Abstract
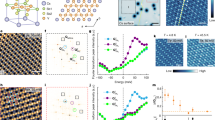
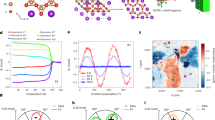
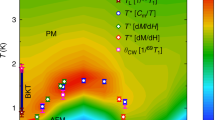
The search for quantum states arising from the interplay between correlation, frustration and topology is a central topic for condensed-matter physics. Recently discovered non-magnetic kagome metals AV3Sb5 (A = K, Cs or Rb) with charge-density-wave and superconducting instabilities may host such exotic states. Here we report evidence that an odd-parity electronic nematic state emerges at a higher temperature than the charge density wave in CsV3Sb5. Our torque measurements reveal a two-fold in-plane magnetic anisotropy that breaks the crystal rotational symmetry. Moreover, in the temperature range between the formation of the charge density wave and a nematic state, rotating an external magnetic field in a conical fashion yields a distinct first-order phase transition, indicating time-reversal symmetry breaking. These results provide thermodynamic evidence for the emergence of an odd-parity nematic order. In addition, elastoresistance shows no discernible anomalies near the onset of nematicity, consistent with the odd-parity order. These findings suggest that an exotic loop current state precedes the charge-density-wave transition in CsV3Sb5.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available via Figshare at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.23557737. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Ortiz, B. R. et al. New kagome prototype materials: discovery of KV3Sb5, RbV3Sb5, and CsV3Sb5. Phys. Rev. Mater. 3, 094407 (2019).
Ortiz, B. R. et al. CsV3Sb5: a Z2 topological kagome metal with a superconducting ground state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 247002 (2020).
Ortiz, B. R. et al. Superconductivity in the Z2 kagome metal KV3Sb5. Phys. Rev. Mater. 5, 034801 (2021).
Zhou, X. et al. Origin of charge density wave in the kagome metal CsV3Sb5 as revealed by optical spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 104, L041101 (2021).
Kang, M. et al. Twofold Van Hove singularity and origin of charge order in topological kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5. Nat. Phys. 18, 301–308 (2022).
Park, T., Ye, M. & Balents, L. Electronic instabilities of kagome metals: saddle points and Landau theory. Phys. Rev. B 104, 035142 (2021).
Tazai, R., Yamakawa, Y. & Kontani, H. Charge-loop current order and Z3 nematicity mediated by bond-order fluctuations in kagome metal AV3Sb5 (A = Cs, Rb, K). Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.08068 (2022).
Varma, C. Non-Fermi-liquid states and pairing instability of a general model of copper oxide metals. Phys. Rev. B 55, 14554 (1997).
Li, Y. et al. Unusual magnetic order in the pseudogap region of the superconductor HgBa2CuO4+δ. Nature 455, 372–375 (2008).
Pershoguba, S. S., Kechedzhi, K. & Yakovenko, V. M. Proposed chiral texture of the magnetic moments of unit-cell loop currents in the pseudogap phase of cuprate superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 047005 (2013).
Zhao, L. et al. Evidence of an odd-parity hidden order in a spin–orbit coupled correlated iridate. Nat. Phys. 12, 32–36 (2016).
Jeong, J., Sidis, Y., Louat, A., Brouet, V. & Bourges, P. Time-reversal symmetry breaking hidden order in Sr2(Ir, Rh)O4. Nat. Commun. 8, 15119 (2017).
Murayama, H. et al. Bond directional anapole order in a spin-orbit coupled Mott insulator Sr2(Ir1−xRhx)O4. Phys. Rev. X 11, 011021 (2021).
Tan, H., Liu, Y., Wang, Z. & Yan, B. Charge density waves and electronic properties of superconducting kagome metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 046401 (2021).
Tazai, R., Yamakawa, Y., Onari, S. & Kontani, H. Mechanism of exotic density-wave and beyond-Migdal unconventional superconductivity in kagome metal AV3Sb5 (A = K, Rb, Cs). Sci. Adv. 8, eabl4108 (2022).
Roppongi, M. et al. Bulk evidence of anisotropic s-wave pairing with no sign change in the kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5. Nat. Commun. 14, 667 (2023).
Xiang, Y. et al. Twofold symmetry of c-axis resistivity in topological kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5 with in-plane rotating magnetic field. Nat. Commun. 12, 6727 (2021).
Nie, L. et al. Charge-density-wave-driven electronic nematicity in a kagome superconductor. Nature 604, 59–64 (2022).
Yu, L. et al. Evidence of a hidden flux phase in the topological kagome metal CsV3Sb5. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.10714 (2021).
Sur, Y., Kim, K.-T., Kim, S. & Kim, K. H. Optimized superconductivity in the vicinity of a nematic quantum critical point in the kagome superconductor Cs(V1−xTix)3Sb5. Nat. Commun. 14, 3899 (2023).
Yang, S.-Y. et al. Giant, unconventional anomalous Hall effect in the metallic frustrated magnet candidate, KV3Sb5. Sci. Adv. 6, eabb6003 (2020).
Yu, F. et al. Concurrence of anomalous Hall effect and charge density wave in a superconducting topological kagome metal. Phys. Rev. B 104, L041103 (2021).
Guo, C. et al. Switchable chiral transport in charge-ordered kagome metal CsV3Sb5. Nature 611, 461–466 (2022).
Hu, Y. et al. Time-reversal symmetry breaking in charge density wave of CsV3Sb5 detected by polar Kerr effect. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08036 (2022).
Xu, Y. et al. Three-state nematicity and magneto-optical Kerr effect in the charge density waves in kagome superconductors. Nat. Phys. 18, 1470–1475 (2022).
Saykin, D. R. et al. High resolution polar Kerr effect studies of CsV3Sb5: tests for time reversal symmetry breaking below the charge order transition. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.131.016901
Jiang, Y.-X. et al. Unconventional chiral charge order in kagome superconductor KV3Sb5. Nat. Mater. 20, 1353–1357 (2021).
Li, H. et al. No observation of chiral flux current in the topological kagome metal CsV3Sb5. Phys. Rev. B 105, 045102 (2022).
Christensen, M. H., Birol, T., Andersen, B. M. & Fernandes, R. M. Loop currents in A V 3 Sb 5 kagome metals: Multipolar and toroidal magnetic orders. Phys. Rev. B 106, 144504 (2022).
Okazaki, R. et al. Rotational symmetry breaking in the hidden-order phase of URu2Si2. Science 331, 439–442 (2011).
Chen, Q., Chen, D., Schnelle, W., Felser, C. & Gaulin, B. D. Charge density wave order and fluctuations above TCDW and below superconducting Tc in the kagome metal CsV3Sb5. Phys. Rev. Lett. 129, 056401 (2022).
Sato, Y. et al. Thermodynamic evidence for a nematic phase transition at the onset of the pseudogap in YBa2Cu3Oy. Nat. Phys. 13, 1074–1078 (2017).
Murayama, H. et al. Diagonal nematicity in the pseudogap phase of HgBa2CuO4+δ. Nat. Commun. 10, 3282 (2019).
Kostylev, I., Yonezawa, S., Wang, Z., Ando, Y. & Maeno, Y. Uniaxial-strain control of nematic superconductivity in SrxBi2Se3. Nat. Commun. 11, 4152 (2020).
Miao, H. et al. Geometry of the charge density wave in the kagome metal AV3Sb5. Phys. Rev. B 104, 195132 (2021).
Holleis, L. et al. Anomalous and anisotropic nonlinear susceptibility in the proximate Kitaev magnet α-RuCl3. npj Quantum Mater. 6, 66 (2021).
Chu, J.-H., Kuo, H.-H., Analytis, J. G. & Fisher, I. R. Divergent nematic susceptibility in an iron arsenide superconductor. Science 337, 710–712 (2012).
Kuo, H.-H., Chu, J.-H., Palmstrom, J. C., Kivelson, S. A. & Fisher, I. R. Ubiquitous signatures of nematic quantum criticality in optimally doped Fe-based superconductors. Science 352, 958–962 (2016).
Kawaguchi, K., Onari, S. & Kontani, H. Spin-fluctuation-driven B1g and B2g bond order and induced in-plane anisotropy in magnetic susceptibility in cuprate superconductors: impact of hot-/cold-spot structure on bond-order symmetry. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 89, 124704 (2020).
Tazai, R., Yamakawa, Y. & Kontani, H. Drastic magnetic-field-induced chiral current order and emergent current-bond-field interplay in kagome metal AV3Sb5 (A = Cs, Rb, K). Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.00623 (2023).
Kautzsch, L. et al. Structural evolution of the kagome superconductors AV3Sb5 (A = K, Rb, and Cs) through charge density wave order. Phys. Rev. Mater. 7, 024806 (2023).
Acknowledgements
A part of this work was supported by CREST (no. JPMJCR19T5; to Y.M. and T.S.) from the Japan Science and Technology (JST), Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) (nos. 18H05227, 18H03680, 18H01180, 21K13881) and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on innovative areas ‘Quantum Liquid Crystals’ (no. JP19H05824) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (to T.S.). S.D.W. gratefully acknowledges support from the UC Santa Barbara NSF Quantum Foundry funded via the Q-AMASE-i program under award DMR-1906325. Work by B.R.O. was supported by the US Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences (BES), Materials Sciences and Engineering Division.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.A., T.S. and Y.M. conceived and supervised the study. T.A., T.K., K.O., S.S. and T.G. performed the torque measurements. A.O., Y. Kageyama and K.H. performed the elastoresistivity measurements. B.R.O., S.D.W., Q.L. and H.-H.W. synthesized the single crystals. T.A., A.O., Y. Kageyama, T.K., K.O. and K.H. analysed the data with inputs from S.S., Y. Kohsaka, Y. Kasahara and H.M. The theoretical models were provided by R.T. and H.K. All authors discussed the results and contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Physics thanks Domenico Di Sante and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–4 and Sections I–III.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Out-of-plane magnetic susceptibility data.
Source Data Fig. 2
In-plane magnetic torque data.
Source Data Fig. 3
Elastoresistance data.
Source Data Fig. 4
Magnetic torque data with conically rotated fields.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Asaba, T., Onishi, A., Kageyama, Y. et al. Evidence for an odd-parity nematic phase above the charge-density-wave transition in a kagome metal. Nat. Phys. 20, 40–46 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-023-02272-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-023-02272-4