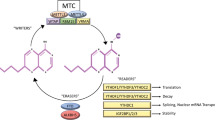
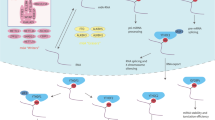
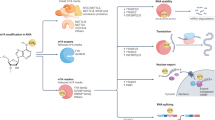
Abstract
The N6‐methyladenosine (m6A) modification is the most common modification of messenger RNAs in eukaryotes and has crucial roles in multiple cancers, including in urological malignancies such as renal cell carcinoma, bladder cancer and prostate cancer. The m6A RNA modification is controlled by three types of regulators, including methyltransferases (writers), demethylases (erasers) and RNA‐binding proteins (readers), which are responsible for gene regulation at the post-transcriptional level. This Review summarizes the current evidence indicating that aberrant or dysregulated m6A modification is associated with urological cancer development, progression and prognosis. The complex and context-dependent effects of dysregulated m6A modifications in urological cancers are described, along with the potential for aberrantly expressed m6A regulators to provide valuable diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers as well as new therapeutic targets.
Key points
-
RNA m6A (N6 methyladenosine) modifications contribute to the occurrence and progression of urological cancers, including renal cell carcinoma, bladder cancer and prostate cancer.
-
Aberrant m6A modification promotes malignant transformation and drives proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion and metastasis of urological cancers via changes in autophagy, glycolysis, mitochondrial metabolism, stemness remodelling and the tumour microenvironment.
-
RNA m6A modifications have complex and heterogeneous roles in urological cancers; some m6A regulators have both tumour-suppressing and tumour-promoting effects on cancer progression.
-
Various m6A modifiers involved in writing, reading and erasing of m6A modifications participate in intricate and dynamic signalling networks associated with urological cancer cell proliferation, differentiation, invasion and treatment resistance.
-
Preclinical studies have demonstrated potential benefits of targeting m6A modifiers in urological malignancies, but no phase II clinical trials have been conducted so far.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray, F. et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394–424 (2018).
Mariotto, A. B., Yabroff, K. R., Shao, Y., Feuer, E. J. & Brown, M. L. Projections of the cost of cancer care in the United States: 2010–2020. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 103, 117–128 (2011).
Li, X. et al. The M6A methyltransferase METTL3: acting as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 8, 96103–96116 (2017).
Chen, M. et al. m6A RNA methylation regulators can contribute to malignant progression and impact the prognosis of bladder cancer. Biosci. Rep. 39, BSR20192892 (2019).
Liu, Q. et al. Molecular characterization and clinical relevance of N6-methyladenosine regulators in metastatic prostate cancer. Front. Oncol. 12, 914692 (2022).
Lin, H., Wang, Y., Wang, P., Long, F. & Wang, T. Mutual regulation between N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and circular RNAs in cancer: impacts on therapeutic resistance. Mol. Cancer 21, 148 (2022).
Shen, S. et al. Comprehensive analyses of m6A regulators and interactive coding and non-coding RNAs across 32 cancer types. Mol. Cancer 20, 67 (2021).
An, Y. & Duan, H. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism. Mol. Cancer 21, 14 (2022).
Liu, Z. et al. Biological and pharmacological roles of m6A modifications in cancer drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 21, 220 (2022).
Deng, L. J. et al. m6A modification: recent advances, anticancer targeted drug discovery and beyond. Mol. Cancer 21, 52 (2022).
Desrosiers, R., Friderici, K. & Rottman, F. Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 71, 3971–3975 (1974).
Ke, S. et al. A majority of m6A residues are in the last exons, allowing the potential for 3′ UTR regulation. Genes. Dev. 29, 2037–2053 (2015).
Zhang, H. et al. Dynamic landscape and evolution of m6A methylation in human. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, 6251–6264 (2020).
Liu, L. et al. Insights into N6-methyladenosine and programmed cell death in cancer. Mol. Cancer 21, 32 (2022).
He, L. et al. Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer. Mol. Cancer 18, 176 (2019).
Qin, Y. et al. Role of m6A RNA methylation in cardiovascular disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 46, 1958–1972 (2020).
Wang, J., Chen, L. & Qiang, P. The role of IGF2BP2, an m6A reader gene, in human metabolic diseases and cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 21, 99 (2021).
Shulman, Z. & Stern-Ginossar, N. The RNA modification N6-methyladenosine as a novel regulator of the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 21, 501–512 (2020).
Dai, D., Wang, H., Zhu, L., Jin, H. & Wang, X. N6-methyladenosine links RNA metabolism to cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 9, 124 (2018).
Huang, J. & Yin, P. Structural insights into N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in the transcriptome. Genomics Proteom. Bioinforma. 16, 85–98 (2018).
Wang, X. et al. Structural basis of N6-adenosine methylation by the METTL3–METTL14 complex. Nature 534, 575–578 (2016).
Ping, X. L. et al. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell. Res. 24, 177–189 (2014).
Yue, Y. et al. VIRMA mediates preferential m6A mRNA methylation in 3′UTR and near stop codon and associates with alternative polyadenylation. Cell. Discov. 4, 10 (2018).
Knuckles, P. et al. Zc3h13/Flacc is required for adenosine methylation by bridging the mRNA-binding factor Rbm15/Spenito to the m6A machinery component Wtap/Fl(2)d. Genes. Dev. 32, 415–429 (2018).
Wen, J. et al. Zc3h13 regulates nuclear RNA m6A methylation and mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Mol. Cell 69, 1028–1038 e6 (2018).
Ma, H. et al. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase ZCCHC4 mediates ribosomal RNA methylation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 15, 88–94 (2019).
Goh, Y. T., Koh, C. W. Q., Sim, D. Y., Roca, X. & Goh, W. S. S. METTL4 catalyzes m6Am methylation in U2 snRNA to regulate pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, 9250–9261 (2020).
van Tran, N. et al. The human 18 S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 is stabilized by TRMT112. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, 7719–7733 (2019).
Nance, D. J. et al. Characterization of METTL16 as a cytoplasmic RNA binding protein. PLoS ONE 15, e0227647 (2020).
Mauer, J. et al. Reversible methylation of m6Am in the 5′ cap controls mRNA stability. Nature 541, 371–375 (2017).
Wang, T., Kong, S., Tao, M. & Ju, S. The potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 19, 88 (2020).
Li, W., Hao, Y., Zhang, X., Xu, S. & Pang, D. Targeting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification: a precise weapon in overcoming tumor immune escape. Mol. Cancer 21, 176 (2022).
Jia, G. et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7, 885–887 (2011).
Gerken, T. et al. The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science 318, 1469–1472 (2007).
Wei, J. et al. Differential m6A, m6Am, and m1A demethylation mediated by FTO in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. Mol. Cell 71, 973–985 e5 (2018).
Fu, Y. et al. FTO-mediated formation of N6-hydroxymethyladenosine and N6-formyladenosine in mammalian RNA. Nat. Commun. 4, 1798 (2013).
Zheng, G. et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol. Cell 49, 18–29 (2013).
Ueda, Y. et al. AlkB homolog 3-mediated tRNA demethylation promotes protein synthesis in cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 7, 42271 (2017).
Ueda, Y. et al. A real-time PCR-based quantitative assay for 3-methylcytosine demethylase activity of ALKBH3. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 5, 476–481 (2016).
Esteve-Puig, R. et al. Epigenetic loss of m1A RNA demethylase ALKBH3 in Hodgkin lymphoma targets collagen, conferring poor clinical outcome. Blood 137, 994–999 (2021).
Yang, Y., Hsu, P. J., Chen, Y. S. & Yang, Y. G. Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 28, 616–624 (2018).
Kasowitz, S. D. et al. Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates alternative polyadenylation and splicing during mouse oocyte development. PLoS Genet. 14, e1007412 (2018).
Wojtas, M. N. et al. Regulation of m6A transcripts by the 3′ → 5′ RNA helicase YTHDC2 is essential for a successful meiotic program in the mammalian germline. Mol. Cell 68, 374–387.e12 (2017).
Saito, Y. et al. YTHDC2 control of gametogenesis requires helicase activity but not m6A binding. Genes. Dev. 36, 180–194 (2022).
Zhang, Z. et al. The YTH domain is a novel RNA binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 14701–14710 (2010).
Shi, H. et al. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 27, 315–328 (2017).
Liu, N. et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature 518, 560–564 (2015).
Wu, B. et al. Molecular basis for the specific and multivariant recognitions of RNA substrates by human hnRNP A2/B1. Nat. Commun. 9, 420 (2018).
Chao, J. A. et al. ZBP1 recognition of β-actin zipcode induces RNA looping. Genes. Dev. 24, 148–158 (2010).
Bell, J. L. et al. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression? Cell Mol. Life Sci. 70, 2657–2675 (2013).
Zhao, Y., Shi, Y. & Shen, H. & Xie, W.m6A-binding proteins: the emerging crucial performers in epigenetics. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13, 35 (2020).
Alarcón, C. R. et al. HNRNPA2B1 is a mediator of m6A-dependent nuclear RNA processing events. Cell 162, 1299–1308 (2015).
Linehan, W. M. & Ricketts, C. J. The Cancer Genome Atlas of renal cell carcinoma: findings and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Urol. 16, 539–552 (2019).
Bi, K. et al. Tumor and immune reprogramming during immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 39, 649–661.e5 (2021).
Shi, Y. et al. The RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of kidney cancer via N6-methyladenosine-dependent translational enhancement of ABCD1. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 737498 (2021).
Baarine, M., Beeson, C., Singh, A. & Singh, I. ABCD1 deletion-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is corrected by SAHA: implication for adrenoleukodystrophy. J. Neurochem. 133, 380–396 (2015).
Zhu, D. et al. The methyltransferase METTL3 promotes tumorigenesis via mediating HHLA2 mRNA m6A modification in human renal cell carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 20, 298 (2022).
Chen, L. et al. Overexpression of HHLA2 in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma is significantly associated with poor survival of the patients. Cancer Cell Int. 19, 101 (2019).
Qi, F. et al. BTG2 suppresses renal cell carcinoma progression through N6-methyladenosine. Front. Oncol. 12, 1049928 (2022).
Wang, Q. et al. Identification of METTL14 in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma using bioinformatics analysis. Dis. Markers 2019, 5648783 (2019).
Zhang, L., Luo, X. & Qiao, S. METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of Pten mRNA inhibits tumour progression in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 127, 30–42 (2022).
Liu, T. et al. Methyltransferase-like 14 suppresses growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by decreasing long noncoding RNA NEAT1. Cancer Sci. 113, 446–458 (2022).
Shen, D. et al. METTL14-mediated Lnc-LSG1 m6A modification inhibits clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis via regulating ESRP2 ubiquitination. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 27, 547–561 (2022).
Liu, Z., Sun, T., Piao, C., Zhang, Z. & Kong, C. METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of ITGB4 mRNA inhibits metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 20, 36 (2022).
Ying, Y. et al. EGR2-mediated regulation of m6A reader IGF2BP proteins drive RCC tumorigenesis and metastasis via enhancing S1PR3 mRNA stabilization. Cell Death Dis. 12, 750 (2021).
Huo, F. C., Xie, M., Zhu, Z. M., Zheng, J. N. & Pei, D. S. SHMT2 promotes the tumorigenesis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating the m6A modification of PPAT. Genomics 114, 110424 (2022).
Jiang, Z. et al. Analysis of RNA-binding protein IMP3 to predict metastasis and prognosis of renal-cell carcinoma: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 7, 556–564 (2006).
Pei, X. et al. Enhanced IMP3 expression activates NF-кB pathway and promotes renal cell carcinoma progression. PLoS ONE 10, e0124338 (2015).
Gu, Y. et al. DMDRMR-mediated regulation of m6A-modified CDK4 by m6A reader IGF2BP3 drives ccRCC progression. Cancer Res. 81, 923–934 (2021).
Li, A. et al. ZNF677 suppresses renal cell carcinoma progression through N6-methyladenosine and transcriptional repression of CDKN3. Clin. Transl. Med. 12, e906 (2022).
Xu, Y. et al. FTO-mediated autophagy promotes progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via regulating SIK2 mRNA stability. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 18, 5943–5962 (2022).
Zhuang, C. et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma through a novel FTO-PGC-1α signalling axis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 23, 2163–2173 (2019).
Zeng, X. et al. Epigenetic activation of RBM15 promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma growth, metastasis and macrophage infiltration by regulating the m6A modification of CXCL11. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 184, 135–147 (2022).
Zhang, X. et al. ALKBH5 promotes the proliferation of renal cell carcinoma by regulating AURKB expression in an m6A-dependent manner. Ann. Transl. Med. 8, 646 (2020).
Yang, L. et al. CircMET promotes tumor proliferation by enhancing CDKN2A mRNA decay and upregulating SMAD3. Mol. Cancer 21, 23 (2022).
Li, Y., Su, R., Deng, X., Chen, Y. & Chen, J. FTO in cancer: functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Trends Cancer 8, 598–614 (2022).
Panneerdoss, S. et al. Cross-talk among writers, readers, and erasers of m6A regulates cancer growth and progression. Sci. Adv. 4, eaar8263 (2018).
Saginala, K. et al. Epidemiology of bladder cancer. Med. Sci. 8, 15 (2020).
Griffiths, T. R., Action on Bladder Cancer. Current perspectives in bladder cancer management. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 67, 435–448 (2013).
Powles, T. & Morrison, L. Biomarker challenges for immune checkpoint inhibitors in urothelial carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 15, 585–587 (2018).
Crabb, S. J. & Douglas, J. The latest treatment options for bladder cancer. Br. Med. Bull. 128, 85–95 (2018).
Yang, F. et al. Dynamic m6A mRNA methylation reveals the role of METTL3-m6A-CDCP1 signaling axis in chemical carcinogenesis. Oncogene 38, 4755–4772 (2019).
Ying, X. et al. Targeted m6A demethylation of ITGA6 mRNA by a multisite dCasRx-m6A editor inhibits bladder cancer development. J. Adv. Res https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2023.03.010 (2023).
Cheng, M. et al. The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes bladder cancer progression via AFF4/NF-κB/MYC signaling network. Oncogene 38, 3667–3680 (2019).
Xie, H. et al. METTL3/YTHDF2 m6A axis promotes tumorigenesis by degrading SETD7 and KLF4 mRNAs in bladder cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24, 4092–4104 (2020).
Gao, Q. et al. The m6A methylation-regulated AFF4 promotes self-renewal of bladder cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Int. 2020, 8849218 (2020).
Wang, G. et al. Deficiency of Mettl3 in bladder cancer stem cells inhibits bladder cancer progression and angiogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 627706 (2021).
Ni, Z. et al. JNK signaling promotes bladder cancer immune escape by regulating METTL3-mediated m6A modification of PD-L1 mRNA. Cancer Res. 82, 1789–1802 (2022).
Azzam, S. K., Alsafar, H. & Sajini, A. A. FTO m6A demethylase in obesity and cancer: implications and underlying molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 3800 (2022).
Deng, H. et al. Identification and validation of N6-methyladenosine-related biomarkers for bladder cancer: implications for immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 12, 820242 (2022).
Tao, L. et al. FTO modifies the m6A level of MALAT and promotes bladder cancer progression. Clin. Transl. Med. 11, e310 (2021).
Song, W., Yang, K., Luo, J., Gao, Z. & Gao, Y. Dysregulation of USP18/FTO/PYCR1 signaling network promotes bladder cancer development and progression. Aging 13, 3909–3925 (2021).
Yi, W. et al. The tumor-suppressive effects of α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase FTO via N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation on bladder cancer patients. Bioengineered 12, 5323–5333 (2021).
Liu, P. et al. m6A-induced lncDBET promotes the malignant progression of bladder cancer through FABP5-mediated lipid metabolism. Theranostics 12, 6291–6307 (2022).
Guimaraes-Teixeira, C. et al. Downregulation of m6A writer complex member METTL14 in bladder urothelial carcinoma suppresses tumor aggressiveness. Mol. Oncol. 16, 1841–1856 (2022).
Huang, J., Zhou, W., Hao, C., He, Q. & Tu, X. The feedback loop of METTL14 and USP38 regulates cell migration, invasion and EMT as well as metastasis in bladder cancer. PLoS Genet. 18, e1010366 (2022).
Gu, C. et al. Mettl14 inhibits bladder TIC self-renewal and bladder tumorigenesis through N6-methyladenosine of Notch1. Mol. Cancer 18, 168 (2019).
Wang, K. et al. m6A writer WTAP targets NRF2 to accelerate bladder cancer malignancy via m6A-dependent ferroptosis regulation. Apoptosis 28, 627–638 (2023).
Barros-Silva, D. et al. VIRMA-dependent N6-methyladenosine modifications regulate the expression of long non-coding RNAs CCAT1 and CCAT2 in prostate cancer. Cancers 12, 771 (2020).
Sung, H. et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71, 209–249 (2021).
Cai, J. et al. RNA m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the growth of prostate cancer by regulating hedgehog pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 12, 9143–9152 (2019).
Ma, X. X., Cao, Z. G. & Zhao, S. L. m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of prostate cancer via m6A-modified LEF1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 3565–3571 (2020).
Chen, Y. et al. Silencing of METTL3 effectively hinders invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer cells. Theranostics 11, 7640–7657 (2021).
Li, J. et al. YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors to induce AKT phosphorylation in N6-methyladenosine-dependent way in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer 19, 152 (2020).
Wang, D. et al. METTL3 promotes prostate cancer progression by regulating miR-182 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Andrologia 54, 1581–1591 (2022).
Liu, J., Yuan, J. F. & Wang, Y. Z. METTL3-stabilized lncRNA SNHG7 accelerates glycolysis in prostate cancer via SRSF1/c-Myc axis. Exp. Cell Res. 416, 113149 (2022).
Mao, Y. et al. METTL3-mediated m6A modification of lncRNA MALAT1 facilitates prostate cancer growth by activation of PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Transpl. 31, 9636897221122997 (2022).
Chen, B. et al. N6-methyladenosine-induced long non-coding RNA PVT1 regulates the miR-27b-3p/BLM axis to promote prostate cancer progression. Int. J. Oncol. 62, 16 (2023).
Zhang, S. et al. RBM3 suppresses stemness remodeling of prostate cancer in bone microenvironment by modulating N6-methyladenosine on CTNNB1 mRNA. Cell Death Dis. 14, 91 (2023).
Zhu, K., Li, Y. & Xu, Y. The FTO m6A demethylase inhibits the invasion and migration of prostate cancer cells by regulating total m6A levels. Life Sci. 271, 119180 (2021).
Li, S. & Cao, L. Demethyltransferase FTO α-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase (FTO) regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and tumor growth of prostate cancer by modulating the expression of melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R). Bioengineered 13, 5598–5612 (2022).
da Cunha, P. A. et al. Interaction between obesity-related genes, FTO and MC4R, associated to an increase of breast cancer risk. Mol. Biol. Rep. 40, 6657–6664 (2013).
Liu, Y. Z. et al. Correlations of MC4R and MSH2 expression with obesity in colon cancer patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 21, 2108–2113 (2017).
Lurie, G. et al. The obesity-associated polymorphisms FTO rs9939609 and MC4R rs17782313 and endometrial cancer risk in non-Hispanic white women. PLoS ONE 6, e16756 (2011).
Zou, L. et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO suppressed prostate cancer progression by maintaining CLIC4 mRNA stability. Cell Death Discov. 8, 184 (2022).
Suh, K. S. et al. Reciprocal modifications of CLIC4 in tumor epithelium and stroma mark malignant progression of multiple human cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 121–131 (2007).
Fernández-Salas, E. et al. mtCLIC/CLIC4, an organellular chloride channel protein, is increased by DNA damage and participates in the apoptotic response to p53. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 3610–3620 (2002).
Shiio, Y. et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis of Myc-induced apoptosis: a direct role for Myc induction of the mitochondrial chloride ion channel, mtCLIC/CLIC4. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 2750–2756 (2006).
Li, P. et al. ELK1-mediated YTHDF1 drives prostate cancer progression by facilitating the translation of Polo-like kinase 1 in an m6A dependent manner. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 18, 6145–6162 (2022).
Yuan, S. et al. A potassium-chloride co-transporter promotes tumor progression and castration resistance of prostate cancer through m6A reader YTHDC1. Cell Death Dis. 14, 7 (2023).
Song, J. et al. Overexpression of YTHDC2 contributes to the progression of prostate cancer and predicts poor outcomes in patients with prostate cancer. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 37, e23308 (2023).
Lothion-Roy, J. et al. Clinical and molecular significance of the RNA m6A methyltransferase complex in prostate cancer. Front. Genet. 13, 1096071 (2022).
Haigh, D. B. et al. The METTL3 RNA methyltransferase regulates transcriptional networks in prostate cancer. Cancers 14, 5148 (2022).
Qu, J. et al. RNA demethylase ALKBH5 in cancer: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential. J. Hematol. Oncol. 15, 8 (2022).
Li, N. et al. ALKBH5 regulates anti-PD-1 therapy response by modulating lactate and suppressive immune cell accumulation in tumor microenvironment. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 20159–20170 (2020).
Baptista, B., Riscado, M., Queiroz, J. A., Pichon, C. & Sousa, F. Non-coding RNAs: emerging from the discovery to therapeutic applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 189, 114469 (2021).
Slack, F. J. & Chinnaiyan, A. M. The role of non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell 179, 1033–1055 (2019).
Qin, S., Mao, Y., Wang, H., Duan, Y. & Zhao, L. The interplay between m6A modification and non-coding RNA in cancer stemness modulation: mechanisms, signaling pathways, and clinical implications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17, 2718–2736 (2021).
Yang, W., Xie, L., Wang, P. & Zhuang, C. MiR-155 regulates m6A level and cell progression by targeting FTO in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell Signal. 91, 110217 (2022).
He, L. et al. MicroRNA-501-3p inhibits the proliferation of kidney cancer cells by targeting WTAP. Cancer Med. 10, 7222–7232 (2021).
Yang, L. et al. Low expression of TRAF3IP2-AS1 promotes progression of NONO-TFE3 translocation renal cell carcinoma by stimulating N6-methyladenosine of PARP1 mRNA and downregulating PTEN. J. Hematol. Oncol. 14, 46 (2021).
Yang, W. et al. Downregulation of lncRNA ZNF582-AS1 due to DNA hypermethylation promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by regulating the N6-methyladenosine modification of MT-RNR1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40, 92 (2021).
Sun, J. et al. SMAD3 and FTO are involved in miR-5581-3p-mediated inhibition of cell migration and proliferation in bladder cancer. Cell Death Discov. 8, 199 (2022).
Xie, F. et al. CircPTPRA blocks the recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine through interacting with IGF2BP1 to suppress bladder cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 20, 68 (2021).
Li, J. et al. Downregulation of N6-methyladenosine binding YTHDF2 protein mediated by miR-493-3p suppresses prostate cancer by elevating N6-methyladenosine levels. Oncotarget 9, 3752–3764 (2018).
Li, X., Liu, B., Wang, S., Li, J. & Ge, X. MiR-141-3p promotes malignant progression in prostate cancer through AlkB homolog 5-mediated m6A modification of protein arginine methyltransferase 6. Chin. J. Physiol. 66, 43–51 (2023).
Zhou, J. et al. Gene signatures and prognostic values of m6A regulators in clear cell renal cell carcinoma — a retrospective study using TCGA database. Aging 11, 1633–1647 (2019).
Wang, Y. et al. Decreased expression of METTL14 predicts poor prognosis and construction of a prognostic signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 21, 46 (2021).
Li, J. et al. The analysis of N6-methyladenosine regulators impacting the immune infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 39, 41 (2022).
Zhang, Q. J. et al. m6A RNA methylation regulators correlate with malignant progression and have potential predictive values in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 392, 112015 (2020).
Wei, J. et al. Establishment of a risk signature based on m6A RNA methylation regulators that predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 14, 413–426 (2021).
Fang, J., Hu, M., Sun, Y., Zhou, S. & Li, H. Expression profile analysis of m6A RNA methylation regulators indicates they are immune signature associated and can predict survival in kidney renal cell carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 39, 1–18 (2020).
Guo, T. et al. N6-methyladenosine writer gene ZC3H13 predicts immune phenotype and therapeutic opportunities in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 11, 718644 (2021).
Strick, A. et al. The N6-methyladenosine (m6A) erasers alkylation repair homologue 5 (ALKBH5) and fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) are prognostic biomarkers in patients with clear cell renal carcinoma. BJU Int. 125, 617–624 (2020).
Guimaraes-Teixeira, C. et al. Deregulation of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification and its erasers FTO/ALKBH5 among the main renal cell tumor subtypes. J. Pers. Med. 11, 996 (2021).
von Hagen, F. et al. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) readers are dysregulated in renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 60, 354–362 (2021).
Huang, Z., Kang, W. & Zhang, Q. N6-methyladenosine methylation related immune biomarkers correlates with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 11, 1576–1586 (2022).
Chen, L. et al. m6A RNA methylation regulators impact prognosis and tumor microenvironment in renal papillary cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 11, 598017 (2021).
Zhang, Y. et al. Systematic analyses of the role of prognostic and immunological EIF3A, a reader protein, in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 21, 680 (2021).
Su, G. et al. YTHDF2 is a potential biomarker and associated with immune infiltration in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 709548 (2021).
Yang, J. et al. Constructing and validating of m6A-related genes prognostic signature for stomach adenocarcinoma and immune infiltration: potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival. Front. Oncol. 12, 1050288 (2022).
Liu, K. et al. Prognostic roles of N6-methyladenosine METTL3 in different cancers: a system review and meta-analysis. Cancer Control. 28, 1073274821997455 (2021).
Wang, X. et al. Copy number variation analysis of m6A regulators identified METTL3 as a prognostic and immune-related biomarker in bladder cancer. Cancer Med. 10, 7804–7815 (2021).
Wu, J. et al. Bioinformatics analysis of the correlation between m6A RNA methylation regulators and the immune infiltration and prognosis of bladder cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 10, 1386 (2022).
Cui, J. et al. Comprehensive analysis of N6-methyladenosine regulators with the tumor immune landscape and correlation between the insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 and programmed death ligand 1 in bladder cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 22, 72 (2022).
Zhao, J. et al. PGM1 and ENO1 promote the malignant progression of bladder cancer via comprehensive analysis of the m6A signature and tumor immune infiltration. J. Oncol. 2022, 8581805 (2022).
Liu, J. et al. Comprehensive analysis of N6-methyladenosine modification patterns associated with multiomic characteristics of bladder cancer. Front. Med. 8, 757432 (2021).
Lu, M. et al. N6-methyladenosine-related non-coding RNAs are potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic responsiveness biomarkers for bladder cancer. EPMA J. 12, 589–604 (2021).
Ma, T. et al. An effective N6-methyladenosine-related long non-coding RNA prognostic signature for predicting the prognosis of patients with bladder cancer. BMC Cancer 21, 1256 (2021).
Xue, M. Q. et al. Comprehensive analysis of the PD-L1 and immune infiltrates of N6-methyladenosine related long non-coding RNAs in bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 12, 10082 (2022).
Huang, Z. et al. N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs in combination with computational histopathology and radiomics predict the prognosis of bladder cancer. Transl. Oncol. 27, 101581 (2023).
Feng, Z. H. et al. m6A-immune-related lncRNA prognostic signature for predicting immune landscape and prognosis of bladder cancer. J. Transl. Med. 20, 492 (2022).
Huang, X., Wang, H. F. & Huang, S. Integrated risk scores from N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs are potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival of bladder cancer patients. Front. Genet. 13, 906880 (2022).
Zhang, Y. et al. N6-methylandenosine-related lncRNAs predict prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder cancer. Front. Oncol. 11, 710767 (2021).
Liang, Y., Zhang, X., Ma, C. & Hu, J. m6A methylation regulators are predictive biomarkers for tumour metastasis in prostate cancer. Cancers 14, 4035 (2022).
Xu, J. et al. The identification of critical m6A RNA methylation regulators as malignant prognosis factors in prostate adenocarcinoma. Front. Genet. 11, 602485 (2020).
Wu, Q. et al. N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation regulators contribute to the progression of prostate cancer. J. Cancer 12, 682–692 (2021).
Liu, Y. et al. Construction of a comprehensive diagnostic scoring model for prostate cancer based on a novel six-gene panel. Front. Genet. 13, 831162 (2022).
Wang, J. et al. The m6A methylation regulator-based signature for predicting the prognosis of prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 16, 2421–2432 (2020).
Quan, Y., Zhang, X. & Ping, H. Construction of a risk prediction model using m6A RNA methylation regulators in prostate cancer: comprehensive bioinformatic analysis and histological validation. Cancer Cell Int. 22, 33 (2022).
Su, H., Wang, Y. & Li, H. RNA m6A methylation regulators multi-omics analysis in prostate cancer. Front. Genet. 12, 768041 (2021).
Liu, J. et al. Construction and validation of N6-methyladenosine long non-coding RNAs signature of prognostic value for early biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 149, 1969–1983 (2023).
Zhao, Y., Sun, H., Zheng, J. & Shao, C. Analysis of RNA m6A methylation regulators and tumour immune cell infiltration characterization in prostate cancer. Artif. Cell Nanomed. Biotechnol. 49, 407–435 (2021).
Ji, G. et al. Comprehensive analysis of m6A regulators prognostic value in prostate cancer. Aging 12, 14863–14884 (2020).
Sun, Z., Jing, C., Xiao, C., Li, T. & Wang, Y. Prognostic risk signature based on the expression of three m6A RNA methylation regulatory genes in kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma. Aging 12, 22078–22094 (2020).
Zheng, Z. et al. N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation regulators participate in malignant progression and have prognostic value in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 43, 1591–1605 (2020).
Cao, C. et al. Targeted demethylation of the PLOD2 mRNA inhibits the proliferation and migration of renal cell carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 8, 675683 (2021).
Chen, J. et al. Targeted methylation of the lncRNA NEAT1 suppresses malignancy of renal cell carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 777349 (2021).
Ying, X. et al. Programmable N6-methyladenosine modification of CDCP1 mRNA by RCas9-methyltransferase like 3 conjugates promotes bladder cancer development. Mol. Cancer 19, 169 (2020).
Dolbois, A. et al. 1,4,9-Triazaspiro[5.5]undecan-2-one derivatives as potent and selective METTL3 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 64, 12738–12760 (2021).
Yankova, E. et al. Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia. Nature 593, 597–601 (2021).
Su, R. et al. R-2HG exhibits anti-tumor activity by targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CEBPA signaling. Cell 172, 90–105.e23 (2018).
Huang, Y. et al. Small-molecule targeting of oncogenic FTO demethylase in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 35, 677–691.e10 (2019).
Wang, J. N. et al. Inhibition of METTL3 attenuates renal injury and inflammation by alleviating TAB3 m6A modifications via IGF2BP2-dependent mechanisms. Sci. Transl. Med. 14, eabk2709 (2022).
Josefin, H. Phase 1 study to evaluate the safety, PK, PD, and clinical activity of STC-15, a METTL-3 inhibitor, in subjects with advanced malignancies. ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT05584111 (2023).
Chen, Y. et al. N6-methyladenosine-modified TRAF1 promotes sunitinib resistance by regulating apoptosis and angiogenesis in a METTL14-dependent manner in renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 21, 111 (2022).
Pan, Y. et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of lncRNA IGFL2-AS1 confers sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 83, 103–116 (2023).
Cotter, K. A. et al. Mapping of m6A and its regulatory targets in prostate cancer reveals a METTL3-low induction of therapy resistance. Mol. Cancer Res. 19, 1398–1411 (2021).
Wei, W. et al. Circ0008399 interaction with WTAP promotes assembly and activity of the m6A methyltransferase complex and promotes cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 81, 6142–6156 (2021).
Yu, H. et al. ALKBH5 inhibited cell proliferation and sensitized bladder cancer cells to cisplatin by m6A-CK2α-mediated glycolysis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 23, 27–41 (2021).
Pei, D. et al. Application of m6A and TME in predicting the prognosis and treatment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2022, 2910491 (2022).
Xu, W. et al. m6A regulator-mediated methylation modification model predicts prognosis, tumor microenvironment characterizations and response to immunotherapies of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 11, 709579 (2021).
Su, R. et al. Targeting FTO suppresses cancer stem cell maintenance and immune evasion. Cancer Cell 38, 79–96.e11 (2020).
Acknowledgements
Q.Z.’s research is supported by funding grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82273151 and 82072826).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.Z. provided direction and guidance throughout the preparation of this Review. L.Y. wrote and edited the manuscript. J.Y. and Q.T. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Urology thanks Carmen Jeronimo, and the other, anonymous, reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Ying, J., Tao, Q. et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine modifications in urological cancers: from mechanism to application. Nat Rev Urol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-023-00851-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-023-00851-x