis and DNA ligation. For PCR amplifications, we used the following thermal cycling program: 5 min at 95 °C; 35 cycles of 15 s at 95 °C, 25 s at 55 °C, and 1–5 min at 72 °C depending on the length of expected PCR products (1 min for a 1-kb product, 2 min for a 2-kb product and 5 min for products 5 kb or longer); and 5 min at 72 °C.
Ligated fragments were transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α, and bacterial clones were screened by PCR amplification with the primers CSN389 and CSN390 to verify the presence of the sgRNA insert. Clones with the correct insert was inoculated in LB and the plasmids were extracted using the GeneJet Plasmid Miniprep Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). The recombinant plasmids were submitted for DNA sequencing (Macrogen, South Korea).
Construction of bar-targeting CRISPR/Cas9 vector (pCas9sgBar)and DNA donor
The CRISPR/Cas9 vector containing sgRNA and Cas9 elements was constructed to generate a DNA DSB at the bar cassette of the Δpks15 mutant. Candidate protospacer sequences targeting bar gene 5′-CCACCTGCTGAAGTCCCTGGAGG-3′ (PAM site underlined) was generated using the sgRNA analysis tool available on the ge-CRISPR website (https://bioinfo.imtech.res.in/manojk/gecrispr/index.php). The CRISPR/Cas9 vectors pFC332 (harboring the hygromycin resistance gene) and pFC334, kindly gifted by Nødvig et al.13, were employed as the backbone vector and sgRNA cassette template, respectively, for the construction of pCas9sgBar. Two fragments for expression of bar-specific sgRNA cassette were amplified using pFC334 as the template. The first 545-bp fragment were amplified with primers CSN389 Fwd (5′-GGGTTTAAUGCGTAAGCTCCCTAATTGGC-3′) and Bar3 RV (5′-AGCTTACUCGTTTCGTCCTCACGGACTCATCAG CCACCTCGGTGATGTCTGCTCAAGCG-3′; the bar sequence is underlined). The second 424-bp fragment was amplified with primers Bar3 Fwd (5′-AGTAAGCUCGTCCCACCTGCTGAAGTCCCTGG GTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAA-3′; the bar sequence is underlined) and CSN390 RV (5′-GGTCTTAAUGAGCCAAGAGCGGATTCCTC-3′). PCR amplification was accomplished using recombinant Taq polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The mentioned two fragments of sgRNA were cloned into two distinct sites PacI/Nt.BbvCI of pFC332 using Uracil-Specific Excision Reagent (USER) fusion (New England Biolabs (NEB), USA).
To construct the circular DNA donor pCR-PKS15-1 k for genetic complementation of the Δpks15 mutant, a 1.0-kb pks15 fragment was cloned into the TA vector pCR™ 2.1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) using PCR amplification of B. bassiana BCC 2660 genomic DNA with the primers PKS15-start (5′-ATGCTCATCGACAAAATGGAG-3′) and PKS15-1182R (5′-CAGCATGAGAGTAGACTTGATGAC-3′). This circular donor DNA has sequences complementary to the 621-bp left arm and 561-bp right arm flanking the bar cassette in the Δpks15 mutant. PCR amplification was performed using Q5 High-Fidelity DNA polymerase (NEB).
PEG-mediated protoplast transformation of ∆pks15 mutant
We performed PEG-mediated protoplast transformation as previously described8. For complementation of Δpks15, pks15 mutant was transformed with pCas9sgBar and/or the donor DNA pCR-PKS15-1 k. For each transformation, a conidial suspension, as harvested from a 7-day old PDA culture, was used as inoculum of 50 ml PDB and shaken at 150 rpm, 25 °C for 16 h. Young mycelia were harvested by centrifugation at 3,000 × g. To generate protoplasts, the mycelia were incubated with the wall-lysing enzyme VinoTaste® Pro (Novozymes, Denmark) at a final concentration of 35 mg ml−1 in 1.2 M MgSO4, 10 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 5.8. The protoplasts were collected by centrifugation at 1,500 × g, 4 °C for 15 min for a pellet of approximately 108 cells. The pellet was gently mixed by pipetting with 160 μl of STC (1.2 M sorbitol, 10 mM CaCl2, 10 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5) and 40 μl of transformation buffer (50% w/v polyethylene glycol (PEG)-4,000 (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and 20 µg of pCas9sgBar (bar-specific sgRNA) and/or 15 µg of pCR-PKS15-1 k (donor DNA). Next, 50% w/v PEG was gently mixed to the protoplast-DNA solution for a total volume of 1,200 µl and left to incubate at room temperature for 20 min. The protoplast solution was then mixed with 8 ml of STC and incubated at room temperature for another 20 min. The mixture was subsequently centrifuged at 1,500 × g, 4 °C for 15 min to collect transformants. The pellet was gently resuspended in 1 ml of PDB supplemented with 1 M sucrose (QReC, New Zealand), and incubated at 28 °C with gentle shaking (70–80 rpm) for 30 min. Finally, 500 μl of the transformation mixture was added to 25 ml of molten PDA supplemented with 1 M sucrose and 200 mg l−1 hygromycin B and poured onto a 150 mm-diameter petri dish. The culture was incubated at 28 °C until fungal colonies appeared (approx. 7–14 days).
Molecular analyses of Δpks15 isolates complemented with pks15
To determine the presence or loss of the bar cassette in the pks15 locus of Δpks15 isolates complemented with pks15, transformed fungi were grown in SDY broth, and genomic DNA was extracted as described above.
We checked for the presence of the bar cassette in the pks15 locus using PCR analysis. For the first two PCR amplifications, two primer pairs: Bar-100F (5′-AAGCACGGTCAACTTCCGTAC-3′) and PKS15-1182R (5′-CAGCATGAGAGTAGACTTGATGAC-3′); and PKS15-start (5′-ATGCTCATCGACAAAATGGAG-3′) and Bar-360R (5′-CTTCAGCAGGTGGGTGTAGA-3′) were used to amplify 1,105-bp and 1,375-bp fragments of the pks15-bar-boundary regions, respectively. For the third PCR amplification, the primer pair PKS15-minus-895F (5′-AATCTGCAGTGCCGAAGCTCCTAACCTCAG-3′) and PKS15-2200R (5′-GCTTATCAATGTGAGCCTCGTC-3′) were used to amplify a 3,095-bp pks15 fragment from the wild type and complemented isolates and a 4,176-bp fragment from the Δpks15 mutant. PCR amplification was performed as described above. Lastly, the PCR fragments were submitted for DNA sequencing (Macrogen).
For Southern analysis, 25 mg of each genomic DNA from B. bassiana wild type, Δpks15 mutant or complemented isolate G6.6 were digested to completion with EcoRI. Digested genomic DNAs were subjected to electrophoresis in a 1% agarose gel, and transferred and cross-linked to a nylon membrane (Hybond N+; GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. To prepare a DNA probe for Southern analysis, a 1.4-kb-long pks15 fragment was amplified with the primers PKS15-minus 925F (5′-TCAAGCTTGCCCGTCACTTG-3′) and PKS15-480R (5′-CAAGCTTCCGGTACGATAGTC-3′), and 100 ng of this DNA fragment was non-radioactively labelled using North2South™ Biotin Random Prime Labeling Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Membrane hybridization and signal detection was performed using North2South™ Chemiluminescent Hybridization and Detection Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The nylon membrane (Amersham Hybond-N + GE Healthcare, Life Sciences) was hybridized with the biotinylated-pks15 probe at 55 °C overnight. After a high stringency wash with 2× saline sodium citrate (SSC)/0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) at 55 °C, the membrane was incubated with a streptavidin–horseradish peroxidase conjugate solution. The hybridized membrane was analysed by a CCD high-resolution chemiluminescence detection system (ChemiDoc™ XRS + System, Bio-Rad, USA).
Insect bioassay and determination of sporulation and germination
To assess insect virulence, conidia of the B. bassiana wild type, Δpks15 mutant, and a complemented isolate were separately harvested in saline (0.85% NaCl), and the density was adjusted to 1 × 105 cells ml−1 using a haemocytometer. Third- to fourth-instar beet armyworm (Spodoptera exigua) larvae were injected with a 3-µl conidial suspension of one of the three fungal strains using a specialized 33-gauge needle-syringe set (Hamilton, USA). Injected larvae were transferred individually into a 24-well plate and fed with an artificial medium6. Saline-injected worms were used as controls. Ten insect larvae were treated for each fungal strain and the saline control. The experiment was repeated three times. Larval mortality was determined on days 1–7 after fungal inoculation. Mean lethal time (LT50) was determined using Probit analysis (SPSS package version 11.5).
To assess sporulation, production of conidia and blastospores were determined on 5-day-old half-strength PDA and in 2-day-old SDY cultures, respectively. PDA and SDY cultures were prepared as described above using 100 µl and 1 ml of conidial suspension at 1 × 107 conidia in sterile water, respectively. To determine conidial germination, conidia were harvested from PDA as described above and resuspended in 5% (v/v) PDB in sterile water. Germination percentage was determined after incubation for 20 h. There were three replicates for each strain, and the experiment was repeated twice.
Phagocytic survival assay
Blastospores were assessed for phagocytic survival in A. castellanii as previously described4, with the yeast S. cerevisiae as a control. Briefly, the B. bassiana wild type and mutants were grown in SDY broth. S. cerevisiae and A. castellanii were grown in YPD broth and PYG broth respectively. After incubation for two days, all cells were collected by centrifugation, filtered (for removal of mycelia in fungal culture) and adjusted to 1 × 105 cells ml−1. Each fungal strain was co-cultured with A. castellanii in 96-well plates at a 1:1 ratio for 72 h in order to determine post-challenge amoeboid survival rates and fungal CFUs. Determination of amoeboid survival rates was performed as previously described4. Trypan blue dye was used to determine the viability of amoebae. The experiment was repeated twice.
Ultrastructural characterization of cell wall surface
For scanning electron microscopy (SEM), PDA-grown conidia were fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde (Electron Microscopy Sciences (EMS), USA) and 2% paraformaldehyde (EMS) in phosphate buffer (0.1 M KH2PO4 and Na2HPO4, pH 7.2), followed by fixation in 1% OsO4 (EMS), as previously described36. The cells were then dehydrated with an ethanol gradient from 30, 50, 70, 80, 90, 95, to 100% ethanol, then critical-point dried using a CO2 drier model HCP-2 (Hitachi, Japan) and sputter-coated with gold-platinum with the Q150R Au/Pt coater (Quorum Technologies, UK). Photographs were taken with SEM model FE-SEM SU-5000 (Hitachi).
For atomic force microscopy (AFM), conidia were prepared by growing fungal strains on PDA for 7 days before conidia were dislodged with 10 ml of sterile water. Conidial suspensions were filtered through eight layers of cheesecloth and the flow-through centrifuged at 13,700 × g for 2 min, rinsed with PBS buffer twice, and finally resuspended in 1 ml of PBS buffer. Sixty microliters of the conidial suspension were dropped on a membrane filter with 1.2 µm pore size (MF-Millipore, Germany) and air-dried overnight. Each conidial sample was mounted on a glass slide and subjected to atomic force microscopy (AFM).
AFM imaging was performed with the NanoWizard 3 AFM system (JPK Instruments, Bruker, USA) mounted on an isolation platform to minimize surrounding noise. Amplitude and phase images were collected in the AC (non-contact) mode under ambient conditions. An amplitude image records the amplitude changes of the oscillating cantilever during the scan, thus reflecting the vertical distance (Z-direction) of the sample. A phase image records the phase difference between the cantilever input signal cycle and the responsive signal cycle, reflecting the mechanical properties of the sample such as stiffness, and adhesion. The AFM cantilever for this study was a non-contact mode silicon AFM cantilever (product no. ACTA, AppNano, USA) with a nominal spring constant of 37 N m−1 and a tip radius of curvature of approximately 6 nm. The images were recorded at a scanning speed of 0.5 Hz at different resolutions, including 256 × 256 pixels, or 512 × 512 pixels.
Cell wall staining
Beauveria bassiana conidia and blastospores were collected from 7-day-old PDA and 2-day-old SDY cultures, respectively, and rinsed once with PBS. Spores were stained with concanavalin A conjugated with the fluorophore FITC (Sigma-Aldrich) and calcofluor white (Sigma-Aldrich). For conA staining, spores were fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde (in 100 µl) for 20 min and rinsed with PBS once. Then, the spores were incubated in 20 µl of 1 mg ml−1 conA in PBS (pH 7.4) for 60 min and rinsed once with PBS. For calcofluor staining, spores were incubated in a 1:1 mixture of 5 mg ml−1 calcofluor white in PBS (pH 7.4) and 1 M KOH in a total volume of 200 µl. The cell staining mixture was incubated at room temperature for 2 min. Stained spores were collected by centrifugation at 6,729 × g for 1 min and rinsed once with PBS.
Confocal and fluorescence microscopy and cell measurements of stained fungal spores
The concanavalin A- and calcofluor-stained fungal spores were wet-mounted onto glass slides and covered with No.1 (0.13-0.16 um thickness) cover glass (BRAND, Germany). Fluorescence images were acquired by the Nikon Eclipse Ti-2E using the Nikon Plan Apo VC 100 × oil objective lens (numerical aperture (N.A.) = 1.40). Images were captured at 2,880 × 2,048 pixels in TIFF format.
For confocal laser scanning microscopy, we used the Olympus FV1000 confocal laser scanning system configured with the Olympus IX81 inverted microscope with the Olympus UIS2 UPLSAPO 100 × oil objective lens (N.A. = 1.4). All images were recorded at a resolution of 1,600 × 1,600 pixels using a 100 × oil immersion objective lens with a 3 × digital zoom. Parameters for calcofluor staining images were as follows: laser power, 20%; HV, 400–500; gain, 1 and pinhole, 150–155 (auto). Parameters for concanavalin A staining images were as follows: laser power, 30%; HV, 600–650; gain, 1–3 and pinhole, 150–155 (auto). For each image, the offset voltage was adjusted until the background appeared black or nearly so. Kalman filtering (n = 6) was generally used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of images. All images were captured as TIFF files.
Spore sizes and shapes were compared using two dimensional image analysis of conA- or calcofluor-stained spores taken by the Eclipse Ti-2E and the NIS-Elements software (Nikon). For determination of spore sizes, the ‘5 Point Ellipse’ feature for area measurement of NIS-Elements was manually used to mark the boundary of a conidium and the ‘Auto Detect’ feature was used to mark the boundary of a blastospore (Supplemental Fig. S3). Consequently, ‘size’ was automatically determined as ‘area’ by the software. Budding blastospores were excluded from the analysis.
In NIS-Elements, shape factor, calculated using the formula shape factor = 4πA/P2 where A = area and P = perimeter, was used to determine whether a spore is circular or elliptical in shape. The shape factor value of a circle equals 1.00, whereas values less than 1.00 indicates an ellipse.
Statistical analyses
All experiments in this study were repeated two or three times. There were three replicates for each fungal strain in a given experiment. Data were analyzed for statistical significance using ANOVA in SPSS package version 11.5 and the student’s t-test. LT50 was determined using Probit analysis in the SPSS package.
References
Roberts, D. W. & Hajek, A. E. Entomopathogenic fungi as bioinsecticides. In Frontiers of industrial mycology (ed. Leatham, G. F.) 144–159 (CRC Press, Kentucky, 1992).
Bidochka, M. J., Kamp, A. M. & De Croos, J. N. A. Insect pathogenic fungi: From genes to populations. In Fungal Pathology (ed Kronstad, J. W.) 171–193 (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000).
Kaiser, D., Bacher, S., Mène-Saffranè, L. & Grabenweger, G. Efficiency of natural substances to protect Beauveria bassiana conidia from UV radiation. Pest. Manag. Sci. 5(2), 556–563 (2018).
Toopaang, W. et al. Targeted disruption of the polyketide synthase gene pks15 affects virulence against insects and phagocytic survival in the fungus Beauveria bassiana. Fungal Biol. 121, 664–675 (2017).
Srisuksam, C. et al. The reducing clade IIb polyketide synthase PKS14 acts as a virulence determinant of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 365(15), fny131 (2018).
Thywißen, A. et al. Conidial dihydroxynaphthalene melanin of the human pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus Interferes with the Host Endocytosis Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2, 96 (2011).
Takano, Y. et al. The Colletotrichum lagenarium MAP kinase gene CMK1 regulates diverse aspects of fungal pathogenesis. Mol. Plant Microbe In. 13(4), 374–383 (2000).
Ao, J., Bandyopadhyay, S. & Free, S. J. Characterization of the Neurospora crassa DHN melanin biosynthetic pathway in developing ascospores and peridium cells. Fungal Biol. 123(1), 1–9 (2019).
Mayorga, M. E. & Timberlake, W. E. The developmentally regulated Aspergillus nidulans wAgene encodes a polypeptide homologous to polyketide and fatty acid synthases. Mol. Genet. Genom. 235, 205–212 (1992).
Watanabe, A. et al. Product identification of polyketide synthase coded by Aspergillus nidulans wA gene. Tetrahedron Lett. 39(42), 7733–7736 (1998).
Yu, X. et al. Melanin is required for the formation of the multi-cellular conidia in the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis microspora. Microbiol. Res. 179, 1–11 (2015).
Sander, J. D. & Joung, J. K. CRISPR/Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 347–355 (2014).
Nødvig, C. S., Nielsen, J. B., Kogle, M. E. & Mortensen, U. H. A CRISPR-Cas9 system for genetic engineering of filamentous fungi. PLoS ONE 10, e0133085 (2015).
Ma, J. C. et al. The size and ratio of homologous sequence to non-homologous sequence in gene disruption cassette influences the gene targeting efficiency in Beauveria bassiana. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 82(5), 891–898 (2009).
Punya, J. et al. Phylogeny of type I polyketide synthases (PKSs) in fungal entomopathogens and expression analysis of PKS genes in Beauveria bassiana BCC 2660. Fungal Biol. 119, 538–550 (2015).
Zhang, S., Xia, Y. X., Kim, B. & Keyhani, N. O. Two hydrophobins are involved in fungal spore coat rodlet layer assembly and each play distinct roles in surface interactions, development and pathogenesis in the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Mol. Microbiol. 80(3), 811–826 (2011).
Cabib, E., Bowers, B., Sburlati, A. & Silverman, S. J. Fungal cell wall synthesis: The construction of a biological structure. Microbiol. Sci. 5, 370–375 (1988).
San-Bias, G. The cell wall of fungal human pathogens: Its possible role in host-parasite relationships. Mycopathologia 79, 159–184 (1982).
Esquenazi, D., de Souza, W., Alviano, C. S. & Rozental, S. The role of surface carbohydrates on the interaction of microconidia of Trichophyton mentagrophytes with epithelial cells. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 35, 113–123 (2003).
Masuoka, J. Surface glycans of Candida albicans and other pathogenic fungi: Physiological roles, clinical uses, and experimental challenges. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 17, 281–310 (2004).
Calderone, R. A. & Braun, P. C. Adherence and receptor relationships of Candida albicans. Microbiol. Rev. 55, 1–20 (1991).
Pendland, J. C. & Boucias, D. G. Variations in the ability of galactose and mannose-specific lectins to bind to cell-wall surfaces during growth of the insect pathogenic fungus Paecilomyces farinosus. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 60, 322–330 (1993).
Pendland, J. C. & Boucias, D. G. Phagocytosis of lectinopsonized fungal cells and endocytosis of the ligand by insect Spodoptera exigua granular hemocytes: An ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 285, 57–67 (1996).
Beauvais, A., Latge, J. P., Vey, A. & Prevost, M. C. The role of surface components of the entomopathogenic fungus Entomophaga aulicae in the cellular immune response of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera). J. Gen. Microbiol. 135, 489–498 (1989).
Portevin, D. et al. A polyketide synthase catalyzes the last condensation step of mycolic acid biosynthesis in mycobacteria and related organisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 314–319 (2004).
Gotoh, K., Mitsuyama, M., Imaizumi, S., Kawamura, I. & Yano, I. Mycolic acid-containing glycolipid as a possible virulence factor of Rhodococcus equi for mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 35, 175–185 (1991).
Feng, P., Shang, Y., Cen, K. & Wang, C. Fungal biosynthesis of the bibenzoquinone oosporein to evade insect immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 11365–11370 (2015).
Fan, Y. et al. Regulatory cascade and biological activity of Beauveria bassiana oosporein that limits bacterial growth after host death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, E1578–E1586 (2017).
Bradshaw, R. E. et al. A polyketide synthase gene required for biosynthesis of the aflatoxin-like toxin, dothistromin. Mycopathol. 161, 283–294 (2006).
Nowrousian, M. A novel polyketide biosynthesis gene cluster is involved in fruiting body morphogenesis in the filamentous fungi Sordaria macrospora and Neurospora crassa. Curr. Genet. 55, 185–198 (2009).
Wang, J. et al. A polyketide synthase, BbpksP, contributes to conidial cell wall structure and UV tolerance in Beauveria bassiana. J. Invertebr. Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2019.107280 (2020).
Chen, J. et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated efficient genome editing via blastospore-based transformation in entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Sci Rep. 8, 45763 (2017).
Nielsen, M. L. et al. Genes linked to production of secondary metabolites in Talaromyces atroroseus revealed using CRISPR-Cas9. PLoS ONE 12(1), e0169712 (2017).
Deng, H., Gao, R., Liao, X. & Cai, Y. Genome editing in Shiraia bambusicola using CRISPR-Cas9 system. J. Biotechnol. 259, 228–234 (2017).
Sambrook, J., Russell, D. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual 3rd edn (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2001).
Amnuaykanjanasin, A. et al. Infection and colonization of tissues of the aphid Myzus persicae and cassava mealybug Phenacoccus manihoti by the fungus Beauveria bassiana. BioControl 58(3), 379–391 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We greatly thank Drs. Nødvig and Mortensen for kindly providing the CRISPR/Cas9 vectors pFC331-334 used in this study, Dr. Samaporn Teeravechyan for critically reading and editing the manuscript and Dr. Kalabaheti, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Topical Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand, for the gift of Acanthamoeba castellanii. We are grateful for use of the AFM system at the National Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC), Thailand. This research was supported by the National Center for Genetic Engineering (BIOTEC) postdoctoral fellowship to SU and grants from the Research Development Innovation Management for National Strategic and Network Division (RNS) and BIOTEC, NSTDA, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.A., S.U. and M.T. designed the research. A.A. and S.U. wrote the manuscript. S.U. and W.T. constructed recombinant DNAs for CRISPR/Cas9 experiments. S.U. performed fungal transformation and molecular and phenotypic analyses of B. bassiana strains. R.W. and C.S. carried out insect bioassay. U.S., S.U., N.W., N.A.S.N. and A.A. conducted cell wall characterizations.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Udompaisarn, S., Toopaang, W., Sae-Ueng, U. et al. The polyketide synthase PKS15 has a crucial role in cell wall formation in Beauveria bassiana. Sci Rep 10, 12630 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69417-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69417-w
This article is cited by
-
Genome editing for resistance against plant pests and pathogens
Transgenic Research (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.