Abstract
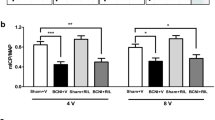
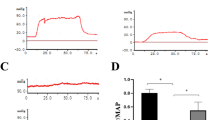
Bilateral cavernous nerve injury-related erectile dysfunction (BCNI-ED) shows a limited response to type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Furthermore, lacosamide (LCM) can alleviate peripheral neuropathy. To explore whether LCM can improve the erectile response after BCNI, we randomly divided 30 young Sprague-Dawley rats into three groups (n = 10 per group), namely, the sham operation, 0.9% normal saline-treated (BCNI + 0.9% NS), and LCM-treated BCNI (BCNI + LCM) groups. LCM was injected intraperitoneally at a dose of 90 mg/kg/day for 7 consecutive days. Erectile function was assessed by measuring the ratio of peak intracavernous pressure (ICP) to mean arterial pressure (MAP), and tissues were harvested for transmission electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, Masson’s trichrome staining, TUNEL staining, and Western blot analysis. The BCNI + 0.9% NS group showed reduced ICP/MAP ratio (0.93 ± 0.04 vs. 0.44 ± 0.05, P < 0.0001). An increased proportion of TUNEL-positive cells (0.04 ± 0.01 vs 0.87 ± 0.03, P < 0.0001) and a decreased smooth muscle/collagen ratio (0.44 ± 0.01 vs. 0.33 ± 0.01, P < 0.001) were observed in the BCNI + 0.9% NS compared with the sham group. Administration of LCM significantly restored the ICP/MAP ratio (0.44 ± 0.05 vs. 0.74 ± 0.05, P < 0.001) and decreased the proportion of TUNEL positive cells (0.87 ± 0.03 vs. 0.60 ± 0.04, P < 0.0001) in the corpus cavernosum following BCNI. The ratio of smooth muscle to collagen (0.43 ± 0.01vs. 0.33 ± 0.01, P < 0.01) and expression of α-SMA (P < 0.0001) in the BCNI + LCM group significantly increased compared with BCNI + 0.9% NS group, indicating alleviation of fibrosis. Apoptotic markers, including Bax/Bcl-2 (P < 0.01) and Caspase-3 (P < 0.0001) in the BCNI + LCM group was significantly lower than that in the BCNI + 0.9% NS group. LCM treatment partially upregulated the expression of vWF and eNOS in cavernous tissue in rats subjected to BCNI (P < 0.05). Increases in S100-β and nNOS expression in the major pelvic ganglion (MPG) were observed after LCM administration. In summary, LCM can recover erectile function in BCNI-ED rat model by suppressing corporal apoptosis and fibrosis, and protecting the cavernous nerve.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare the availability of data upon request.
References
NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH consensus development panel on impotence. JAMA. 1993;270:83–90.
Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. 2017;71:618–29.
Mobley DF, Khera M, Baum N. Recent advances in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Postgrad Med J. 2017;93:679–85.
Burnett AL. Erectile dysfunction following radical prostatectomy. JAMA. 2005;293:2648–53.
Michel MC. Although the phosphodiesterase inhibitors have revolutionised the treatment of ED, postoperative ED due to nerve damage remains a therapeutic challenge. Eur Urol. 2007;52:580–1.
Campbell JD, Burnett AL. Neuroprotective and nerve regenerative approaches for treatment of erectile dysfunction after cavernous nerve injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:1794.
Wang Y, Meng XH, Zhang QJ, Wang YM, Chen C, Wang YC, et al. Losartan improves erectile function through suppression of corporal apoptosis and oxidative stress in rats with cavernous nerve injury. Asian J Androl. 2019;21:452–9.
Wang HS, Ruan Y, Banie L, Cui K, Kang N, Peng D, et al. Delayed low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy ameliorates impaired penile hemodynamics in rats subjected to pelvic neurovascular injury. J Sex Med. 2019;16:17–26.
Li M, Lei H, Xu Y, Li H, Yang B, Yu C, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells exert therapeutic effect in a rat model of cavernous nerves injury. Andrology. 2018;6:927–35.
Bee LA, Dickenson AH. Effects of lacosamide, a novel sodium channel modulator, on dorsal horn neuronal responses in a rat model of neuropathy. Neuropharmacology. 2009;57:472–9.
Zhao T, Li HJ, Ma L, Feng J, Wang TT, Yu J, et al. Safety, efficacy, and tolerability of lacosamide for the treatment of epilepsy in pediatric patients in Uygur, China. Epilepsy Behav. 2021;117:107814.
Demiroz S, Ur K, Ulucan A, Bengu AS, Ur FD, Gergin OO, et al. Neuroprotective effects of lacosamide in experimental traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. Turk Neurosurg. 2019;29:718–23.
Demiroz S, Ur K, Bengu AS, Ulucan A, Atici Y, Erdogan S, et al. Neuroprotective effects of lacosamide in experimental peripheral nerve injury in rats: a prospective randomized and placebo-controlled trial. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63:171–7.
Jin HR, Chung YG, Kim WJ, Zhang LW, Piao S, Tuvshintur B, et al. A mouse model of cavernous nerve injury-induced erectile dysfunction: functional and morphological characterization of the corpus cavernosum. J Sex Med. 2010;7:3351–64.
Zhou X, Zhang T, Song L, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Cong R, et al. Prenatal exposure to di-n-butyl phthalate induces erectile dysfunction in male adult rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;219:112323.
Resnick MJ, Koyama T, Fan KH, Albertsen PC, Goodman M, Hamilton AS, et al. Long-term functional outcomes after treatment for localized prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:436–45.
Montorsi F, Brock G, Stolzenburg JU, Mulhall J, Moncada I, Patel HR, et al. Effects of tadalafil treatment on erectile function recovery following bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy: a randomised placebo-controlled study (REACTT). Eur Urol. 2014;65:587–96.
Yang W, Chen Z, Ma X, Ouyang X, Fang J, Wei H. Co-overexpression of VEGF and GDNF in adipose-derived stem cells optimizes therapeutic effect in neurogenic erectile dysfunction model. Cell Prolif. 2020;53:e12756.
Wu H, Tang WH, Zhao LM, Liu DF, Yang YZ, Zhang HT, et al. Nanotechnology-assisted adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) therapy for erectile dysfunction of cavernous nerve injury: In vivo cell tracking, optimized injection dosage, and functional evaluation. Asian J Androl. 2018;20:442–7.
Wu J, Chen Z, Zhong F, Yang W, Ouyang X, Ma X, et al. Transplantation of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates neurotic erectile dysfunction in a rat model. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:630076.
Shindel AW, Xin ZC, Lin G, Fandel TM, Huang YC, Banie L, et al. Erectogenic and neurotrophic effects of icariin, a purified extract of horny goat weed (Epimedium spp.) in vitro and in vivo. J Sex Med. 2010;7:1518–28.
Liu GM, Xu K, Li J, Luo YG. Curcumin upregulates S100 expression and improves regeneration of the sciatic nerve following its complete amputation in mice. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11:1304–11.
Sang Q, Sun D, Chen Z, Zhao W. NGF and PI3K/Akt signaling participate in the ventral motor neuronal protection of curcumin in sciatic nerve injury rat models. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:1146–53.
Draganski A, Tar MT, Villegas G, Friedman JM, Davies KP. Topically applied curcumin-loaded nanoparticles treat erectile dysfunction in a rat model of Type-2 diabetes. J Sex Med. 2018;15:645–53.
Ye M, Zhao F, Ma K, Zhou K, Ma J, Fu H, et al. Enhanced effects of salidroside on erectile function and corpora cavernosa autophagy in a cavernous nerve injury rat model. Andrologia. 2021;53:e14044.
Sheng QS, Wang ZJ, Zhang J, Zhang YG. Salidroside promotes peripheral nerve regeneration following crush injury to the sciatic nerve in rats. Neuroreport. 2013;24:217–23.
Licko T, Seeger N, Zellinger C, Russmann V, Matagne A, Potschka H. Lacosamide treatment following status epilepticus attenuates neuronal cell loss and alterations in hippocampal neurogenesis in a rat electrical status epilepticus model. Epilepsia. 2013;54:1176–85.
Ge P, Guo Y, Shen J. IcarisideII facilitates the differentiation of ADSCs to SCs via let-7i/STAT3 axis to preserve erectile function. Biol Res. 2019;52:54.
Chen Z, Han X, Ouyang X, Fang J, Huang X, Wei H. Transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improved erectile dysfunction induced by cavernous nerve injury. Theranostics. 2019;9:6354–68.
Li H, Matheu MP, Sun F, Wang L, Sanford MT, Ning H, et al. Low-energy shock wave therapy ameliorates erectile dysfunction in a pelvic neurovascular injuries rat model. J Sex Med. 2016;13:22–32.
Nocera G, Jacob C. Mechanisms of Schwann cell plasticity involved in peripheral nerve repair after injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77:3977–89.
Wang L, Sanford MT, Xin Z, Lin G, Lue TF. Role of Schwann cells in the regeneration of penile and peripheral nerves. Asian J Androl. 2015;17:776–82.
Shamloul R, Ghanem H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet. 2013;381:153–65.
Chen YL, Chao TT, Wu YN, Chen MC, Lin YH, Liao CH, et al. nNOS-positive minor-branches of the dorsal penile nerves is associated with erectile function in the bilateral cavernous injury model of rats. Sci Rep. 2018;8:929.
Wu YN, Liao CH, Chen KC, Liu SP, Chiang HS. Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb-761) on recovery of erectile dysfunction in bilateral cavernous nerve injury rat model. Urology. 2015;85:1214.e7–e15.
Liao CH, Wu YN, Chen BH, Lin YH, Ho HO, Chiang HS. Neuroprotective effect of docosahexaenoic acid nanoemulsion on erectile function in a rat model of bilateral cavernous nerve injury. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33040.
Wang ZM, Dai CF, Kanoh N, Chi FL, Li KY. Apoptosis and expression of BCL-2 in facial motoneurons after facial nerve injury. Otol Neurotol. 2002;23:397–404.
Darzynkiewicz Z, Galkowski D, Zhao H. Analysis of apoptosis by cytometry using TUNEL assay. Methods. 2008;44:250–4.
Polat İ, Cilaker Mıcılı S, Çalışır M, Bayram E, Yiş U, Ayanoğlu M, et al. Neuroprotective effects of lacosamide and memantine on hyperoxic brain injury in rats. Neurochem Res. 2020;45:1920–9.
Al-Massri KF, Ahmed LA, El-Abhar HS. Pregabalin and lacosamide ameliorate paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy via inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and Notch-1 receptor. Neurochem Int. 2018;120:164–71.
Lin G, Zhang H, Sun F, Lu Z, Reed-Maldonado A, Lee YC, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes nerve regeneration by activating the JAK/STAT pathway in Schwann cells. Transl Androl Urol. 2016;5:167–75.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the researchers and The Urology and Andrology Laboratory of The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University for the contributions.
Funding
This article was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number: 82071638; 81801438].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NS designed the project; LY, RC, and Xuan Zhou drafted the manuscript; LY, RC, Xuan Zhou, and Xiang Zhou carried out the experiments. NS and XM guided the experiment directions and edited the manuscript. XW and CJ conducted the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, L., Cong, R., Zhou, X. et al. Lacosamide alleviates bilateral cavernous nerve injury-induced erectile dysfunction in the rat model by ameliorating pathological changes in the corpus cavernosum. Int J Impot Res 36, 283–290 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-023-00674-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-023-00674-9