Abstract
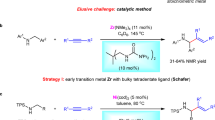
Amines are prominent in natural products, pharmaceutical agents and agrochemicals. Moreover, they are synthetically valuable building blocks for the construction of complex organic molecules and functional materials. However, amines, especially aliphatic and aromatic amines with free N–H bonds, tend to coordinate with transition metals and deactivate the catalyst, posing a tremendous challenge to applying Lewis basic amines in the amination of olefins. Here we present an example of oxidative amination of simple olefins with various Lewis basic amines. The combination of a palladium catalyst, 2,6-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone and a phosphorous ligand leads to the efficient synthesis of alkyl and aryl allylamines. A series of allylamines were obtained with good yields and excellent regio- and stereoselectivities. Intramolecular amination to synthesize tetrahydropyrrole and piperidine derivatives was also realized. Mechanistic investigations reveal that the reaction undergoes allylic C(sp3)–H activation and subsequent functionalization.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Crystallographic data for the structure reported in this article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, under deposition number CCDC 2038362 (62). A copy of the data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/. All other data are available in the main text or Supplementary Information.
References
Vitaku, E., Smith, D. T. & Njardarson, J. T. Analysis of the structural diversity, substitution patterns, and frequency of nitrogen heterocycles among US FDA approved pharmaceuticals. J. Med. Chem. 57, 10257–10274 (2014).
Mayol-Llinàs, J., Nelson, A., Farnaby, W. & Ayscough, A. Assessing molecular scaffolds for CNS drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today. 22, 965–969 (2017).
Stütz, A. & Petranyi, G. Synthesis and antifungal activity of (E)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethanamine (SF 86-327) and related allylamine derivatives with enhanced oral activity. J. Med. Chem. 27, 1539–1543 (1984).
Stütz, A., Georgopoulos, A., Granitzer, W., Petranyi, G. & Berney, D. Synthesis and structure–activity relationships of naftifine-related allylamine antimycotics. J. Med. Chem. 29, 112–125 (1986).
Johannsen, M. & Jørgensen, K. A. Allylic amination. Chem. Rev. 98, 1689–1708 (1998).
Sweeney, J. B., Ball, A. K., Lawrence, P. A., Sinclair, M. C. & Smith, L. J. A simple, broad-scope nickel(0) precatalyst system for the direct amination of allyl alcohols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 10202–10206 (2018).
Cheng, Q., Chen, J.-T., Lin, S.-Y. & Ritter, T. Allylic amination of alkenes with iminothianthrenes to afford alkyl allylamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 17287–17293 (2020).
Xie, Y.-J., Hu, J.-H., Wang, Y.-Y., Xia, C.-G. & Huang, H.-M. Palladium-catalyzed vinylation of aminals with simple alkenes: a new strategy to construct allylamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 20613–20616 (2012).
Wang, P.-S., Shen, M.-L., Wang, T.-C., Lin, H.-C. & Gong, L.-Z. Access to chiral hydropyrimidines through palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic C–H amination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 16032–16036 (2017).
Vemula, S. R., Kumar, D. & Cook, G. R. Palladium-catalyzed allylic amidation with N-heterocycles via sp3 C–H oxidation. ACS Catal. 6, 5295–5301 (2016).
Reed, S. A. & White, M. C. Catalytic intermolecular linear allylic C–H amination via heterobimetallic catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 3316–3318 (2008).
Timokhin, V. I., Anastasi, N. R. & Stahl, S. S. Dioxygen-coupled oxidative amination of styrene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 12996–12997 (2003).
McDonald, R. I., Liu, G.-S. & Stahl, S. S. Palladium(II)-catalyzed alkene functionalization via nucleopalladation: stereochemical pathways and enantioselective catalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 111, 2981–3019 (2011).
Shimizu, Y., Obora, Y. & Ishii, Y. Intermolecular aerobic oxidative allylic amination of simple alkenes with diarylamines catalyzed by the Pd(OCOCF3)2/NPMoV/O2 system. Org. Lett. 12, 1372–1374 (2010).
Willcox, D. B. et al. A general catalytic β-C–H carbonylation of aliphatic amines to β-lactams. Science 354, 851–857 (2016).
Åkermark, B. et al. Palladium-promoted addition of amines to isolated double bonds. J. Organomet. Chem. 72, 127–133 (1974).
Brice, J. L., Harang, J. E., Timokhin, V. I., Anastasi, N. R. & Stahl, S. S. Aerobic oxidative amination of unactivated alkenes catalyzed by palladium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 2868–2869 (2005).
Yin, G.-Y., Wu, Y.-C. & Liu, G.-S. Scope and mechanism of allylic C–H amination of terminal alkenes by the palladium/PhI(OPiv)2 catalyst system: insights into the effect of naphthoquinone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 11978–11987 (2010).
Kohler, D. G., Gockel, S. N., Kennemur, J. L., Waller, P. J. & Hull, K. L. Palladium-catalysed anti-Markovnikov selective oxidative amination. Nat. Chem. 10, 333–340 (2018).
Ma, R. & White, M. C. C–H to C–N cross-coupling of sulfonamides with olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 3202–3205 (2018).
McNally, A., Haffemayer, B., Collins, B. S. L. & Gaunt, M. J. Palladium-catalysed C–H activation of aliphatic amines to give strained nitrogen heterocycles. Nature 510, 129–133 (2014).
Calleja, J. et al. A steric tethering approach enables palladium-catalyzed C–H activation of primary amino alcohols. Nat. Chem. 7, 1009–1016 (2015).
Ji, X.-C., Huang, H.-W., Wu, W.-Q. & Jiang, H.-F. Palladium-catalyzed intermolecular dehydrogenative aminohalogenation of alkenes under molecular oxygen: an approach to brominated enamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 5286–5289 (2013).
Ouyang, L. et al. Access to α-amino acid esters through palladium-catalyzed oxidative amination of vinyl ethers with hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant and oxygen source. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 15926–15930 (2017).
Ali, S. Z. et al. Allylic C–H amination cross-coupling furnishes tertiary amines by electrophilic metal catalysis. Science 376, 276–283 (2022).
Trost, B. M., Weber, L., Strege, P. E., Fullerton, T. J. & Dietsche, T. J. Allylic alkylation: nucleophilic attack on π-allylpalladium complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100, 3416–3426 (1978).
Pattillo, C. C. et al. Aerobic linear allylic C–H amination: overcoming benzoquinone inhibition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 1265–1272 (2016).
Qi, X.-X., Chen, P.-H. & Liu, G.-S. Catalytic oxidative trifluoromethoxylation of allylic C–H bonds using a palladium catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 9517–9521 (2017).
Petranyi, G., Ryder, N. S. & Stutz, A. Allylamine derivatives: new class of synthetic antifungal agents inhibiting fungal squalene epoxidase. Science 224, 1239–1241 (1984).
Ye, Z.-S., Brust, T. F., Watts, V. J. & Dai, M.-J. Palladium-catalyzed regio- and stereoselective γ-arylation of tertiary allylic amines: identification of potent adenylyl cyclase inhibitors. Org. Lett. 17, 892–895 (2015).
Kitahata, N. et al. A 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase inhibitor for use in the elucidation of abscisic acid action mechanisms. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14, 5555–5561 (2006).
Hanley, P. S. & Hartwig, J. F. Intermolecular migratory insertion of unactivated olefins into palladium–nitrogen bonds. Steric and electronic effects on the rate of migratory insertion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 15661–15673 (2011).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (2016YFA0602900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21420102003) and the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2020B010188001) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The project was conceived of and supervised by H.J. Y. Jin developed the palladium-catalysed selective oxidative amination of olefins with Lewis basic amines. C.L. contributed to expanding the scope for aromatic amines. M.L. and Y. Jin performed the reaction mechanism studies. Y. Jing and Z.K. performed DFT studies. W.W. wrote the manuscript and incorporated revisions suggested by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Chemistry thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–18, Tables 1–10, experimental procedures, synthetic procedures, characterization data, DFT calculations and references.
Supplementary Data 1
Crystallographic data for compound 62; CCDC reference 2038362.
Supplementary Data 2
Crystallographic data for compound 62; CCDC reference 2038362.
Supplementary Data 3
Cartesian coordinates (x,y,z) for all optimized structures.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Jing, Y., Li, C. et al. Palladium-catalysed selective oxidative amination of olefins with Lewis basic amines. Nat. Chem. 14, 1118–1125 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-022-01023-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-022-01023-x
This article is cited by
-
Cooperative Cu/azodiformate system-catalyzed allylic C–H amination of unactivated internal alkenes directed by aminoquinoline
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Back to basics
Nature Chemistry (2022)