Abstract
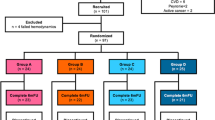
The erectile mechanism depends, in part on the intactness of the collagen components in the penis. As such, impaired collagen may have a deleterious effect on erectile function. Radiofrequency energy has been shown to renew and restore spatial structural arrangement of collagen fibers; therefore, treatment of erectile dysfunction with radiofrequency could lead to anatomical and physiological changes at the penile tissue level and could lead to improvement in the erectile mechanism. We conducted this study to assess the effect of radiofrequency treatment on erection quality. We evaluated the safety, applicability, and efficacy of a self-applied, handheld, low-intensity radiofrequency device (Vertica®) in men with moderate and mild-to-moderate organic erectile dysfunction. The treatment protocol consisted of 12 treatments (twice a week during the 1st month, and once a week during the 2nd month), and each participant treated himself individually. Treatment outcomes were evaluated using the International Index of Erectile Function, Erection Hardness Scale, Erectile Dysfunction Index of Treatment Satisfaction, Benefit, Satisfaction & Willingness to continue, Quality of Erection Questionnaire, Sexual Quality of Life questionnaires and specific questions addressing side effects and ease of use. Twenty-eight out of 32 men (mean age 59.5 ± 9.8, range: 41–78 years) completed a one-month follow-up after treatment. Mean International Index of Erectile Function (43.7. ± 7.8 vs. 60.9 ± 10.8, p < 0.01), International Index of Erectile Function -Erection Function domain (16.8 ± 3.1 vs. 24.4 ± 4.4, p < 0.001), and Erection Hardness Scores (2.2 ± 0.8 vs. 3.2 ± 0.5, p = 0.01) were all significantly improved. Fifty percent of patients achieved normal erectile function parameters according to the International Index of Erectile Function -Erection Function domain score >25. High mean scores were achieved in the Erectile Dysfunction Index of Treatment Satisfaction (76.8 ± 20.3), Benefit, Satisfaction & Willingness to continue (4.83 ± 1.1), Quality of Erection Questionnaire (73.4 ± 23.8), and Sexual Quality of Life (67 ± 29.4) questionnaires. No side effects were reported and participants rated the device as very comfortable, simple, and easy to operate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated and analyzed during this study can be found within the results section of this published article, Additional information on the device and background can be found at www.vertica-labs.com. Additional data/ information are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Atalla E, Balon R, Fisher AD, Laumann E, et al. Definitions of sexual dysfunctions in women and men: a consensus statement from the fourth international consultation on sexual medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:135–43.
Kessler A, Sollie S, Challacombe B, Briggs K, Van, Hemelrijck M. The global prevalence of erectile dysfunction: a review. BJU Int 2019;124:587–99.
Debasis B, Ann SP, Bhimrao FS, Sonia M. Erectile Dysfunction: A Review on Prevalence, Perceptions, Diagnosis and Management in India. J Assoc Physicians India. 2020;68:57–61.
Olsen AB, Persiani M, Boie S, Hanna M, Lund L. Can low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy improve erectile dysfunction? A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Scand J Urol. 2015;49:329–33.
Meyer PF, de Oliveira P, Silva FKBA, da Costa ACS, Pereira CRA, Casenave S, et al. Radiofrequency treatment induces fibroblast growth factor 2 expression and subsequently promotes neocollagenesis and neoangiogenesis in the skin tissue. Lasers Med Sci. 2017;32:1727–36.
Ilangovan G, Venkatakrishnan CD, Bratasz A, Osinbowale S, Cardounel AJ, Zweier JL, et al. Heat shock-induced attenuation of hydroxyl radical generation and mitochondrial aconitase activity in cardiac H9c2 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;290:C313-24. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00362.2005.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A. The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 1997;49:822–30.
Mulhall JP, Goldstein I, Bushmakin AG, Cappelleri JC, Hvidsten K. Validation of the erection hardness score. J Sex Med. 2007;4:1626–34.
Cappelleri JC, Tseng LJ, Stecher VJ, Althof SE. Clinically important difference on the erectile dysfunction inventory of treatment satisfaction questionnaire in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int J Clin Pract. 2018;72:e13073.
Pleil AM, Coyne KS, Reese PR, Jumadilova Z, Rovner ES, Kelleher CJ. The validation of patient-rated global assessments of treatment benefit, satisfaction, and willingness to continue-the BSW. Value Health. 2005;8:S25–34.
Porst H, Gilbert C, Collins S, Huang X, Symonds T, Stecher V, et al. Development and validation of the quality of erection questionnaire. J Sex Med. 2007;4:372–81.
Abraham L, Symonds T, Morris MF. Psychometric validation of a sexual quality of life questionnaire for use in men with premature ejaculation or erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 2008;5:595–601.
Rosen RC, Allen KR, Ni X, Araujo AB. Minimal clinically important differences in the erectile function domain of the international index of erectile function scale. Eur Urol. 2011;60:1010–6.
Vardi Y, Dayan L, Apple B, Gruenwald I, Ofer Y, Jacob G. Penile and systemic endothelial function in men with and without erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol. 2009;55:979–85.
Capogrosso P, Frey A, Jensen CFS, Rastrelli G, Russo GI, Torremade J, et al. Low-intensity shock wave therapy in sexual medicine—clinical recommendations from the European Society of Sexual Medicine (ESSM). J Sex Med. 2019;16:1490–505.
Bonjorno AR, Gomes TB, Pereira MC, de Carvalho CM, Gabardo MCL, Kaizer MR, et al. Radiofrequency therapy in esthetic dermatology: A review of clinical evidences. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:278–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13206.
El-Domyati M, El-Ammawi TS, Medhat W, Moawad O, Brennan D, Mahoney MG, et al. Radiofrequency facial rejuvenation: evidence- based effect. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:524–35.
Beasley KL, Weiss RA. Radiofrequency in cosmetic dermatology. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:79–90.
Lolis MS, Goldberg DJ. Radiofrequency in cosmetic dermatology: a review. Dermatologic Surg. 2012;38:1765–76.
de Araújo AR, Soares VPC, da Silva FS, da Silva Moreira T. Radiofrequency for the treatment of skin laxity: mith or truth. Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:707–21.
Zelickson BD, Kist D, Bernstein E, Brown DB, Ksenzenko S, Burns J, et al. Histological and ultrastructural evaluation of the effects of a radiofrequency- based nonablative dermal remodeling device: a pilot study. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:204–9.
Leibaschoff G, Izasa PG, Cardona JL, Miklos JR, Moore RD. Transcutaneous temperature controlled radiofrequency (TTCRF) for the treatment of menopausal vaginal/genitourinary symptoms. SurgTechnol Int. 2016;29:149–59.
Dean RC, Lue TF. Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 2005;32:379–95.
Raviv G, Kiss R, Vanegas JP, Petein M, Danguy A, Schulman C, et al. Objective measurement of the different collagen types in the corpus cavernosum of potent and impotent men: an immunohistochemical staining with computerized-image analysis. World J Urol. 1997;15:50–5.
Luangkhot R, Rutchik S, Agarwal V, Puglia K, Bhargava G, Melman A. Collagen alterations in the corpus cavernosum of men with sexual dysfunction. J Urol. 1992;148:467–71.
Goldstein AMB, Meehan JP, Morrow JW, Buckley PA, Rogers FA. The fibrous skeleton of the corpora cavernosa and its probable function in the mechanism of erection. Br J Urol. 1985;57:574–8.
Pozzi A, Yurchenco PD, Iozzo RV. The nature and biology of basement membranes. Matrix Biol. 2017;57, 58:1–11.
Longo C, Galimberti M, De Pace B, Pellacani G, Bencini PL. Laser skin rejuvenation: epidermal changes and collagen remodeling evaluated by in vivo confocal microscopy. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28:769–76.
Vardi Y, Appel B, Jacob G, Massarwi O, Gruenwald I. Can low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy improve erectile function? A 6-monthfollow-up pilot study in patients with organic erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol. 2010;58:243–8.
Ciampa AR, De Prati AC, Amelio E, Cavalieri E, Persichini T, Colasanti M, et al. Nitric oxide mediates anti-inflammatory action of extracorporeal shock waves. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:6839–45.
Kim N, Vardi Y, Padma-Nathan H, Daley J, Goldstein I, De Tejada IS. Oxygen tension regulates the nitric oxide pathway. Physiological role in penile erection. J Clin Invest. 1993;91:437–42.
Harris MB, Blackstone MA, Ju H, Venema VJ, Venema RC. Heat-induced increases in endothelial NO synthase expression and activity and endothelial NO release. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285:H333-40. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00726.2002.
Mamede c, Quibervile a S p. Non-ablative radiofrequency improves hemodynamic parameters in patients with erectile dysfunction: preliminary data. www.ics.org/2021/abstract/525.
Majesky MW, Dong XR, Hoglund V, Daum G, Mahoney WM. The adventitia: a progenitor cell niche for the vessel wall. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;195:73–81.
Majesky MW, Dong XR, Hoglund V, Mahoney WM, Daum G. The adventitia: a dynamic interface containing resident progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:1530–9.
Korshunov VA, Schwartz SM, Berk BC. Vascular remodeling: Hemodynamic and biochemical mechanisms underlying Glagov’s phenomenon. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:1722–8.
Deshpande P, Sudeepthi BL, Rajan S, Abdul Nazir C. Patient-reported outcomes: A new era in clinical research. Perspect Clin Res. 2011;2:137.
Funding
This study was funded by Ohhmed (Tiberia, Israel).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I.G.: designed the protocol, participated in executing the study protocol, performed the data extraction and evaluation, review and editing of the manuscript, provided feedback on the report. B.A.: helped in designing the protocol, participated in executing the study protocol, accumulation of data, extraction and evaluation, reviewing and editing the manuscript. A.S.: designed the protocol, participated in executing the study protocol, extraction of data and statistical analysis. Aided in reviewing and editing the manuscript. A.G.: designed the protocol, participated in executing the study protocol data extraction and evaluation, reviewing and editing the manuscript, provided feedback on the report.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Granted by the local Institutional Research Board, Rambam Healthcare Campus, Haifa, Israel.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gruenwald, I., Appel, B., Shechter, A. et al. Radiofrequency energy in the treatment of erectile dysfunction—a novel cohort pilot study on safety, applicability, and short-term efficacy. Int J Impot Res (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-023-00733-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-023-00733-1