Abstract
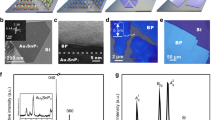
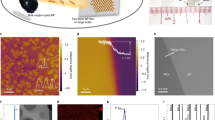
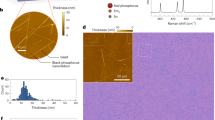
Black phosphorus (BP), a fascinating semiconductor with high mobility and a tunable direct bandgap, has emerged as a candidate beyond traditional silicon-based devices for next-generation electronics and optoelectronics. The ability to grow large-scale, high-quality BP films is a prerequisite for scalable integrated applications but has thus far remained a challenge due to unmanageable nucleation events. Here we develop a sustained feedstock release strategy to achieve subcentimetre-size single-crystal BP films by facilitating the lateral growth mode under a low nucleation rate. The as-grown single-crystal BP films exhibit high crystal quality, which brings excellent field-effect electrical properties and observation of pronounced Shubnikov–de Haas oscillations, with high mobilities up to ~6,500 cm2 V−1 s−1 at low temperatures. We further extend this approach to the growth of single-crystal BP alloy films, which broaden the infrared emission regime of BP from 3.7 μm to 6.9 μm at room temperature. This work will greatly facilitate the development of high-performance electronics and optoelectronics based on BP family materials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within this paper and its Supplementary Information files or from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Li, L. et al. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 372–377 (2014).
Buscema, M. et al. Fast and broadband photoresponse of few-layer black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nano Lett. 14, 3347–3352 (2014).
Liu, H. et al. Phosphorene: an unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano 8, 4033–4041 (2014).
Qiao, J., Kong, X., Hu, Z.-X., Yang, F. & Ji, W. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 5, 4475 (2014).
Li, L. et al. Quantum Hall effect in black phosphorus two-dimensional electron system. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 593–597 (2016).
Chen, X. et al. Widely tunable black phosphorus mid-infrared photodetector. Nat. Commun. 8, 1672 (2017).
Mao, N. et al. Optical anisotropy of black phosphorus in the visible regime. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 300–305 (2016).
Castellanos-Gomez, A. Black phosphorus: narrow gap, wide applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6, 4280–4291 (2015).
Ling, X., Wang, H., Huang, S., Xia, F. & Dresselhaus, M. S. The renaissance of black phosphorus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 4523–4530 (2015).
Li, J. et al. Wafer-scale single-crystal monolayer graphene grown on sapphire substrate. Nat. Mater. 21, 740–747 (2022).
Li, T. Epitaxial growth of wafer-scale molybdenum disulfide semiconductor single crystals on sapphire. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1201–1207 (2021).
Shriber, P., Samanta, A., Nessim, G. D. & Grinberg, I. First-principles investigation of black phosphorus synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 1759–1764 (2018).
Endo, S., Akahama, Y., Terada, S. & Narita, S. Growth of large single crystals of black phosphorus under high pressure. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 21, L482–L484 (1982).
Li, C. et al. Synthesis of crystalline black phosphorus thin film on sapphire. Adv. Mater. 30, 1703748 (2018).
Wu, Z. et al. Large-scale growth of few-layer two-dimensional black phosphorus. Nat. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-021-01001-7 (2021).
Nilges, T., Kersting, M. & Pfeifer, T. A fast low-pressure transport route to large black phosphorus single crystals. J. Solid State Chem. 181, 1707–1711 (2008).
Liu, M. et al. High yield growth and doping of black phosphorus with tunable electronic properties. Mater. Today 36, 91–101 (2020).
Xu, Y. et al. Epitaxial nucleation and lateral growth of high-crystalline black phosphorus films on silicon. Nat. Commun. 11, 1330 (2020).
Cantwell, B. J., Brinkman, A. W. & Basu, A. Control of mass transport in the vapour growth of bulk crystals of CdTe and related compounds. J. Cryst. Growth 275, e543–e547 (2005).
Hao, Y. et al. Oxygen-activated growth and bandgap tunability of large single-crystal bilayer graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 426–431 (2016).
Han, D. et al. Synthesis of highly crystalline black phosphorus thin films on GaN. Nanoscale 12, 24429–24436 (2020).
Zhang, Z. et al. Two-step heating synthesis of sub-3 millimeter-sized orthorhombic black phosphorus single crystal by chemical vapor transport reaction method. Sci. China Mater. 59, 122–134 (2016).
Li, J. et al. Growth of black phosphorus nanobelts and microbelts. Small 14, 1702501 (2018).
Favron, A. et al. Photooxidation and quantum confinement effects in exfoliated black phosphorus. Nat. Mater. 14, 826–832 (2015).
Chen, C. et al. Widely tunable mid-infrared light emission in thin-film black phosphorus. Sci. Adv. 6, eaay6134 (2020).
Izquierdo, N., Myers, J. C., Seaton, N. C. A., Pandey, S. K. & Campbell, S. A. Thin-film deposition of surface passivated black phosphorus. ACS Nano 13, 7091–7099 (2019).
Li, X. et al. Synthesis of thin-film black phosphorus on a flexible substrate. 2D Mater. 2, 031002 (2015).
Feng, X. et al. High mobility anisotropic black phosphorus nanoribbon field-effect transistor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1801524 (2018).
Yan, X., Wang, H. & Sanchez Esqueda, I. Temperature-dependent transport in ultrathin black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nano Lett. 19, 482–487 (2019).
He, D. et al. High-performance black phosphorus field-effect transistors with long-term air stability. Nano Lett. 19, 331–337 (2019).
Li, L., Engel, M., Farmer, D. B., Han, S. & Wong, H.-S. P. High-performance p-type black phosphorus transistor with scandium contact. ACS Nano 10, 4672–4677 (2016).
Yang, Z. et al. Field-effect transistors based on amorphous black phosphorus ultrathin films by pulsed laser deposition. Adv. Mater. 27, 3748–3754 (2015).
Liu, B. et al. Black arsenic–phosphorus: layered anisotropic infrared semiconductors with highly tunable compositions and properties. Adv. Mater. 27, 4423–4429 (2015).
Long, M. et al. Room temperature high-detectivity mid-infrared photodetectors based on black arsenic phosphorus. Sci. Adv. 3, e1700589 (2017).
Young, E. P. et al. Wafer-scale black arsenic–phosphorus thin-film synthesis validated with density functional perturbation theory predictions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 1, 4737–4745 (2018).
Izquierdo, N. et al. Growth of black arsenic phosphorus thin films and its application for field-effect transistors. Nanotechnology 32, 325601 (2021).
Chen, Z. et al. Spectroscopy of buried states in black phosphorus with surface doping. 2D Mater. 7, 035027 (2020).
Kim, J. et al. Observation of tunable band gap and anisotropic Dirac semimetal state in black phosphorus. Science 349, 723–726 (2015).
Li, L. et al. Direct observation of the layer-dependent electronic structure in phosphorene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 21–25 (2017).
Zhang, S. et al. Extraordinary photoluminescence and strong temperature/angle-dependent Raman responses in few-layer phosphorene. ACS Nano 8, 9590–9596 (2014).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169–11186 (1996).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Blöchl, P. E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 50, 17953–17979 (1994).
Kresse, G. & Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758–1775 (1999).
Grimme, S., Antony, J., Ehrlich, S. & Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H–Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 132, 154104 (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0703700 to J.H.; 2021YFA1200804 to K.Z.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61927813, 61922082 and 61875223 to K.Z.; 62274175 to J.W.; 12274276 to H.Z.; 52221001, 62090035 and U19A2090 to A.P.; 22173031 to Q.H.Y.), the Jiangsu Province Key R&D Program (BE2021007-3 to K.Z.) and the Key Program of Science and Technology Department of Hunan Province (2019XK2001 and 2020XK2001 to A.P.). The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the Vacuum Interconnected Nanotech Workstation (Nano-X) of the Suzhou Institute of Nano-tech and Nano-bionics (SINANO), Chinese Academy of Sciences. We also thank X. Song for analysing the EBSD measurement results and S. Xiao for performing the ARPES measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.Z., A.P. and C.C. conceived and designed the study. K.Z., A.P. and J.H. supervised the project. C.C. developed the synthesis technique and grew the SCBP films. C.C., Y.Z., J.C., C.L., J.L., L.F., Q.Y., H.Z., Z.Z., R.C., X.X. and Z.D. performed the measurements and analyses, including AFM, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, PL measurement, TEM, STEM, XPS, FTIR spectroscopy and ARPES. Q.Y. and Y.Y. conducted theoretical calculations. Y.X., R.Z., J.W. and Y.Z. fabricated and measured the electrical devices. C.C., K.Z., A.P. Q.Y. and J.H. co-wrote the manuscript. All of the authors commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Methods, Figs. 1–15 and Table 1.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Statistical source data of nucleation density and XRD.
Source Data Fig. 2
Statistical source data of angle counts.
Source Data Fig. 3
Statistical source data of DFT.
Source Data Fig. 4
Statistical source data of electronic properties.
Source Data Fig. 5
Statistical source data of alloy bandgap.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Yin, Y., Zhang, R. et al. Growth of single-crystal black phosphorus and its alloy films through sustained feedstock release. Nat. Mater. 22, 717–724 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-023-01516-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-023-01516-1
This article is cited by
-
Realization of large-area ultraflat chiral blue phosphorene
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Black phosphorus boosts wet-tissue adhesion of composite patches by enhancing water absorption and mechanical properties
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Seeded growth of single-crystal black phosphorus nanoribbons
Nature Materials (2024)
-
Synthesis of black phosphorus films
Nature Materials (2023)