Abstract
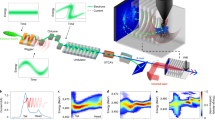
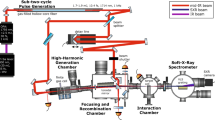
Intense attosecond X-ray pulses are key for ultrafast nonlinear spectroscopy and diffractive imaging. Here we demonstrate the generation of terawatt-scale isolated attosecond pulses with a two-stage cascaded X-ray free-electron laser. These pulses have a median energy in excess of 100 μJ in the soft X-ray region. The temporal profile is characterized with an angular streaking measurement, revealing a maximum peak power of 1.1 TW. Our data show an increase in the average peak power of attosecond X-ray pulses by one order of magnitude over previous reported results and provide strong evidence of soliton-like superradiant behaviour in the X-ray regime.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
A subset of the raw data used to produce Figs. 1–4 is publicly available via figshare at https://figshare.com/projects/Terawatt-scale_Attosecond_X-ray_Pulses_from_a_Cascaded_Superradiant_Free-electron_Laser/193178 (ref. 49). This repository also contains a copy of the analysis script used to reconstruct the attosecond pulses from the streaking data. All other data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Strickland, D. & Mourou, G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 55, 447–449 (1985).
Spence, D. E., Kean, P. N. & Sibbett, W. 60-fsec pulse generation from a self-mode-locked Ti:sapphire laser. Opt. Lett. 16, 42–44 (1991).
Sarukura, N., Ishida, Y. & Nakano, H. Generation of 50-fsec pulses from a pulse-compressed, CW, passively mode-locked Ti:sapphire laser. Opt. Lett. 16, 153–155 (1991).
Agostini, P., Fabre, F., Mainfray, G., Petite, G. & Rahman, N. K. Free-free transitions following six-photon ionization of xenon atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 42, 1127–1130 (1979).
Ferray, M. et al. Multiple-harmonic conversion of 1064 nm radiation in rare gases. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 21, L31 (1988).
Lewenstein, M., Balcou, P., Ivanov, M. Y., L’huillier, A. & Corkum, P. B. Theory of high-harmonic generation by low-frequency laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 49, 2117 (1994).
Corkum, P. á & Krausz, F. Attosecond science. Nat. Phys. 3, 381–387 (2007).
Esarey, E., Schroeder, C. B. & Leemans, W. P. Physics of laser-driven plasma-based electron accelerators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1229–1285 (2009).
Geddes, C. et al. High-quality electron beams from a laser wakefield accelerator using plasma-channel guiding. Nature 431, 538–541 (2004).
Emma, P. et al. First lasing and operation of an ångstrom-wavelength free-electron laser. Nat. Photon. 4, 641–647 (2010).
Bostedt, C. et al. Linac Coherent Light Source: the first five years. Rev. Mod. Phys. 88, 015007 (2016).
March, A., Pratt, S., Southworth, S. & DiMauro, L. et al. Femtosecond electronic response of atoms to ultra-intense X-rays. Nature 466, 56–61 (2010).
O’Neal, J. T. et al. Electronic population transfer via impulsive stimulated X-ray Raman scattering with attosecond soft-X-ray pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 073203 (2020).
Eichmann, U. et al. Photon-recoil imaging: expanding the view of nonlinear X-ray physics. Science 369, 1630–1633 (2020).
Seibert, M. M. et al. Single mimivirus particles intercepted and imaged with an X-ray laser. Nature 470, 78–81 (2011).
Sobolev, E. et al. Megahertz single-particle imaging at the European XFEL. Commun. Phys. 3, 97 (2020).
Duris, J. et al. Tunable isolated attosecond X-ray pulses with gigawatt peak power from a free-electron laser. Nat. Photon. 14, 30–36 (2020).
Maroju, P. K. et al. Attosecond pulse shaping using a seeded free-electron laser. Nature 578, 386–391 (2020).
Li, S. et al. Attosecond coherent electron motion in Auger-Meitner decay. Science 375, 285–290 (2022).
Cryan, J. P. et al. The development of attosecond XFELs for understanding ultrafast electron motion. Adv. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 71, 1–64 (2022).
Pellegrini, C., Marinelli, A. & Reiche, S. The physics of X-ray free-electron lasers. Rev. Mod. Phys. 88, 015006 (2016).
Guetg, M. W. et al. Generation of high-power high-intensity short X-ray free-electron-laser pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 014801 (2018).
Lutman, A. A. et al. High-power femtosecond soft X rays from fresh-slice multistage free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 264801 (2018).
Zholents, A. A. Method of an enhanced self-amplified spontaneous emission for X-ray free electron lasers. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 8, 040701 (2005).
Zhang, Z. et al. Experimental demonstration of enhanced self-amplified spontaneous emission by photocathode temporal shaping and self-compression in a magnetic wiggler. New J. Phys. 22, 083030 (2020).
Duris, J. P. et al. Controllable X-ray pulse trains from enhanced self-amplified spontaneous emission. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 104802 (2021).
MacArthur, J. P. et al. Phase-stable self-modulation of an electron beam in a magnetic wiggler. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 214801 (2019).
Tiedtke, K. et al. Absolute pulse energy measurements of soft X-rays at the Linac Coherent Light Source. Opt. Express 22, 21214–21226 (2014).
Heimann, P. et al. Laser power meters as an X-ray power diagnostic for LCLS-II. J. Synchrotron Rad. 25, 72–76 (2018).
Larsen, K. A. et al. Compact single-shot soft X-ray photon spectrometer for free-electron laser diagnostics. Opt. Express 31, 35822–35834 (2023).
Hartmann, N. et al. Attosecond time–energy structure of X-ray free-electron laser pulses. Nat. Photon. 12, 215–220 (2018).
Champenois, E. et al. A co-axial velocity map imaging spectrometer for electrons. AIP Adv. 8, 115308 (2018).
Bonifacio, R., Piovella, N. & McNeil, B. W. J. Superradiant evolution of radiation pulses in a free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. A 44, R3441–R3444 (1991).
Giannessi, L. et al. Superradiant cascade in a seeded free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 044801 (2013).
Gover, A. et al. Superradiant and stimulated-superradiant emission of bunched electron beams. Rev. Mod. Phys. 91, 035003 (2019).
Watanabe, T. et al. Experimental characterization of superradiance in a single-pass high-gain laser-seeded free-electron laser amplifier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 034802 (2007).
Mirian, N. S. et al. Generation and measurement of intense few-femtosecond superradiant extreme-ultraviolet free-electron laser pulses. Nat. Photon. 15, 523–529 (2021).
Reiche, S. GENESIS 1.3: a fully 3D time-dependent FEL simulation code. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 429, 243–248 (1999).
Yang, X., Mirian, N. & Giannessi, L. Postsaturation dynamics and superluminal propagation of a superradiant spike in a free-electron laser amplifier. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23, 010703 (2020).
Zen, H., Hajima, R. & Ohgaki, H. Full characterization of superradiant pulses generated from a free-electron laser oscillator. Sci. Rep. 13, 6350 (2023).
Decking, W. et al. A MHz-repetition-rate hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a superconducting linear accelerator. Nat. Photon. 14, 391–397 (2020).
Emma, P. et al. Linear accelerator design for the LCLS-II FEL facility. In Proc. 36th International Free Electron Laser Conference THP025 (2014).
Hemsing, E., Halavanau, A. & Zhang, Z. Enhanced self-seeding with ultrashort electron beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 044801 (2020).
Li, K. et al. Ghost-imaging-enhanced noninvasive spectral characterization of stochastic X-ray free-electron-laser pulses. Commun. Phys. 5, 191 (2022).
Giannessi, L. & Musumeci, P. The free-electron laser harmonic cascade. New J. Phys. 8, 294 (2006).
Saldin, E. L., Schneidmiller, E. A. & Yurkov, M. V. Self-amplified spontaneous emission FEL with energy-chirped electron beam and its application for generation of attosecond X-ray pulses. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 9, 050702 (2006).
Ratner, D. et al. Experimental demonstration of a soft X-ray self-seeded free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 054801 (2015).
Li, S. et al. Characterizing isolated attosecond pulses with angular streaking. Opt. Express 26, 4531–4547 (2018).
Franz, P. Terawatt-scale attosecond x-ray pulses from a cascaded superradiant free-electron laser. figshare https://figshare.com/projects/Terawatt-scale_Attosecond_X-ray_Pulses_from_a_Cascaded_Superradiant_Free-electron_Laser/193178 (2024).
Acknowledgements
Use of the LCLS, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, is supported by the US Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under contract no. DE-AC02-76SF00515. A.M., D.C., P.F. and Z.G. acknowledge support from the Accelerator and Detector Research Program of the Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences (BES) division. Z.G., R.R.R. and P.F. also acknowledge support from the Robert Siemann Fellowship of Stanford University. Effort of T.D., J.W., M.F.K. and J.P.C. is supported by the DOE, BES, Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences Division (CSGB). A.M. would like to acknowledge L. Giannessi and T. Gorkhover for useful discussions and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.F., S.L., Z.G., T.D., J.P.D., J.P.C. and A.M. conceived the experiment. P.F., R.R.R., D.C., Z.G., J.P.D., N.S., Z.Z. and A.M. set up the attosecond XFEL configuration. P.F., S.L., T.D., Z.G., J.W., E.I., K.L., J.M.G., X.C., M.C.H., X.L., M.-F.L., A.K., R.O., A.S., E.T., M.F.K., J.P.C. and A.M. conducted the angular streaking measurements to determine the pulse durations. P.F., S.L., T.D., R.R.R., E.I., Z.G., J.W., J.P.C. and A.M. performed the data analysis. R.R.R., Z.G., Z.Z. and D.C. conducted the numerical simulations of the FEL. All authors were involved in the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Photonics thanks Nina Rohringer and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Sections I–IV, Figs. 1–10, Table 1 and discussion.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Franz, P., Li, S., Driver, T. et al. Terawatt-scale attosecond X-ray pulses from a cascaded superradiant free-electron laser. Nat. Photon. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01427-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01427-w